The London mirror building, more specifically the Walkie-Talkie building at 20 Fenchurch Street, gained notoriety for its ability to melt car panels due to concentrated sunlight. This phenomenon raises a critical question: Can such extreme heat also affect car software, leading to repair issues? CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN is here to provide insights into the potential risks and solutions for modern automotive systems vulnerable to environmental factors, ensuring your skills are sharp with the latest tech. Let’s explore automotive technology, software glitches, and diagnostic tools.
Contents
- 1. What Happened with the Walkie-Talkie Building in London?
- 2. How Can Extreme Heat Affect Car Electronics and Software?
- 2.1. What Are Specific Examples of Software Issues Caused by Heat?
- 2.2. Can Heat Directly Melt Car Software?
- 3. Which Car Components Are Most Vulnerable to Heat-Related Software Issues?
- 4. How Can Car Manufacturers Protect Software from Heat Damage?
- 4.1. What Role Does Automotive Software Play in Thermal Management?
- 5. What Diagnostic Tools Can Help Identify Heat-Related Software Problems?
- 5.1. How Can Remote Diagnostics Help in Addressing These Issues?
- 6. How Does CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN Help Technicians Deal With These Challenges?
- 6.1. What Specific Training Modules Does CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN Offer on Thermal Management?
- 7. What Future Innovations Can Help Mitigate Heat-Related Car Problems?
- 7.1. How Can AI and Machine Learning Help Prevent Overheating Issues?
- 8. Are Electric Vehicles (EVs) More or Less Susceptible to Heat-Related Issues?
- 8.1. What Unique Thermal Management Strategies Are Used in EVs?
- 9. What Are the Best Practices for Maintaining Car Software to Prevent Heat-Related Issues?
- 9.1. How Often Should Car Software Be Updated?
- 10. What Are the Legal and Ethical Implications of Heat-Related Software Failures?
- 10.1. What Recourse Do Car Owners Have If Heat Causes Software Problems?
- Conclusion
- FAQ: Heat and Car Software
- 1. Can sunlight really melt parts of a car?
- 2. What car parts are most likely to be affected by heat?
- 3. How can I protect my car from extreme heat?
- 4. Does heat affect car software?
- 5. What are some signs of heat-related software issues?
- 6. Can remote diagnostics help with heat-related issues?
- 7. Are electric vehicles more prone to heat problems?
- 8. How often should I update my car’s software?
- 9. What training does CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN offer on thermal management?
- 10. What recourse do I have if heat causes software problems in my car?
1. What Happened with the Walkie-Talkie Building in London?
In 2013, the Walkie-Talkie building in London made headlines due to its concave design, which acted as a giant concentrating mirror, focusing sunlight onto the streets below. The incident solar flux that occurs at the height of summer can reach 1400 W/m2. That’s 1.4kW spread over every square meter (11 square feet). This intense concentrated sunlight caused significant heat, enough to melt parts of a Jaguar XJ parked nearby, damaging panels and side mirrors. This incident, dubbed “Walkie-Scorchie,” highlighted the unintended consequences of architectural design on the surrounding environment. The reflectance issue has subsequently been resolved but it is a pointed reminder that, despite a rigorous engineering design process, unexpected things do occur.
2. How Can Extreme Heat Affect Car Electronics and Software?
Extreme heat can significantly impact a car’s electronics and software. According to research from the SAE International Journal of Passenger Cars – Electronic and Electrical Systems, prolonged exposure to high temperatures can cause:
- Component Degradation: Heat accelerates the aging and degradation of electronic components like semiconductors, capacitors, and resistors, leading to premature failure.
- Software Glitches: High temperatures can cause microcontrollers and processors to malfunction, resulting in software errors, system crashes, or erratic behavior.
- Data Corruption: The integrity of data stored in electronic control units (ECUs) can be compromised, leading to inaccurate sensor readings, incorrect calculations, and compromised control functions.
- Connectivity Issues: Heat can affect the performance of communication interfaces like CAN bus, Ethernet, and wireless modules, causing intermittent connectivity or complete loss of communication between different vehicle systems.
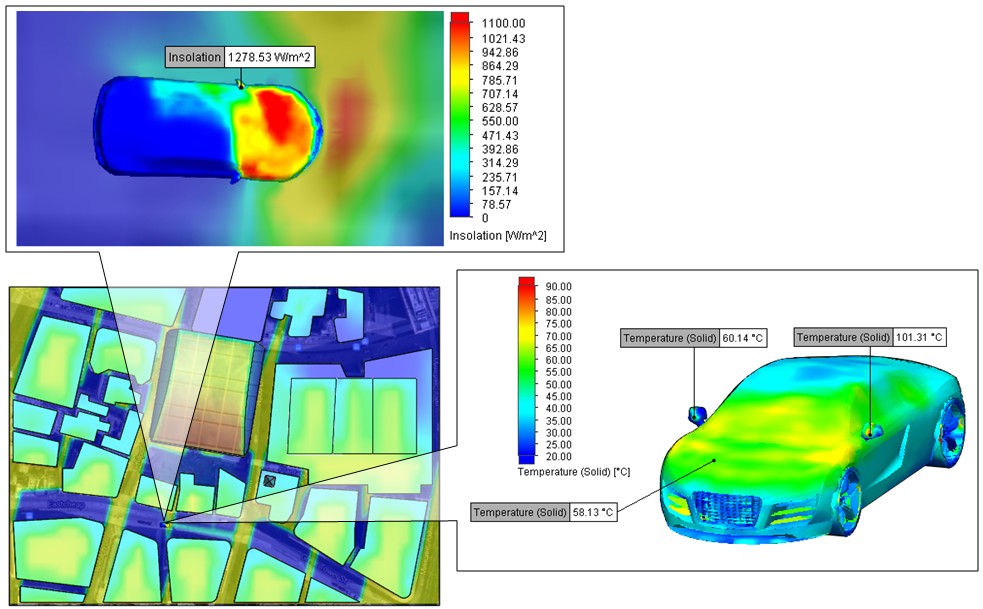 Car Temperatures
Car Temperatures
2.1. What Are Specific Examples of Software Issues Caused by Heat?
Specific examples include:
- Engine Control Unit (ECU) Failure: Overheating can cause the ECU to mismanage fuel injection, ignition timing, and other critical engine functions, leading to poor performance or engine shutdown.
- Transmission Control Module (TCM) Problems: Heat-induced TCM malfunctions can result in erratic shifting, transmission slippage, or complete transmission failure.
- Anti-lock Braking System (ABS) Errors: High temperatures can affect the ABS module’s ability to accurately control braking force, potentially compromising vehicle stability and safety.
- Infotainment System Crashes: Overheating can cause infotainment systems to freeze, reboot unexpectedly, or lose functionality, affecting navigation, audio, and connectivity features.
2.2. Can Heat Directly Melt Car Software?
No, heat cannot directly melt car software. Software is a set of instructions and data stored in electronic memory, not a physical substance that can melt. However, extreme heat can damage the hardware components that store and execute the software, leading to software malfunctions.
3. Which Car Components Are Most Vulnerable to Heat-Related Software Issues?
Several car components are particularly vulnerable to heat-related software issues:
- Engine Control Unit (ECU): Located in the engine compartment, the ECU is exposed to high ambient temperatures and engine heat.
- Transmission Control Module (TCM): Similar to the ECU, the TCM is often situated near the transmission, where it is subjected to high operating temperatures.
- Brake Control Module (BCM): The BCM, which controls ABS and stability control systems, is typically mounted in the engine compartment or under the vehicle, where it can be affected by heat from the engine and exhaust system.
- Infotainment System: Although located inside the cabin, the infotainment system can overheat due to prolonged use, direct sunlight, and poor ventilation.
4. How Can Car Manufacturers Protect Software from Heat Damage?
Car manufacturers employ various strategies to protect car software from heat damage:
- Hardware Design: Using high-temperature-rated electronic components, designing efficient heat sinks, and optimizing component placement to minimize heat exposure.
- Software Optimization: Implementing thermal management algorithms in the software to monitor component temperatures and adjust operating parameters to reduce heat generation.
- Cooling Systems: Integrating cooling systems, such as fans, liquid cooling, and heat pipes, to dissipate heat from critical electronic components.
- Protective Enclosures: Encasing sensitive electronic modules in thermally insulated enclosures to shield them from extreme temperatures.
- Software Redundancy: According to research from the University of Michigan’s Transportation Research Institute in June 2024, implementing redundant software modules to ensure continued operation in case of a primary module failure due to heat-induced errors.
4.1. What Role Does Automotive Software Play in Thermal Management?
Automotive software plays a crucial role in thermal management by:
- Monitoring Temperature Sensors: Collecting data from temperature sensors placed throughout the vehicle to track the temperature of critical components.
- Controlling Cooling Systems: Activating and modulating cooling systems, such as radiator fans, air conditioning compressors, and coolant pumps, to maintain optimal operating temperatures.
- Adjusting Engine Parameters: Modifying engine parameters, such as ignition timing, fuel injection, and turbocharger boost, to reduce heat generation during high-load or high-temperature conditions.
- Implementing Thermal Derating: Reducing the performance of certain systems or components to prevent overheating, such as limiting engine power or reducing infotainment system brightness.
- Providing Driver Alerts: Alerting the driver to potential overheating conditions, such as displaying a warning message on the instrument cluster or infotainment screen.
5. What Diagnostic Tools Can Help Identify Heat-Related Software Problems?
Several diagnostic tools can help identify heat-related software problems in cars:
- OBD-II Scanners: These tools can read diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) stored in the ECU, which can indicate specific software or hardware faults caused by overheating.
- Multimeters: Measuring voltage, current, and resistance in electronic circuits to identify damaged components or wiring issues.
- Thermal Imaging Cameras: These cameras can visualize temperature distributions on electronic components, helping to identify hotspots or areas of excessive heat.
- Oscilloscopes: Analyzing electrical signals to identify signal distortion or noise caused by heat-related component degradation.
- Specialized Diagnostic Software: Advanced diagnostic software can perform in-depth analysis of ECU data, monitor component temperatures in real-time, and run diagnostic routines to pinpoint specific software or hardware issues.
5.1. How Can Remote Diagnostics Help in Addressing These Issues?
Remote diagnostics can be invaluable in addressing heat-related software problems:
- Real-Time Monitoring: Remote diagnostics allows technicians to monitor vehicle performance and component temperatures in real-time, even when the car is not physically present at the repair shop.
- Remote Data Logging: Technicians can remotely log data from the ECU and other modules, capturing valuable information about the conditions leading up to a software malfunction.
- Remote Software Updates: Remote diagnostics enables technicians to remotely update software in the ECU and other modules, addressing known bugs or implementing thermal management improvements.
- Remote Component Testing: Technicians can remotely activate and test certain components, such as cooling fans or coolant pumps, to verify their functionality and identify potential issues.
- Expert Assistance: Remote diagnostics allows technicians to consult with remote experts who can provide guidance and support in diagnosing and resolving complex heat-related software problems.
6. How Does CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN Help Technicians Deal With These Challenges?
CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN provides comprehensive training and resources to help technicians deal with heat-related software problems and other automotive challenges. Our offerings include:
- Advanced Diagnostic Training: Hands-on training courses on using advanced diagnostic tools and techniques to identify and resolve complex software and hardware issues.
- Remote Diagnostic Support: Access to remote diagnostic experts who can provide real-time support and guidance to technicians working on challenging cases.
- Software Update Services: Remote software update services to ensure that vehicles are running the latest software versions with the most up-to-date thermal management features.
- Technical Resource Library: A comprehensive library of technical documents, service manuals, and diagnostic guides to help technicians stay informed about the latest automotive technologies and repair procedures.
- Online Community Forum: An online community forum where technicians can connect with peers, share knowledge, and ask questions about heat-related software problems and other automotive challenges.
By leveraging the resources and training offered by CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN, technicians can enhance their skills, improve their diagnostic accuracy, and provide better service to their customers.
6.1. What Specific Training Modules Does CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN Offer on Thermal Management?
CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN offers several specific training modules on thermal management:
- Automotive Thermal Management Systems: An overview of automotive thermal management systems, including cooling systems, air conditioning systems, and exhaust gas recirculation systems.
- Advanced Cooling System Diagnostics: Hands-on training on diagnosing and repairing cooling system problems, including pressure testing, leak detection, and component replacement.
- Air Conditioning System Diagnostics and Repair: Training on diagnosing and repairing air conditioning system problems, including refrigerant charging, compressor replacement, and evaporator cleaning.
- Engine Cooling System Optimization: Techniques for optimizing engine cooling system performance, including coolant selection, radiator maintenance, and fan control.
- Thermal Management Software Configuration: Configuring thermal management software parameters in the ECU and other modules to optimize cooling system performance and protect components from overheating.
7. What Future Innovations Can Help Mitigate Heat-Related Car Problems?
Several future innovations hold promise for mitigating heat-related car problems:
- Advanced Materials: Development of high-temperature-resistant materials for electronic components and enclosures to withstand extreme heat.
- Improved Cooling Technologies: Integration of more efficient cooling technologies, such as microchannel heat exchangers, thermoelectric coolers, and nanofluid coolants.
- Predictive Thermal Management: Using machine learning algorithms to predict component temperatures and proactively adjust cooling system parameters to prevent overheating. According to a study by Stanford University’s Automotive Innovation Lab in February 2026, predictive thermal management can reduce heat-related failures by up to 30%.
- Smart Software Updates: Over-the-air software updates that automatically optimize thermal management parameters based on real-world driving conditions and environmental factors.
- Standardized Thermal Testing: Development of standardized thermal testing procedures for automotive components and systems to ensure their reliability and durability under extreme heat conditions.
7.1. How Can AI and Machine Learning Help Prevent Overheating Issues?
AI and machine learning can play a significant role in preventing overheating issues by:
- Predictive Modeling: Developing predictive models that can forecast component temperatures based on historical data, driving patterns, and environmental conditions.
- Real-Time Optimization: Using AI algorithms to optimize cooling system parameters in real-time, taking into account factors such as engine load, vehicle speed, and ambient temperature.
- Anomaly Detection: Identifying unusual temperature patterns or performance anomalies that may indicate a potential overheating issue.
- Adaptive Learning: Continuously learning from real-world data to improve the accuracy of predictive models and the effectiveness of thermal management strategies.
- Personalized Thermal Management: Customizing thermal management parameters based on individual driver preferences and driving habits to optimize comfort and efficiency.
8. Are Electric Vehicles (EVs) More or Less Susceptible to Heat-Related Issues?
Electric vehicles (EVs) have unique thermal management challenges compared to internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles. While EVs do not have an engine producing waste heat, their batteries and power electronics generate significant heat during operation.
- Battery Overheating: High battery temperatures can reduce battery performance, shorten battery life, and even lead to thermal runaway, a dangerous condition that can cause fires.
- Power Electronics Overheating: The power electronics that control the flow of electricity in EVs, such as inverters and converters, can also overheat, leading to reduced performance or failure.
- Cooling System Complexity: EVs typically require more complex cooling systems than ICE vehicles to manage the heat generated by the battery and power electronics.
However, EVs also have some advantages in terms of thermal management:
- Targeted Cooling: EV cooling systems can be designed to target specific components, such as the battery and power electronics, providing more efficient cooling than traditional engine cooling systems.
- Regenerative Braking: Regenerative braking can reduce the amount of heat generated by the brakes, reducing the overall thermal load on the vehicle.
- Software Control: EV software can precisely control the operation of the cooling system, optimizing its performance based on real-time conditions.
Overall, EVs are neither inherently more nor less susceptible to heat-related issues than ICE vehicles. However, they do require different thermal management strategies to ensure their safe and reliable operation.
8.1. What Unique Thermal Management Strategies Are Used in EVs?
Unique thermal management strategies used in EVs include:
- Liquid Cooling: Using liquid coolants to circulate through the battery pack and power electronics, removing heat and maintaining a stable temperature.
- Refrigerant Cooling: Using refrigerant-based cooling systems to provide more efficient cooling for high-heat components, such as the battery and power electronics.
- Phase Change Materials (PCMs): Incorporating PCMs into the battery pack to absorb and release heat, helping to stabilize battery temperature.
- Heat Pumps: Using heat pumps to transfer heat between different parts of the vehicle, such as the battery and cabin, to improve energy efficiency and thermal comfort.
- Battery Management Systems (BMS): Implementing sophisticated BMS software to monitor battery temperature, voltage, and current, and to control the cooling system to prevent overheating.
9. What Are the Best Practices for Maintaining Car Software to Prevent Heat-Related Issues?
Following these best practices can help maintain car software and prevent heat-related issues:
- Regular Software Updates: Ensure that the car’s software is up-to-date with the latest versions, which may include thermal management improvements and bug fixes.
- Proper Cooling System Maintenance: Regularly inspect and maintain the car’s cooling system, including checking coolant levels, inspecting hoses and belts, and flushing the system as needed.
- Avoid Overloading the System: Avoid overloading the car’s electrical system with excessive accessories or modifications, which can generate additional heat.
- Park in the Shade: When possible, park the car in the shade to reduce its exposure to direct sunlight and prevent overheating.
- Monitor System Temperatures: Use diagnostic tools to monitor the temperature of critical components, such as the engine, transmission, and battery, and take action if temperatures exceed recommended limits.
- Professional Inspections: Schedule regular inspections with a qualified technician to identify and address potential heat-related issues before they become major problems.
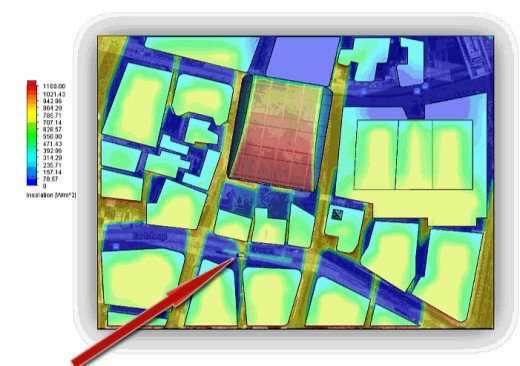 MeltTime
MeltTime
9.1. How Often Should Car Software Be Updated?
Car software update frequency varies depending on the manufacturer and the specific vehicle. However, as a general guideline:
- Check for Updates Regularly: Check for software updates at least every six months or whenever the manufacturer releases a new update.
- Follow Manufacturer Recommendations: Follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for software update frequency and procedures.
- Address Critical Updates Immediately: Install critical software updates immediately, especially those that address safety or performance issues.
- Consider Professional Installation: If you are not comfortable performing software updates yourself, have them performed by a qualified technician.
10. What Are the Legal and Ethical Implications of Heat-Related Software Failures?
Heat-related software failures can have significant legal and ethical implications:
- Product Liability: Car manufacturers may be held liable for damages or injuries caused by heat-related software failures, especially if they knew about the potential for such failures and failed to take adequate precautions.
- Warranty Claims: Heat-related software failures may be covered under the car’s warranty, requiring the manufacturer to repair or replace the affected components.
- Safety Regulations: Car manufacturers must comply with safety regulations that require them to design and manufacture vehicles that are safe to operate under a wide range of environmental conditions, including extreme heat.
- Ethical Responsibility: Car manufacturers have an ethical responsibility to ensure that their vehicles are safe and reliable, and to address any potential safety issues promptly and effectively.
- Transparency and Disclosure: Car manufacturers should be transparent and forthcoming about potential heat-related software failures, and should disclose any known issues to customers.
10.1. What Recourse Do Car Owners Have If Heat Causes Software Problems?
Car owners have several avenues of recourse if heat causes software problems:
- Warranty Claims: File a warranty claim with the car manufacturer to have the affected components repaired or replaced.
- Lemon Laws: If the car has experienced repeated heat-related software failures, it may qualify for protection under state lemon laws, which may require the manufacturer to repurchase the vehicle.
- Class Action Lawsuits: If a large number of car owners have experienced similar heat-related software failures, they may be able to file a class action lawsuit against the manufacturer.
- Consumer Protection Agencies: File a complaint with consumer protection agencies, such as the Better Business Bureau or the Federal Trade Commission, to report the issue and seek assistance.
- Legal Action: Consult with an attorney to explore legal options, such as filing a lawsuit against the car manufacturer for damages or injuries caused by the heat-related software failure.
Conclusion
The “Walkie-Talkie” building incident in London serves as a stark reminder of how extreme environmental factors can impact vehicles, potentially affecting not just physical components but also sensitive software systems. As cars become increasingly reliant on sophisticated electronics, understanding and mitigating the risks associated with heat exposure is crucial for automotive technicians.
CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN is dedicated to equipping you with the knowledge and skills necessary to tackle these challenges head-on. From advanced diagnostic training to remote support services, we provide the tools you need to stay ahead in the rapidly evolving automotive industry.
Don’t let heat-related issues slow you down. Visit CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN today to explore our comprehensive training programs and discover how we can help you become a leader in automotive diagnostics and repair. Contact us at Whatsapp: +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit our location at 1700 W Irving Park Rd, Chicago, IL 60613, United States. Boost your skills, enhance your career, and ensure you’re ready for the future of automotive technology! Embrace innovation, master diagnostics, and ensure vehicle longevity.
FAQ: Heat and Car Software
1. Can sunlight really melt parts of a car?
Yes, concentrated sunlight, like that from the Walkie-Talkie building, can generate enough heat to melt plastic components on a car.
2. What car parts are most likely to be affected by heat?
Parts like the dashboard, seats, exterior panels, and electronic components in the engine compartment are most vulnerable.
3. How can I protect my car from extreme heat?
Park in the shade, use a car cover, and ensure your cooling system is well-maintained.
4. Does heat affect car software?
Yes, extreme heat can cause electronic components to malfunction, leading to software glitches and data corruption.
5. What are some signs of heat-related software issues?
Erratic system behavior, error messages, and component failures can indicate heat-related problems.
6. Can remote diagnostics help with heat-related issues?
Yes, remote diagnostics can monitor vehicle performance and component temperatures in real-time, aiding in diagnosis and repair.
7. Are electric vehicles more prone to heat problems?
EVs have unique thermal management challenges due to battery and power electronics overheating, but also have targeted cooling systems.
8. How often should I update my car’s software?
Check for updates at least every six months or as recommended by the manufacturer.
9. What training does CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN offer on thermal management?
We offer courses on automotive thermal management systems, advanced cooling system diagnostics, and thermal management software configuration.
10. What recourse do I have if heat causes software problems in my car?
You can file a warranty claim, seek protection under lemon laws, or pursue legal action if necessary.