Embarking on a Career Progression In Software Sales offers dynamic opportunities for growth and significant earning potential, and CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN provides specialized insights for success. By understanding the various roles, required skills, and advancement paths, you can strategically plan your journey. Software sales offers many career opportunities, including tech sales career and tech sales jobs.
Contents
- 1. What Exactly is Software Sales?
- 2. What Types of Software Sales Positions Are Available?
- 2.1 Sales Development Rep (SDR)
- 2.2 Outside Sales Rep
- 2.3 Account Executive (AE)
- 2.4 Post-Sales Account Manager
- 2.5 Sales Manager
- 2.6 VP of Sales
- 2.7 Sales Operations
- 2.8 Sales Engineer
- 3. What Essential Skills Are Needed to Succeed in Software Sales?
- 3.1 Communication
- 3.2 Active Listening
- 3.3 Product Knowledge
- 3.4 Problem-Solving
- 3.5 Negotiation
- 3.6 Time Management
- 3.7 Relationship Building
- 3.8 Technical Proficiency
- 3.9 Resilience
- 3.10 Business Acumen
- 4. How to Visualize Your Software Sales Career Path
- 4.1 Define Your End Goal
- 4.2 Identify Intermediate Steps
- 4.3 Map Out Required Skills and Knowledge
- 4.4 Create a Visual Diagram
- 4.5 Regularly Review and Update
- 5. What are the Ways to Advance in Software Sales?
- 5.1 Continuous Learning
- 5.2 Networking
- 5.3 Mentorship
- 5.4 Certifications
- 5.5 Performance Tracking
- 5.6 Taking on New Challenges
- 5.7 Seeking Feedback
- 5.8 Building a Personal Brand
- 5.9 Strategic Job Changes
- 5.10 Leadership Opportunities
- 6. How Does CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN Support Your Career Growth in Software Sales?
- 6.1 Specialized Training Programs
- 6.2 Comprehensive Resources
- 6.3 Networking Opportunities
- 6.4 Personalized Career Guidance
- 7. What Are the Latest Trends in Software Sales?
- 7.1 Remote Selling
- 7.2 AI and Automation
- 7.3 Data-Driven Sales
- 7.4 Customer Experience
- 7.5 Value-Based Selling
- 8. What are Some Common Mistakes to Avoid in Software Sales?
- 8.1 Lack of Preparation
- 8.2 Poor Listening Skills
- 8.3 Focusing on Features, Not Benefits
1. What Exactly is Software Sales?
Software sales involves selling software products or services to businesses or individuals. It requires understanding customer needs and matching them with the appropriate software solutions. Elite sales professionals act as advocates, finding the best solutions for both their company and their clients. The primary responsibility is to provide technology that solves a client’s specific problem.
Expanding on this, software sales isn’t just about pushing a product; it’s about understanding a client’s challenges and offering tailored solutions. This often involves:
- Needs Analysis: Identifying the client’s pain points and requirements.
- Product Demonstration: Showcasing how the software addresses those needs.
- Relationship Building: Establishing trust and rapport with key decision-makers.
- Negotiation: Reaching mutually beneficial agreements.
- Closing Deals: Securing the sale and ensuring client satisfaction.
The software sales landscape is broad, encompassing various sectors from enterprise solutions to niche applications. Success hinges on a deep understanding of both the technology and the sales process.
2. What Types of Software Sales Positions Are Available?
There are several types of sales positions within the software industry, each with unique responsibilities and career progression opportunities. The right sales role for you depends on your skills and goals, offering diverse paths for career development and financial reward. These roles include:
- Sales Development Rep (SDR)
- Outside Sales Rep
- Account Executive (AE)
- Post-Sales Account Manager
- Sales Manager
- VP of Sales
- Sales Operations
- Sales Engineer
Let’s explore each role in detail:
2.1 Sales Development Rep (SDR)
What Does an SDR Do? A Sales Development Representative (SDR) focuses on generating new leads and qualifying them for further sales engagement. SDRs identify potential clients through cold-calling, emailing, and social selling, setting the stage for Account Executives to close deals. The SDR role serves as the gateway to commission-based sales positions.
Key Responsibilities:
- Lead Generation: Identifying and researching potential clients.
- Cold Outreach: Initiating contact through calls, emails, and social media.
- Qualification: Determining if leads are a good fit for the company’s products.
- Appointment Setting: Scheduling meetings between qualified leads and Account Executives.
- CRM Management: Maintaining accurate records of interactions and lead status.
Compensation:
- Average Base Salary: $48,000
- Average Total Compensation: $75,000
Pros:
- Excellent entry point into software sales.
- Opportunity to learn sales fundamentals and product knowledge.
- Clear path for advancement to Account Executive roles.
Cons:
- Lower base salary compared to other sales positions.
- Heavy reliance on outbound activities and rejection.
Advancement Opportunities:
- Account Executive (AE)
- Sales Manager
The SDR role is crucial for building the sales pipeline. According to a study by HubSpot, companies with dedicated SDR teams experience significantly higher growth rates.
2.2 Outside Sales Rep
What Does an Outside Sales Rep Do? Outside Sales Reps build relationships with clients in external markets, often operating remotely. They focus on developing new business opportunities and managing client accounts in their assigned territory. The remote nature of the job offers flexibility and independence.
Key Responsibilities:
- Territory Management: Developing and executing sales strategies for a specific geographic area.
- Client Acquisition: Identifying and pursuing new business opportunities.
- Relationship Building: Establishing and maintaining strong relationships with clients.
- Product Presentations: Demonstrating the value of software solutions to potential customers.
- Negotiation and Closing: Securing deals and meeting sales targets.
Compensation:
- Average Base Salary: Varies based on location and experience
- Average Total Compensation: Competitive, with commission and bonuses
Pros:
- High degree of autonomy and flexibility.
- Opportunity to work in diverse markets and industries.
- Direct impact on revenue generation.
Cons:
- Requires strong self-discipline and motivation.
- Can be isolating due to remote work.
Advancement Opportunities:
- Account Executive (AE)
- Sales Manager
The role of an Outside Sales Rep is essential for expanding market reach. Research from the Sales Management Association indicates that companies with strong outside sales teams achieve higher market penetration.
2.3 Account Executive (AE)
What Does an Account Executive Do? Account Executives (AEs) are central to closing deals and driving revenue growth. They work directly with potential clients, understanding their needs and presenting tailored software solutions. AEs are responsible for managing the entire sales cycle, from initial contact to closing the deal.
Key Responsibilities:
- Client Engagement: Building and maintaining relationships with potential clients.
- Needs Assessment: Understanding client requirements and business challenges.
- Solution Presentation: Demonstrating how the software meets client needs.
- Negotiation: Working with clients to reach mutually beneficial agreements.
- Closing Deals: Securing contracts and generating revenue.
Compensation:
- Average Base Salary: $62,000
- Average On-Target Earnings (OTE): $126,000
Pros:
- High earning potential with commission and bonuses.
- Opportunity to develop strong sales and negotiation skills.
- Direct impact on company revenue.
Cons:
- Performance-based compensation can be unpredictable.
- Requires strong sales acumen and resilience.
Advancement Opportunities:
- Sales Manager
- VP of Sales
Account Executives are vital for driving revenue growth. According to a report by CSO Insights, companies with high-performing AEs achieve significantly higher sales quotas.
2.4 Post-Sales Account Manager
What Does a Post-Sales Account Manager Do? Post-Sales Account Managers focus on maintaining and growing relationships with existing clients. They ensure client satisfaction, drive renewals, and identify opportunities for upselling and cross-selling. This role is crucial for maximizing customer lifetime value.
Key Responsibilities:
- Client Relationship Management: Building and maintaining strong relationships with existing clients.
- Customer Success: Ensuring clients achieve their desired outcomes with the software.
- Renewal Management: Securing contract renewals and minimizing churn.
- Upselling and Cross-selling: Identifying opportunities to sell additional products or services.
- Technical Support: Addressing client inquiries and resolving technical issues.
Compensation:
- Average Base Salary: Higher than AEs, SDRs or Outside Sales Reps.
- Average Total Compensation: Variable, with some commission and bonuses.
Pros:
- Opportunity to build long-term relationships with clients.
- Focus on customer success and satisfaction.
- Potential for recurring revenue through renewals and upsells.
Cons:
- Can be challenging to balance client needs with company goals.
- Requires strong communication and problem-solving skills.
Advancement Opportunities:
- Sales Manager
- VP of Sales
Post-Sales Account Managers are critical for customer retention and revenue growth. Research from Bain & Company shows that increasing customer retention rates by 5% can increase profits by 25-95%.
2.5 Sales Manager
What Does a Sales Manager Do? Sales Managers lead and motivate sales teams to achieve their targets. They provide coaching, training, and support to help team members succeed. Sales Managers also play a key role in developing and executing sales strategies.
Key Responsibilities:
- Team Leadership: Managing and motivating a team of sales professionals.
- Coaching and Training: Providing guidance and support to improve sales performance.
- Sales Strategy: Developing and executing sales plans to achieve revenue targets.
- Performance Monitoring: Tracking sales metrics and identifying areas for improvement.
- Reporting: Communicating sales results and insights to senior management.
Compensation:
- Base Salary: $89,000 – $95,000
- On-Target Earnings (OTE): $127,000 – $147,000
Pros:
- Opportunity to lead and develop a high-performing sales team.
- Direct impact on revenue growth and company success.
- Competitive salary and earning potential.
Cons:
- Requires strong leadership and management skills.
- Can be stressful due to performance pressures.
Advancement Opportunities:
- Sales Leadership
- VP or Head of Sales
Sales Managers are essential for driving team performance and achieving revenue goals. A study by the Sales Executive Council found that effective sales managers can increase team performance by up to 27%.
2.6 VP of Sales
What Does a VP of Sales Do? The VP of Sales (also known as Head of Sales) is an executive responsible for the overall sales strategy and performance of the company. They work closely with marketing to align sales and marketing efforts and ensure the company meets its revenue targets.
Key Responsibilities:
- Sales Strategy: Developing and implementing a comprehensive sales strategy.
- Revenue Management: Setting and achieving revenue targets for the company.
- Team Leadership: Overseeing sales managers and the entire sales organization.
- Marketing Alignment: Collaborating with marketing to ensure aligned sales and marketing efforts.
- Executive Reporting: Communicating sales performance and strategic insights to senior leadership.
Pros:
- High level of responsibility and impact.
- Opportunity to shape the company’s sales strategy and direction.
- Competitive salary and earning potential.
Cons:
- High-pressure role with significant accountability.
- Requires strong strategic thinking and leadership skills.
Advancement Opportunities:
- Other Executive Positions (CFO, CEO)
- Founder or Leader of Own Company
The VP of Sales is a critical leadership role that drives the company’s revenue and growth. According to a report by Gartner, effective sales leadership can significantly improve sales performance and drive revenue growth.
2.7 Sales Operations
What Does Sales Operations Do? Sales Operations provides support to the sales team, ensuring they have the resources and processes needed to succeed. They focus on improving sales efficiency, optimizing processes, and providing data-driven insights.
Key Responsibilities:
- Process Optimization: Streamlining sales processes to improve efficiency.
- Data Analysis: Analyzing sales data to identify trends and opportunities.
- Technology Management: Managing sales technology and tools.
- Reporting: Creating reports and dashboards to track sales performance.
- Marketing Support: Providing marketing materials and support to the sales team.
Pros:
- Opportunity to work in a strategic and analytical role.
- Direct impact on sales team efficiency and performance.
- Competitive salary and benefits.
Cons:
- Limited opportunity for commission-based earnings.
- Requires strong analytical and problem-solving skills.
Advancement Opportunities:
- Sales Leadership
- VP of Sales
Sales Operations is essential for driving sales efficiency and performance. A study by McKinsey found that companies with strong sales operations functions achieve higher revenue growth and profitability.
2.8 Sales Engineer
What Does a Sales Engineer Do? Sales Engineers provide technical expertise to support the sales process. They work closely with the sales team to understand client requirements and demonstrate how the software can meet their needs. This role is critical for selling complex software solutions.
Key Responsibilities:
- Technical Support: Providing technical expertise to the sales team.
- Solution Demonstration: Demonstrating how the software meets client needs.
- Technical Presentations: Delivering technical presentations to potential clients.
- Proof of Concept: Developing and implementing proof-of-concept solutions.
- Client Consultation: Consulting with clients to understand their technical requirements.
Pros:
- Opportunity to combine technical expertise with sales skills.
- High earning potential, with some companies offering commission.
- Opportunity to work on challenging and innovative projects.
Cons:
- Requires strong technical and communication skills.
- Can be demanding due to the need to stay up-to-date with technology.
Advancement Opportunities:
- Account Executive (AE)
- Sales Manager
- Executive Positions (CTO, CRO, CEO)
Sales Engineers are essential for selling complex software solutions. According to a report by Forrester, companies that leverage sales engineers effectively achieve higher sales conversion rates.
 pre-sales process
pre-sales process
3. What Essential Skills Are Needed to Succeed in Software Sales?
Mastering several essential skills is crucial for thriving in software sales. A combination of soft skills and technical knowledge will set you apart. These skills include:
- Communication
- Active Listening
- Product Knowledge
- Problem-Solving
- Negotiation
- Time Management
- Relationship Building
- Technical Proficiency
- Resilience
- Business Acumen
Let’s delve into each skill and its significance:
3.1 Communication
Why is Communication Important? Effective communication is at the heart of sales. It involves clearly conveying information about the software, actively listening to client needs, and articulating the value proposition. Strong communication skills enable you to build rapport and trust with potential customers.
How to Improve:
- Practice Active Listening: Focus on understanding the client’s perspective.
- Clarity and Conciseness: Use clear and concise language to explain complex concepts.
- Verbal and Written Skills: Develop both your verbal and written communication abilities.
- Storytelling: Use storytelling techniques to engage and persuade clients.
3.2 Active Listening
Why is Active Listening Important? Active listening is more than just hearing; it’s about fully understanding the client’s needs, concerns, and objectives. By actively listening, you can tailor your pitch to address their specific pain points and offer relevant solutions.
How to Improve:
- Focus and Attention: Give your full attention to the speaker.
- Non-Verbal Cues: Pay attention to non-verbal cues such as body language.
- Clarifying Questions: Ask questions to ensure you understand the client’s message.
- Summarize and Reflect: Summarize and reflect on what you’ve heard to confirm understanding.
3.3 Product Knowledge
Why is Product Knowledge Important? A deep understanding of the software you’re selling is essential. You need to know its features, benefits, and how it solves specific client problems. This knowledge allows you to confidently address questions and demonstrate the software’s value.
How to Improve:
- Training Programs: Participate in comprehensive training programs.
- Hands-On Experience: Use the software yourself to gain firsthand experience.
- Stay Updated: Keep up-to-date with new features and updates.
- Competitive Analysis: Understand how your software compares to competitors.
3.4 Problem-Solving
Why is Problem-Solving Important? Software sales often involves addressing complex client challenges. Being able to identify problems, analyze them, and propose effective solutions is crucial for closing deals and building long-term relationships.
How to Improve:
- Analytical Skills: Develop your analytical and critical thinking skills.
- Creative Thinking: Think creatively to come up with innovative solutions.
- Collaboration: Work with team members to brainstorm and solve problems.
- Case Studies: Study case studies to learn how others have solved similar problems.
3.5 Negotiation
Why is Negotiation Important? Negotiation is a key part of the sales process. You need to be able to reach mutually beneficial agreements with clients while protecting the company’s interests. Strong negotiation skills lead to higher closing rates and better deal terms.
How to Improve:
- Preparation: Thoroughly prepare for negotiations by understanding client needs and your own goals.
- Compromise: Be willing to compromise to reach a mutually beneficial agreement.
- Value Proposition: Emphasize the value proposition of your software.
- Closing Techniques: Learn and practice effective closing techniques.
3.6 Time Management
Why is Time Management Important? Software sales can be fast-paced and demanding. Effective time management is crucial for prioritizing tasks, managing your pipeline, and meeting deadlines. Good time management leads to increased productivity and better sales results.
How to Improve:
- Prioritization: Prioritize tasks based on their importance and urgency.
- Scheduling: Create a daily or weekly schedule to manage your time.
- Task Management Tools: Use task management tools to stay organized.
- Avoid Multitasking: Focus on one task at a time to improve concentration.
3.7 Relationship Building
Why is Relationship Building Important? Building strong relationships with clients is essential for long-term success in software sales. Trust and rapport can lead to repeat business, referrals, and a solid reputation in the industry.
How to Improve:
- Personalization: Personalize your interactions with clients by understanding their individual needs.
- Follow-Up: Follow up promptly after meetings and conversations.
- Networking: Attend industry events and network with potential clients.
- Value-Added Service: Provide value-added service to clients to build loyalty.
3.8 Technical Proficiency
Why is Technical Proficiency Important? While you don’t need to be a software developer, a solid understanding of technology is essential. You need to be able to explain technical concepts to clients and demonstrate how the software works.
How to Improve:
- Technical Training: Participate in technical training programs.
- Hands-On Experience: Use the software and related technologies yourself.
- Stay Updated: Keep up-to-date with the latest technology trends.
- Ask Questions: Don’t be afraid to ask questions to improve your understanding.
3.9 Resilience
Why is Resilience Important? Sales can be challenging, with frequent rejection and setbacks. Resilience is the ability to bounce back from adversity, stay positive, and keep pushing forward.
How to Improve:
- Positive Attitude: Maintain a positive attitude even in the face of rejection.
- Learn from Mistakes: Analyze your mistakes and learn from them.
- Set Realistic Goals: Set realistic goals to avoid discouragement.
- Seek Support: Seek support from mentors, colleagues, and friends.
3.10 Business Acumen
Why is Business Acumen Important? Understanding the business landscape, industry trends, and client’s business objectives is crucial. Business acumen allows you to position your software as a strategic solution that drives business value.
How to Improve:
- Industry Research: Stay informed about industry trends and developments.
- Financial Literacy: Develop your understanding of financial concepts.
- Business Strategy: Learn about business strategy and how it relates to sales.
- Market Analysis: Analyze the market to identify opportunities and challenges.
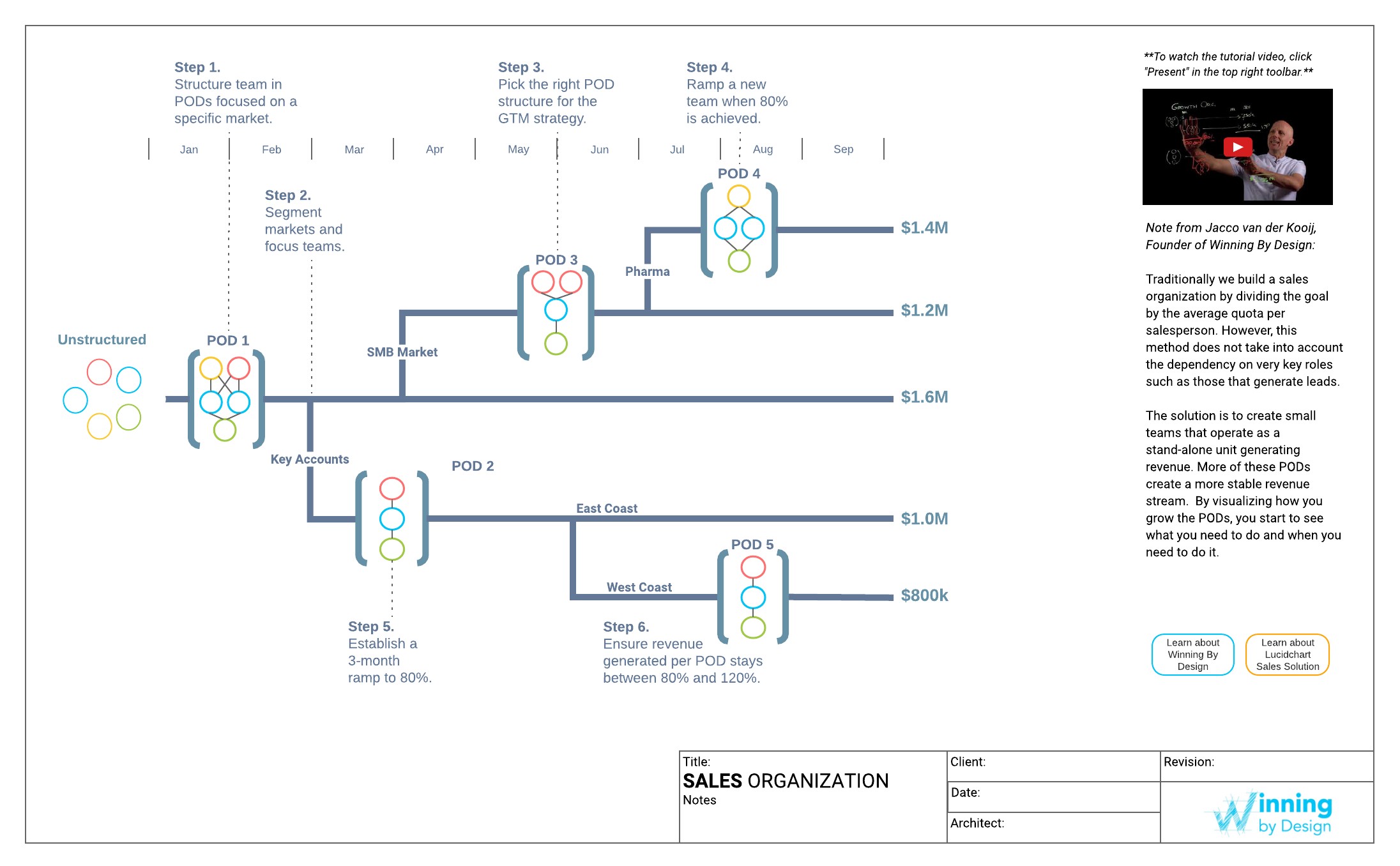
4. How to Visualize Your Software Sales Career Path
Career advancement in software sales requires a clear vision and strategic planning. Visualizing your career path can help you set goals, identify necessary skills, and track your progress. Lucidchart and similar tools can be invaluable for mapping out your career trajectory.
Here’s how to effectively visualize your software sales career path:
4.1 Define Your End Goal
Why is Defining Your End Goal Important? Knowing where you want to end up helps you make informed decisions along the way. Whether it’s becoming a VP of Sales, a Sales Director, or even starting your own company, having a clear end goal is essential.
How to Define:
- Self-Assessment: Identify your strengths, interests, and values.
- Career Research: Research different roles and career paths in software sales.
- Mentorship: Seek advice from mentors and experienced professionals.
- Long-Term Vision: Develop a long-term vision for your career.
4.2 Identify Intermediate Steps
Why is Identifying Intermediate Steps Important? Breaking down your career path into smaller, manageable steps makes it easier to track your progress and stay motivated. Each step should build upon the previous one and help you acquire new skills and experiences.
How to Identify:
- Role Progression: Map out the typical progression of roles in software sales.
- Skill Requirements: Identify the skills and qualifications needed for each role.
- Experience Needed: Determine the amount of experience required for each step.
- Timeline: Create a realistic timeline for achieving each step.
4.3 Map Out Required Skills and Knowledge
Why is Mapping Out Skills and Knowledge Important? Understanding the skills and knowledge required for each role helps you focus your development efforts. Identify any gaps in your skill set and create a plan to address them.
How to Map Out:
- Job Descriptions: Analyze job descriptions for your target roles.
- Industry Standards: Research industry standards and best practices.
- Training Programs: Identify relevant training programs and certifications.
- Skill Matrix: Create a matrix to track your skills and knowledge.
4.4 Create a Visual Diagram
Why is Creating a Visual Diagram Important? A visual diagram provides a clear and concise overview of your career path. It helps you see the big picture and understand how each step contributes to your overall goal.
How to Create:
- Lucidchart or Similar Tools: Use Lucidchart or other diagramming tools to create a visual representation of your career path.
- Milestones: Include key milestones and achievements along the way.
- Skill Development: Highlight the skills and knowledge you need to acquire.
- Timeline: Include a timeline to track your progress.
4.5 Regularly Review and Update
Why is Regularly Reviewing and Updating Important? Your career path may evolve as you gain new experiences and insights. Regularly review and update your diagram to ensure it reflects your current goals and aspirations.
How to Review and Update:
- Quarterly Reviews: Review your career path quarterly.
- Adjust Goals: Adjust your goals and timeline as needed.
- Seek Feedback: Seek feedback from mentors and colleagues.
- Stay Flexible: Be open to new opportunities and possibilities.
5. What are the Ways to Advance in Software Sales?
Advancing in software sales involves continuous learning, skill development, and strategic career planning. Here are several effective ways to progress:
- Continuous Learning
- Networking
- Mentorship
- Certifications
- Performance Tracking
- Taking on New Challenges
- Seeking Feedback
- Building a Personal Brand
- Strategic Job Changes
- Leadership Opportunities
Let’s explore each strategy in detail:
5.1 Continuous Learning
Why is Continuous Learning Important? The software industry is constantly evolving, so continuous learning is essential for staying relevant and competitive. Keep up with the latest trends, technologies, and sales techniques.
How to Implement:
- Industry Publications: Read industry publications and blogs.
- Online Courses: Take online courses on platforms like Coursera and Udemy.
- Webinars and Conferences: Attend webinars and industry conferences.
- Books and Articles: Read books and articles on sales and technology.
5.2 Networking
Why is Networking Important? Networking can open doors to new opportunities and provide valuable insights. Build relationships with colleagues, industry professionals, and potential mentors.
How to Implement:
- Industry Events: Attend industry events and conferences.
- Professional Organizations: Join professional organizations and associations.
- LinkedIn: Use LinkedIn to connect with professionals in your field.
- Informational Interviews: Conduct informational interviews to learn from others.
5.3 Mentorship
Why is Mentorship Important? A mentor can provide guidance, support, and valuable insights based on their experience. Seek out a mentor who can help you navigate your career path and achieve your goals.
How to Implement:
- Identify Potential Mentors: Identify experienced professionals you admire.
- Reach Out: Reach out and ask if they would be willing to mentor you.
- Regular Meetings: Schedule regular meetings to discuss your career goals and challenges.
- Act on Advice: Act on the advice and guidance provided by your mentor.
5.4 Certifications
Why are Certifications Important? Certifications can demonstrate your expertise and commitment to professional development. Consider obtaining certifications related to sales, technology, or specific software products.
How to Implement:
- Identify Relevant Certifications: Research relevant certifications in your field.
- Training Programs: Enroll in training programs to prepare for certification exams.
- Certification Exams: Take and pass certification exams.
- Promote Your Certifications: Highlight your certifications on your resume and LinkedIn profile.
5.5 Performance Tracking
Why is Performance Tracking Important? Tracking your performance helps you identify areas for improvement and demonstrate your achievements to potential employers.
How to Implement:
- Set Goals: Set specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals.
- Track Metrics: Track key performance metrics such as sales volume, conversion rates, and customer satisfaction.
- Analyze Results: Analyze your results to identify trends and patterns.
- Adjust Strategies: Adjust your strategies based on your performance data.
5.6 Taking on New Challenges
Why is Taking on New Challenges Important? Taking on new challenges can help you develop new skills and demonstrate your willingness to grow and learn.
How to Implement:
- Volunteer for Projects: Volunteer for new projects and assignments.
- Seek Out Stretch Goals: Set stretch goals that push you beyond your comfort zone.
- Embrace Change: Embrace change and be open to new ways of doing things.
- Learn from Failure: Learn from your failures and use them as opportunities for growth.
5.7 Seeking Feedback
Why is Seeking Feedback Important? Feedback can provide valuable insights into your strengths and weaknesses. Seek feedback from colleagues, managers, and clients to identify areas for improvement.
How to Implement:
- Ask for Feedback: Regularly ask for feedback on your performance.
- Be Open to Criticism: Be open to criticism and use it as an opportunity to learn.
- Act on Feedback: Act on the feedback you receive to improve your performance.
- Thank Feedback Providers: Thank those who provide you with feedback.
5.8 Building a Personal Brand
Why is Building a Personal Brand Important? Building a personal brand can help you stand out from the competition and attract new opportunities.
How to Implement:
- LinkedIn Profile: Create a professional LinkedIn profile.
- Content Creation: Create and share valuable content on social media.
- Speaking Engagements: Seek out speaking engagements at industry events.
- Networking: Network with professionals in your field.
5.9 Strategic Job Changes
Why are Strategic Job Changes Important? Strategic job changes can help you gain new experiences, develop new skills, and advance your career.
How to Implement:
- Research Potential Employers: Research potential employers and identify those that align with your career goals.
- Network: Network with professionals at your target companies.
- Tailor Your Resume: Tailor your resume to highlight your relevant skills and experience.
- Prepare for Interviews: Prepare for interviews by researching the company and practicing your answers to common interview questions.
5.10 Leadership Opportunities
Why are Leadership Opportunities Important? Taking on leadership opportunities can help you develop your management skills and demonstrate your potential for advancement.
How to Implement:
- Volunteer for Leadership Roles: Volunteer for leadership roles within your company.
- Mentor Others: Mentor junior colleagues and share your knowledge and experience.
- Lead Projects: Lead projects and initiatives that demonstrate your leadership skills.
- Seek Management Training: Seek out management training and development opportunities.
 Sales Organization
Sales Organization
6. How Does CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN Support Your Career Growth in Software Sales?
CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN can significantly support your career growth in software sales by providing specialized training, resources, and networking opportunities. Our platform is designed to equip you with the skills and knowledge needed to excel in this dynamic field.
6.1 Specialized Training Programs
How Do the Training Programs Help? We offer specialized training programs that focus on the specific skills needed for software sales roles. These programs cover topics such as sales techniques, product knowledge, and customer relationship management.
Key Benefits:
- Targeted Curriculum: Our curriculum is designed to address the unique challenges of software sales.
- Expert Instructors: Our instructors are experienced sales professionals who can provide practical insights and guidance.
- Hands-On Experience: Our programs include hands-on exercises and simulations to help you apply what you’ve learned.
- Certification: Upon completion of our programs, you’ll receive a certification that demonstrates your expertise.
6.2 Comprehensive Resources
How Do the Resources Help? We provide a wide range of resources to support your learning and development. These resources include articles, videos, webinars, and case studies.
Key Benefits:
- Up-to-Date Information: Our resources are regularly updated to reflect the latest trends and technologies.
- Diverse Content: We offer a variety of content formats to cater to different learning styles.
- Practical Insights: Our resources provide practical insights and actionable advice.
- Convenient Access: Our resources are accessible online, so you can learn at your own pace and on your own schedule.
6.3 Networking Opportunities
How Do the Networking Opportunities Help? We offer networking opportunities to connect with other sales professionals, potential employers, and industry experts. These opportunities can help you build relationships, find new opportunities, and advance your career.
Key Benefits:
- Industry Events: We organize and sponsor industry events and conferences.
- Online Community: We host an online community where you can connect with other professionals.
- Mentorship Programs: We offer mentorship programs to connect you with experienced sales professionals.
- Job Board: We maintain a job board with listings for software sales positions.
6.4 Personalized Career Guidance
How Does the Career Guidance Help? We provide personalized career guidance to help you identify your strengths, set goals, and develop a strategic career plan.
Key Benefits:
- Career Assessments: We offer career assessments to help you identify your skills and interests.
- One-on-One Coaching: We provide one-on-one coaching sessions with experienced career advisors.
- Resume and Interview Preparation: We offer resume and interview preparation services to help you land your dream job.
- Job Placement Assistance: We provide job placement assistance to help you find and secure a software sales position.
7. What Are the Latest Trends in Software Sales?
Staying informed about the latest trends in software sales is crucial for maintaining a competitive edge. Here are some key trends shaping the industry:
- Remote Selling
- AI and Automation
- Data-Driven Sales
- Customer Experience
- Value-Based Selling
Let’s explore each trend in detail:
7.1 Remote Selling
Why is Remote Selling Important? With the rise of remote work, remote selling has become increasingly important. Sales professionals need to be proficient in using virtual tools and techniques to connect with clients and close deals.
Key Strategies:
- Virtual Meeting Tools: Master virtual meeting tools such as Zoom and Microsoft Teams.
- Digital Communication: Use digital communication channels such as email and social media to connect with clients.
- Remote Demonstrations: Conduct remote product demonstrations using screen sharing and video conferencing.
- Virtual Networking: Participate in virtual networking events and online communities.
7.2 AI and Automation
Why are AI and Automation Important? AI and automation are transforming the sales process by streamlining tasks, improving efficiency, and providing valuable insights.
Key Applications:
- Lead Generation: Use AI-powered tools to identify and qualify leads.
- Sales Automation: Automate repetitive tasks such as email marketing and data entry.
- Predictive Analytics: Use predictive analytics to forecast sales and identify opportunities.
- Chatbots: Use chatbots to engage with customers and answer their questions.
7.3 Data-Driven Sales
Why is Data-Driven Sales Important? Data-driven sales involves using data and analytics to make informed decisions and improve sales performance.
Key Practices:
- Sales Analytics: Track and analyze key sales metrics.
- CRM Systems: Use CRM systems to manage customer data and sales processes.
- Data Visualization: Use data visualization tools to create dashboards and reports.
- A/B Testing: Conduct A/B testing to optimize sales strategies and tactics.
7.4 Customer Experience
Why is Customer Experience Important? Providing a positive customer experience is essential for building loyalty and driving repeat business.
Key Strategies:
- Personalization: Personalize your interactions with customers by understanding their individual needs.
- Proactive Communication: Communicate proactively with customers to address their concerns and provide updates.
- Customer Feedback: Solicit and act on customer feedback.
- Value-Added Service: Provide value-added service to customers to build loyalty.
7.5 Value-Based Selling
Why is Value-Based Selling Important? Value-based selling focuses on demonstrating the value and ROI of your software to potential clients.
Key Practices:
- Needs Analysis: Conduct a thorough needs analysis to understand the client’s challenges and objectives.
- Value Proposition: Clearly articulate the value proposition of your software.
- ROI Calculation: Calculate the ROI of your software for potential clients.
- Case Studies: Use case studies to demonstrate the value of your software to other clients.
8. What are Some Common Mistakes to Avoid in Software Sales?
Even with the best training and preparation, it’s easy to make mistakes in software sales. Awareness of these common pitfalls can help you navigate the sales process more effectively:
- Lack of Preparation
- Poor Listening Skills
- Focusing on Features, Not Benefits
- Neglecting Follow-Up
- Not Building Relationships
Let’s explore each mistake in detail:
8.1 Lack of Preparation
Why is Lack of Preparation a Mistake? Walking into a sales meeting without adequate preparation can undermine your credibility and reduce your chances of closing a deal.
How to Avoid:
- Research the Client: Thoroughly research the client’s business, industry, and needs.
- Prepare Your Pitch: Prepare a tailored sales pitch that addresses the client’s specific challenges.
- Anticipate Questions: Anticipate potential questions and prepare your answers in advance.
- Gather Materials: Gather all necessary materials, such as presentations, demos, and case studies.
8.2 Poor Listening Skills
Why are Poor Listening Skills a Mistake? Failing to listen actively to your clients can lead to misunderstandings and missed opportunities.
How to Avoid:
- Focus on the Client: Give your full attention to the client and avoid distractions.
- Ask Questions: Ask clarifying questions to ensure you understand the client’s needs.
- Summarize and Reflect: Summarize and reflect on what you’ve heard to confirm understanding.
- Take Notes: Take notes to capture important information and demonstrate your interest.
8.3 Focusing on Features, Not Benefits
Why is Focusing on Features a Mistake? Clients are more interested in how your software can solve their problems than in its technical features.
How to Avoid:
- Highlight Benefits: Focus on the benefits of your software rather than its features.
- Quantify Value: Quantify the value of your software in terms of cost savings, increased revenue, or improved efficiency.
- Use Case Studies: Use case studies to demonstrate how your software has helped other clients achieve their goals