Social Care Management Software streamlines workflows and enhances client care, making it a game-changer for social work practices in the US. At CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN, we understand the importance of efficient tools. This article explores how this software can transform your practice, covering everything from initial assessments to ongoing support and remote repair solutions. Learn how the right platform boosts productivity, improves client outcomes, and secures sensitive data, empowering your team to focus on what matters most: providing exceptional care. Let’s dive into optimizing your operations with telehealth integration, data analytics, and cloud-based solutions.
Contents
- 1. What is Social Care Management Software?
- 1.1. Core Features of Social Care Management Software
- 1.2. How Social Care Management Software Differs from Generic CRMs
- 1.3. Key Benefits of Using Social Care Management Software
- 2. Who Benefits from Social Care Management Software?
- 2.1. Social Workers and Case Managers
- 2.2. Non-Profit Organizations
- 2.3. Social Work Agencies
- 2.4. Educational Institutions
- 2.5. Private Practices
- 2.6. Government Agencies
- 3. Key Features to Look For in Social Care Management Software
- 3.1. Client Management and Tracking
- 3.2. Case Management Tools
- 3.3. Assessment and Evaluation
- 3.4. Reporting and Analytics
- 3.5. Compliance and Security
- 3.6. Communication and Collaboration Tools
- 3.7. Integration Capabilities
- 4. Implementing Social Care Management Software: A Step-by-Step Guide
- 4.1. Assessing Your Needs
- 4.2. Selecting the Right Software
- 4.3. Data Migration and Setup
- 4.4. Training and Onboarding
- 4.5. Testing and Go-Live
- 4.6. Ongoing Optimization
- 5. Social Care Management Software and Telehealth
- 5.1. Benefits of Integrating Telehealth
- 5.2. Key Telehealth Features to Look For
- 5.3. Best Practices for Telehealth Implementation
- 6. Cost Considerations for Social Care Management Software
- 6.1. Common Pricing Models
- 6.2. Hidden Costs to Watch Out For
- 6.3. Calculating ROI
- 7. Future Trends in Social Care Management Software
- 7.1. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Automation
- 7.2. Cloud-Based Solutions
- 7.3. Mobile Accessibility
- 7.4. Enhanced Data Security
- 7.5. Focus on Client Engagement
- 8. Social Care Management Software: Overcoming Challenges in US Practices
- 8.1. Addressing Administrative Burdens
- 8.2. Improving Client Care
- 8.3. Ensuring Data Security and Compliance
- 8.4. Enhancing Collaboration
- 8.5. Adapting to Remote Work
- 9. Case Studies: Successful Implementation of Social Care Management Software
1. What is Social Care Management Software?
Social care management software is a comprehensive platform designed to streamline and enhance the operations of social work practices by centralizing client data, automating administrative tasks, and facilitating collaboration among team members. This type of software acts as a central hub, integrating various functions such as client intake, case notes, scheduling, reporting, and compliance, thereby reducing administrative burdens and allowing social workers to focus more on direct client care.
1.1. Core Features of Social Care Management Software
Social care management software offers a range of features that are vital for modern social work practices. These functionalities are designed to improve efficiency, enhance client care, and ensure data security.
| Feature | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Client Management | Centralized database for storing client information, including demographics, contact details, case history, and progress notes. | Ensures easy access to client data, reduces redundancy, and improves accuracy. |
| Case Management | Tools for managing cases, including assignment, tracking progress, and documenting interventions. | Streamlines case workflow, ensures timely interventions, and enhances accountability. |
| Scheduling & Appointment Management | Automates appointment scheduling, sends reminders, and manages staff calendars. | Reduces no-shows, optimizes staff utilization, and improves client satisfaction. |
| Reporting & Analytics | Generates reports on caseloads, client outcomes, and program effectiveness. | Provides insights for decision-making, program evaluation, and compliance reporting. |
| Compliance & Security | Ensures adherence to HIPAA, GDPR, and other regulatory requirements, with features like data encryption and access controls. | Protects client privacy, reduces the risk of data breaches, and ensures legal compliance. |
| Communication Tools | Secure messaging, email integration, and client portals for communication between social workers, clients, and other stakeholders. | Enhances communication, improves client engagement, and ensures confidentiality. |
| Telehealth Integration | Enables virtual consultations and remote monitoring. | Extends reach to clients in remote areas, reduces travel time, and improves access to care. |
| Billing & Invoicing | Automates billing processes, generates invoices, and tracks payments. | Simplifies financial management, reduces errors, and improves cash flow. |
| Task Management | Helps social workers organize and prioritize tasks, set deadlines, and track progress on various activities related to client care. | Ensures that important tasks are not overlooked, improves productivity, and promotes better time management. |
| Document Management | Provides a centralized repository for storing and managing documents, such as assessment reports, consent forms, and legal documents, ensuring easy access and organization of important client-related information. | Reduces paperwork, improves document organization, and enhances compliance with record-keeping requirements. |
1.2. How Social Care Management Software Differs from Generic CRMs
While generic Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems might seem like a viable option, social care management software is specifically tailored to meet the unique needs of social work practices. CRMs are designed primarily for sales and marketing, lacking the specific features required for social care, such as compliance with healthcare regulations and specialized documentation templates. Social care management software includes features like HIPAA compliance, specific assessment templates (e.g., mental health assessments), and tools for managing sensitive client data, which are essential for maintaining ethical and legal standards in social work.
1.3. Key Benefits of Using Social Care Management Software
Implementing social care management software offers numerous benefits to social work practices:
- Enhanced Efficiency: Automation of administrative tasks reduces the time spent on paperwork, freeing up social workers to focus on client care.
- Improved Client Care: Centralized client data and streamlined workflows enable social workers to provide more personalized and effective services.
- Better Data Security: Compliance with regulations like HIPAA and GDPR ensures that client data is protected from unauthorized access.
- Enhanced Collaboration: Facilitates communication and collaboration among team members, leading to better coordination of care.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Reporting and analytics tools provide insights into client outcomes and program effectiveness, enabling evidence-based decision-making.
- Cost Savings: Reduction in administrative costs and improved efficiency can lead to significant cost savings for social work practices.
By understanding the core features and benefits of social care management software, social work practices can make informed decisions about implementing the right solution to meet their needs, ultimately improving the quality of care they provide to their clients.
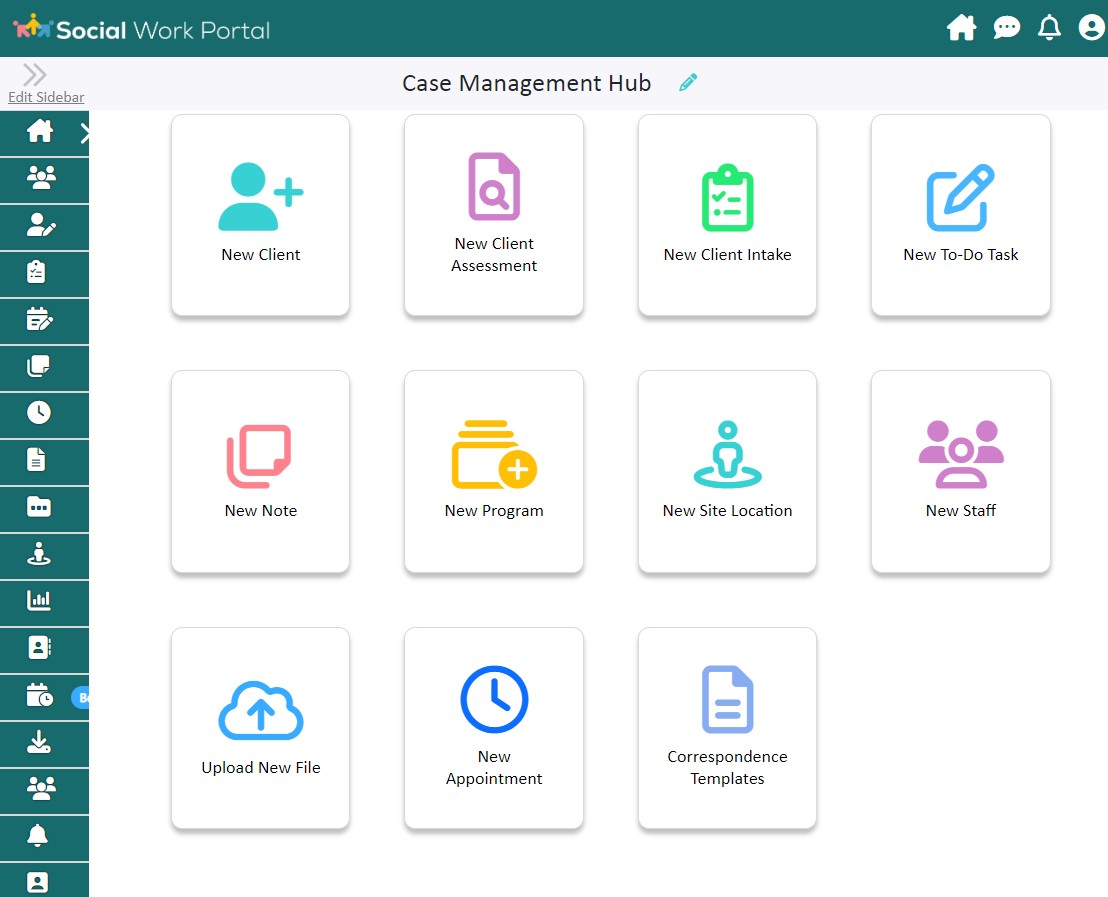 Best Case Management Hub for Social Services
Best Case Management Hub for Social Services
Best Case Management Hub: The image illustrates a user-friendly dashboard designed to centralize key social service functions, enhancing accessibility and efficiency.
2. Who Benefits from Social Care Management Software?
Social care management software offers distinct advantages to various stakeholders within the social services sector, each experiencing unique improvements in their daily operations and overall effectiveness. From individual social workers to large agencies, the software’s tailored features cater to a wide range of needs, ultimately enhancing the quality and reach of care provided.
2.1. Social Workers and Case Managers
For social workers and case managers, social care management software can significantly reduce administrative burdens and improve the quality of direct client interaction.
- Streamlined Documentation: Social workers can quickly record and access client information, progress notes, and assessment results, all in one centralized location. This reduces time spent on paperwork and allows more focus on client needs.
- Efficient Case Management: The software facilitates better organization of cases, tracking of interventions, and management of tasks, ensuring that no critical details are overlooked.
- Improved Communication: Secure messaging and client portals enhance communication between social workers and their clients, as well as with other members of the care team.
- Time Savings: By automating administrative tasks and providing quick access to client data, social workers can manage their caseloads more efficiently and spend more time providing direct support to clients.
- Reduced Burnout: Efficient tools and processes help reduce stress and burnout by streamlining tasks and improving work-life balance.
2.2. Non-Profit Organizations
Non-profit organizations benefit greatly from social care management software by improving their operational efficiency, enhancing service delivery, and strengthening accountability.
- Efficient Resource Allocation: The software helps non-profits allocate resources more effectively by providing insights into program performance, client demographics, and service utilization.
- Improved Program Management: Non-profits can use the software to manage and track programs, ensuring that they are aligned with organizational goals and client needs.
- Enhanced Reporting: The software generates reports on program outcomes, funding utilization, and client satisfaction, which are essential for grant applications, donor relations, and board meetings.
- Better Compliance: The software helps non-profits comply with regulatory requirements, such as HIPAA and GDPR, by ensuring that client data is secure and confidential.
- Increased Funding Opportunities: With detailed data on program outcomes and client impact, non-profits can strengthen their funding proposals and attract more donors.
2.3. Social Work Agencies
Social work agencies, whether public or private, can leverage social care management software to improve their overall efficiency, enhance client care, and ensure compliance with regulatory standards.
- Centralized Data Management: The software provides a centralized platform for managing client data, ensuring that all team members have access to the most up-to-date information.
- Streamlined Workflows: Agencies can automate workflows, such as client intake, assessment, and referral processes, reducing administrative bottlenecks and improving efficiency.
- Enhanced Collaboration: The software facilitates communication and collaboration among team members, enabling better coordination of care and improved client outcomes.
- Improved Compliance: Agencies can use the software to ensure compliance with regulatory requirements, such as HIPAA and GDPR, by implementing data security measures and access controls.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: The software provides insights into agency performance, client demographics, and service utilization, enabling data-driven decision making and strategic planning.
2.4. Educational Institutions
Educational institutions offering social work programs can benefit from social care management software by providing students with hands-on experience using industry-standard tools, preparing them for real-world practice.
- Practical Training: Students can use the software to practice case management, documentation, and assessment skills in a simulated environment, gaining valuable experience before entering the field.
- Curriculum Enhancement: The software can be integrated into the social work curriculum, providing students with a comprehensive understanding of how technology is used in social work practice.
- Research Opportunities: The software can be used for research purposes, enabling students and faculty to analyze client data, evaluate program outcomes, and identify best practices in social work.
- Career Readiness: By gaining experience with social care management software, students are better prepared for employment opportunities in social work agencies, non-profits, and other organizations.
- Improved Student Outcomes: Hands-on experience with the software can enhance student learning, improve their skills, and increase their confidence in their ability to provide effective social work services.
2.5. Private Practices
Private social work practices can enhance client care and streamline operations with social care management software.
- Efficient Practice Management: The software supports client scheduling, billing, and communication, centralizing administrative functions.
- Improved Client Engagement: Secure portals enable easy communication and information sharing with clients.
- Customized Documentation: The software offers customizable templates for progress notes and assessments, enhancing the quality of care and client outcomes.
2.6. Government Agencies
Government agencies can efficiently manage public assistance programs and streamline workflows with social care management software.
- Streamlined Program Delivery: The software supports eligibility determination, case management, and reporting, ensuring efficient program delivery.
- Enhanced Data Security: Compliance with regulations like HIPAA and GDPR ensures that client data is protected and secure.
- Improved Collaboration: The software facilitates coordination and communication among various government agencies, promoting collaboration and improving service delivery.
By addressing the unique needs of each sector, social care management software empowers professionals to deliver more effective, efficient, and compassionate care, ultimately strengthening communities and improving lives.
![]() Online Case Management Software – Intakes
Online Case Management Software – Intakes
Online Case Management Software Intakes: The icon symbolizes a streamlined, paperless intake process, essential for efficient social work management.
3. Key Features to Look For in Social Care Management Software
Choosing the right social care management software involves careful consideration of its features, ensuring they align with the specific needs of your social work practice. A robust software solution can significantly enhance efficiency, improve client care, and streamline operations. Here’s a detailed look at the essential features to consider.
3.1. Client Management and Tracking
Effective client management is the cornerstone of any social care practice. The software should provide a comprehensive system for storing and managing client information.
- Centralized Client Records: A unified database to store all client-related data, including demographics, contact information, case history, and progress notes.
- Customizable Fields: The ability to add custom fields to client profiles, allowing you to capture specific data relevant to your practice.
- Client Portal: A secure online portal where clients can access their information, complete forms, and communicate with their social worker.
- Tracking and Reporting: Tools to track client progress, monitor outcomes, and generate reports for program evaluation.
- Data Import/Export: Seamlessly import existing client data from other systems or export data for analysis and reporting.
- Data Segmentation: Organize clients into different groups for targeted communication and program delivery.
3.2. Case Management Tools
Efficient case management tools are essential for organizing and tracking client interventions, ensuring that social workers can provide timely and effective support.
- Case Assignment: Easily assign cases to social workers based on their expertise, caseload, and availability.
- Task Management: Create and assign tasks related to client cases, set deadlines, and track progress.
- Workflow Automation: Automate routine tasks, such as sending reminders, generating reports, and updating case status.
- Progress Notes: Streamlined tools for documenting client interactions, progress, and interventions, with customizable templates to suit different practice settings.
- Case Notes Formatting: Quick generation of case & progress notes using templates (SOAP, DAP, GIRP, BIRP, and more).
- Referral Management: Facilitate referrals to other services and agencies, track referral outcomes, and manage referral relationships.
- Goal Setting: Enable social workers to set measurable goals with clients and track progress toward achieving those goals.
- Alerts and Reminders: Set up alerts and reminders for appointments, deadlines, and other important events related to client cases.
3.3. Assessment and Evaluation
Comprehensive assessment tools are critical for gathering data, identifying client needs, and developing effective intervention plans.
- Assessment Templates: Pre-built templates for conducting various types of assessments, such as mental health assessments, needs assessments, and risk assessments.
- Customizable Assessments: The ability to create custom assessment forms tailored to your specific practice needs.
- Scoring and Analysis: Automated scoring and analysis of assessment results, providing insights into client strengths and areas for improvement.
- Reporting: Generate reports on assessment results, track trends, and evaluate the effectiveness of interventions.
3.4. Reporting and Analytics
Robust reporting and analytics tools provide valuable insights into program performance, client outcomes, and service utilization, enabling data-driven decision-making.
- Customizable Reports: Create custom reports tailored to your specific needs, with options to filter data, choose metrics, and format the output.
- Dashboards: Interactive dashboards that provide a visual overview of key performance indicators (KPIs) and trends.
- Data Export: Export data in various formats, such as Excel, CSV, and PDF, for further analysis and reporting.
- Data Visualization: Tools for creating charts, graphs, and other visualizations to communicate data effectively.
- Program Evaluation: Evaluate the effectiveness of programs and interventions by tracking client outcomes, service utilization, and other relevant metrics.
3.5. Compliance and Security
Ensuring compliance with regulations like HIPAA and GDPR is essential for protecting client data and maintaining ethical standards.
- HIPAA Compliance: Features to ensure compliance with HIPAA regulations, such as data encryption, access controls, and audit trails.
- GDPR Compliance: Tools to comply with GDPR requirements, such as data anonymization, consent management, and data breach notification.
- Data Encryption: Encrypt data both in transit and at rest to protect it from unauthorized access.
- Access Controls: Implement role-based access controls to limit access to sensitive data based on user roles and responsibilities.
- Audit Trails: Maintain a comprehensive audit trail of all user activity, including logins, data access, and modifications.
- Regular Security Updates: Ensure that the software is regularly updated with the latest security patches and vulnerability fixes.
3.6. Communication and Collaboration Tools
Effective communication and collaboration tools are essential for coordinating care, engaging clients, and facilitating teamwork.
- Secure Messaging: Encrypted messaging platform for secure communication between social workers, clients, and other members of the care team.
- Email Integration: Seamless integration with email platforms for sending and receiving client communications.
- Client Portal: A secure online portal where clients can access information, complete forms, and communicate with their social worker.
- Task Assignment: Assign tasks to team members, set deadlines, and track progress.
- Calendar Sharing: Share calendars among team members to coordinate schedules and appointments.
- Document Sharing: Securely share documents and files with clients and team members.
3.7. Integration Capabilities
The ability to integrate with other systems, such as electronic health records (EHRs) and accounting software, is essential for streamlining workflows and avoiding data silos.
- API Access: An open API that allows you to integrate the software with other systems.
- EHR Integration: Seamless integration with EHR systems for sharing client data and coordinating care.
- Accounting Software Integration: Integration with accounting software for managing billing, invoicing, and financial reporting.
- Third-Party App Integration: Integration with other third-party apps and services, such as telehealth platforms and payment processors.
By carefully evaluating these key features, social work practices can select the social care management software that best meets their needs, enabling them to provide more efficient, effective, and compassionate care to their clients.
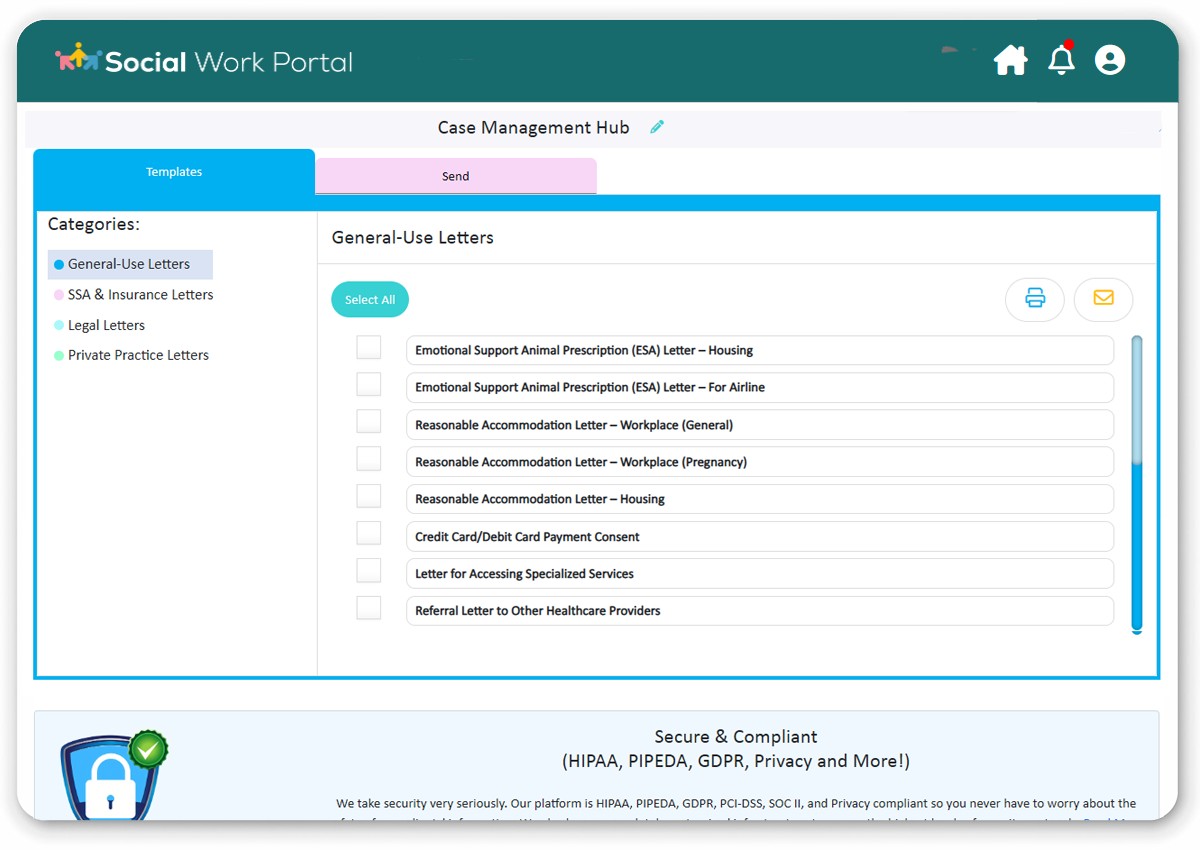
![]() Case Management Platform – Letters
Case Management Platform – Letters
Case Management Platform Letters: The image represents efficient correspondence through pre-built templates, enhancing communication.
4. Implementing Social Care Management Software: A Step-by-Step Guide
Implementing social care management software can transform your social work practice, enhancing efficiency, improving client care, and ensuring compliance. However, a successful implementation requires careful planning and execution. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you navigate the process.
4.1. Assessing Your Needs
Before selecting a social care management software, it’s essential to conduct a thorough assessment of your practice’s needs.
- Identify Pain Points: Determine the areas where your practice is struggling, such as inefficient documentation, communication breakdowns, or compliance issues.
- Define Goals: Set clear, measurable goals for what you want to achieve with the software, such as reducing administrative time, improving client outcomes, or enhancing data security.
- Stakeholder Input: Gather input from all stakeholders, including social workers, case managers, administrators, and clients, to understand their needs and preferences.
- Workflow Analysis: Analyze your existing workflows to identify opportunities for automation and streamlining.
- Technical Infrastructure: Evaluate your current IT infrastructure to ensure it can support the new software.
4.2. Selecting the Right Software
Choosing the right social care management software is a critical decision that can impact your practice for years to come.
- Research Options: Explore different software vendors and solutions, comparing features, pricing, and customer reviews.
- Request Demos: Schedule demos with multiple vendors to see the software in action and ask questions about its capabilities.
- Consider Scalability: Choose a software solution that can scale with your practice as it grows.
- Check Compatibility: Ensure the software is compatible with your existing systems and integrates seamlessly with other tools you use.
- Evaluate Security: Verify that the software meets industry standards for data security and privacy, such as HIPAA and GDPR compliance.
4.3. Data Migration and Setup
Migrating your existing data to the new software and setting up the system correctly are crucial steps for a successful implementation.
- Plan Data Migration: Develop a detailed plan for migrating your existing data to the new software, including timelines, data cleansing procedures, and testing protocols.
- Cleanse Data: Review and cleanse your existing data to remove duplicates, correct errors, and ensure accuracy.
- Import Data: Import your data into the new software, following the vendor’s instructions and best practices.
- Configure Settings: Customize the software settings to align with your practice’s workflows and preferences.
- Set Up User Accounts: Create user accounts for all staff members and assign appropriate roles and permissions.
4.4. Training and Onboarding
Proper training and onboarding are essential for ensuring that your staff can effectively use the new software.
- Develop Training Materials: Create training manuals, videos, and other resources to help staff learn how to use the software.
- Conduct Training Sessions: Schedule training sessions for all staff members, covering the core features and functions of the software.
- Provide Ongoing Support: Offer ongoing support and assistance to staff members as they begin using the software in their daily work.
- Assign Super Users: Identify and train super users who can serve as internal experts and provide support to other staff members.
4.5. Testing and Go-Live
Before fully launching the new software, it’s important to thoroughly test it to identify and resolve any issues.
- Conduct Testing: Perform thorough testing of all features and functions, including data entry, reporting, and integrations.
- Address Issues: Resolve any issues or bugs identified during testing, working with the vendor to find solutions.
- Develop a Go-Live Plan: Create a detailed plan for launching the new software, including timelines, communication strategies, and contingency plans.
- Monitor Performance: Continuously monitor the software’s performance after launch, tracking key metrics and addressing any issues that arise.
4.6. Ongoing Optimization
Implementing social care management software is not a one-time event; it’s an ongoing process of optimization and improvement.
- Gather Feedback: Regularly solicit feedback from staff members and clients to identify areas for improvement.
- Track Metrics: Monitor key metrics, such as administrative time, client outcomes, and user satisfaction, to measure the impact of the software.
- Implement Updates: Stay up-to-date with the latest software updates and features, and implement them as appropriate.
- Refine Workflows: Continuously refine your workflows to take full advantage of the software’s capabilities.
By following these steps, social work practices can successfully implement social care management software, transforming their operations and improving the quality of care they provide to their clients.
![]() Case Management Tools – Reporting
Case Management Tools – Reporting
Case Management Tools Reporting: The icon illustrates a streamlined process for generating insightful reports, aiding in informed decision-making.
5. Social Care Management Software and Telehealth
The integration of telehealth capabilities into social care management software is revolutionizing how social workers deliver services, particularly in today’s digital age. Telehealth extends the reach of social work practices, offering convenient and accessible care to clients regardless of their location.
5.1. Benefits of Integrating Telehealth
Integrating telehealth into social care management software offers numerous advantages:
- Expanded Access: Telehealth removes geographical barriers, allowing social workers to serve clients in remote or underserved areas.
- Convenience: Clients can access services from the comfort of their homes, reducing travel time and costs.
- Improved Engagement: Telehealth can increase client engagement, particularly for those who may be hesitant to seek in-person services.
- Enhanced Efficiency: Social workers can manage their time more efficiently by conducting virtual appointments and reducing travel time.
- Cost Savings: Telehealth can reduce costs for both clients and social work practices by eliminating the need for travel and physical office space.
- Continuity of Care: Telehealth ensures continuity of care during emergencies, such as pandemics or natural disasters.
5.2. Key Telehealth Features to Look For
When selecting social care management software with telehealth capabilities, consider the following features:
- Video Conferencing: Secure, HIPAA-compliant video conferencing tools for conducting virtual appointments.
- Screen Sharing: The ability to share screens for presentations, document review, and collaborative work.
- Chat Messaging: Secure chat messaging for quick communication between social workers and clients.
- Appointment Scheduling: Integrated appointment scheduling for telehealth appointments, with automated reminders and confirmations.
- Remote Monitoring: Tools for remote monitoring of client health and well-being, such as wearable devices and mobile apps.
- Integration with Assessment Tools: Seamless integration with assessment tools for conducting virtual assessments and evaluations.
- HIPAA Compliance: Ensure the telehealth platform is fully HIPAA compliant to protect client privacy and security.
5.3. Best Practices for Telehealth Implementation
To ensure a successful telehealth implementation, consider the following best practices:
- Develop Telehealth Policies: Create clear policies and procedures for telehealth services, including informed consent, confidentiality, and emergency protocols.
- Train Staff: Provide training to staff members on how to use the telehealth platform and deliver effective virtual services.
- Address Technology Barriers: Identify and address any technology barriers that clients may face, such as lack of access to computers or internet connectivity.
- Ensure Privacy and Security: Take steps to protect client privacy and security, such as using secure video conferencing platforms and encrypting data.
- Obtain Informed Consent: Obtain informed consent from clients before providing telehealth services, explaining the benefits, risks, and limitations of virtual care.
- Evaluate Outcomes: Track and evaluate the outcomes of telehealth services to assess their effectiveness and identify areas for improvement.
By integrating telehealth into social care management software, social work practices can expand their reach, improve client engagement, and deliver more efficient and effective care.
 Web-based Case Management Software
Web-based Case Management Software
Web-based Case Management Software: The visual represents accessibility and streamlined communication through web-based platforms, supporting efficient case management.
6. Cost Considerations for Social Care Management Software
When evaluating social care management software, it’s essential to consider the costs involved to ensure the solution fits within your budget and provides a good return on investment. The costs can vary widely depending on the software’s features, the size of your organization, and the pricing model.
6.1. Common Pricing Models
Understanding the different pricing models can help you make an informed decision:
- Subscription-Based: This is the most common pricing model, where you pay a recurring fee (monthly or annually) for access to the software. The fee may be based on the number of users, the features included, or the number of clients served.
- Per-User Pricing: You pay a fixed fee for each user who accesses the software. This model is suitable for practices with a consistent number of users.
- Tiered Pricing: The software is offered in different tiers with varying features and pricing. You choose the tier that best fits your needs and budget.
- One-Time License Fee: You pay a one-time fee for a perpetual license to use the software. This model may also include annual maintenance and support fees.
- Free or Open-Source: Some social care management software is available for free or as open-source solutions. While there may be no upfront cost, you may need to pay for customization, support, and maintenance.
6.2. Hidden Costs to Watch Out For
In addition to the upfront costs, be aware of potential hidden costs:
- Implementation Fees: Some vendors charge a fee for setting up the software, migrating data, and configuring settings.
- Training Fees: Training for staff members may incur additional costs.
- Customization Fees: Customizing the software to meet your specific needs may require additional fees.
- Support Fees: Ongoing technical support may be an additional cost.
- Data Migration Fees: If you need assistance migrating data from your existing system, the vendor may charge a fee.
- Integration Fees: Integrating the software with other systems may require additional fees.
- Storage Fees: If you exceed the storage limits included in your subscription, you may incur additional fees.
- Upgrade Fees: Upgrading to a newer version of the software may require additional fees.
6.3. Calculating ROI
To determine whether social care management software is a worthwhile investment, calculate the return on investment (ROI).
- Identify Cost Savings: Determine how the software will save you money, such as reducing administrative time, improving efficiency, and preventing compliance violations.
- Quantify Benefits: Quantify the benefits of the software, such as increased revenue, improved client outcomes, and enhanced data security.
- Calculate ROI: Divide the total cost savings and benefits by the total cost of the software to calculate the ROI.
- Consider Intangible Benefits: In addition to the quantifiable benefits, consider the intangible benefits of the software, such as improved staff morale, enhanced client satisfaction, and better decision-making.
By carefully considering the costs and benefits of social care management software, you can make an informed decision that aligns with your budget and supports your practice’s goals.
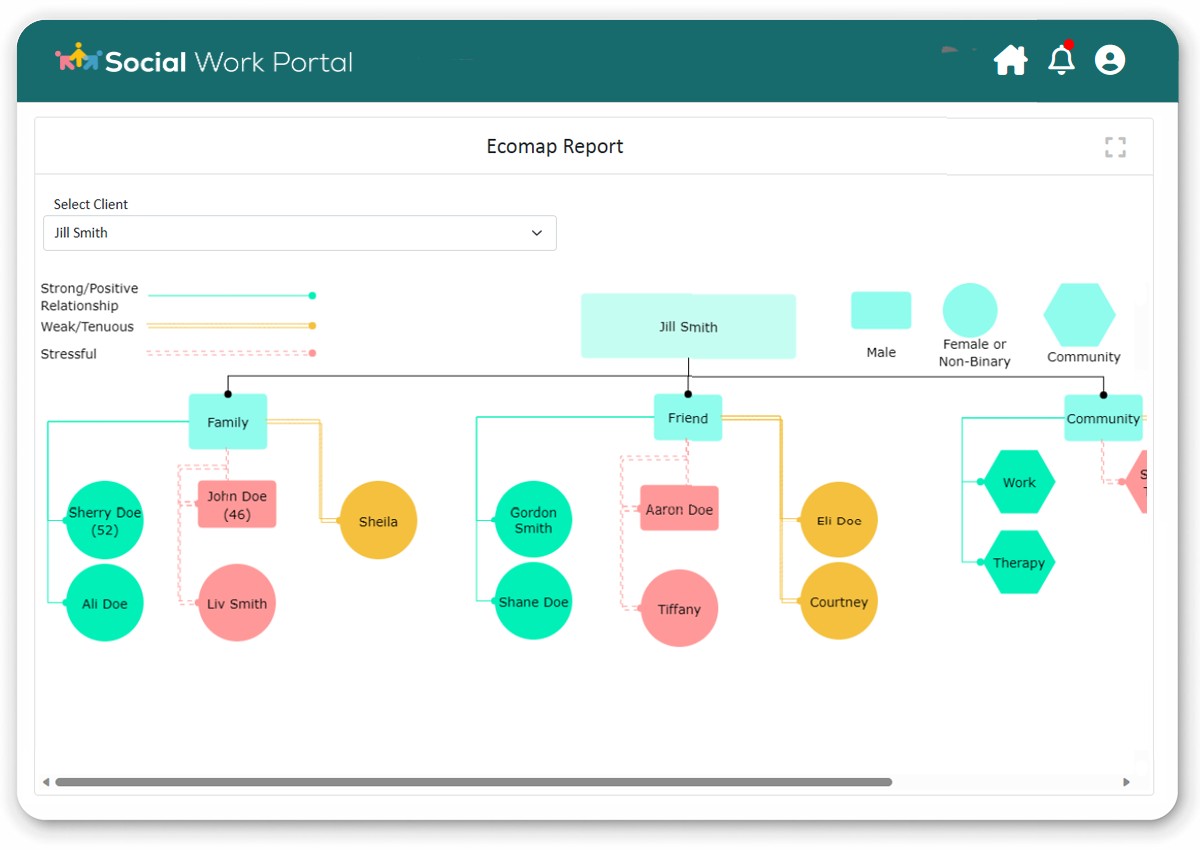 Ecomap Social Work
Ecomap Social Work
Ecomap Social Work: The image represents a visual tool for mapping client’s social ecosystems, enhancing treatment planning and support.
7. Future Trends in Social Care Management Software
The field of social care is constantly evolving, and social care management software is adapting to meet the changing needs of social work practices. Several emerging trends are shaping the future of these software solutions.
7.1. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Automation
AI and automation are poised to transform social care management software, streamlining processes and enhancing decision-making.
- AI-Powered Assessments: AI algorithms can analyze client data to identify patterns, predict risks, and generate personalized assessment reports.
- Automated Workflows: AI can automate routine tasks, such as scheduling appointments, sending reminders, and generating reports.
- Chatbots: AI-powered chatbots can provide instant support to clients, answer questions, and guide them through the intake process.
- Predictive Analytics: AI can analyze historical data to predict future outcomes, such as client relapse rates and program effectiveness.
7.2. Cloud-Based Solutions
Cloud-based social care management software offers numerous advantages over traditional on-premise solutions.
- Accessibility: Access the software from anywhere with an internet connection, enabling remote work and collaboration.
- Scalability: Easily scale your software resources up or down as needed, without having to invest in additional hardware.
- Cost Savings: Reduce IT costs by eliminating the need for on-premise servers, maintenance, and support.
- Security: Benefit from the enhanced security features of cloud platforms, such as data encryption and regular backups.
7.3. Mobile Accessibility
Mobile accessibility is becoming increasingly important, as social workers need to access client data and communicate with clients while in the field.
- Mobile Apps: Mobile apps allow social workers to access client data, schedule appointments, and communicate with clients from their smartphones or tablets.
- Responsive Design: Responsive design ensures that the software is accessible and user-friendly on any device, regardless of screen size.
- Offline Access: Offline access allows social workers to access client data even when they don’t have an internet connection.
7.4. Enhanced Data Security
With the increasing threat of cyberattacks, enhanced data security is a top priority for social care management software vendors.
- Encryption: Data encryption protects sensitive client data from unauthorized access.
- Multi-Factor Authentication: Multi-factor authentication adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to verify their identity through multiple channels.
- Regular Security Audits: Regular security audits help identify and address potential vulnerabilities in the software.
- Data Breach Response Plans: Data breach response plans ensure that vendors are prepared to respond quickly and effectively in the event of a security incident.
7.5. Focus on Client Engagement
Future social care management software will focus on enhancing client engagement through various features.
- Client Portals: Secure online portals allow clients to access their data, communicate with their social worker, and complete forms.
- Telehealth Integration: Telehealth integration enables virtual appointments and remote monitoring, improving access to care.
- Gamification: Gamification techniques can be used to motivate clients to engage in their care plans and achieve their goals.
By staying informed about these future trends, social work practices can select social care management software that is well-positioned to meet their evolving needs and support their mission of providing high-quality care to clients.
8. Social Care Management Software: Overcoming Challenges in US Practices
Social care management software addresses numerous challenges faced by social work practices in the US. These challenges range from administrative inefficiencies to the need for improved client care and data security. By implementing the right software, practices can streamline operations, enhance service delivery, and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements.
8.1. Addressing Administrative Burdens
Administrative tasks, such as documentation, scheduling, and reporting, can consume a significant amount of time for social workers, reducing the time they can spend on direct client care. Social care management software automates many of these tasks, freeing up social workers to focus on their clients.
- Automated Documentation: The software includes customizable templates for progress notes, assessments, and other documents, reducing the time spent on paperwork.
- Streamlined Scheduling: Automated scheduling tools help manage appointments, send reminders, and coordinate staff calendars.
- Efficient Reporting: The software generates reports on caseloads, client outcomes, and program effectiveness, reducing the time spent on manual data collection and analysis.
8.2. Improving Client Care
Social care management software enhances the quality of client care by providing social workers with easy access to client data, tools for tracking progress, and secure communication channels.
- Centralized Client Records: A unified database stores all client-related data, including demographics, contact information, case history, and progress notes.
- Progress Tracking: Tools to track client progress, monitor outcomes, and generate reports for program evaluation.
- Secure Communication: Secure messaging and client portals facilitate communication between social workers and clients, as well as with other members of the care team.
8.3. Ensuring Data Security and Compliance
Protecting client data and complying with regulations like HIPAA and GDPR are critical concerns for social work practices. Social care management software includes features to ensure data security and compliance.
- HIPAA Compliance: Features to ensure compliance with HIPAA regulations, such as data encryption, access controls, and audit trails.
- GDPR Compliance: Tools to comply with GDPR requirements, such as data anonymization, consent management, and data breach notification.
- Data Encryption: Encrypt data both in transit and at rest to protect it from unauthorized access.
- Access Controls: Implement role-based access controls to limit access to sensitive data based on user roles and responsibilities.
- Audit Trails: Maintain a comprehensive audit trail of all user activity, including logins, data access, and modifications.
8.4. Enhancing Collaboration
Effective collaboration among team members is essential for providing coordinated care. Social care management software facilitates communication and collaboration among social workers, case managers, and other members of the care team.
- Secure Messaging: Encrypted messaging platform for secure communication between social workers, clients, and other members of the care team.
- Task Assignment: Assign tasks to team members, set deadlines, and track progress.
- Calendar Sharing: Share calendars among team members to coordinate schedules and appointments.
- Document Sharing: Securely share documents and files with clients and team members.
8.5. Adapting to Remote Work
With the increasing prevalence of remote work, social care management software enables social workers to provide services from anywhere with an internet connection.
- Cloud-Based Access: Access the software from anywhere with an internet connection, enabling remote work and collaboration.
- Mobile Apps: Mobile apps allow social workers to access client data, schedule appointments, and communicate with clients from their smartphones or tablets.
- Telehealth Integration: Telehealth integration enables virtual appointments and remote monitoring, improving access to care.
By addressing these challenges, social care management software empowers social work practices to provide more efficient, effective, and compassionate care to their clients.
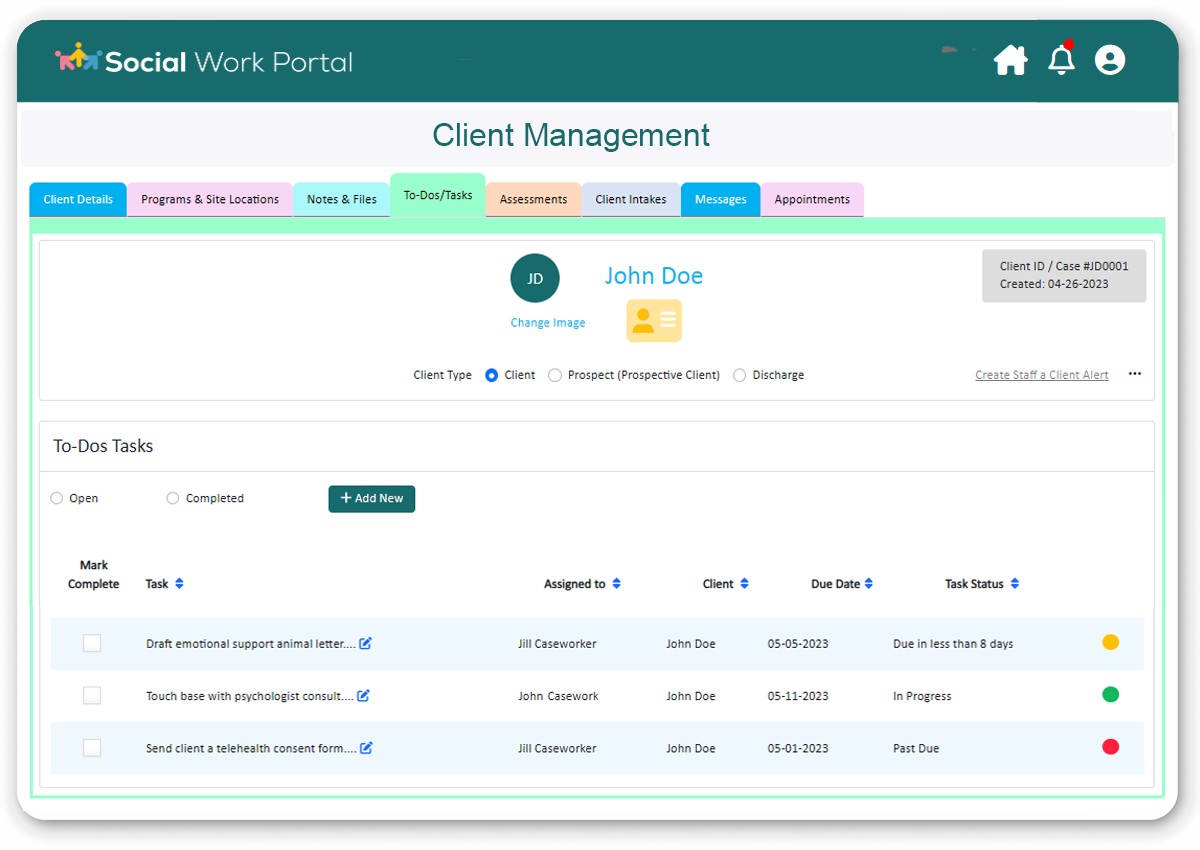 Social Worker Case Management
Social Worker Case Management
Social Worker Case Management: This image showcases a social worker using a digital platform to manage client information, emphasizing streamlined case management.
9. Case Studies: Successful Implementation of Social Care Management Software
To illustrate the real-world benefits of social care management software, let’s explore a few case studies of practices that have successfully implemented these solutions.