Car Dealership Software Attacks are a growing threat, but how deeply do they impact your business? At CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN, we’ll explore the anatomy of these cyberattacks, their far-reaching consequences, and, most importantly, how to protect your dealership. Understanding these risks and implementing robust cybersecurity measures is crucial in today’s digital landscape, safeguarding your operations from data breaches and financial losses. Explore proactive incident response plans and data recovery strategies to fortify your business against cyber threats.
Contents
- 1. What Is A Car Dealership Software Attack?
- 1.1 What Are Common Types of Car Dealership Software Attacks?
- 1.2 Why Are Car Dealerships Targeted for Cyberattacks?
- 2. What is the Impact of Car Dealership Software Attack?
- 2.1 Financial Losses
- 2.2 Operational Disruptions
- 2.3 Reputational Damage
- 2.4 Data Breaches and Compliance Issues
- 3. How Can Dealerships Prevent Car Dealership Software Attacks?
- 3.1 Implement Strong Cybersecurity Measures
- 3.2 Train Employees on Cybersecurity Best Practices
- 3.3 Develop an Incident Response Plan
- 3.4 Stay Informed About the Latest Threats
- 3.5 Secure Third-Party Vendor Relationships
- 4. What Role Does Car Dealership Software Play in Cybersecurity?
- 4.1 Secure Software Development Practices
- 4.2 Software Updates and Patch Management
- 4.3 Access Controls and Permissions
- 4.4 Data Encryption and Protection
- 5. What Are the Latest Trends in Car Dealership Software Attacks?
- 5.1 Increase in Ransomware Attacks
- 5.2 Phishing Attacks Targeting Dealership Employees
- 5.3 Supply Chain Attacks
- 5.4 Increase in Data Breaches
- 6. What Are the Compliance Requirements for Car Dealerships Regarding Cybersecurity?
- 6.1 The Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act (GLBA)
- 6.2 The California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA)
- 6.3 The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)
- 6.4 The Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS)
- 7. How Can Car-Remote-Repair.Edu.Vn Help Dealerships With Cybersecurity?
- 7.1 Cybersecurity Training Programs
- 7.2 Vulnerability Assessments and Penetration Testing
- 7.3 Incident Response Planning and Support
- 7.4 Managed Security Services
- 7.5 Compliance Consulting
- 8. Real-World Examples of Car Dealership Software Attacks
- 8.1 The CDK Global Cyberattack (2024)
- 8.2 The Penske Automotive Group Ransomware Attack (2019)
- 8.3 The Group 1 Automotive Data Breach (2020)
- 8.4 The Sewell Automotive Companies Phishing Attack (2021)
- 9. Future Trends in Car Dealership Cybersecurity
- 9.1 Increased Use of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Cybersecurity
- 9.2 Greater Emphasis on Zero Trust Security
- 9.3 Expansion of Cybersecurity Regulations
- 9.4 Growing Importance of Cybersecurity Insurance
- 10. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Car Dealership Software Attacks
- 10.1 What is a car dealership software attack?
- 10.2 What are the common types of car dealership software attacks?
- 10.3 Why are car dealerships targeted for cyberattacks?
- 10.4 What is the impact of a car dealership software attack?
- 10.5 How can dealerships prevent car dealership software attacks?
- 10.6 What role does car dealership software play in cybersecurity?
- 10.7 What are the latest trends in car dealership software attacks?
- 10.8 What are the compliance requirements for car dealerships regarding cybersecurity?
- 10.9 How can CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN help dealerships with cybersecurity?
- 10.10 What are some real-world examples of car dealership software attacks?
- 10.11 What are the future trends in car dealership cybersecurity?
1. What Is A Car Dealership Software Attack?
A car dealership software attack is a cyberattack targeting the software systems used by dealerships to manage their operations. This includes dealership management systems (DMS), customer relationship management (CRM) software, and other critical applications. These attacks can take many forms, including ransomware, malware, and phishing, all aimed at disrupting operations, stealing data, or extorting money. According to a 2023 report by the National Automobile Dealers Association (NADA), cyberattacks on dealerships increased by 45% compared to the previous year, highlighting the growing threat.
1.1 What Are Common Types of Car Dealership Software Attacks?
Understanding the different types of attacks can help dealerships prepare and protect themselves. These are some of the most common:
- Ransomware: This involves encrypting a dealership’s data and demanding a ransom payment for the decryption key. Ransomware attacks can bring operations to a standstill and result in significant financial losses.
- Malware: Malware includes viruses, worms, and Trojans that can infect a dealership’s systems, causing damage and stealing sensitive information.
- Phishing: Phishing attacks involve tricking employees into revealing their login credentials or other sensitive information, which can then be used to gain unauthorized access to dealership systems.
- Data Breaches: These occur when sensitive data, such as customer information or financial records, is accessed and stolen by unauthorized individuals.
- Denial-of-Service (DoS) Attacks: These attacks flood a dealership’s systems with traffic, making them unavailable to legitimate users and disrupting operations.
1.2 Why Are Car Dealerships Targeted for Cyberattacks?
Car dealerships are attractive targets for cybercriminals for several reasons:
- High Value Data: Dealerships handle vast amounts of sensitive data, including customer personal information, credit card details, and financial records. This data is valuable to cybercriminals for identity theft and financial fraud.
- Complex IT Infrastructure: Dealerships often rely on a complex IT infrastructure, including multiple software systems, network devices, and cloud services. This complexity can create vulnerabilities that cybercriminals can exploit.
- Limited Cybersecurity Resources: Many dealerships, especially smaller ones, lack the resources and expertise to implement robust cybersecurity measures. This makes them easier targets for cyberattacks.
- Operational Dependence on Software: Dealerships heavily rely on software systems to manage their daily operations. A successful cyberattack can disrupt these operations and cause significant financial losses.
- Potential for High Ransom Payments: Cybercriminals know that dealerships are often willing to pay a ransom to regain access to their data and systems quickly, making ransomware attacks a lucrative option.
 Car Dealership Software Attack Targets
Car Dealership Software Attack Targets
2. What is the Impact of Car Dealership Software Attack?
The impact of a car dealership software attack can be devastating, affecting every aspect of the business. From financial losses to reputational damage, the consequences can be long-lasting.
2.1 Financial Losses
A cyberattack can result in significant financial losses for a dealership, including:
- Ransom Payments: If a dealership falls victim to a ransomware attack, they may be forced to pay a ransom to regain access to their data and systems.
- Lost Revenue: A cyberattack can disrupt operations, leading to lost sales, service appointments, and other revenue-generating activities.
- Recovery Costs: Recovering from a cyberattack can be expensive, involving costs for IT support, data recovery, and system repairs.
- Legal and Compliance Costs: Dealerships may incur legal and compliance costs related to data breach notifications, regulatory investigations, and potential lawsuits.
- Insurance Premiums: Following a cyberattack, a dealership’s cybersecurity insurance premiums are likely to increase, adding to their ongoing expenses.
2.2 Operational Disruptions
A successful cyberattack can bring a dealership’s operations to a standstill, affecting:
- Sales: Dealerships may be unable to process sales transactions, access vehicle inventory, or generate sales reports.
- Service: Service departments may be unable to schedule appointments, access customer service records, or process repair orders.
- Parts: Parts departments may be unable to order parts, track inventory, or fulfill customer orders.
- Accounting: Accounting departments may be unable to process payments, reconcile accounts, or generate financial reports.
- Customer Communication: Dealerships may be unable to communicate with customers via email, phone, or other channels, leading to frustration and dissatisfaction.
2.3 Reputational Damage
A cyberattack can damage a dealership’s reputation and erode customer trust, resulting in:
- Loss of Customer Trust: Customers may be hesitant to do business with a dealership that has experienced a data breach or cyberattack.
- Negative Reviews: Customers may post negative reviews online, damaging the dealership’s reputation and deterring potential customers.
- Brand Damage: A cyberattack can damage a dealership’s brand and reduce its perceived value in the market.
- Loss of Competitive Advantage: A dealership that has experienced a cyberattack may lose its competitive advantage compared to dealerships with stronger cybersecurity measures.
2.4 Data Breaches and Compliance Issues
A cyberattack can result in data breaches that expose sensitive customer and business information, leading to:
- Customer Data Exposure: A data breach can expose customer personal information, credit card details, and other sensitive data.
- Compliance Violations: Dealerships may violate data privacy regulations, such as the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) or the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), resulting in fines and penalties.
- Legal Liabilities: Dealerships may face lawsuits from customers and other parties affected by a data breach.
- Regulatory Investigations: Regulatory agencies may launch investigations into a dealership’s data security practices following a data breach.
3. How Can Dealerships Prevent Car Dealership Software Attacks?
Preventing car dealership software attacks requires a multi-layered approach that includes implementing robust cybersecurity measures, training employees, and staying informed about the latest threats.
3.1 Implement Strong Cybersecurity Measures
Dealerships should implement a range of cybersecurity measures to protect their systems and data, including:
- Firewalls: Firewalls act as a barrier between a dealership’s network and the outside world, blocking unauthorized access and malicious traffic.
- Antivirus Software: Antivirus software can detect and remove malware from a dealership’s systems, preventing infections and data breaches.
- Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDS/IPS): IDS/IPS can monitor network traffic for suspicious activity and automatically block or mitigate threats.
- Data Encryption: Encrypting sensitive data can protect it from unauthorized access, even if a data breach occurs.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): MFA requires users to provide multiple forms of identification, such as a password and a code from their mobile device, making it more difficult for cybercriminals to gain unauthorized access.
- Regular Security Audits: Conducting regular security audits can help identify vulnerabilities and ensure that cybersecurity measures are effective.
- Patch Management: Keeping software and systems up to date with the latest security patches can prevent cybercriminals from exploiting known vulnerabilities.
3.2 Train Employees on Cybersecurity Best Practices
Employees are often the first line of defense against cyberattacks. Dealerships should provide regular training on cybersecurity best practices, including:
- Identifying Phishing Emails: Training employees to recognize phishing emails can prevent them from falling victim to these attacks and revealing sensitive information.
- Creating Strong Passwords: Employees should be instructed to create strong, unique passwords and to avoid using the same password for multiple accounts.
- Avoiding Suspicious Links and Attachments: Employees should be warned to avoid clicking on suspicious links or opening attachments from unknown senders.
- Reporting Security Incidents: Employees should be trained to report any suspected security incidents to the IT department or a designated security officer.
- Data Handling Procedures: Employees should be educated on proper data handling procedures, including how to protect sensitive customer information.
3.3 Develop an Incident Response Plan
An incident response plan outlines the steps a dealership should take in the event of a cyberattack. This plan should include:
- Identifying and Containing the Attack: The first step is to identify the type of attack and contain it to prevent further damage.
- Notifying Stakeholders: Stakeholders, including customers, employees, and regulatory agencies, should be notified of the attack as soon as possible.
- Recovering Data and Systems: The dealership should have a plan in place for recovering data and systems from backups or other sources.
- Conducting a Post-Incident Analysis: After the attack, a post-incident analysis should be conducted to determine the cause of the attack and identify areas for improvement in the dealership’s cybersecurity measures.
- Regularly Testing the Plan: The incident response plan should be tested regularly to ensure that it is effective and that employees know their roles and responsibilities.
3.4 Stay Informed About the Latest Threats
Cyber threats are constantly evolving, so dealerships must stay informed about the latest threats and vulnerabilities. This can be achieved by:
- Subscribing to Cybersecurity Newsletters: Subscribing to cybersecurity newsletters can provide dealerships with timely information about new threats and vulnerabilities.
- Attending Cybersecurity Conferences and Webinars: Attending cybersecurity conferences and webinars can provide dealerships with insights from industry experts and opportunities to network with other professionals.
- Working with a Cybersecurity Vendor: A cybersecurity vendor can provide dealerships with ongoing threat intelligence and support.
- Monitoring Security Alerts: Dealerships should monitor security alerts from software vendors and other sources to stay informed about potential vulnerabilities.
3.5 Secure Third-Party Vendor Relationships
Dealerships often rely on third-party vendors for various services, such as software, cloud storage, and payment processing. It is essential to ensure that these vendors have strong cybersecurity measures in place. Dealerships should:
- Conduct Due Diligence: Before partnering with a vendor, dealerships should conduct due diligence to assess their cybersecurity practices.
- Review Vendor Contracts: Vendor contracts should include clauses that require vendors to maintain strong cybersecurity measures and to notify the dealership in the event of a data breach.
- Monitor Vendor Security Practices: Dealerships should regularly monitor vendor security practices to ensure that they remain effective.
- Implement Access Controls: Dealerships should implement access controls to limit vendor access to sensitive data and systems.
 Car Dealership Software Attack Targets
Car Dealership Software Attack Targets
4. What Role Does Car Dealership Software Play in Cybersecurity?
Car dealership software is a critical component of a dealership’s operations, and it also plays a significant role in cybersecurity.
4.1 Secure Software Development Practices
Software vendors should follow secure software development practices to minimize vulnerabilities in their products. This includes:
- Security Testing: Conducting regular security testing to identify and address vulnerabilities.
- Code Reviews: Performing code reviews to ensure that code is secure and free from errors.
- Input Validation: Implementing input validation to prevent attackers from injecting malicious code into the system.
- Access Controls: Implementing access controls to restrict access to sensitive data and functions.
- Encryption: Using encryption to protect sensitive data in transit and at rest.
4.2 Software Updates and Patch Management
Software vendors should provide regular updates and security patches to address vulnerabilities in their products. Dealerships should promptly install these updates to protect their systems from attack.
- Automated Patch Management: Implementing automated patch management can ensure that software is updated promptly and efficiently.
- Testing Patches: Before deploying patches, dealerships should test them in a non-production environment to ensure that they do not cause any compatibility issues.
- Monitoring Patch Status: Dealerships should monitor the status of patches to ensure that they are installed correctly and that all systems are protected.
4.3 Access Controls and Permissions
Car dealership software should provide robust access controls and permissions to restrict access to sensitive data and functions.
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Implementing RBAC can ensure that users only have access to the data and functions they need to perform their jobs.
- Least Privilege Principle: Following the least privilege principle can minimize the risk of unauthorized access and data breaches.
- Regular Access Reviews: Conducting regular access reviews can help identify and remove unnecessary access privileges.
4.4 Data Encryption and Protection
Car dealership software should use encryption to protect sensitive data in transit and at rest.
- Data Encryption at Rest: Encrypting data at rest can protect it from unauthorized access, even if a data breach occurs.
- Data Encryption in Transit: Encrypting data in transit can protect it from eavesdropping and interception.
- Tokenization: Using tokenization can protect sensitive data, such as credit card numbers, by replacing it with a non-sensitive token.
5. What Are the Latest Trends in Car Dealership Software Attacks?
Staying informed about the latest trends in car dealership software attacks is crucial for protecting your business.
5.1 Increase in Ransomware Attacks
Ransomware attacks are becoming increasingly common and sophisticated, targeting dealerships of all sizes.
- Double Extortion: Cybercriminals are now using double extortion tactics, demanding a ransom payment to decrypt data and threatening to release it publicly if the ransom is not paid.
- Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS): RaaS makes it easier for cybercriminals to launch ransomware attacks, even if they lack technical skills.
- Targeting Backup Data: Cybercriminals are increasingly targeting backup data to prevent dealerships from recovering their systems without paying the ransom.
5.2 Phishing Attacks Targeting Dealership Employees
Phishing attacks remain a popular method for cybercriminals to gain access to dealership systems.
- Spear Phishing: Spear phishing attacks target specific individuals within a dealership, making them more difficult to detect.
- Business Email Compromise (BEC): BEC attacks involve impersonating dealership executives or vendors to trick employees into transferring funds or revealing sensitive information.
- Credential Stuffing: Credential stuffing attacks involve using stolen usernames and passwords to gain unauthorized access to dealership systems.
5.3 Supply Chain Attacks
Supply chain attacks involve targeting third-party vendors to gain access to dealership systems.
- Targeting Software Vendors: Cybercriminals are increasingly targeting software vendors to compromise the software used by dealerships.
- Compromising Managed Service Providers (MSPs): MSPs provide IT services to dealerships, making them a valuable target for cybercriminals.
- Exploiting Vulnerabilities in Third-Party Applications: Cybercriminals are exploiting vulnerabilities in third-party applications to gain access to dealership systems.
5.4 Increase in Data Breaches
Data breaches are becoming more frequent and severe, exposing sensitive customer and business information.
- Insider Threats: Insider threats, whether malicious or unintentional, can result in data breaches.
- Cloud Storage Vulnerabilities: Misconfigured cloud storage can expose sensitive data to unauthorized access.
- Lack of Data Encryption: Failure to encrypt sensitive data can result in data breaches if systems are compromised.
6. What Are the Compliance Requirements for Car Dealerships Regarding Cybersecurity?
Car dealerships must comply with various regulations and standards regarding cybersecurity and data protection.
6.1 The Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act (GLBA)
The GLBA requires financial institutions, including car dealerships that offer financing, to protect customer nonpublic personal information (NPI).
- Developing a Written Information Security Plan (WISP): Dealerships must develop a WISP that outlines their cybersecurity measures.
- Designating a Security Officer: Dealerships must designate a security officer responsible for implementing and maintaining the WISP.
- Conducting Risk Assessments: Dealerships must conduct regular risk assessments to identify and address vulnerabilities in their systems.
- Implementing Security Measures: Dealerships must implement security measures to protect customer NPI, including firewalls, antivirus software, and data encryption.
- Overseeing Service Providers: Dealerships must oversee their service providers to ensure that they are protecting customer NPI.
6.2 The California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA)
The CCPA grants California residents certain rights regarding their personal information, including the right to know, the right to delete, and the right to opt-out of the sale of their personal information.
- Providing Notice to Consumers: Dealerships must provide notice to consumers about their data collection practices.
- Responding to Consumer Requests: Dealerships must respond to consumer requests to know, delete, and opt-out of the sale of their personal information.
- Implementing Security Measures: Dealerships must implement security measures to protect consumer personal information.
6.3 The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)
The GDPR applies to organizations that process the personal data of individuals in the European Union (EU).
- Obtaining Consent: Dealerships must obtain consent from individuals before processing their personal data.
- Providing Transparency: Dealerships must provide transparency about their data processing practices.
- Implementing Security Measures: Dealerships must implement security measures to protect personal data.
- Data Breach Notification: Dealerships must notify data protection authorities and affected individuals in the event of a data breach.
6.4 The Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS)
The PCI DSS applies to organizations that handle credit card information.
- Building and Maintaining a Secure Network: Dealerships must build and maintain a secure network to protect credit card information.
- Protecting Cardholder Data: Dealerships must protect cardholder data by encrypting it and implementing access controls.
- Maintaining a Vulnerability Management Program: Dealerships must maintain a vulnerability management program to identify and address security vulnerabilities.
- Implementing Strong Access Control Measures: Dealerships must implement strong access control measures to restrict access to cardholder data.
- Regularly Monitoring and Testing Networks: Dealerships must regularly monitor and test their networks to detect and prevent security breaches.
- Maintaining an Information Security Policy: Dealerships must maintain an information security policy to guide their cybersecurity efforts.
7. How Can Car-Remote-Repair.Edu.Vn Help Dealerships With Cybersecurity?
CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN offers a range of services to help dealerships strengthen their cybersecurity posture and protect their businesses from car dealership software attacks.
7.1 Cybersecurity Training Programs
CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN offers comprehensive cybersecurity training programs for dealership employees, covering topics such as:
- Phishing Awareness: Training employees to recognize and avoid phishing attacks.
- Password Security: Teaching employees how to create strong, unique passwords.
- Data Handling Procedures: Educating employees on proper data handling procedures.
- Incident Reporting: Training employees to report security incidents promptly.
7.2 Vulnerability Assessments and Penetration Testing
CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN conducts vulnerability assessments and penetration testing to identify vulnerabilities in dealership systems.
- Vulnerability Scanning: Scanning systems for known vulnerabilities.
- Penetration Testing: Simulating real-world attacks to identify weaknesses in security measures.
- Reporting and Remediation: Providing detailed reports and recommendations for remediation.
7.3 Incident Response Planning and Support
CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN helps dealerships develop incident response plans and provides support during security incidents.
- Incident Response Planning: Developing a comprehensive incident response plan tailored to the dealership’s needs.
- Incident Response Support: Providing expert support during security incidents, including containment, eradication, and recovery.
- Post-Incident Analysis: Conducting post-incident analysis to identify the cause of the attack and improve security measures.
7.4 Managed Security Services
CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN offers managed security services to provide ongoing protection for dealership systems.
- Managed Firewall: Providing and managing firewalls to protect dealership networks.
- Managed Antivirus: Providing and managing antivirus software to protect dealership systems.
- Intrusion Detection and Prevention: Monitoring network traffic for suspicious activity and automatically blocking or mitigating threats.
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM): Collecting and analyzing security logs to detect and respond to security incidents.
7.5 Compliance Consulting
CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN provides compliance consulting services to help dealerships meet their regulatory requirements.
- GLBA Compliance: Helping dealerships comply with the GLBA requirements for protecting customer NPI.
- CCPA Compliance: Helping dealerships comply with the CCPA requirements for protecting consumer personal information.
- GDPR Compliance: Helping dealerships comply with the GDPR requirements for protecting the personal data of individuals in the EU.
- PCI DSS Compliance: Helping dealerships comply with the PCI DSS requirements for protecting credit card information.
By partnering with CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN, dealerships can strengthen their cybersecurity posture, protect their businesses from car dealership software attacks, and meet their regulatory requirements.
8. Real-World Examples of Car Dealership Software Attacks
Examining real-world examples of car dealership software attacks can provide valuable insights and lessons for dealerships looking to improve their cybersecurity.
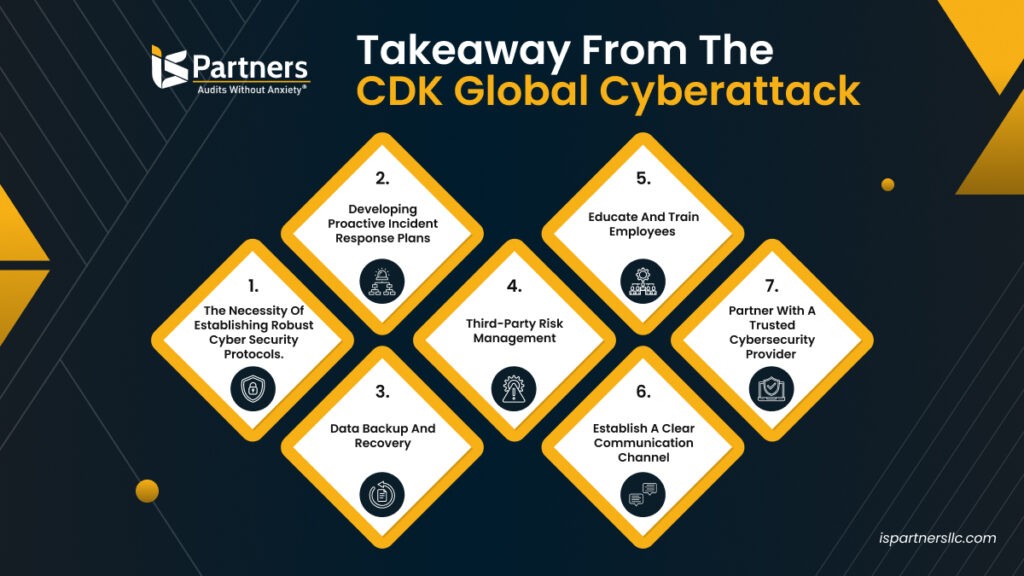
8.1 The CDK Global Cyberattack (2024)
In June 2024, CDK Global, a major provider of software to car dealerships, suffered a significant cyberattack that disrupted operations for thousands of dealerships across North America. The attack, attributed to the BlackSuit ransomware group, forced CDK to shut down its systems, causing widespread disruptions to sales, service, and other critical functions. This incident highlighted the vulnerability of dealerships that rely on third-party software providers and the importance of having robust cybersecurity measures in place.
- Impact: Thousands of dealerships were affected, with disruptions to sales, service, and other critical functions.
- Cause: The attack was attributed to the BlackSuit ransomware group.
- Lessons Learned: The incident highlighted the vulnerability of dealerships that rely on third-party software providers and the importance of having robust cybersecurity measures in place.
8.2 The Penske Automotive Group Ransomware Attack (2019)
In 2019, Penske Automotive Group, one of the largest auto retailers in the world, was hit by a ransomware attack that disrupted its operations and resulted in significant financial losses. The attack forced Penske to shut down its IT systems, impacting sales, service, and internal communications. While the company did not disclose the amount of the ransom paid, it acknowledged that the attack had a material impact on its financial results.
- Impact: Penske’s IT systems were shut down, impacting sales, service, and internal communications.
- Cause: The attack was a ransomware attack.
- Lessons Learned: The incident demonstrated the potential financial impact of a cyberattack on a large automotive retailer and the importance of having a robust incident response plan in place.
8.3 The Group 1 Automotive Data Breach (2020)
In 2020, Group 1 Automotive, another large auto retailer, disclosed a data breach that exposed the personal information of more than 200,000 customers. The breach occurred when an unauthorized party gained access to a company database containing customer names, addresses, dates of birth, and Social Security numbers. The company notified affected customers and offered them credit monitoring services.
- Impact: The personal information of more than 200,000 customers was exposed.
- Cause: An unauthorized party gained access to a company database.
- Lessons Learned: The incident highlighted the importance of protecting customer data and implementing strong access controls.
8.4 The Sewell Automotive Companies Phishing Attack (2021)
In 2021, Sewell Automotive Companies, a Texas-based auto retailer, fell victim to a phishing attack that compromised employee email accounts. The attackers used the compromised accounts to send fraudulent emails to customers, attempting to trick them into transferring funds. The company detected the attack and took steps to contain it, but not before some customers had been defrauded.
- Impact: Employee email accounts were compromised, and fraudulent emails were sent to customers.
- Cause: The attack was a phishing attack.
- Lessons Learned: The incident demonstrated the importance of training employees to recognize and avoid phishing attacks.
These real-world examples illustrate the diverse types of car dealership software attacks, their potential impact, and the importance of implementing robust cybersecurity measures to protect your business.
9. Future Trends in Car Dealership Cybersecurity
The cybersecurity landscape is constantly evolving, and car dealerships must stay ahead of the curve to protect their businesses from emerging threats.
9.1 Increased Use of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Cybersecurity
AI is being increasingly used in cybersecurity to detect and prevent attacks.
- AI-Powered Threat Detection: AI can be used to analyze network traffic and identify suspicious activity that may indicate a cyberattack.
- AI-Powered Incident Response: AI can be used to automate incident response, helping dealerships contain and eradicate attacks more quickly.
- AI-Powered Vulnerability Management: AI can be used to identify and prioritize vulnerabilities in dealership systems.
9.2 Greater Emphasis on Zero Trust Security
Zero trust security is a security model that assumes that no user or device should be trusted by default.
- Verifying Every User and Device: Zero trust security requires verifying every user and device before granting access to dealership systems.
- Limiting Access to Only What is Needed: Users and devices should only be granted access to the data and resources they need to perform their jobs.
- Continuously Monitoring Access: Access to dealership systems should be continuously monitored to detect and prevent unauthorized access.
9.3 Expansion of Cybersecurity Regulations
Cybersecurity regulations are likely to expand in the future, requiring dealerships to implement more stringent security measures.
- Increased Enforcement of Existing Regulations: Regulatory agencies are likely to increase their enforcement of existing cybersecurity regulations, such as the GLBA, CCPA, and GDPR.
- New Cybersecurity Regulations: New cybersecurity regulations may be introduced at the state and federal levels, requiring dealerships to implement additional security measures.
9.4 Growing Importance of Cybersecurity Insurance
Cybersecurity insurance is becoming increasingly important for dealerships to protect themselves from the financial impact of a cyberattack.
- Coverage for Ransom Payments: Cybersecurity insurance can cover the cost of ransom payments in the event of a ransomware attack.
- Coverage for Data Breach Costs: Cybersecurity insurance can cover the costs associated with a data breach, such as notification costs, legal fees, and credit monitoring services.
- Coverage for Business Interruption: Cybersecurity insurance can cover the costs associated with business interruption resulting from a cyberattack.
By staying informed about these future trends and implementing proactive cybersecurity measures, car dealerships can protect their businesses from emerging threats and maintain a strong security posture.
10. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Car Dealership Software Attacks
Here are some frequently asked questions about car dealership software attacks:
10.1 What is a car dealership software attack?
A car dealership software attack is a cyberattack targeting the software systems used by dealerships to manage their operations, including DMS, CRM, and other critical applications.
10.2 What are the common types of car dealership software attacks?
Common types of attacks include ransomware, malware, phishing, data breaches, and denial-of-service (DoS) attacks.
10.3 Why are car dealerships targeted for cyberattacks?
Dealerships are targeted due to the high value of the data they handle, complex IT infrastructure, limited cybersecurity resources, operational dependence on software, and potential for high ransom payments.
10.4 What is the impact of a car dealership software attack?
The impact can include financial losses, operational disruptions, reputational damage, and data breaches.
10.5 How can dealerships prevent car dealership software attacks?
Dealerships can prevent attacks by implementing strong cybersecurity measures, training employees, developing an incident response plan, and staying informed about the latest threats.
10.6 What role does car dealership software play in cybersecurity?
Car dealership software plays a critical role in cybersecurity by implementing secure software development practices, providing regular updates and patch management, implementing access controls and permissions, and using data encryption and protection.
10.7 What are the latest trends in car dealership software attacks?
Latest trends include an increase in ransomware attacks, phishing attacks targeting dealership employees, supply chain attacks, and data breaches.
10.8 What are the compliance requirements for car dealerships regarding cybersecurity?
Compliance requirements include the GLBA, CCPA, GDPR, and PCI DSS.
10.9 How can CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN help dealerships with cybersecurity?
CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN offers cybersecurity training programs, vulnerability assessments and penetration testing, incident response planning and support, managed security services, and compliance consulting.
10.10 What are some real-world examples of car dealership software attacks?
Real-world examples include the CDK Global cyberattack, the Penske Automotive Group ransomware attack, the Group 1 Automotive data breach, and the Sewell Automotive Companies phishing attack.
10.11 What are the future trends in car dealership cybersecurity?
Future trends include increased use of AI in cybersecurity, greater emphasis on zero trust security, expansion of cybersecurity regulations, and growing importance of cybersecurity insurance.
Protect your dealership from car dealership software attacks by partnering with CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN. Contact us today at Address: 1700 W Irving Park Rd, Chicago, IL 60613, United States, WhatsApp: +1 (641) 206-8880, or visit our website at CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN to learn more about our comprehensive cybersecurity solutions. Ensure your dealership remains secure and compliant with our expert guidance and support.