Want to share your laptop’s internet connection? This article from CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN shows you how to easily turn your Windows laptop into a Wi-Fi hotspot without needing to install any additional software. Learn how to create a hotspot on your laptop today! Boost your auto repair skills and learn remote diagnostics at CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN. Discover expert training and services for efficient auto repair.
Contents
- 1. Why Turn Your Laptop into a Hotspot?
- 2. How to Create a Laptop Hotspot on Windows
- 2.1. Using Settings on Windows 10 and 11
- 2.2. How to Change the Hotspot Name and Password?
- 2.3. Creating a Hotspot Using Command Prompt (CMD) for All Windows Versions
- 2.4. How to Share Your Internet Connection
- 3. Understanding the Technical Aspects of Hotspots
- 3.1. Network Address Translation (NAT)
- 3.2. Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP)
- 3.3. Wireless Security Protocols (WPA2/WPA3)
- 3.4. Understanding Wireless Standards (802.11n/ac/ax)
- 3.5. Channel Selection and Interference Management
- 4. Advanced Hotspot Configuration
- 4.1. Using Netsh Commands for Advanced Configuration
- 4.2. Setting Up a Static IP Address for the Hotspot
- 4.3. Configuring Firewall Settings for the Hotspot
- 4.4. Monitoring Hotspot Usage and Performance
- 5. Troubleshooting Common Hotspot Issues
- 5.1. Hotspot Not Showing Up on Other Devices
- 5.2. Devices Can Connect But Have No Internet Access
- 5.3. Slow Internet Speed on Connected Devices
- 5.4. Hotspot Disconnecting Frequently
- 6. Case Studies: Real-World Applications
- 6.1. Remote Auto Diagnostics and Repair
- 6.2. On-Site Technical Support
- 6.3. Educational Workshops and Training
- 7. Staying Secure: Best Practices for Hotspot Security
- 8. The Future of Mobile Hotspots
- 9. Why Choose CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN for Your Auto Repair Training?
- 10. Ready to Upgrade Your Skills?
- FAQ: Turning Your Laptop into a Hotspot
- FAQ 1: Can I turn my laptop into a hotspot without software?
- FAQ 2: What Windows versions support the built-in hotspot feature?
- FAQ 3: How do I change the name and password of my laptop hotspot?
- FAQ 4: Why can devices connect to my hotspot but have no internet access?
- FAQ 5: How many devices can connect to my laptop hotspot?
- FAQ 6: Can using my laptop as a hotspot slow down my internet speed?
- FAQ 7: Is it safe to use my laptop as a public Wi-Fi hotspot?
- FAQ 8: How do I stop my laptop from being a hotspot?
- FAQ 9: What do I do if my laptop hotspot is not showing up on other devices?
- FAQ 10: Are there any benefits to using a laptop as a hotspot for remote auto repair?
1. Why Turn Your Laptop into a Hotspot?
Why bother turning your laptop into a hotspot? There are several great reasons.
- Save Money on Public Wi-Fi: If you frequently use public Wi-Fi hotspots that require a voucher or login, turning your laptop into a hotspot can save you money. Instead of buying separate vouchers for each device, you can purchase one voucher, connect your laptop, and then share the connection with your smartphone or other devices.
- Share with Friends: When traveling or working in a group, you can share your laptop’s internet connection with friends and colleagues. This is particularly useful in areas with limited or expensive internet access.
- File Sharing and Wireless Printing: A laptop hotspot enables wireless file sharing between devices and allows you to turn a wired printer into a wireless printer, improving convenience and productivity. According to a study by CompTIA, 66% of companies report improved productivity after implementing wireless printing solutions.
 sharing internet connection
sharing internet connection
Alt text: Sharing a Laptop’s Internet Connection via a WiFi Hotspot with Multiple Devices.
2. How to Create a Laptop Hotspot on Windows
You don’t need to install any additional software to turn your Windows laptop into a hotspot. Windows has built-in features that make it easy to share your internet connection.
2.1. Using Settings on Windows 10 and 11
If you’re using Windows 10 or 11, the easiest way to create a hotspot is through the Settings app. How to use the settings app on Windows 10 and 11 to create a hotspot? Follow these simple steps:
- Ensure Internet Connection: Make sure your laptop is connected to the internet via Wi-Fi or Ethernet.
- Open Quick Settings: Click the Wi-Fi, speaker, or battery icon in the taskbar to open Quick Settings.
- Activate Mobile Hotspot: Click the “Mobile hotspot” button. It will turn blue when activated.
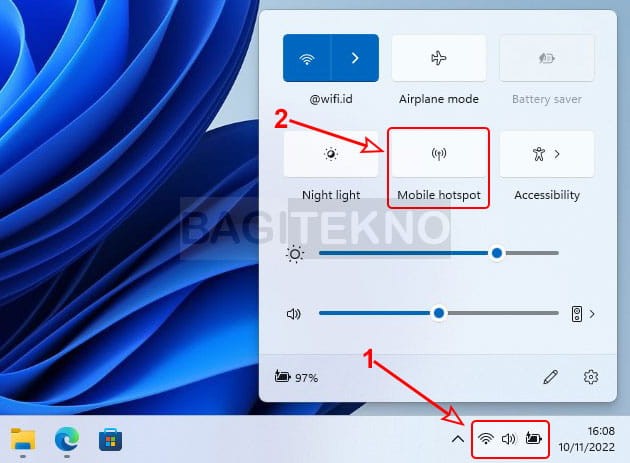 Activating mobile hotspot
Activating mobile hotspot
Alt text: Turning on the Mobile Hotspot Feature in Windows 11 Quick Settings to Share Internet.
2.2. How to Change the Hotspot Name and Password?
Customize your hotspot for easier access and security. How do I change the hotspot name and password on Windows 10 or 11?
- Return to Quick Settings: Open Quick Settings again by clicking the Wi-Fi, speaker, or battery icon.
- Go to Settings: Right-click on the “Mobile hotspot” icon and select “Go to Settings”.
- Edit Network Properties: In the Settings window, click “Edit” under “Network properties”.
- Change Name and Password: Enter your desired network name (SSID) and password (at least 8 characters).
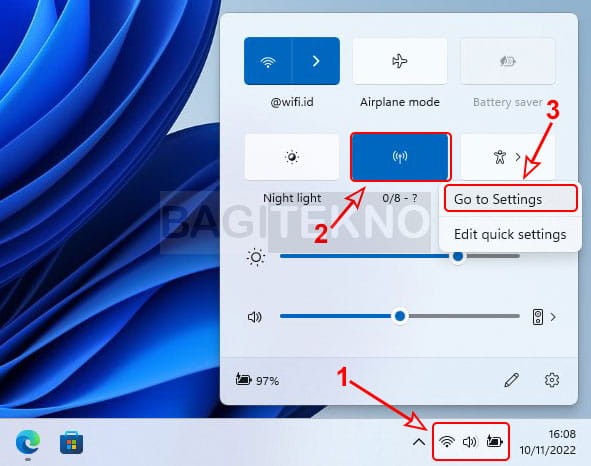 Configuring WiFi hotspot settings
Configuring WiFi hotspot settings
Alt text: Accessing WiFi Hotspot Settings in Windows 11 to Customize the Network.
2.3. Creating a Hotspot Using Command Prompt (CMD) for All Windows Versions
Using the Command Prompt (CMD) is a universal method that works on all Windows versions, including Windows 7, 8, 10, and 11. How do I enable a hotspot via CMD on any Windows version?
-
Open CMD as Administrator: Search for “CMD” in the Start menu, right-click on “Command Prompt,” and select “Run as administrator”.
-
Set Up the Hosted Network: Type or paste the following command and press Enter:
netsh wlan set hostednetwork mode=allow ssid="YourWiFiName" key="YourPassword"Replace
"YourWiFiName"with your desired hotspot name and"YourPassword"with a password of at least 8 characters. -
Start the Hosted Network: Type or paste the following command and press Enter:
netsh wlan start hostednetwork
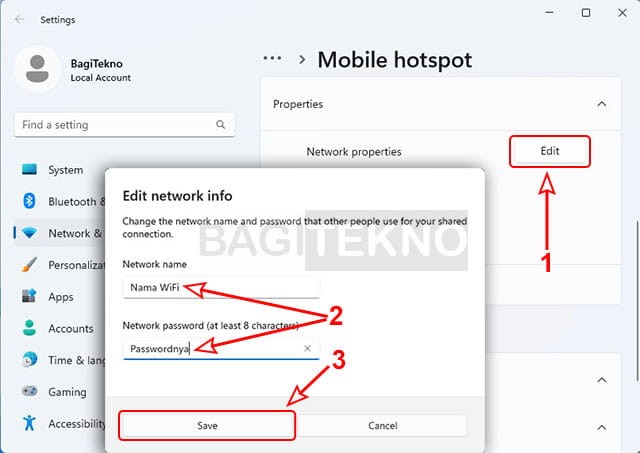 Entering commands into CMD
Entering commands into CMD
Alt text: Setting Up a Mobile Hotspot Using Command Prompt on Windows 11.
2.4. How to Share Your Internet Connection
If you’re using CMD, you need to share your internet connection to the hotspot. How to allow devices to connect to the internet through the hotspot? Follow these instructions:
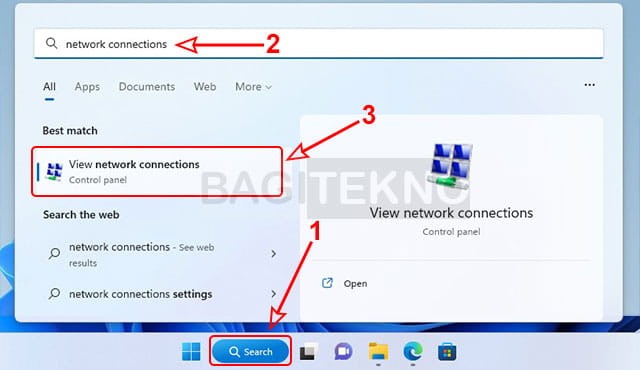
- Open Network Connections: Press the Windows key, type “network connections,” and select “View network connections”.
- Open Properties: Right-click on your active internet connection (Wi-Fi or Ethernet) and select “Properties”.
- Sharing Tab: In the Properties window, click the “Sharing” tab.
- Allow Sharing: Check the box that says “Allow other network users to connect through this computer’s Internet connection”.
- Select Hotspot Connection: In the “Home networking connection” dropdown, select the hotspot connection you created (usually named “Local Area Connection* x”).
 Sharing connection with a Laptop
Sharing connection with a Laptop
Alt text: Sharing the Internet Connection to Enable Hotspot Access on Windows 11.
3. Understanding the Technical Aspects of Hotspots
Creating a hotspot involves several technical aspects that are essential for understanding how it works and optimizing its performance.
3.1. Network Address Translation (NAT)
Network Address Translation (NAT) is a fundamental component of creating a hotspot on a laptop. NAT allows multiple devices connected to the hotspot to share a single public IP address. How does NAT enable multiple devices to share a single internet connection?
- IP Address Management: NAT translates the private IP addresses of devices connected to the hotspot into the public IP address of the laptop.
- Port Address Translation (PAT): NAT uses different port numbers to distinguish between different devices and applications, ensuring that data is correctly routed.
- Security: NAT acts as a basic firewall by hiding the internal IP addresses of devices on the network, providing an additional layer of security.
3.2. Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP)
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) is essential for automatically assigning IP addresses to devices that connect to the hotspot. DHCP simplifies network administration and ensures that each device has a unique IP address. What is the role of DHCP in a laptop hotspot?
- Automatic IP Assignment: DHCP automatically assigns IP addresses, subnet masks, default gateways, and DNS server addresses to devices connecting to the hotspot.
- Address Leasing: DHCP leases IP addresses for a limited time, ensuring that IP addresses are reused when devices disconnect from the network.
- Centralized Management: DHCP simplifies network management by automatically configuring network settings for connected devices, reducing the need for manual configuration.
3.3. Wireless Security Protocols (WPA2/WPA3)
Wireless security protocols such as WPA2 (Wi-Fi Protected Access 2) and WPA3 (Wi-Fi Protected Access 3) are crucial for securing the hotspot and protecting the data transmitted over the network. How do WPA2 and WPA3 enhance the security of a laptop hotspot?
- Encryption: WPA2 and WPA3 use advanced encryption algorithms to protect data transmitted between the laptop and connected devices.
- Authentication: WPA2 and WPA3 require users to enter a password to access the hotspot, preventing unauthorized access.
- Enhanced Security Features: WPA3 includes additional security features such as Simultaneous Authentication of Equals (SAE) to protect against password-based attacks.
According to a study by the Wi-Fi Alliance, WPA3 provides a significant improvement in security compared to WPA2, making it the preferred choice for securing wireless networks.
3.4. Understanding Wireless Standards (802.11n/ac/ax)
The 802.11 standards define the protocols for wireless communication. Understanding these standards can help optimize the performance and compatibility of the hotspot. How do 802.11n/ac/ax standards affect the performance of a laptop hotspot?
- 802.11n (Wi-Fi 4): Supports data rates up to 600 Mbps and uses multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) technology to improve performance.
- 802.11ac (Wi-Fi 5): Supports data rates up to 3.5 Gbps and uses wider channels and more advanced modulation techniques.
- 802.11ax (Wi-Fi 6): Supports data rates up to 9.6 Gbps and includes features such as orthogonal frequency-division multiple access (OFDMA) to improve efficiency and reduce latency.
3.5. Channel Selection and Interference Management
Selecting the right channel for the hotspot and managing interference from other wireless networks can significantly improve performance. How to optimize channel selection and manage interference for a laptop hotspot?
- Channel Scanning: Use a Wi-Fi analyzer tool to scan for available channels and identify the least congested channel.
- Channel Width: Use a narrower channel width (20 MHz) in crowded environments to reduce interference and improve stability.
- Interference Mitigation: Position the laptop away from other electronic devices and use a Wi-Fi extender to improve signal strength in areas with poor coverage.
4. Advanced Hotspot Configuration
For users who need more control over their hotspot settings, there are several advanced configuration options available.
4.1. Using Netsh Commands for Advanced Configuration
The netsh command-line tool in Windows allows for advanced configuration of network settings, including hotspot settings. How do I use netsh commands to configure advanced hotspot settings?
- View Hotspot Settings: Use the command
netsh wlan show hostednetworkto view the current settings of the hotspot. - Change SSID and Password: Use the command
netsh wlan set hostednetwork ssid="NewSSID" key="NewPassword"to change the SSID and password of the hotspot. - Disable and Enable Hotspot: Use the commands
netsh wlan stop hostednetworkandnetsh wlan start hostednetworkto disable and enable the hotspot.
4.2. Setting Up a Static IP Address for the Hotspot
Assigning a static IP address to the hotspot can simplify network management and ensure consistent connectivity. How to set up a static IP address for the hotspot?
- Open Network Connections: Go to “View network connections” in the Control Panel.
- Properties of Hotspot Connection: Right-click on the hotspot connection (usually named “Local Area Connection* x”) and select “Properties”.
- Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4): Select “Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4)” and click “Properties”.
- Use the Following IP Address: Select “Use the following IP address” and enter the desired IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway.
4.3. Configuring Firewall Settings for the Hotspot
Configuring firewall settings is essential for securing the hotspot and protecting the devices connected to it. How to configure firewall settings for the hotspot?
- Open Windows Defender Firewall: Search for “Windows Defender Firewall” in the Start menu and open it.
- Advanced Settings: Click on “Advanced settings” in the left pane.
- Inbound and Outbound Rules: Configure inbound and outbound rules to allow or block specific types of network traffic.
4.4. Monitoring Hotspot Usage and Performance
Monitoring hotspot usage and performance can help identify and resolve issues such as slow speeds or connection problems. How to monitor hotspot usage and performance?
- Task Manager: Use Task Manager to monitor network usage and identify processes that are consuming bandwidth.
- Resource Monitor: Use Resource Monitor to view detailed network statistics and identify potential bottlenecks.
- Third-Party Tools: Use third-party network monitoring tools to track hotspot usage, monitor network traffic, and identify security threats.
5. Troubleshooting Common Hotspot Issues
Even with careful setup, you might encounter issues. Here are some common problems and how to fix them:
5.1. Hotspot Not Showing Up on Other Devices
If your hotspot isn’t visible on other devices, try these solutions:
- Check Hotspot Status: Ensure the hotspot is enabled on your laptop.
- Verify SSID: Double-check the hotspot name (SSID) on your laptop and the device you’re trying to connect.
- Restart Hotspot: Disable and re-enable the hotspot on your laptop.
- Update Network Drivers: Ensure your network drivers are up to date.
5.2. Devices Can Connect But Have No Internet Access
If devices can connect to the hotspot but have no internet access, try these steps:
- Check Internet Connection: Verify that your laptop has an active internet connection.
- Sharing Settings: Make sure you’ve enabled internet sharing in the network connection properties.
- Firewall Settings: Check your firewall settings to ensure they’re not blocking internet access for the hotspot.
- Restart Connection: Restart both your laptop and the connected device.
5.3. Slow Internet Speed on Connected Devices
If connected devices are experiencing slow internet speeds, consider these tips:
- Limit Connected Devices: Reduce the number of devices connected to the hotspot.
- Close Bandwidth-Heavy Applications: Close any applications on your laptop that are consuming a lot of bandwidth.
- Optimize Channel Selection: Use a Wi-Fi analyzer to find a less congested channel.
- Upgrade Hardware: Consider upgrading to a faster router or network adapter.
5.4. Hotspot Disconnecting Frequently
If the hotspot disconnects frequently, try these solutions:
- Power Management Settings: Adjust your power management settings to prevent the network adapter from being turned off to save power.
- Driver Issues: Update or reinstall your network drivers.
- Hardware Issues: Check for any hardware issues with your network adapter.
- Proximity: Ensure devices are within a reasonable range of the hotspot.
6. Case Studies: Real-World Applications
6.1. Remote Auto Diagnostics and Repair
CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN provides expert training in remote auto diagnostics and repair. A technician in Chicago can use a laptop hotspot to connect to a vehicle in Los Angeles, diagnose issues, and guide a local mechanic through the repair process.
6.2. On-Site Technical Support
A field technician can use a laptop hotspot to provide on-site technical support to clients in remote locations. The hotspot allows the technician to access online resources, collaborate with remote experts, and troubleshoot issues in real-time.
6.3. Educational Workshops and Training
Instructors can use a laptop hotspot to conduct educational workshops and training sessions in locations without reliable internet access. The hotspot allows participants to access online learning materials, participate in interactive exercises, and collaborate with instructors and peers.
7. Staying Secure: Best Practices for Hotspot Security
Securing your laptop hotspot is essential to protect your data and prevent unauthorized access. How do I ensure the hotspot is secure? Consider these best practices:
- Use a Strong Password: Use a strong, unique password for your hotspot.
- Enable WPA3 Encryption: Use WPA3 encryption for the highest level of security.
- Keep Software Updated: Keep your operating system and network drivers updated.
- Enable Firewall: Enable the Windows Firewall and configure it to block unauthorized access.
- Monitor Connected Devices: Monitor the devices connected to your hotspot and disconnect any unauthorized devices.
- Disable File Sharing: Disable file sharing to prevent unauthorized access to your files.
- Use a VPN: Use a Virtual Private Network (VPN) to encrypt your internet traffic and protect your privacy.
8. The Future of Mobile Hotspots
The future of mobile hotspots is likely to involve faster speeds, improved security, and more advanced features. What future trends can we expect in mobile hotspot technology?
- 5G Connectivity: 5G technology will enable faster hotspot speeds and lower latency.
- Wi-Fi 6E: Wi-Fi 6E will provide access to the 6 GHz band, reducing congestion and improving performance.
- Enhanced Security: Advanced security protocols such as WPA4 will provide even greater protection against cyber threats.
- AI-Powered Optimization: Artificial intelligence (AI) will be used to optimize hotspot performance and manage network traffic.
- Integrated Hotspot Solutions: Hotspot functionality will be integrated into more devices, such as smartphones, tablets, and laptops.
9. Why Choose CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN for Your Auto Repair Training?
CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN offers cutting-edge training in remote auto diagnostics and repair. Here’s why you should consider our programs:
- Expert Instructors: Learn from experienced professionals in the auto repair industry.
- Hands-On Training: Gain practical skills through hands-on exercises and real-world case studies.
- Latest Technology: Stay up-to-date with the latest diagnostic tools and techniques.
- Remote Support: Access remote support from our team of experts.
- Career Advancement: Enhance your career prospects with specialized training in remote auto repair.
10. Ready to Upgrade Your Skills?
Ready to take your auto repair skills to the next level? Visit CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN today to learn more about our training programs and services. Don’t miss out on this opportunity to become a leader in the future of auto repair! Contact us at Whatsapp: +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit our location at 1700 W Irving Park Rd, Chicago, IL 60613, United States.
FAQ: Turning Your Laptop into a Hotspot
FAQ 1: Can I turn my laptop into a hotspot without software?
Yes, you can turn your Windows laptop into a Wi-Fi hotspot without installing any additional software by using the built-in Mobile Hotspot feature in Settings or through Command Prompt (CMD).
FAQ 2: What Windows versions support the built-in hotspot feature?
Windows 10 and Windows 11 have a built-in Mobile Hotspot feature in the Settings app, while older versions like Windows 7 and 8 require using Command Prompt (CMD).
FAQ 3: How do I change the name and password of my laptop hotspot?
On Windows 10 and 11, you can change the hotspot name and password by going to Settings > Network & Internet > Mobile hotspot and clicking “Edit”. For CMD, you need to use the netsh wlan set hostednetwork command.
FAQ 4: Why can devices connect to my hotspot but have no internet access?
This issue typically occurs if you haven’t shared your internet connection with the hotspot. You need to go to Network Connections, right-click on your active internet connection, select Properties, go to the Sharing tab, and check “Allow other network users to connect through this computer’s Internet connection.”
FAQ 5: How many devices can connect to my laptop hotspot?
The number of devices that can connect to your laptop hotspot depends on your hardware and the demands of each device, but generally, Windows allows up to eight devices to connect simultaneously.
FAQ 6: Can using my laptop as a hotspot slow down my internet speed?
Yes, using your laptop as a hotspot can reduce the internet speed on both your laptop and connected devices, especially if multiple devices are consuming bandwidth at the same time.
FAQ 7: Is it safe to use my laptop as a public Wi-Fi hotspot?
Using your laptop as a public Wi-Fi hotspot can pose security risks. It’s essential to use a strong password, enable WPA3 encryption, keep your software updated, and use a firewall to protect your data and prevent unauthorized access.
FAQ 8: How do I stop my laptop from being a hotspot?
On Windows 10 and 11, you can turn off the Mobile hotspot switch in Settings > Network & Internet > Mobile hotspot. If you created the hotspot using CMD, you can stop it by running the command netsh wlan stop hostednetwork.
FAQ 9: What do I do if my laptop hotspot is not showing up on other devices?
Ensure that the hotspot is enabled on your laptop, verify the SSID, restart the hotspot, and update your network drivers. If problems persist, check for any hardware issues with your network adapter.
FAQ 10: Are there any benefits to using a laptop as a hotspot for remote auto repair?
Yes, using a laptop as a hotspot can be beneficial for remote auto repair by allowing technicians to connect to vehicles in remote locations, access online resources, collaborate with remote experts, and troubleshoot issues in real-time.