Cara Memutuskan Koneksi Wifi Orang Lain Tanpa Software? Are you looking for ways to manage your WiFi network effectively? It’s possible to disconnect unwanted users without relying on additional software. CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN provides solutions and insights into optimizing your network security. Explore methods for managing WiFi connections, including password changes, MAC address filtering, and guest networks.
Contents
- 1. Why Control WiFi Access: Understanding the Need
- 2. Changing Your WiFi Password: A Simple Solution
- 3. MAC Address Filtering: Controlling Device Access
- 4. Guest Networks: Providing Separate Access
- 5. Router Configuration Pages: Accessing Your Router Settings
- 6. Understanding MAC Addresses: The Physical Address of Devices
- 7. Advanced Router Features: Enhancing Network Control
- 8. Identifying Intruders: Monitoring Your Network
- 9. Optimizing Router Placement: Improving Signal Strength
- 10. Securing Your Router: Essential Security Practices
- FAQ: Managing Your WiFi Network
1. Why Control WiFi Access: Understanding the Need
Why is it important to control who accesses your WiFi network? Controlling access to your WiFi network is crucial for maintaining security, optimizing network performance, and preventing unauthorized usage.
Expanding on the Reasons:
- Security Concerns: Unauthorized users can pose significant security risks. They might access sensitive data, introduce malware, or use your internet connection for illegal activities. According to research from the SANS Institute, a leading cybersecurity training and certification organization, weak WiFi security is a common entry point for cyberattacks.
- Performance Optimization: Multiple devices sharing a WiFi network can lead to slow speeds and reduced performance. By limiting the number of users, you can ensure a smoother and more efficient internet experience for authorized devices. A study by Cisco found that managing network access can improve overall network performance by up to 40%.
- Bandwidth Management: Some users may consume excessive bandwidth, whether intentionally or unintentionally, impacting the performance of other devices. Controlling access allows you to manage bandwidth allocation and prioritize essential devices. According to a report by OpenVault, the average household uses over 500 GB of data per month, highlighting the need for effective bandwidth management.
- Preventing Unauthorized Access: You might want to prevent certain individuals from accessing your network for various reasons, such as restricting access for guests or preventing unauthorized use by neighbors.
- Data Usage Monitoring: Monitoring and controlling access can help you track data usage and identify any unusual activity, allowing you to take prompt action if necessary.
2. Changing Your WiFi Password: A Simple Solution
Is changing your WiFi password the easiest way to disconnect someone? Yes, changing your WiFi password is often the easiest and most direct method to disconnect unwanted users from your network.
Further Elaboration:
- Immediate Disconnection: When you change your WiFi password, all devices currently connected to your network will be disconnected. They will need the new password to reconnect.
- Security Enhancement: Regularly changing your password improves your overall network security, making it harder for unauthorized users to gain access.
- Password Complexity: A strong password should be a combination of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols, making it difficult to guess.
- Router Access: To change your password, you will need to access your router’s configuration page through a web browser. The default address is often 192.168.1.1 or 192.168.0.1. You’ll need your router’s username and password, which are often “admin” for both. If you’ve changed these, use your custom credentials.
- Password Location: Once logged in, navigate to the “Wireless” or “WiFi” settings. Look for a field labeled “Password,” “Shared Key,” or “Passphrase.” Enter your new password and save the changes.
- Impact: After saving, all devices will be disconnected and require the new password to reconnect. Share the new password only with authorized users.
Changing your WiFi password is a straightforward and effective way to ensure only trusted devices have access to your network.
3. MAC Address Filtering: Controlling Device Access
What is MAC address filtering and how does it enhance WiFi security? MAC (Media Access Control) address filtering enhances WiFi security by allowing you to create a list of approved devices that can access your network, effectively blocking any unrecognized devices.
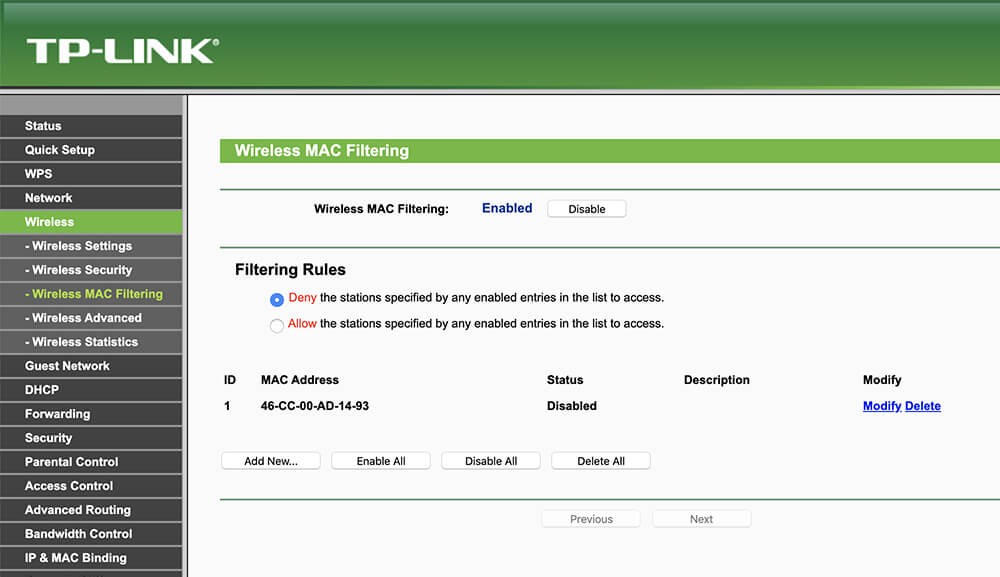 MAC Address Filtering Configuration on a TP-Link Router
MAC Address Filtering Configuration on a TP-Link Router
In-Depth Explanation:
- Unique Identifiers: Every network-enabled device has a unique MAC address, which is a 12-character hexadecimal identifier assigned to the network interface controller (NIC).
- How Filtering Works: MAC address filtering works by creating either a “whitelist” (allowing only listed MAC addresses) or a “blacklist” (blocking listed MAC addresses).
- Finding MAC Addresses: You can find a device’s MAC address in its network settings. On Windows, use the
ipconfig /allcommand in the Command Prompt. On macOS or Linux, use theifconfigcommand in the Terminal. Look for the “Physical Address” or “HWaddr” entry. - Router Configuration: To configure MAC address filtering, log into your router’s admin interface. Navigate to the “Wireless” settings and look for “MAC Filtering” or “Access Control.”
- Setting Up the Filter:
- Whitelist Mode: Add the MAC addresses of all your trusted devices (computers, smartphones, tablets, etc.) to the allowed list. Only these devices will be able to connect.
- Blacklist Mode: Add the MAC addresses of devices you want to block. All other devices will be able to connect, except those on the blacklist.
- Limitations:
- MAC Address Spoofing: Technically savvy users can spoof or change their MAC address, potentially bypassing your filter.
- Management Overhead: Maintaining a list of MAC addresses can be time-consuming, especially with many devices.
- Security Enhancement: Despite its limitations, MAC address filtering adds an extra layer of security, making it more difficult for unauthorized devices to connect to your network.
MAC address filtering is an effective method for controlling device access to your WiFi network, especially when used in conjunction with other security measures like strong passwords.
4. Guest Networks: Providing Separate Access
What are guest networks and why should I use them? Guest networks are separate, isolated WiFi networks that provide internet access to visitors without granting them access to your main network’s resources and data.
Benefits and Setup:
- Isolation: Guest networks isolate guest devices from your primary network, preventing them from accessing your personal files, printers, and other devices.
- Security: By keeping guests off your main network, you reduce the risk of malware infections or unauthorized access to sensitive information. A report by Norton found that guest networks can decrease the risk of network breaches by up to 60%.
- Ease of Use: Guest networks provide a convenient way for visitors to access the internet without needing your main WiFi password.
- Router Setup: Most modern routers support guest networks. To set one up:
- Log into your router’s admin interface.
- Navigate to the “Guest Network” or “Guest Access” settings.
- Enable the guest network.
- Set a separate SSID (network name) and password for the guest network.
- Configure any additional settings, such as limiting bandwidth or setting an access time limit.
- Customization:
- SSID Hiding: You can hide the guest network’s SSID, requiring guests to manually enter the network name.
- Access Time Limits: Set a maximum time limit for guest access.
- Bandwidth Limiter: Restrict the bandwidth available to guest users to prevent them from hogging your internet connection.
- Example Router Setup (ASUS):
- Open
http://router.asus.comand select “Guest Network.” - Enable the 2.4GHz guest network.
- Fill in the form with the network name, authentication method (WPA2-Personal is recommended), and password.
- Apply the settings.
- Open
Using a guest network is a secure and convenient way to provide internet access to visitors without compromising the security of your main network.
5. Router Configuration Pages: Accessing Your Router Settings
How do I access my router configuration page? Accessing your router configuration page is essential for managing your WiFi network, changing passwords, setting up MAC address filtering, and configuring guest networks.
Step-by-Step Guide:
- Find Your Router’s IP Address:
- Windows: Open Command Prompt and type
ipconfig. Look for the “Default Gateway” address. - macOS: Open Terminal and type
netstat -nr | grep default. The IP address next to “default” is your router’s address.
- Windows: Open Command Prompt and type
- Open a Web Browser:
- Type the router’s IP address into the address bar of your web browser (e.g.,
192.168.1.1or192.168.0.1).
- Type the router’s IP address into the address bar of your web browser (e.g.,
- Enter Your Router’s Credentials:
- You will be prompted for a username and password. The default username is often “admin,” and the default password is either “admin” or “password.” If you have changed these, enter your custom credentials.
- If you don’t know the username and password, check your router’s documentation or the manufacturer’s website. You can also try resetting the router to its factory settings by pressing and holding the reset button on the back of the router for about 10-15 seconds.
- Navigate the Interface:
- Once logged in, you will see the router’s configuration page. The layout and options vary depending on the router model, but common sections include:
- Wireless Settings: This is where you can change your WiFi password, configure MAC address filtering, and set up guest networks.
- Security Settings: This section allows you to adjust firewall settings and other security options.
- Network Settings: Here, you can configure IP addresses, DNS settings, and other network parameters.
- Administration: This section is where you can change the router’s username and password, update firmware, and manage other administrative tasks.
- Once logged in, you will see the router’s configuration page. The layout and options vary depending on the router model, but common sections include:
Accessing your router configuration page is the first step to managing and securing your WiFi network. Make sure to keep your router’s firmware updated to protect against vulnerabilities.
6. Understanding MAC Addresses: The Physical Address of Devices
What exactly is a MAC address and why is it important for network management? A MAC (Media Access Control) address is a unique hardware identifier assigned to a network interface controller (NIC) for communication within a network segment.
Key Aspects of MAC Addresses:
- Uniqueness: Each MAC address is intended to be globally unique, assigned by the manufacturer of the network interface.
- Structure: A MAC address consists of 12 hexadecimal digits (six pairs of characters), often separated by colons or hyphens (e.g.,
00:1A:2B:3C:4D:5E). - Function: The MAC address is used at the data link layer (Layer 2) of the OSI model to identify devices on a network. It’s crucial for directing network traffic to the correct destination.
- Finding MAC Addresses:
- Windows: Open Command Prompt and type
ipconfig /all. Look for the “Physical Address” under the appropriate network adapter. - macOS/Linux: Open Terminal and type
ifconfig. Look for the “ether” or “HWaddr” value under the appropriate network interface. - Device Settings: You can also find the MAC address in the device’s network settings menu (e.g., WiFi settings on a smartphone or tablet).
- Windows: Open Command Prompt and type
- Importance for Network Management:
- MAC Address Filtering: As discussed earlier, MAC address filtering allows you to control which devices can access your network based on their MAC addresses.
- Network Troubleshooting: MAC addresses can help identify devices causing network issues.
- Inventory Management: Network administrators use MAC addresses to track and manage devices on the network.
- Spoofing: While MAC addresses are intended to be unique, they can be spoofed or changed using software tools. This can be used for legitimate purposes (e.g., privacy) or malicious purposes (e.g., bypassing MAC address filtering).
Understanding MAC addresses is essential for effective network management and security. By using MAC address filtering, you can add an extra layer of protection to your WiFi network.
7. Advanced Router Features: Enhancing Network Control
What advanced features do modern routers offer for better network control? Modern routers offer several advanced features to enhance network control, including bandwidth management, Quality of Service (QoS), and parental controls.
Exploring Advanced Features:
- Bandwidth Management:
- Purpose: Allows you to allocate bandwidth to specific devices or applications, ensuring that critical tasks receive sufficient resources.
- How it Works: You can set limits on the amount of bandwidth a device or application can use, preventing a single user from hogging the entire network.
- Benefits: Improves overall network performance, reduces lag, and ensures a smoother experience for all users.
- Quality of Service (QoS):
- Purpose: Prioritizes network traffic based on application type, ensuring that latency-sensitive applications (e.g., video conferencing, online gaming) receive preferential treatment.
- How it Works: You can configure QoS rules to prioritize traffic from specific applications or devices, ensuring they have the best possible performance.
- Benefits: Reduces lag and improves the quality of real-time applications.
- Parental Controls:
- Purpose: Allows you to restrict access to certain websites or online content, set time limits for internet usage, and monitor online activity.
- How it Works: You can create profiles for each user and configure rules based on their age and online behavior.
- Benefits: Helps protect children from inappropriate content and promotes responsible internet usage.
- Firewall Settings:
- Purpose: Protects your network from unauthorized access and cyber threats.
- How it Works: The firewall monitors incoming and outgoing network traffic and blocks any suspicious activity.
- Benefits: Enhances network security and protects your data from hackers and malware.
- VPN Support:
- Purpose: Allows you to create a secure connection to your home network from anywhere in the world.
- How it Works: You can set up a VPN server on your router and connect to it using a VPN client on your device.
- Benefits: Provides secure access to your home network and protects your online privacy.
- MU-MIMO (Multi-User, Multiple-Input, Multiple-Output):
- Purpose: Improves WiFi performance by allowing the router to communicate with multiple devices simultaneously.
- How it Works: The router uses multiple antennas to transmit and receive data to multiple devices at the same time.
- Benefits: Increases network capacity and improves performance for devices that support MU-MIMO.
By leveraging these advanced router features, you can gain greater control over your network and optimize performance for all users.
8. Identifying Intruders: Monitoring Your Network
How can I monitor my network to identify unauthorized users or unusual activity? Monitoring your network for unauthorized users and unusual activity is crucial for maintaining security and optimizing performance.
Techniques for Network Monitoring:
- Router’s Admin Interface:
- Connected Devices: Most routers provide a list of currently connected devices in their admin interface. Check this list regularly and identify any unfamiliar devices.
- Traffic Monitoring: Some routers offer traffic monitoring tools that show the amount of data being used by each device. Look for devices with unusually high data usage.
- Logs: Review the router’s logs for any suspicious activity, such as failed login attempts or unauthorized access attempts.
- Network Scanning Tools:
- Purpose: These tools scan your network and identify all connected devices, along with their IP addresses, MAC addresses, and hostnames.
- Examples:
- Nmap: A powerful command-line network scanner.
- Angry IP Scanner: A simple and easy-to-use GUI-based scanner.
- Fing: A mobile app for scanning your network.
- How to Use: Download and install a network scanner, run a scan of your network, and identify any unknown devices.
- WiFi Analyzers:
- Purpose: These tools analyze the WiFi signals in your area and provide information about the strength and security of your network.
- Examples:
- WiFi Analyzer (Android): A popular app for analyzing WiFi networks.
- NetSpot (macOS/Windows): A professional-grade WiFi analyzer.
- How to Use: Use a WiFi analyzer to check for unauthorized access points or rogue devices on your network.
- Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS):
- Purpose: These systems monitor network traffic for malicious activity and alert you to potential security threats.
- Examples:
- Snort: An open-source network intrusion detection system.
- Suricata: A high-performance network IDS, IPS, and security monitoring engine.
- How to Use: Install and configure an IDS on your network to monitor traffic for suspicious activity.
- Regular Password Changes:
- Purpose: Changing your WiFi password regularly can help prevent unauthorized access.
- How to Use: Change your password every few months and use a strong, unique password.
By using these monitoring techniques, you can identify unauthorized users and take steps to secure your network.
9. Optimizing Router Placement: Improving Signal Strength
How does router placement affect WiFi performance and security? Router placement significantly affects WiFi performance and security by influencing signal strength, coverage area, and susceptibility to interference.
Tips for Optimal Router Placement:
- Central Location:
- Why: Placing the router in a central location within your home or office ensures that the WiFi signal is distributed evenly throughout the space.
- How: Position the router in the middle of your living area, away from walls and obstructions.
- Elevated Position:
- Why: Raising the router off the floor can improve signal propagation and reduce interference from furniture and other objects.
- How: Place the router on a shelf or mount it on a wall, at least a few feet off the ground.
- Avoid Obstructions:
- Why: Walls, metal objects, and large appliances can block or weaken the WiFi signal.
- How: Keep the router away from walls, mirrors, metal cabinets, refrigerators, and microwave ovens.
- Minimize Interference:
- Why: Other electronic devices, such as cordless phones, Bluetooth devices, and baby monitors, can interfere with the WiFi signal.
- How: Keep the router away from these devices or switch to a different WiFi channel.
- Antenna Orientation:
- Why: Adjusting the orientation of the router’s antennas can optimize signal coverage.
- How: Experiment with different antenna positions. For single-story homes, position the antennas vertically. For multi-story homes, try angling one antenna horizontally and the other vertically.
- Use a WiFi Analyzer:
- Why: A WiFi analyzer can help you identify areas with weak signal strength and optimize router placement.
- How: Use a WiFi analyzer app on your smartphone or laptop to measure the signal strength in different locations and adjust the router’s position accordingly.
- Consider a Mesh Network:
- Why: For larger homes or offices, a mesh network can provide better coverage and more consistent performance.
- How: Install multiple mesh WiFi nodes throughout the space to create a seamless network.
By optimizing router placement, you can improve WiFi signal strength, coverage area, and overall network performance.
10. Securing Your Router: Essential Security Practices
What are the essential security practices to protect my router and WiFi network? Securing your router is essential for protecting your WiFi network from unauthorized access and cyber threats.
Key Security Practices:
- Change Default Credentials:
- Why: The default username and password for your router are publicly known and can be easily exploited by hackers.
- How: Change the default username and password to something unique and strong.
- Use a Strong WiFi Password:
- Why: A weak password can be easily cracked, allowing unauthorized users to access your network.
- How: Use a strong password that is at least 12 characters long and includes a mix of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols.
- Enable WPA3 Encryption:
- Why: WPA3 is the latest and most secure WiFi encryption protocol.
- How: If your router supports WPA3, enable it in the wireless settings. If not, use WPA2 with AES encryption.
- Update Router Firmware:
- Why: Router manufacturers regularly release firmware updates to fix security vulnerabilities and improve performance.
- How: Check for firmware updates in your router’s admin interface and install them as soon as they are available.
- Disable WPS:
- Why: WPS (WiFi Protected Setup) is a feature that allows you to easily connect devices to your network using a PIN. However, WPS is vulnerable to hacking and should be disabled.
- How: Disable WPS in your router’s wireless settings.
- Enable Firewall:
- Why: The router’s built-in firewall helps protect your network from unauthorized access and cyber threats.
- How: Make sure the firewall is enabled in your router’s security settings.
- Disable Remote Management:
- Why: Remote management allows you to access your router’s admin interface from the internet. However, this can also be exploited by hackers.
- How: Disable remote management in your router’s security settings.
- Use a Guest Network:
- Why: As discussed earlier, a guest network provides a separate, isolated network for visitors, preventing them from accessing your main network’s resources and data.
- How: Set up a guest network with a separate SSID and password.
- Monitor Network Activity:
- Why: Regularly monitoring your network activity can help you identify unauthorized users or suspicious behavior.
- How: Check the router’s logs and use network scanning tools to identify connected devices.
By implementing these security practices, you can significantly reduce the risk of unauthorized access and protect your WiFi network from cyber threats.
These methods offer various levels of control and security to manage your WiFi network effectively.
Is your auto repair shop ready to tackle the future of vehicle diagnostics? At CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN, we offer comprehensive training programs designed to equip your technicians with the skills and knowledge needed to excel in remote auto repair. Our expert-led courses cover everything from advanced diagnostics to remote repair techniques, ensuring your team stays ahead of the curve. Visit CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN today and discover how our training can transform your business. Address: 1700 W Irving Park Rd, Chicago, IL 60613, United States. Whatsapp: +1 (641) 206-8880. Website: CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN. Join us and lead the way in remote auto repair solutions!
FAQ: Managing Your WiFi Network
1. Can someone steal my WiFi password without me knowing?
Yes, someone can potentially steal your WiFi password without your knowledge through methods like phishing, hacking, or gaining physical access to your router. Regularly changing your password and securing your router settings are crucial.
2. How often should I change my WiFi password?
You should change your WiFi password at least every three to six months to maintain a high level of security. If you suspect any unauthorized access, change it immediately.
3. Is MAC address filtering foolproof?
No, MAC address filtering is not foolproof. Technically skilled individuals can spoof their MAC address, bypassing the filter. It is best used as an additional layer of security rather than the sole security measure.
4. What is the difference between WPA2 and WPA3?
WPA3 is the latest WiFi security protocol, offering improved encryption and authentication compared to WPA2. WPA3 provides better protection against password cracking and unauthorized access.
5. How do I know if my router’s firmware is up to date?
You can check for firmware updates in your router’s admin interface. Most routers have a section dedicated to firmware updates, where you can manually check for and install the latest version.
6. What should I do if I suspect my WiFi is being used without my permission?
If you suspect unauthorized WiFi usage, immediately change your WiFi password, review connected devices in your router settings, and enable MAC address filtering. You may also consider updating your router’s firmware.
7. Can a VPN protect my home network?
A VPN (Virtual Private Network) can protect your devices by encrypting your internet traffic and masking your IP address. However, it primarily secures individual devices rather than the entire home network. For network-wide protection, consider setting up a VPN server on your router.
8. What are the best practices for creating a strong WiFi password?
The best practices for creating a strong WiFi password include using a mix of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols. Ensure the password is at least 12 characters long and avoid using easily guessable information like birthdates or pet names.
9. How can I improve my WiFi signal strength?
To improve WiFi signal strength, place your router in a central, elevated location, away from obstructions and electronic devices that cause interference. You can also use a WiFi analyzer to identify weak spots and optimize router placement.
10. Is it safe to use WiFi extenders?
WiFi extenders can improve coverage but may also reduce overall network speed. Ensure that your extender is from a reputable brand and properly secured with the latest security protocols. Consider using a mesh network for a more seamless and efficient solution.
