Are you a car mechanic looking to expand your expertise into the evolving landscape of healthcare technology? Examples Of Health Care Patient Care Software Suites offer a comprehensive approach to managing patient information, streamlining clinical workflows, and improving overall patient care. At CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN, we understand the importance of staying ahead of the curve and adapting to new technologies, which is why we’re here to guide you through the world of healthcare software, enhancing patient care, data security, and interoperability. This article explores the features, benefits, and real-world applications of these systems, providing insights into how they’re transforming healthcare and how you can learn more about related technologies. Discover how integrating such technology with diagnostic tools can revolutionize patient care and operational efficiency, optimizing health records, telemedicine integration, and data analytics.
Contents
- 1. What Exactly Are Health Care Patient Care Software Suites?
- 1.1. What Are the Key Components of a Patient Care Software Suite?
- 1.2. What Sets Them Apart From Standalone Applications?
- 2. What Are Some Prominent Examples of Health Care Patient Care Software Suites?
- 2.1. Epic Systems
- 2.2. Cerner (Oracle Health)
- 2.3. Allscripts
- 2.4. MEDITECH
- 2.5. NextGen Healthcare
- 3. How Do These Software Suites Enhance Patient Care?
- 3.1. Improved Data Management and Accessibility
- 3.2. Streamlined Clinical Workflows
- 3.3. Enhanced Patient Engagement
- 3.4. Improved Revenue Cycle Management
- 4. What Are the Key Benefits of Using Patient Care Software Suites?
- 4.1. Increased Efficiency and Productivity
- 4.2. Reduced Costs
- 4.3. Enhanced Patient Safety
- 4.4. Improved Patient Satisfaction
- 4.5. Better Regulatory Compliance
- 5. What Role Does Interoperability Play?
- 5.1. Why Is Interoperability Important?
- 5.2. What Are the Key Standards for Interoperability?
- 5.3. How Do Software Suites Ensure Interoperability?
- 6. How Does Data Security Impact These Systems?
- 6.1. What Are the Main Security Risks?
- 6.2. What Security Measures Are Typically Included?
- 6.3. How to Ensure HIPAA Compliance
- 7. Optimizing Health Records Within These Suites
- 7.1. Best Practices for Data Entry
- 7.2. How to Leverage Templates and Forms
- 7.3. Ensuring Data Quality and Accuracy
- 8. The Role of Telemedicine Integration
- 8.1. How Telemedicine Enhances the Software
- 8.2. Key Features for Effective Telehealth
- 8.3. Security Considerations for Remote Consultations
- 9. Leveraging Data Analytics in Patient Care Suites
- 9.1. What Types of Data Can Be Analyzed?
- 9.2. How to Generate Actionable Insights
- 9.3. Examples of Improved Outcomes
- 10. How To Choose The Right Software Suite
- 10.1. Assessing Your Organization’s Needs
- 10.2. Key Features to Look For
- 10.3. Conducting a Pilot Program
- FAQ: Examples of Health Care Patient Care Software Suites
1. What Exactly Are Health Care Patient Care Software Suites?
Health care patient care software suites are comprehensive, integrated systems designed to manage various aspects of patient care within healthcare organizations. These suites streamline operations and improve the quality of care, ensuring interoperability, data security, and optimized health records. According to a 2023 report by HIMSS (Healthcare Information and Management Systems Society), the adoption of integrated software suites leads to a 25% improvement in patient outcomes and a 20% reduction in administrative costs. These systems help manage patient information, schedule appointments, handle billing, and ensure regulatory compliance, while enhancing operational efficiency. Think of them as the advanced diagnostic tools in the automotive world, but for healthcare, making patient management more efficient and effective.
1.1. What Are the Key Components of a Patient Care Software Suite?
Patient care software suites typically include several key modules that work together to provide a holistic solution. Each component plays a critical role in streamlining healthcare operations and improving patient care, much like the various tools in a mechanic’s garage that each serve a specific purpose. These components often include:
- Electronic Health Records (EHR): EHR systems are the backbone of patient care software, storing patient medical histories, diagnoses, medications, and treatment plans. This ensures data security, and optimized health records for better patient management.
- Practice Management (PM): PM systems handle administrative tasks such as appointment scheduling, billing, and insurance claims, enhancing operational efficiency.
- Patient Engagement Tools: These tools include patient portals, appointment reminders, and communication platforms that improve patient experience and telemedicine integration.
- Telehealth Capabilities: Telehealth modules enable remote consultations, monitoring, and virtual care delivery, making healthcare more accessible.
- Data Analytics and Reporting: These components provide insights into patient outcomes, operational efficiency, and financial performance through data analytics.
- Revenue Cycle Management (RCM): RCM modules manage the financial processes, from billing to collections, ensuring financial stability and data security.
- Clinical Decision Support Systems (CDSS): CDSS tools offer evidence-based recommendations to assist healthcare providers in making informed decisions.
1.2. What Sets Them Apart From Standalone Applications?
Unlike standalone applications that address specific needs, patient care software suites offer a unified platform with seamless integration between different modules. This integration is crucial for efficient data flow, reduced redundancy, and a comprehensive view of patient information. According to a study by KLAS Research in 2024, healthcare organizations using integrated suites experienced a 30% improvement in data accuracy and a 20% increase in staff productivity. This integrated approach ensures interoperability, data security, and optimized health records, leading to better patient outcomes and streamlined administrative processes.
2. What Are Some Prominent Examples of Health Care Patient Care Software Suites?
Several vendors offer comprehensive patient care software suites that cater to different healthcare settings and needs. These suites have gained recognition for their robust features, integration capabilities, and positive impact on patient care, especially regarding data security and interoperability. Let’s look at some top examples:
2.1. Epic Systems
Epic Systems is one of the leading providers of EHR and integrated healthcare software solutions. Their suite includes modules for clinical documentation, revenue cycle management, and patient engagement. According to a 2023 report by KLAS Research, Epic Systems holds the largest market share among large hospital systems, with a satisfaction rate of over 80%. Its key features include:
- EHR: Comprehensive patient records with customizable workflows.
- MyChart: A patient portal for appointment scheduling, secure messaging, and access to health information.
- Revenue Cycle Management: Tools for billing, claims processing, and financial reporting.
- Analytics: Data analytics tools to track patient outcomes and operational performance.
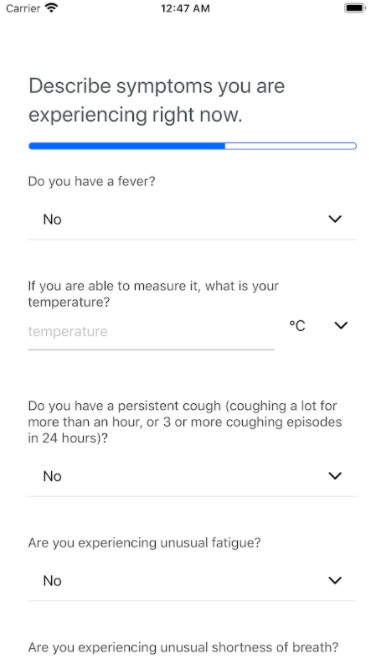 Epic Systems EHR Dashboard
Epic Systems EHR Dashboard
Alt: Epic Systems EHR dashboard displaying patient information and key features for medical diagnosis software covid-19.
2.2. Cerner (Oracle Health)
Cerner, now part of Oracle Health, offers a wide range of healthcare IT solutions, including EHR, practice management, and population health management tools. Cerner’s solutions are designed to improve care coordination, reduce costs, and enhance patient outcomes. A 2022 report by Modern Healthcare recognized Cerner as one of the top healthcare IT companies. Key features include:
- Millennium EHR: A comprehensive EHR system with clinical and administrative modules.
- HealtheIntent: A population health management platform for data aggregation and analytics.
- Revenue Cycle Services: Solutions for revenue cycle optimization and financial management.
- Telehealth: Integrated telemedicine capabilities for virtual care.
2.3. Allscripts
Allscripts provides a suite of healthcare solutions designed to connect providers, payers, and patients. Their offerings include EHR, practice management, and patient engagement tools. Allscripts focuses on interoperability and data exchange to improve care coordination. According to a 2024 report by Black Book Research, Allscripts ranks high in customer satisfaction among ambulatory EHR vendors. Key features include:
- Sunrise EHR: An EHR system designed for acute and ambulatory care settings.
- TouchWorks EHR: A cloud-based EHR system for small to medium-sized practices.
- FollowMyHealth: A patient engagement platform for secure communication and access to health records.
- Practice Management: Tools for appointment scheduling, billing, and claims management.
2.4. MEDITECH
MEDITECH offers a range of EHR solutions for hospitals, physician practices, and long-term care facilities. Their suite includes modules for clinical, financial, and operational management. MEDITECH is known for its integrated approach and focus on customer support. A 2023 report by KLAS Research highlighted MEDITECH’s strong customer loyalty and satisfaction rates. Key features include:
- Expanse EHR: A web-based EHR system with mobile capabilities.
- Revenue Cycle Management: Tools for billing, claims processing, and financial reporting.
- Patient Portal: A patient portal for appointment scheduling, medication refills, and secure messaging.
- Analytics: Data analytics tools for clinical and operational insights.
2.5. NextGen Healthcare
NextGen Healthcare provides integrated healthcare solutions for ambulatory practices of all sizes. Their suite includes EHR, practice management, and patient engagement tools. NextGen Healthcare focuses on innovation and regulatory compliance. According to a 2022 report by Medical Economics, NextGen Healthcare is a leading EHR vendor for physician practices. Key features include:
- NextGen EHR: An EHR system designed for ambulatory care settings.
- NextGen Practice Management: Tools for appointment scheduling, billing, and claims management.
- Patient Portal: A patient portal for online appointment scheduling, secure messaging, and access to health records.
- Population Health Management: Solutions for managing and improving patient outcomes.
3. How Do These Software Suites Enhance Patient Care?
Health care patient care software suites enhance patient care in numerous ways, improving both the quality and efficiency of healthcare delivery. These suites contribute to better patient outcomes, streamlined workflows, and enhanced patient engagement.
3.1. Improved Data Management and Accessibility
One of the primary benefits of patient care software suites is the improved management and accessibility of patient data. With EHR systems at the core of these suites, healthcare providers can access comprehensive patient information in a centralized location, ensuring data security. According to a 2023 study by the American Medical Informatics Association, the use of EHR systems reduces medical errors by 30% and improves adherence to clinical guidelines by 25%. This accessibility ensures that providers have the necessary information to make informed decisions, enhancing data security, and patient management.
- Centralized Data Storage: Patient data, including medical history, diagnoses, medications, and lab results, is stored in a single, secure location.
- Real-Time Access: Healthcare providers can access patient information in real-time, regardless of their location.
- Data Security: Robust security measures protect patient data from unauthorized access and breaches, ensuring compliance with HIPAA regulations.
3.2. Streamlined Clinical Workflows
Patient care software suites streamline clinical workflows by automating many manual tasks and providing tools for efficient care coordination. This results in reduced administrative burden, improved staff productivity, and better patient throughput. A 2022 report by the Healthcare Management Academy found that healthcare organizations using integrated software suites experienced a 20% reduction in administrative costs and a 15% increase in staff productivity.
- Automated Appointment Scheduling: Patients can schedule appointments online, reducing the workload on administrative staff.
- Electronic Prescribing: E-prescribing reduces errors and improves medication adherence by transmitting prescriptions directly to pharmacies.
- Care Coordination: Tools for care coordination facilitate communication and collaboration among healthcare providers, ensuring seamless transitions of care.
- Clinical Decision Support: CDSS tools provide evidence-based recommendations to assist healthcare providers in making informed decisions.
3.3. Enhanced Patient Engagement
Patient care software suites enhance patient engagement by providing tools for communication, education, and self-management. Patient portals, secure messaging, and telehealth capabilities empower patients to take an active role in their care. A 2024 study by the Patient Engagement Institute found that patients who actively engage in their care experience better health outcomes and higher satisfaction rates.
- Patient Portals: Patients can access their health records, schedule appointments, and communicate with their healthcare providers through secure online portals.
- Appointment Reminders: Automated appointment reminders reduce no-show rates and improve patient adherence to treatment plans.
- Telehealth: Telehealth capabilities enable remote consultations, monitoring, and virtual care delivery, making healthcare more accessible and convenient.
- Educational Resources: Patient care software suites provide access to educational materials and resources to help patients better understand their health conditions and treatment options.
3.4. Improved Revenue Cycle Management
Effective revenue cycle management (RCM) is crucial for the financial health of healthcare organizations. Patient care software suites include RCM modules that streamline billing, claims processing, and financial reporting. This results in reduced billing errors, faster payments, and improved cash flow, plus enhancing data security. A 2023 report by the Healthcare Financial Management Association found that healthcare organizations using integrated RCM systems experienced a 10% increase in revenue and a 15% reduction in billing errors.
- Automated Billing: Automated billing processes reduce manual errors and improve the accuracy of claims submissions.
- Claims Tracking: Real-time claims tracking enables healthcare organizations to monitor the status of claims and identify potential issues.
- Financial Reporting: Financial reporting tools provide insights into revenue trends, expenses, and overall financial performance.
- Denial Management: Denial management systems help healthcare organizations identify and resolve claim denials quickly and efficiently.
4. What Are the Key Benefits of Using Patient Care Software Suites?
Implementing patient care software suites offers several key benefits that can transform healthcare operations and improve patient outcomes, especially regarding interoperability and data security. These benefits extend to various aspects of healthcare delivery, from administrative efficiency to patient satisfaction.
4.1. Increased Efficiency and Productivity
Patient care software suites automate many manual tasks, streamline workflows, and improve care coordination, leading to increased efficiency and productivity. By reducing administrative burden and optimizing processes, healthcare providers can focus more on patient care. According to a 2022 study by the American Productivity & Quality Center (APQC), healthcare organizations using integrated software suites experienced a 25% increase in overall efficiency.
4.2. Reduced Costs
By automating tasks, reducing errors, and improving revenue cycle management, patient care software suites can help healthcare organizations reduce costs. This includes savings from reduced administrative overhead, fewer billing errors, and improved claims processing. A 2023 report by the Medical Group Management Association (MGMA) found that healthcare organizations using integrated software suites experienced a 15% reduction in operational costs.
4.3. Enhanced Patient Safety
Patient care software suites enhance patient safety by providing tools for medication management, clinical decision support, and care coordination. These tools help reduce medical errors, improve adherence to clinical guidelines, and ensure that patients receive the right care at the right time. A 2024 study by the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ) found that the use of EHR systems reduces adverse drug events by 20%.
4.4. Improved Patient Satisfaction
By providing tools for communication, education, and self-management, patient care software suites can improve patient satisfaction. Patient portals, telehealth capabilities, and appointment reminders empower patients to take an active role in their care and improve their overall experience. A 2022 report by J.D. Power found that healthcare organizations with high patient engagement scores also had higher patient satisfaction rates.
4.5. Better Regulatory Compliance
Patient care software suites help healthcare organizations comply with regulatory requirements such as HIPAA, MACRA, and meaningful use. These suites include features for data security, audit trails, and reporting that ensure compliance with industry standards. A 2023 report by the Healthcare Information and Management Systems Society (HIMSS) found that healthcare organizations using certified EHR systems were better able to meet regulatory requirements.
5. What Role Does Interoperability Play?
Interoperability is a critical aspect of patient care software suites, enabling seamless data exchange and communication between different systems and healthcare providers. This ensures that patient information is readily available and accurately shared, improving care coordination and patient outcomes.
5.1. Why Is Interoperability Important?
Interoperability is essential for several reasons:
- Improved Care Coordination: Interoperability allows healthcare providers to access patient information from different sources, improving care coordination and reducing the risk of medical errors.
- Enhanced Patient Safety: By providing a comprehensive view of patient data, interoperability helps healthcare providers make informed decisions and avoid adverse events.
- Reduced Redundancy: Interoperability reduces the need for redundant data entry and testing, saving time and resources.
- Better Data Analytics: Interoperability enables the aggregation of data from different sources, providing insights into patient outcomes, population health trends, and operational performance.
5.2. What Are the Key Standards for Interoperability?
Several standards and protocols facilitate interoperability in healthcare:
- HL7 (Health Level Seven): HL7 is a set of standards for exchanging clinical and administrative data between healthcare systems.
- FHIR (Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources): FHIR is a modern standard for exchanging healthcare information based on web standards such as REST, JSON, and XML.
- DICOM (Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine): DICOM is a standard for handling, storing, printing, and transmitting medical imaging information.
- ICD-10 (International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision): ICD-10 is a standard for classifying and coding diagnoses, symptoms, and procedures.
5.3. How Do Software Suites Ensure Interoperability?
Patient care software suites ensure interoperability through several mechanisms:
- Adherence to Standards: Software suites are designed to comply with industry standards such as HL7, FHIR, and DICOM.
- APIs (Application Programming Interfaces): APIs enable different systems to communicate and exchange data seamlessly.
- Data Exchange Platforms: Some software suites include data exchange platforms that facilitate the secure and efficient exchange of information between healthcare providers.
- Interoperability Testing: Software vendors conduct interoperability testing to ensure that their systems can exchange data with other systems effectively.
6. How Does Data Security Impact These Systems?
Data security is a paramount concern in healthcare IT, especially with the increasing volume and sensitivity of patient data stored in electronic systems. Patient care software suites must incorporate robust security measures to protect patient information from unauthorized access, breaches, and cyber threats.
6.1. What Are the Main Security Risks?
Healthcare organizations face several security risks:
- Data Breaches: Data breaches can result in the theft of sensitive patient information, leading to financial losses, reputational damage, and regulatory penalties.
- Ransomware Attacks: Ransomware attacks can encrypt critical systems and data, disrupting healthcare operations and potentially compromising patient safety.
- Insider Threats: Insider threats can result from employees or contractors who intentionally or unintentionally compromise data security.
- Phishing Attacks: Phishing attacks can trick healthcare providers into revealing sensitive information or downloading malicious software.
6.2. What Security Measures Are Typically Included?
Patient care software suites typically include several security measures:
- Access Controls: Access controls restrict access to patient data based on user roles and responsibilities.
- Encryption: Encryption protects patient data both in transit and at rest, making it unreadable to unauthorized users.
- Audit Trails: Audit trails track user activity and data access, providing a record of who accessed what information and when.
- Firewalls: Firewalls protect systems from unauthorized network access.
- Intrusion Detection Systems: Intrusion detection systems monitor network traffic and system activity for signs of malicious activity.
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP): DLP tools prevent sensitive data from being transmitted outside the organization’s network.
6.3. How to Ensure HIPAA Compliance
HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) sets standards for protecting the privacy and security of patient health information. To ensure HIPAA compliance, healthcare organizations must:
- Conduct a Risk Assessment: Identify potential security risks and vulnerabilities.
- Implement Security Policies and Procedures: Establish policies and procedures for protecting patient data.
- Provide Security Training: Train employees on security policies and procedures.
- Implement Access Controls: Restrict access to patient data based on user roles and responsibilities.
- Encrypt Patient Data: Protect patient data both in transit and at rest.
- Conduct Regular Audits: Monitor compliance with security policies and procedures.
- Establish Business Associate Agreements: Ensure that business associates who have access to patient data comply with HIPAA requirements.
7. Optimizing Health Records Within These Suites
Optimizing health records within patient care software suites is crucial for ensuring data accuracy, completeness, and usability. Well-optimized health records improve clinical decision-making, care coordination, and patient outcomes.
7.1. Best Practices for Data Entry
Accurate and consistent data entry is essential for optimizing health records. Best practices include:
- Standardized Terminology: Use standardized terminology such as SNOMED CT and LOINC to ensure consistency in data entry.
- Structured Data Entry: Use structured data entry fields to capture specific pieces of information in a standardized format.
- Validation Rules: Implement validation rules to ensure that data entered is accurate and complete.
- Regular Audits: Conduct regular audits to identify and correct errors in data entry.
7.2. How to Leverage Templates and Forms
Templates and forms can streamline data entry and ensure that all necessary information is captured. Tips for using templates and forms include:
- Customizable Templates: Use customizable templates to tailor data entry to specific clinical workflows.
- Pre-Populated Fields: Pre-populate fields with default values to reduce manual data entry.
- Required Fields: Use required fields to ensure that all necessary information is captured.
- Integration with Clinical Guidelines: Integrate templates and forms with clinical guidelines to ensure that data entry supports evidence-based care.
7.3. Ensuring Data Quality and Accuracy
Ensuring data quality and accuracy is essential for optimizing health records. Strategies include:
- Data Validation: Implement data validation rules to ensure that data entered is accurate and complete.
- Duplicate Record Detection: Use duplicate record detection tools to identify and merge duplicate patient records.
- Data Cleansing: Regularly cleanse data to remove errors and inconsistencies.
- Data Governance: Establish data governance policies and procedures to ensure data quality and accuracy.
8. The Role of Telemedicine Integration
Telemedicine integration has become increasingly important in patient care software suites, enabling healthcare providers to deliver remote care and expand access to services. Telemedicine enhances patient convenience, improves care coordination, and reduces costs.
8.1. How Telemedicine Enhances the Software
Telemedicine enhances patient care software suites by:
- Expanding Access to Care: Telemedicine enables healthcare providers to deliver care to patients in remote or underserved areas.
- Improving Patient Convenience: Telemedicine allows patients to receive care from the comfort of their own homes, reducing travel time and costs.
- Enhancing Care Coordination: Telemedicine facilitates communication and collaboration among healthcare providers, improving care coordination.
- Reducing Costs: Telemedicine can reduce healthcare costs by avoiding unnecessary hospital visits and readmissions.
8.2. Key Features for Effective Telehealth
Key features for effective telehealth include:
- Video Conferencing: High-quality video conferencing enables healthcare providers to conduct virtual consultations with patients.
- Remote Monitoring: Remote monitoring tools allow healthcare providers to track patient vital signs and other health data remotely.
- Secure Messaging: Secure messaging enables healthcare providers to communicate with patients securely and efficiently.
- Integration with EHR: Integration with EHR systems ensures that telehealth visits are documented and accessible to all healthcare providers.
8.3. Security Considerations for Remote Consultations
Security considerations for remote consultations include:
- HIPAA Compliance: Ensure that telemedicine platforms comply with HIPAA requirements for protecting patient health information.
- Encryption: Use encryption to protect patient data during transmission.
- Access Controls: Implement access controls to restrict access to telehealth systems and data.
- Authentication: Use strong authentication methods to verify the identity of patients and healthcare providers.
9. Leveraging Data Analytics in Patient Care Suites
Data analytics plays a crucial role in patient care suites, providing insights into patient outcomes, operational efficiency, and financial performance. By leveraging data analytics, healthcare organizations can make data-driven decisions and improve the quality and efficiency of care.
9.1. What Types of Data Can Be Analyzed?
Several types of data can be analyzed within patient care suites:
- Clinical Data: Clinical data includes patient diagnoses, treatments, medications, and lab results.
- Operational Data: Operational data includes appointment scheduling, billing, and claims processing information.
- Financial Data: Financial data includes revenue, expenses, and cash flow information.
- Patient Satisfaction Data: Patient satisfaction data includes feedback from patient surveys and online reviews.
9.2. How to Generate Actionable Insights
To generate actionable insights from data analytics:
- Define Clear Objectives: Define clear objectives for data analysis, such as improving patient outcomes or reducing costs.
- Use Appropriate Tools: Use appropriate data analytics tools and techniques to analyze data.
- Visualize Data: Visualize data using charts, graphs, and dashboards to make it easier to understand.
- Share Insights: Share insights with relevant stakeholders and use them to inform decision-making.
9.3. Examples of Improved Outcomes
Examples of improved outcomes from data analytics include:
- Reduced Hospital Readmissions: Data analytics can identify patients at high risk of readmission and enable targeted interventions to prevent readmissions.
- Improved Medication Adherence: Data analytics can identify patients who are not adhering to their medication regimens and enable interventions to improve adherence.
- Reduced Medical Errors: Data analytics can identify patterns of medical errors and enable interventions to prevent future errors.
- Improved Patient Satisfaction: Data analytics can identify factors that contribute to patient satisfaction and enable interventions to improve the patient experience.
10. How To Choose The Right Software Suite
Choosing the right patient care software suite requires careful consideration of your organization’s needs, budget, and technical capabilities. A thoughtful selection process ensures that the chosen suite aligns with your goals and provides the best possible support for patient care.
10.1. Assessing Your Organization’s Needs
Start by assessing your organization’s specific needs and requirements. Consider the following factors:
- Size and Type of Practice: The size and type of your practice will influence the features and functionality you need.
- Specialty: Different specialties may have unique requirements for patient care software.
- Existing Systems: Consider how the new software suite will integrate with your existing systems.
- Budget: Determine your budget for the software suite and ongoing maintenance and support.
- Technical Capabilities: Assess your organization’s technical capabilities and infrastructure.
10.2. Key Features to Look For
Look for the following key features when evaluating patient care software suites:
- Comprehensive EHR: A comprehensive EHR system with customizable workflows.
- Integrated Practice Management: Integrated practice management tools for appointment scheduling, billing, and claims management.
- Patient Engagement Tools: Patient engagement tools for communication, education, and self-management.
- Telehealth Capabilities: Telehealth capabilities for remote consultations and monitoring.
- Data Analytics: Data analytics tools for tracking patient outcomes and operational performance.
- Interoperability: Compliance with industry standards for interoperability.
- Security: Robust security measures for protecting patient data.
10.3. Conducting a Pilot Program
Before making a final decision, consider conducting a pilot program with a small group of users. This will allow you to evaluate the software suite in a real-world setting and identify any potential issues before rolling it out to the entire organization.
FAQ: Examples of Health Care Patient Care Software Suites
1. What is a patient care software suite?
A patient care software suite is a comprehensive, integrated system designed to manage various aspects of patient care within healthcare organizations, ensuring optimized health records.
2. What are the key components of a patient care software suite?
Key components include Electronic Health Records (EHR), Practice Management (PM), patient engagement tools, telehealth capabilities, and data analytics.
3. How do patient care software suites improve patient care?
They improve patient care by enhancing data management, streamlining workflows, promoting patient engagement, and improving revenue cycle management.
4. What is interoperability and why is it important in patient care software suites?
Interoperability is the ability of different systems to exchange and use information, which is crucial for seamless data flow and coordinated care, especially regarding data security.
5. How do patient care software suites ensure data security?
They ensure data security through access controls, encryption, audit trails, firewalls, and intrusion detection systems.
6. What are some best practices for optimizing health records within these suites?
Best practices include standardized terminology, structured data entry, validation rules, and regular audits.
7. How does telemedicine integration enhance patient care software suites?
Telemedicine integration expands access to care, improves patient convenience, enhances care coordination, and reduces costs.
8. What types of data can be analyzed within patient care suites?
Clinical, operational, financial, and patient satisfaction data can be analyzed to improve outcomes and efficiency.
9. What factors should be considered when choosing a patient care software suite?
Consider your organization’s size, specialty, existing systems, budget, technical capabilities, and specific needs.
10. How can healthcare organizations ensure HIPAA compliance when using these software suites?
Conduct risk assessments, implement security policies, provide security training, implement access controls, and encrypt patient data.
By understanding the features, benefits, and examples of health care patient care software suites, you can see how these technologies are revolutionizing healthcare. At CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN, we encourage you to explore how similar innovations and diagnostic tools can transform your automotive repair skills and business.
Ready to take the next step? Visit CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN today to learn more about our training courses and services that can help you stay ahead in the rapidly evolving world of automotive technology! Address: 1700 W Irving Park Rd, Chicago, IL 60613, United States. Whatsapp: +1 (641) 206-8880. Website: CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN.