Nursing Home Care Plan Software is a crucial tool for creating and updating patient-centered care plans, coordinating services, and overseeing medication management, all of which CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN can help you learn more about. This comprehensive software facilitates systematic assessments, timely preventive care, medication reconciliation, and care coordination. Let’s explore how nursing home care plan software enhances patient care, streamlines workflows, and ensures compliance. Learn how to create better care plans, understand the value of these platforms, and boost your expertise today with our repair training programs.
Contents
- 1. What Should Nurses Consider for a Care Plan?
- 2. What Are the Key Components of a Nursing Home Care Plan?
- 2.1 Defining the Patient’s Goals
- 2.2 Identify Barriers to Achieving Care Plan Goals
- 2.3 Identify Patient Symptoms
- 2.4 List Potential Clinical Interventions
- 2.5 Document the Complete Patient Care Team
- 2.6 Identify Patient Allergies and Medications
- 2.7 Decide Which Metrics to Track
- 2.8 Regularly Monitor Expected Outcomes from Treatment
- 3. How Are Care Plans Updated in Nursing Homes?
- 4. What Software Features Are Essential for Effective Care Planning in Nursing Homes?
- 4.1 Comprehensive Assessment Tools
- 4.2 Customizable Templates
- 4.3 Medication Management
- 4.4 Real-Time Updates
- 4.5 Reporting and Analytics
- 4.6 Integration with EHR Systems
- 4.7 User-Friendly Interface
- 5. How Does Nursing Home Care Plan Software Improve Patient Outcomes?
- 5.1 Personalized Care Plans
- 5.2 Better Medication Management
- 5.3 Enhanced Communication
- 5.4 Proactive Risk Management
- 5.5 Data-Driven Decision-Making
- 6. What Are the Regulatory Requirements for Care Plans in Nursing Homes?
- 6.1 Comprehensive Assessments
- 6.2 Individualized Care Plans
- 6.3 Interdisciplinary Team Involvement
- 6.4 Regular Reviews and Updates
- 6.5 Documentation
- 7. What Are the Benefits of Using Cloud-Based Nursing Home Care Plan Software?
- 7.1 Accessibility
- 7.2 Cost Savings
- 7.3 Enhanced Security
- 7.4 Automatic Updates
- 7.5 Improved Collaboration
- 8. How Can Nursing Homes Ensure Data Privacy and Security with Care Plan Software?
- 8.1 Use HIPAA-Compliant Software
- 8.2 Implement Access Controls
- 8.3 Conduct Regular Security Audits
- 8.4 Train Staff on Data Security
- 8.5 Have a Data Breach Response Plan
- 9. How Can Nursing Home Care Plan Software Help with Staff Training and Onboarding?
- 9.1 Standardized Workflows
- 9.2 Built-In Training Modules
- 9.3 Access to Best Practices
- 9.4 Performance Tracking
- 9.5 Compliance Monitoring
- 10. What Are the Future Trends in Nursing Home Care Plan Software?
- 10.1 AI-Powered Decision Support
- 10.2 Predictive Analytics
- 10.3 Telehealth Integration
- 10.4 Patient Engagement Tools
- 10.5 Interoperability
1. What Should Nurses Consider for a Care Plan?
A comprehensive care plan should include systematic assessment of patient needs, system-based approaches for preventive services, medication reconciliation, oversight of patient self-management, and coordination with clinical service providers.
A well-structured care plan is foundational for effective care coordination. According to the American Nurses Association (ANA), a patient-centered care plan should address the patient’s medical, functional, and psychosocial needs. This holistic approach ensures all aspects of a patient’s health are considered, leading to better outcomes and improved quality of life.
To ensure the care plan is comprehensive and patient-centered, consider the following elements:
- Systematic Assessment: Evaluate the patient’s medical, functional, and psychosocial needs.
- Preventive Services: Implement system-based approaches to ensure timely preventive care.
- Medication Reconciliation: Review adherence and potential interactions.
- Self-Management Oversight: Oversee the patient’s self-management of medications.
- Care Coordination: Coordinate care with home- and community-based clinical service providers.
2. What Are the Key Components of a Nursing Home Care Plan?
Key components include defining patient goals, identifying barriers, listing symptoms, detailing clinical interventions, documenting the care team, listing allergies and medications, tracking metrics, and monitoring outcomes.
Each of these components plays a crucial role in creating a holistic and effective care plan. Let’s explore these components in detail:
2.1 Defining the Patient’s Goals
The first step in creating a care plan is identifying and solidifying the patient’s goals. According to a study by the National Institutes of Health (NIH), patient-centered goals improve health outcomes.
Goals should be measurable, trackable, and regularly updated, providing focus for patients, care teams, and providers. For example, if a patient has diabetes, their goal might be to lower their blood sugar levels to a specific range and stay active. Here’s how that goal can be broken down:
- Lower blood sugar: Work with a dietitian to develop a meal plan that helps maintain healthy blood sugar levels.
- Increase physical activity: Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise, such as walking or swimming, most days of the week.
- Regular Monitoring: Check blood sugar levels regularly and keep a log to track progress.
2.2 Identify Barriers to Achieving Care Plan Goals
Identifying potential roadblocks to patients reaching their goals is critical for anticipating obstacles and determining necessary actions. According to research from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), addressing barriers can significantly improve adherence to care plans.
For example, if a patient’s goal is to exercise more regularly, common barriers might include lack of motivation, physical limitations, or lack of access to exercise facilities. To overcome these barriers:
- Lack of Motivation: Set realistic goals and find an exercise buddy for moral support.
- Physical Limitations: Consult with a physical therapist for exercises that accommodate limitations.
- Lack of Access: Find low-cost or free exercise options, such as walking in a local park or using online workout videos.
2.3 Identify Patient Symptoms
Discussing and uncovering the symptoms the patient has been experiencing for identified conditions is crucial. A study in the Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA) highlights the importance of symptom management in improving patient comfort and quality of life.
For example, if a patient has arthritis, they may experience symptoms like joint pain, stiffness, and swelling. Effective management strategies include:
- Pain Management: Use pain relievers, both over-the-counter and prescription, as directed by a healthcare provider.
- Physical Therapy: Engage in exercises that improve joint mobility and reduce stiffness.
- Lifestyle Adjustments: Use assistive devices, such as canes or walkers, to reduce strain on joints.
2.4 List Potential Clinical Interventions
Interventions are actions the nurse or care manager takes to achieve patient goals and realize desired outcomes. Common interventions include patient education, self-management coaching, reviewing medications, checking vital signs, and assessing pain levels. According to the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ), targeted interventions improve patient outcomes.
For a patient with heart failure, some common interventions could include:
- Patient Education: Educate the patient on the importance of a low-sodium diet and fluid restriction.
- Medication Review: Regularly review medications to ensure they are effective and to monitor for side effects.
- Vital Sign Monitoring: Monitor weight, blood pressure, and heart rate to detect any signs of worsening heart failure.
2.5 Document the Complete Patient Care Team
Having an accurate list of all providers involved in the patient’s healthcare is extremely important. Active collaboration and shared decision-making between patients, families, and providers are key to a successful patient-centered care plan. The American Geriatrics Society emphasizes the importance of interdisciplinary collaboration in geriatric care.
Ensure the list includes contact information for everyone involved in the patient’s health, such as:
- Primary Care Physician: Responsible for overall healthcare management.
- Specialists: Such as cardiologists, endocrinologists, or neurologists, depending on the patient’s conditions.
- Therapists: Including physical therapists, occupational therapists, and speech therapists.
- Social Workers: Assist with psychosocial support and resource coordination.
2.6 Identify Patient Allergies and Medications
Ensuring that any prescribed new treatment won’t trigger allergies or be contraindicated with their medications is critical. If the patient’s clinical picture is complex, engage a pharmacist for review. The Institute for Safe Medication Practices (ISMP) stresses the importance of medication safety in patient care.
Key considerations include:
- Allergy Documentation: Maintain an up-to-date list of all patient allergies and sensitivities.
- Medication Reconciliation: Regularly review and reconcile all medications to prevent interactions and errors.
- Pharmacist Consultation: Consult with a pharmacist for complex medication regimens to ensure safety and efficacy.
2.7 Decide Which Metrics to Track
First, determine which patient vitals are primary, which may include weight, BMI, and blood pressure. Next, identify needed lab work. For a patient with diabetes, consider tracking lab results like HgbA1C, LDL cholesterol, HDL cholesterol, total cholesterol levels, INR (if on Warfarin), and Triglyceride levels. The National Committee for Quality Assurance (NCQA) emphasizes the importance of tracking metrics to improve care quality.
Effective metrics to track include:
- Vital Signs: Regular monitoring of weight, BMI, blood pressure, and heart rate.
- Lab Results: Tracking key lab values relevant to the patient’s conditions, such as HgbA1C for diabetes or cholesterol levels for heart disease.
- Functional Status: Monitoring the patient’s ability to perform activities of daily living (ADLs) and instrumental activities of daily living (IADLs).
2.8 Regularly Monitor Expected Outcomes from Treatment
Expected outcomes are similar to goals but take a broader view of what the patient looks forward to seeing more or less in a future state. For a patient with heart failure, expected outcomes could include less worry that their blood pressure is high, less worry about having a stroke or heart attack, less worry about their kidney function, increased confidence in taking their blood pressure at home, less reliance on medications, and feeling more motivated to increase activity. The Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute (PCORI) supports the use of patient-centered outcomes in healthcare.
These outcomes should be:
- Realistic: Achievable and aligned with the patient’s overall health status.
- Measurable: Able to be tracked and assessed over time.
- Patient-Centered: Reflecting the patient’s values, preferences, and goals.
 Nurse Explaining Care Plan
Nurse Explaining Care Plan
3. How Are Care Plans Updated in Nursing Homes?
Care plans should be updated monthly, noting changes, improvements, or interventions needed, accounting for specific patient health problems.
CMS requires providers to update the patient care plan monthly with any relevant information. Care plans should be written to enable systematic assessment on a month-to-month basis, noting changes, improvements, or interventions needed, accounting for specific patient health problems. The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) mandates regular updates to ensure care plans remain relevant and effective.
For example, each month, the care manager should review the medication list and any associated problems and, if necessary, inform the physician of new issues or needs. Using the initial care plan as a baseline, the care manager can discuss and document any relevant issues or concerns in regard to the patient’s health. The update should include any actions the patient is taking to address those issues to ensure progress is being made toward their goals.
Additionally, the care manager should review any preventive services or upcoming screenings that are due and address any care gaps. Once discussed, the care manager can order needed services.
While CMS doesn’t provide details on what they look for in care plan updates, these steps ensure the care plan is current.
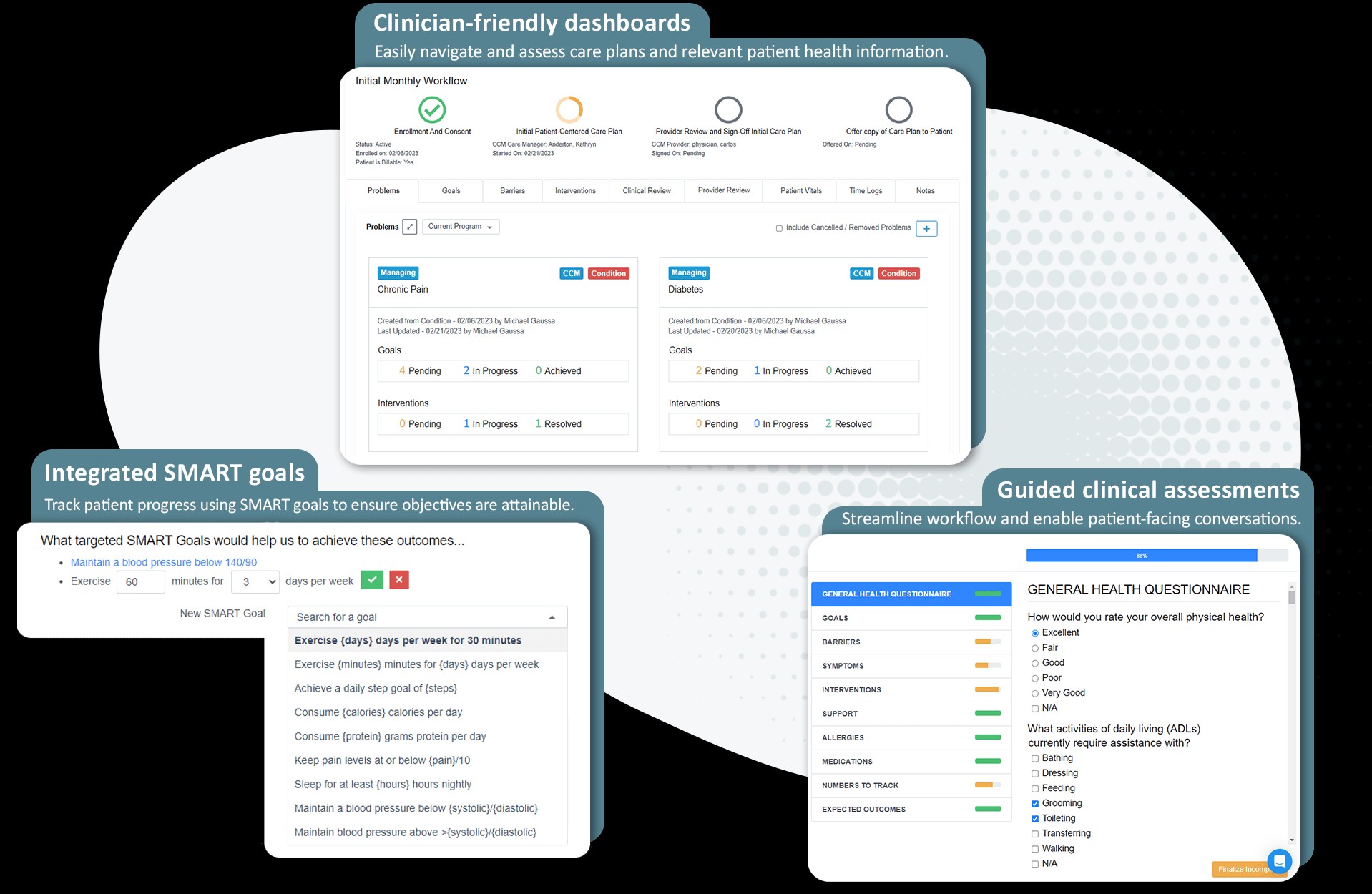
4. What Software Features Are Essential for Effective Care Planning in Nursing Homes?
Essential features include comprehensive assessment tools, customizable templates, medication management, real-time updates, reporting and analytics, integration with EHR systems, and user-friendly interface.
To effectively manage patient care, the right software is essential. Here’s a detailed look at the key features to consider:
4.1 Comprehensive Assessment Tools
Software should include tools for assessing various aspects of patient health, such as physical, cognitive, and psychosocial well-being. According to a study by the American Medical Informatics Association (AMIA), comprehensive assessment tools improve the accuracy of care plans.
These tools should:
- Capture Detailed Data: Collect thorough information about the patient’s condition, history, and needs.
- Standardized Assessments: Use validated assessment scales and questionnaires to ensure consistency.
- Automated Scoring: Automatically score assessments to reduce manual effort and improve accuracy.
4.2 Customizable Templates
Care plans should be tailored to individual patient needs. Customizable templates allow nurses to create personalized plans that address specific health issues and goals. A survey by the Healthcare Information and Management Systems Society (HIMSS) found that customizable templates enhance user satisfaction.
Key benefits include:
- Flexibility: Adapt the template to fit the unique needs of each patient.
- Standardization: Maintain a consistent format across all care plans.
- Efficiency: Save time by using pre-built sections and prompts.
4.3 Medication Management
This feature helps nurses manage patient medications, track dosages, monitor for interactions, and ensure adherence. The Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ) emphasizes the importance of medication management in preventing adverse events.
Essential aspects include:
- Medication Lists: Maintain a complete and up-to-date list of all patient medications.
- Interaction Checks: Automatically check for potential drug interactions and contraindications.
- Adherence Tracking: Monitor whether patients are taking their medications as prescribed.
4.4 Real-Time Updates
Care plans should be updated in real-time to reflect changes in patient condition, new interventions, and progress towards goals. According to a report by the National Quality Forum (NQF), real-time updates improve care coordination and outcomes.
This feature ensures:
- Up-to-Date Information: All team members have access to the latest patient data.
- Timely Interventions: Respond quickly to changes in patient condition.
- Improved Communication: Facilitate seamless communication between care providers.
4.5 Reporting and Analytics
Software should offer reporting and analytics capabilities to track key metrics, identify trends, and evaluate the effectiveness of care plans. The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) use data analytics to monitor the quality of care in nursing homes.
Key functionalities include:
- Performance Metrics: Track key indicators such as patient outcomes, medication adherence, and care plan completion rates.
- Trend Analysis: Identify trends and patterns to improve care strategies.
- Custom Reports: Generate reports tailored to specific needs and requirements.
4.6 Integration with EHR Systems
Integrating care plan software with electronic health record (EHR) systems ensures seamless data exchange and reduces the risk of errors. A study in the Journal of the American Medical Informatics Association (JAMIA) found that EHR integration improves data accuracy and efficiency.
This integration enables:
- Data Sharing: Seamlessly share patient data between systems.
- Reduced Redundancy: Avoid duplicate data entry and reduce errors.
- Comprehensive View: Access a complete view of the patient’s health history.
4.7 User-Friendly Interface
The software should be easy to use and navigate, with an intuitive interface that minimizes training time and maximizes efficiency. A survey by the American Nurses Association (ANA) found that user-friendly software improves nurse satisfaction and productivity.
Key design elements include:
- Intuitive Navigation: Easy-to-understand menus and navigation tools.
- Clear Layout: Organized and uncluttered interface.
- Customizable Dashboards: Personalized dashboards that display relevant information.
5. How Does Nursing Home Care Plan Software Improve Patient Outcomes?
It improves patient outcomes through personalized care plans, better medication management, enhanced communication, proactive risk management, and data-driven decision-making.
By leveraging the right technology, nursing homes can provide higher-quality care and achieve better outcomes for their residents. Let’s delve into these benefits in detail:
5.1 Personalized Care Plans
Nursing home care plan software enables the creation of personalized care plans tailored to each patient’s unique needs and goals. According to a study published in the Journal of the American Geriatrics Society, individualized care plans lead to better health outcomes and improved quality of life for elderly patients.
Here’s how personalized care plans make a difference:
- Tailored Interventions: Care plans address the specific health issues and concerns of each patient.
- Patient Involvement: Patients and their families are actively involved in the care planning process, ensuring their preferences are considered.
- Goal Setting: Clear, measurable goals are established to guide care and track progress.
5.2 Better Medication Management
Effective medication management is crucial for preventing adverse drug events and ensuring patients receive the right medications at the right doses. Nursing home care plan software offers features such as medication tracking, drug interaction alerts, and automated dispensing to improve medication safety. The Institute for Safe Medication Practices (ISMP) emphasizes the importance of medication safety in long-term care facilities.
Key benefits of improved medication management include:
- Reduced Medication Errors: Automated checks and alerts help prevent medication errors.
- Improved Adherence: Patients are more likely to take their medications as prescribed.
- Fewer Adverse Events: Proactive monitoring and intervention reduce the risk of adverse drug events.
5.3 Enhanced Communication
Clear and timely communication is essential for coordinating care and ensuring everyone is on the same page. Nursing home care plan software facilitates communication between care providers, patients, and families through features such as secure messaging, automated notifications, and shared care plans. A study by the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ) found that improved communication leads to better patient outcomes and increased satisfaction.
Specific communication benefits include:
- Real-Time Updates: All team members have access to the latest patient information.
- Secure Messaging: Confidential and secure communication between providers.
- Family Involvement: Families are kept informed about their loved one’s care and progress.
5.4 Proactive Risk Management
Nursing home care plan software helps identify and manage potential risks to patient safety, such as falls, infections, and pressure ulcers. By tracking risk factors and implementing preventive measures, care providers can reduce the incidence of adverse events and improve patient outcomes. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) offers guidelines for preventing infections and falls in long-term care facilities.
Proactive risk management strategies include:
- Risk Assessments: Regular assessments to identify potential risks.
- Preventive Interventions: Implementation of evidence-based interventions to mitigate risks.
- Monitoring and Tracking: Continuous monitoring of risk factors and outcomes.
5.5 Data-Driven Decision-Making
Nursing home care plan software provides valuable data and analytics that can be used to improve care quality and efficiency. By tracking key metrics and identifying trends, care providers can make informed decisions about resource allocation, staffing, and care strategies. The National Quality Forum (NQF) promotes the use of data-driven decision-making to improve healthcare quality.
Data-driven insights include:
- Performance Metrics: Tracking key indicators such as patient outcomes, satisfaction scores, and cost of care.
- Trend Analysis: Identifying trends and patterns to improve care strategies.
- Benchmarking: Comparing performance against industry benchmarks to identify areas for improvement.
6. What Are the Regulatory Requirements for Care Plans in Nursing Homes?
Regulatory requirements include comprehensive assessments, individualized care plans, interdisciplinary team involvement, regular reviews and updates, and documentation.
Nursing homes must adhere to strict regulations to ensure the safety and well-being of their residents. These regulations cover various aspects of care planning, including assessment, documentation, and review processes.
6.1 Comprehensive Assessments
Nursing homes are required to conduct comprehensive assessments of each resident’s physical, mental, and psychosocial well-being. These assessments must be completed within a specified timeframe after admission and updated regularly. The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) mandates the use of the Minimum Data Set (MDS) for resident assessments.
Key components of comprehensive assessments include:
- Medical History: Gathering information about the resident’s past and present medical conditions.
- Physical Examination: Assessing the resident’s physical health and functional abilities.
- Cognitive and Mental Health Evaluation: Evaluating the resident’s cognitive function, mood, and behavior.
- Psychosocial Assessment: Assessing the resident’s social support, emotional well-being, and preferences.
6.2 Individualized Care Plans
Based on the comprehensive assessment, nursing homes must develop individualized care plans that address each resident’s unique needs and goals. These care plans must be developed in collaboration with the resident, their family, and an interdisciplinary team of healthcare professionals. The Resident Assessment Instrument (RAI) User’s Manual provides guidance on developing individualized care plans.
Essential elements of individualized care plans include:
- Goals: Clearly defined goals that are measurable and achievable.
- Interventions: Specific actions that will be taken to achieve the goals.
- Timelines: Established timelines for achieving the goals.
- Responsible Parties: Identification of the individuals responsible for implementing the interventions.
6.3 Interdisciplinary Team Involvement
Care plans must be developed and implemented by an interdisciplinary team of healthcare professionals, including nurses, physicians, therapists, and social workers. This team works together to ensure that all aspects of the resident’s needs are addressed. The American Geriatrics Society emphasizes the importance of interdisciplinary collaboration in geriatric care.
The interdisciplinary team should include:
- Registered Nurse (RN): Provides direct care and coordinates the care plan.
- Physician: Oversees the resident’s medical care and provides medical direction.
- Therapist (Physical, Occupational, Speech): Provides therapy services to improve the resident’s functional abilities.
- Social Worker: Provides psychosocial support and assists with resource coordination.
6.4 Regular Reviews and Updates
Care plans must be reviewed and updated regularly to ensure they remain relevant and effective. CMS requires that care plans be reviewed at least quarterly and revised as needed to reflect changes in the resident’s condition or goals.
The review process should include:
- Assessment of Progress: Evaluating the resident’s progress towards their goals.
- Identification of New Needs: Identifying any new needs or concerns.
- Revision of Care Plan: Making necessary revisions to the care plan to address the resident’s current needs.
6.5 Documentation
Nursing homes must maintain accurate and complete documentation of all assessments, care plans, and interventions. This documentation is essential for demonstrating compliance with regulatory requirements and for providing continuity of care. The American Health Information Management Association (AHIMA) provides guidance on documentation best practices.
Key documentation requirements include:
- Assessment Results: Detailed documentation of the results of all assessments.
- Care Plan Details: Comprehensive documentation of the care plan, including goals, interventions, and timelines.
- Progress Notes: Regular progress notes that document the resident’s progress towards their goals and any changes in their condition.
7. What Are the Benefits of Using Cloud-Based Nursing Home Care Plan Software?
Benefits include accessibility, cost savings, enhanced security, automatic updates, and improved collaboration.
Cloud-based nursing home care plan software offers a range of advantages over traditional on-premises solutions. By leveraging the power of the cloud, nursing homes can streamline their operations, reduce costs, and improve the quality of care they provide. Let’s explore the key benefits of cloud-based software in detail:
7.1 Accessibility
Cloud-based software can be accessed from anywhere with an internet connection, allowing care providers to access patient information and update care plans from any location. This accessibility is particularly beneficial for remote care providers and those who need to access information outside of the nursing home facility. According to a report by the Healthcare Information and Management Systems Society (HIMSS), cloud-based solutions improve accessibility and collaboration in healthcare.
Key accessibility benefits include:
- Remote Access: Care providers can access patient information from any location with an internet connection.
- Mobile Compatibility: Many cloud-based solutions offer mobile apps, allowing providers to access and update care plans on their smartphones or tablets.
- 24/7 Availability: Cloud-based software is typically available 24/7, ensuring that care providers can access the information they need at any time.
7.2 Cost Savings
Cloud-based software eliminates the need for expensive hardware and IT infrastructure, reducing upfront costs and ongoing maintenance expenses. Additionally, many cloud-based solutions offer subscription-based pricing, allowing nursing homes to pay only for the features they need. A study by the American Hospital Association (AHA) found that cloud-based solutions can reduce IT costs by up to 20%.
Cost-saving benefits include:
- Reduced Hardware Costs: No need to purchase and maintain expensive servers and other hardware.
- Lower IT Costs: Reduced IT staff and maintenance expenses.
- Subscription-Based Pricing: Pay only for the features you need, with flexible pricing options.
7.3 Enhanced Security
Cloud-based software providers invest heavily in security measures to protect patient data from cyber threats and unauthorized access. These security measures include encryption, firewalls, and regular security audits. The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) requires healthcare providers to protect the privacy and security of patient information.
Key security benefits include:
- Data Encryption: Encrypting data both in transit and at rest to protect it from unauthorized access.
- Firewalls and Intrusion Detection Systems: Protecting against cyber threats and unauthorized access.
- Regular Security Audits: Conducting regular security audits to identify and address potential vulnerabilities.
7.4 Automatic Updates
Cloud-based software providers handle all software updates and maintenance, freeing up nursing home staff to focus on patient care. These automatic updates ensure that the software is always up-to-date with the latest features and security patches. A report by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) emphasizes the importance of regular software updates for maintaining security and reliability.
Benefits of automatic updates include:
- Reduced IT Burden: No need for nursing home staff to manage software updates and maintenance.
- Access to Latest Features: Always have access to the latest features and improvements.
- Improved Security: Ensure that the software is always protected against the latest cyber threats.
7.5 Improved Collaboration
Cloud-based software facilitates collaboration between care providers, patients, and families by providing a centralized platform for sharing information and communicating. This improved collaboration can lead to better care coordination and improved patient outcomes. A study by the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ) found that improved collaboration leads to better patient outcomes and increased satisfaction.
Key collaboration benefits include:
- Centralized Platform: A single platform for sharing information and communicating.
- Secure Messaging: Secure messaging features for communicating with care providers, patients, and families.
- Shared Care Plans: Shared care plans that can be accessed by all members of the care team.
8. How Can Nursing Homes Ensure Data Privacy and Security with Care Plan Software?
Ensure data privacy and security by using HIPAA-compliant software, implementing access controls, conducting regular security audits, training staff on data security, and having a data breach response plan.
Data privacy and security are paramount concerns for nursing homes, especially when using software to manage sensitive patient information. Protecting patient data is not only a legal requirement but also an ethical responsibility. Here’s how nursing homes can ensure data privacy and security with care plan software:
8.1 Use HIPAA-Compliant Software
The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) sets the standard for protecting sensitive patient information. Nursing homes should only use care plan software that is fully compliant with HIPAA regulations. The U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) provides guidance on HIPAA compliance.
Key aspects of HIPAA compliance include:
- Data Encryption: Protecting patient data both in transit and at rest using encryption.
- Access Controls: Implementing access controls to limit access to patient data to authorized personnel only.
- Audit Trails: Maintaining audit trails to track access to patient data and identify any unauthorized activity.
- Business Associate Agreements (BAAs): Ensuring that all software vendors sign BAAs, which outline their responsibilities for protecting patient data.
8.2 Implement Access Controls
Access controls are essential for limiting access to patient data to authorized personnel only. Nursing homes should implement role-based access controls, which grant different levels of access based on job responsibilities. The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) provides guidance on access control best practices.
Types of access controls include:
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Granting access based on job roles and responsibilities.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Requiring users to provide multiple forms of authentication, such as a password and a security code, to access the software.
- Password Policies: Implementing strong password policies that require users to create complex passwords and change them regularly.
8.3 Conduct Regular Security Audits
Regular security audits are essential for identifying and addressing potential vulnerabilities in the care plan software. Nursing homes should conduct both internal and external security audits to ensure that the software is secure. The SANS Institute offers cybersecurity training and certification programs.
Security audits should include:
- Vulnerability Scanning: Scanning the software for known vulnerabilities.
- Penetration Testing: Simulating cyberattacks to identify weaknesses in the software’s security.
- Security Code Review: Reviewing the software’s code to identify potential security flaws.
- Compliance Audits: Ensuring that the software is compliant with relevant regulations, such as HIPAA.
8.4 Train Staff on Data Security
Staff training is crucial for ensuring that all employees understand their responsibilities for protecting patient data. Nursing homes should provide regular training on data security best practices, including password security, phishing awareness, and data breach response. The Federal Trade Commission (FTC) offers resources for businesses on data security.
Training should cover:
- Password Security: Creating strong passwords and keeping them confidential.
- Phishing Awareness: Identifying and avoiding phishing scams.
- Data Breach Response: Knowing how to respond in the event of a data breach.
- HIPAA Compliance: Understanding HIPAA regulations and their responsibilities for complying with them.
8.5 Have a Data Breach Response Plan
Despite best efforts, data breaches can still occur. Nursing homes should have a comprehensive data breach response plan in place to minimize the impact of a breach. The U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) provides guidance on data breach response.
A data breach response plan should include:
- Incident Response Team: A team responsible for managing the response to a data breach.
- Containment: Steps to contain the breach and prevent further damage.
- Investigation: Investigating the breach to determine its cause and scope.
- Notification: Notifying affected individuals, regulatory agencies, and law enforcement.
- Remediation: Taking steps to prevent future breaches.
9. How Can Nursing Home Care Plan Software Help with Staff Training and Onboarding?
It helps with staff training and onboarding by providing standardized workflows, built-in training modules, access to best practices, performance tracking, and compliance monitoring.
Effective staff training and onboarding are crucial for ensuring that nursing home employees are equipped to provide high-quality care and comply with regulatory requirements. Nursing home care plan software can play a significant role in streamlining the training process and ensuring that staff members are well-prepared for their roles. Let’s explore the ways in which care plan software can assist with staff training and onboarding:
9.1 Standardized Workflows
Care plan software provides standardized workflows that guide staff members through the care planning process. These workflows ensure that all necessary steps are followed and that care plans are developed consistently. Standardized workflows can also help reduce errors and improve efficiency. The Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ) emphasizes the importance of standardized workflows in healthcare.
Benefits of standardized workflows include:
- Consistency: Ensuring that care plans are developed consistently across all residents.
- Efficiency: Streamlining the care planning process and reducing the time it takes to develop care plans.
- Reduced Errors: Minimizing the risk of errors by guiding staff members through the process.
9.2 Built-In Training Modules
Many care plan software solutions include built-in training modules that provide staff members with the knowledge and skills they need to use the software effectively. These training modules can cover topics such as care planning best practices, regulatory requirements, and software features. The American Health Care Association (AHCA) offers training and education resources for nursing home staff.
Training modules can include:
- Video Tutorials: Short videos that demonstrate how to use the software’s features.
- Interactive Simulations: Simulations that allow staff members to practice using the software in a safe environment.
- Quizzes and Assessments: Quizzes and assessments to test staff members’ knowledge and skills.
9.3 Access to Best Practices
Care plan software can provide staff members with access to best practices in care planning. Some solutions include libraries of evidence-based interventions and care protocols that staff members can use to develop care plans. Access to best practices can help improve the quality of care and ensure that residents receive the most effective treatments. The Gerontological Society of America (GSA) promotes evidence-based practices in gerontology.
Best practices resources can include:
- Evidence-Based Interventions: A library of interventions that have been shown to be effective in improving outcomes.
- Care Protocols: Step-by-step protocols for managing common conditions.
- Clinical Guidelines: Guidelines from professional organizations on best practices in care planning.
9.4 Performance Tracking
Care plan software can track staff members’ performance in developing and implementing care plans. This performance tracking can help identify areas where staff members need additional training or support. Performance data can also be used to evaluate the effectiveness of training programs and identify areas for improvement. The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) uses performance data to evaluate the quality of care in nursing homes.
Performance metrics can include:
- Care Plan Completion Rates: The percentage of residents who have completed care plans.
- Care Plan Quality Scores: Scores based on the quality of the care plans.
- Staff Training Completion Rates: The percentage of staff members who have completed required training.
9.5 Compliance Monitoring
Care plan software can help nursing homes monitor compliance with regulatory requirements. Some solutions include features that track compliance with specific regulations and alert staff members when they are at risk of non-compliance. Compliance monitoring can help ensure that nursing homes meet regulatory requirements and avoid penalties. The U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) Office of Inspector General (OIG) provides resources for healthcare compliance.
Compliance monitoring features can include:
- Regulatory Alerts: Alerts that notify staff members when they are at risk of non-compliance.
- Compliance Dashboards: Dashboards that provide an overview of compliance status.
- Audit Trails: Audit trails that track compliance activities.
10. What Are the Future Trends in Nursing Home Care Plan Software?
Future trends include AI-powered decision support, predictive analytics, telehealth integration, patient engagement tools, and interoperability.
As technology continues to evolve, nursing home care plan software is expected to become even more sophisticated and integrated with other healthcare systems. Here’s a look at some of the future trends in nursing home care plan software:
10.1 AI-Powered Decision Support
Artificial intelligence (AI) is expected to play an increasingly important role in nursing home care plan software. AI-powered decision support tools can help care providers make more informed decisions by analyzing patient data and providing insights into potential risks and treatment options. The National Institutes of Health (NIH) is funding research on the use of AI in healthcare.
AI-powered features can include:
- Risk Prediction: Identifying patients who are at high risk of adverse events, such as falls or infections.
- Treatment Recommendations: Providing recommendations for the most effective treatments based on patient data.
- Automated Alerts: Alerting care providers to potential problems or concerns.
10.2 Predictive Analytics
Predictive analytics can be used to forecast future trends and outcomes based on historical data. This information can help nursing homes proactively manage resources and improve the quality of care. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) uses predictive analytics to track and prevent outbreaks of infectious diseases.
Predictive analytics can be used to:
- Forecast Staffing Needs: Predicting future staffing needs based on patient census and acuity levels.
- Identify Patients at Risk of Readmission: Identifying patients who are at high risk of being readmitted to the hospital.
- Predict the Spread of Infectious Diseases: Forecasting the spread of infectious diseases and implementing preventive measures.
10.3 Telehealth Integration
Telehealth is becoming increasingly popular in nursing homes, allowing care providers to remotely monitor patients and provide virtual consultations. Future care plan software is expected to be tightly integrated with telehealth platforms, allowing for seamless data sharing and communication. The American Telemedicine Association (ATA) promotes the use of telehealth to improve access to care.
Telehealth integration can enable:
- Remote Monitoring: Remotely monitoring patients’ vital signs and other health data.
- Virtual Consultations: Conducting virtual consultations with patients and specialists.
- Medication Management: Providing medication management services remotely.
10.4 Patient Engagement Tools
Engaging patients and their families in the care planning process is essential for improving outcomes and satisfaction. Future care plan software is expected to include patient engagement tools that allow patients and families to actively participate in their care. The Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute (PCORI) supports patient engagement in healthcare research and decision-making.
Patient engagement tools can include:
- Patient Portals: Online portals that allow patients to access their care plans and communicate with their care team.
- Mobile Apps: Mobile apps that allow patients to track their health data and receive reminders about appointments and medications.
- Shared Decision-Making Tools: Tools that help patients and their families make informed decisions about their care.
10.5 Interoperability
Interoperability is the ability of different healthcare systems to exchange and use electronic health information. Future care plan software is expected to be highly interoperable with other healthcare systems, allowing for seamless data sharing and communication. The Office of the National Coordinator for Health Information Technology (ONC) is working to promote interoperability across the healthcare system.
Interoperability can enable:
- Seamless Data Sharing: Sharing patient data with other healthcare providers and systems.
- Improved Care Coordination: Coordinating care across different settings and providers.
- Reduced Administrative Burden: Reducing the administrative burden of exchanging health information.
By staying informed about these future trends, nursing homes can prepare for the future and ensure that they are using the most effective tools and technologies to provide high-quality care.
 Nurse Explaining Care Plan
Nurse Explaining Care Plan
Looking to enhance your skills and knowledge in nursing home care plan software and remote repair? CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN offers specialized training programs tailored to your needs. Visit our website or contact us at Address: