Software sales can be a fulfilling and lucrative career path, particularly for those with strong interpersonal skills and a passion for technology, and CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN is here to help you explore if it’s the right fit for you. It offers excellent earning potential, job stability, and opportunities for professional growth, providing a solid foundation for success, let’s dive into why software sales is a great career in 2024, covering everything from earning potential and job stability to required skills, career advancement, and the impact of remote work including remote diagnostic services and automotive repair technology.
Contents
- 1. What Makes Software Sales a Good Career Choice?
- 2. What Is The Earning Potential In Software Sales?
- 2.1 Base Salary Expectations
- 2.2 Commission Structures
- 2.3 Bonus Opportunities
- 2.4 Income Examples
- 2.5 Geographical Variations
- 2.6 Factors Influencing Earning Potential
- 3. How Stable Is A Career In Software Sales?
- 3.1 Growing Demand for Software
- 3.2 Recession-Resistant Industry
- 3.3 High Job Placement Rate
- 3.4 Essential Role in Revenue Generation
- 3.5 Transferable Skills
- 3.6 Company Stability
- 3.7 Continuous Learning and Adaptation
- 3.8 Networking and Relationships
- 3.9 Performance-Based Security
- 3.10 Industry Growth
- 4. What Skills And Qualifications Are Needed For Software Sales?
- 4.1 Technical Knowledge
- 4.2 Sales Acumen
- 4.3 Communication Skills
- 4.4 Interpersonal Skills
- 4.5 Problem-Solving Skills
- 4.6 Education and Certifications
- 4.7 Adaptability
- 5. What Are The Daily Responsibilities Of A Software Sales Professional?
- 5.1 Prospecting and Lead Generation
- 5.2 Client Communication
- 5.3 Sales Process Management
- 5.4 Administrative Tasks
- 5.5 Collaboration with Internal Teams
- 5.6 Continuous Learning
- 5.7 Time Management
- 6. What Are The Career Advancement Opportunities In Software Sales?
- 6.1 Sales Representative
- 6.2 Senior Sales Representative
- 6.3 Sales Team Lead
- 6.4 Sales Manager
- 6.5 Regional Sales Manager
- 6.6 Sales Director
- 6.7 VP of Sales
- 6.8 Account Executive
- 6.9 Sales Operations Manager
- 6.10 Training and Development Manager
- 7. How Does Remote Work Impact Software Sales Careers?
- 7.1 Increased Flexibility
- 7.2 Expanded Talent Pool
- 7.3 Enhanced Productivity
- 7.4 Improved Work-Life Balance
- 7.5 Challenges in Communication
- 7.6 Maintaining Team Cohesion
- 7.7 Client Relationship Management
- 7.8 Technological Requirements
- 7.9 Impact on Training and Onboarding
- 7.10 Adapting Sales Strategies
- 8. How Can CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN Help You In Your Automotive Career?
- 8.1 Specialized Training Programs
- 8.2 Hands-On Experience
- 8.3 Industry-Relevant Curriculum
- 8.4 Career Guidance and Placement
- 8.5 Networking Opportunities
- 8.6 Advanced Diagnostic Techniques
- 8.7 Software Proficiency
- 8.8 Remote Assistance Skills
- 8.9 Automotive Cybersecurity
- 8.10 Business and Management Skills
- 9. What Are The Challenges In Software Sales?
- 9.1 Intense Competition
- 9.2 Rapid Product Updates
- 9.3 Handling Rejection
- 9.4 Complex Sales Cycles
- 9.5 Building Trust with Clients
- 9.6 Maintaining Product Knowledge
- 9.7 Adapting to Market Changes
- 9.8 Overcoming Objections
- 9.9 Managing Time Effectively
- 9.10 Ethical Considerations
- 10. FAQ: Is Software Sales A Good Career?
- 10.1 Is software sales a lucrative career?
- 10.2 What skills are essential for software sales?
- 10.3 How stable is a career in software sales?
- 10.4 What are the daily responsibilities of a software sales professional?
- 10.5 What career advancement opportunities are available in software sales?
- 10.6 How does remote work impact software sales?
- 10.7 What are the challenges in software sales?
- 10.8 How can I stay updated with the latest trends in software sales?
- 10.9 Is a specific degree required for software sales?
- 10.10 How can CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN help me in my automotive career?
1. What Makes Software Sales a Good Career Choice?
Software sales can be a fantastic career if you enjoy technology, communication, and problem-solving, offering high earning potential and continuous growth. Let’s explore what makes it a good career move.
- High Earning Potential: Software sales positions often come with attractive base salaries, commissions, and bonuses, significantly increasing your earning potential.
- Job Stability: The demand for software solutions is consistently growing, making software sales a stable career choice with numerous job opportunities.
- Professional Development: Working in software sales requires continuous learning and adaptation, providing ongoing opportunities for professional growth.
- Networking: You’ll meet various professionals, including software developers, business owners, and CEOs, expanding your network and opening doors to future opportunities.
- Job Satisfaction: Helping clients solve their problems with software solutions can be highly rewarding, providing a sense of accomplishment and satisfaction.
2. What Is The Earning Potential In Software Sales?
The earning potential in software sales is substantial, with opportunities to significantly increase your income through commissions and bonuses, often exceeding the average income.
2.1 Base Salary Expectations
The average base salary for a software sales representative can range from $60,000 to $120,000 per year, depending on experience, location, and the specific company. According to a 2023 report by Glassdoor, the median base salary for a software sales representative in the United States is around $85,000.
2.2 Commission Structures
In addition to the base salary, software sales professionals typically earn commissions based on their sales performance, with some companies offering uncapped commission structures. According to research from LinkedIn, sales reps can expect to earn between 10% and 30% of the total contract value as commission, depending on the company and the product being sold.
2.3 Bonus Opportunities
Many companies offer bonuses for achieving or exceeding sales targets, providing additional income opportunities. A study by the Alexander Group found that approximately 70% of software companies offer quarterly or annual bonuses to their sales teams, with the average bonus ranging from 5% to 15% of the base salary.
2.4 Income Examples
- Entry-Level: A junior sales representative with 1-3 years of experience might earn a base salary of $60,000 plus $30,000 in commissions, totaling $90,000 per year.
- Mid-Level: An experienced sales representative with 5-7 years of experience could earn a base salary of $90,000 plus $60,000 in commissions, totaling $150,000 per year.
- Senior-Level: A senior sales executive with 10+ years of experience can earn a base salary of $120,000 plus $100,000 or more in commissions, potentially earning $220,000+ per year.
2.5 Geographical Variations
Salaries in software sales can vary significantly depending on the location. Major tech hubs like Silicon Valley, New York City, and Boston typically offer higher salaries due to the high cost of living and the concentration of tech companies.
For instance, a software sales representative in San Francisco might earn 15-20% more than someone in a smaller city like Atlanta or Dallas, according to data from Salary.com.
2.6 Factors Influencing Earning Potential
- Company Size: Larger companies with established sales processes and resources often pay higher base salaries and offer more lucrative commission structures.
- Product Complexity: Selling complex software solutions may result in higher commissions due to the increased effort and expertise required to close deals.
- Sales Performance: Consistently exceeding sales targets and achieving high sales volumes can lead to higher bonuses and promotions.
- Industry Demand: In-demand software niches such as cybersecurity, AI, and cloud computing may command higher salaries and commissions due to the shortage of skilled sales professionals.
3. How Stable Is A Career In Software Sales?
A career in software sales offers considerable stability due to the increasing reliance on software solutions across industries, making it a secure field for skilled professionals.
3.1 Growing Demand for Software
The increasing reliance on software solutions in various industries drives the demand for skilled software sales professionals. According to a report by Statista, the global software market is projected to reach $826.90 billion in 2024, indicating continuous growth and demand for software sales roles.
3.2 Recession-Resistant Industry
Software sales tend to be more resilient during economic downturns compared to other industries. Businesses often invest in software solutions to improve efficiency and reduce costs, even during recessions, which sustains the demand for software sales professionals.
3.3 High Job Placement Rate
Skilled software sales professionals typically have a high job placement rate due to the constant demand for their expertise. A study by LinkedIn found that software sales roles have a lower unemployment rate compared to other sales positions, indicating a stable job market for qualified candidates.
3.4 Essential Role in Revenue Generation
Sales professionals are essential for revenue generation, making them valuable assets to companies, especially in the software industry. According to research from HubSpot, sales teams directly contribute to business growth and sustainability, providing job security for successful sales representatives.
3.5 Transferable Skills
The skills acquired in software sales, such as communication, negotiation, and relationship-building, are transferable to other industries, providing flexibility and career options. If you ever decide to switch careers, your experience in software sales can open doors to other sales or management roles.
3.6 Company Stability
Choosing to work for a stable and well-established software company can enhance job security. Researching the company’s financial performance, market position, and growth potential can help you assess its stability and long-term prospects.
3.7 Continuous Learning and Adaptation
To maintain job security, software sales professionals must stay updated with the latest technologies, sales strategies, and market trends. Continuous learning and adaptation can help you remain competitive and valuable in the job market.
3.8 Networking and Relationships
Building a strong professional network can provide job opportunities and support in your career. Maintaining relationships with colleagues, clients, and industry professionals can help you stay informed about job openings and industry developments.
3.9 Performance-Based Security
Job security in software sales is often performance-based, with successful sales representatives being less likely to face layoffs or termination. Consistently meeting or exceeding sales targets can solidify your position within the company and provide long-term job security.
3.10 Industry Growth
The software industry is projected to continue growing in the coming years, creating even more opportunities for software sales professionals. According to a report by Gartner, the global IT spending is forecast to reach $5.1 trillion in 2024, indicating a positive outlook for the software industry and related job roles.
 Software sales career path
Software sales career path
4. What Skills And Qualifications Are Needed For Software Sales?
To succeed in software sales, you need a combination of technical knowledge, sales acumen, and strong interpersonal skills, enabling you to effectively communicate the value of the software.
4.1 Technical Knowledge
A fundamental understanding of software and technology is crucial for effectively selling software solutions. According to a survey by Salesforce, 75% of sales professionals believe that technical knowledge is essential for success in software sales.
- Software Basics: Understand the different types of software, such as SaaS, on-premise, and open-source, to cater to various client needs.
- Industry Trends: Stay updated with the latest trends in the software industry, including AI, cloud computing, and cybersecurity, to position yourself as a knowledgeable resource.
- Product Knowledge: Develop a deep understanding of the software products you are selling, including features, benefits, and competitive advantages, to address client inquiries effectively.
4.2 Sales Acumen
Strong sales skills are essential for identifying leads, building relationships, and closing deals.
- Lead Generation: Learn effective techniques for identifying and qualifying potential leads, such as cold calling, social selling, and networking.
- Sales Process: Understand the sales process from prospecting to closing, and develop strategies for moving leads through the sales funnel efficiently.
- Negotiation Skills: Master negotiation techniques to overcome objections and secure favorable deals for both your company and your clients.
4.3 Communication Skills
Excellent communication skills are vital for conveying complex technical information in a clear and persuasive manner. According to a study by the National Association of Sales Professionals (NASP), effective communication is the most important skill for sales success.
- Verbal Communication: Articulate the value proposition of your software solutions concisely and persuasively.
- Written Communication: Craft compelling emails, proposals, and presentations to engage potential clients.
- Active Listening: Listen attentively to clients’ needs and concerns to tailor your sales approach and build trust.
4.4 Interpersonal Skills
Building and maintaining strong relationships with clients is essential for long-term success in software sales.
- Empathy: Understand and relate to clients’ challenges and pain points to build rapport and establish trust.
- Relationship Building: Develop strategies for building and nurturing client relationships, such as regular check-ins, personalized communication, and providing value-added services.
- Networking: Attend industry events, join professional organizations, and leverage social media to expand your network and connect with potential clients and partners.
4.5 Problem-Solving Skills
Software sales often involves addressing complex client challenges with tailored solutions.
- Analytical Skills: Analyze clients’ business needs and identify how your software solutions can address their pain points and improve efficiency.
- Creative Thinking: Develop innovative solutions to meet clients’ unique requirements and differentiate your offerings from competitors.
- Technical Troubleshooting: Assist clients with technical issues and provide guidance on how to maximize the value of your software solutions.
4.6 Education and Certifications
While a specific degree is not always required, a bachelor’s degree in business, marketing, or a related field can be beneficial.
- Bachelor’s Degree: A bachelor’s degree can provide a solid foundation in business principles, communication, and critical thinking.
- Sales Certifications: Consider obtaining sales certifications from reputable organizations such as the Sales Education Foundation or the American Association of Inside Sales Professionals (AA-ISP) to enhance your credibility and knowledge.
- Software Training: Participate in software training programs and workshops to deepen your understanding of specific software products and sales techniques.
4.7 Adaptability
The software industry is constantly evolving, so adaptability is crucial for staying ahead of the curve.
- Continuous Learning: Stay informed about new technologies, market trends, and sales strategies through ongoing education and training.
- Flexibility: Adapt your sales approach to meet changing client needs and market conditions.
- Resilience: Bounce back from setbacks and learn from failures to improve your sales performance and achieve long-term success.
5. What Are The Daily Responsibilities Of A Software Sales Professional?
The daily responsibilities of a software sales professional involve a mix of prospecting, client communication, product demonstrations, and administrative tasks, all aimed at driving sales and building client relationships.
5.1 Prospecting and Lead Generation
Identifying potential clients and generating leads is a crucial daily task for software sales professionals.
- Cold Calling: Reach out to potential clients via phone to introduce your software solutions and assess their interest. According to a study by HubSpot, cold calling remains an effective lead generation technique when done strategically.
- Email Marketing: Send targeted emails to prospects to showcase the benefits of your software and encourage them to learn more. A report by Mailchimp indicates that personalized email campaigns can significantly improve open and click-through rates.
- Social Selling: Utilize social media platforms like LinkedIn to connect with potential clients, share valuable content, and engage in industry discussions. Research from LinkedIn suggests that social selling can increase sales opportunities by 45%.
- Networking: Attend industry events, conferences, and webinars to network with potential clients and partners. Networking can provide valuable leads and insights into market trends.
5.2 Client Communication
Maintaining regular communication with clients is essential for building relationships and driving sales.
- Client Meetings: Schedule and conduct meetings with clients to understand their needs, present your software solutions, and address any concerns. Effective client meetings can lead to stronger relationships and increased sales.
- Product Demonstrations: Provide live or recorded product demonstrations to showcase the features and benefits of your software. Visual demonstrations can help clients understand the value of your solutions.
- Follow-Up: Follow up with clients after meetings, demonstrations, or initial contact to answer questions, provide additional information, and move the sales process forward. Timely follow-up can significantly increase your chances of closing a deal.
5.3 Sales Process Management
Managing the sales process efficiently is crucial for closing deals and achieving sales targets.
- CRM Management: Utilize customer relationship management (CRM) software to track leads, manage client interactions, and monitor sales progress. According to a report by Forrester, companies using CRM systems can see a 29% increase in sales.
- Proposal Development: Create customized proposals for clients that outline the scope of work, pricing, and expected outcomes. A well-crafted proposal can differentiate you from competitors and win deals.
- Negotiation: Negotiate pricing, terms, and conditions with clients to reach mutually beneficial agreements. Effective negotiation skills are essential for closing deals and maximizing profitability.
- Closing Deals: Work to finalize sales agreements and close deals with clients. Closing deals requires persistence, effective communication, and a focus on meeting client needs.
5.4 Administrative Tasks
Completing administrative tasks is necessary for maintaining accurate records and supporting sales efforts.
- Sales Reporting: Prepare and submit regular sales reports to track progress, identify trends, and forecast future sales. Accurate sales reporting is essential for making informed business decisions.
- Expense Reporting: Track and submit expense reports for business-related expenses, such as travel, meals, and client entertainment. Proper expense reporting ensures compliance with company policies.
- Sales Training: Participate in ongoing sales training programs to enhance your skills and knowledge. Continuous learning is essential for staying competitive and achieving sales success.
5.5 Collaboration with Internal Teams
Collaborating with internal teams, such as marketing, product development, and customer support, is essential for delivering value to clients.
- Marketing Alignment: Work with the marketing team to develop effective marketing campaigns and sales collateral. Aligning sales and marketing efforts can improve lead generation and conversion rates.
- Product Feedback: Provide feedback to the product development team based on client interactions and market trends. Client feedback is valuable for improving product features and functionality.
- Customer Support: Collaborate with the customer support team to ensure clients receive excellent service and support. Strong customer support can lead to increased client satisfaction and retention.
5.6 Continuous Learning
Staying updated with industry trends, new technologies, and sales techniques is essential for long-term success in software sales.
- Industry Research: Conduct ongoing research to stay informed about industry trends, competitor activities, and new technologies. Continuous research can help you identify new opportunities and stay ahead of the curve.
- Professional Development: Attend industry conferences, webinars, and training programs to enhance your skills and knowledge. Professional development can improve your sales performance and career prospects.
- Product Updates: Stay informed about new product features, updates, and enhancements to effectively communicate the value of your software solutions to clients.
5.7 Time Management
Effective time management is crucial for prioritizing tasks, meeting deadlines, and maximizing productivity.
- Prioritization: Prioritize tasks based on their importance and urgency to ensure you focus on the most critical activities.
- Scheduling: Create a daily schedule to allocate time for prospecting, client communication, administrative tasks, and professional development.
- Organization: Maintain an organized workspace and utilize time management tools to stay on track and avoid distractions.
6. What Are The Career Advancement Opportunities In Software Sales?
Software sales offers numerous career advancement opportunities, from team leadership roles to executive positions, providing a clear path for professional growth and higher earning potential.
6.1 Sales Representative
Starting as a sales representative is the entry point for many careers in software sales, where you focus on generating leads, closing deals, and meeting sales targets.
- Responsibilities: Identify and qualify leads, conduct product demonstrations, negotiate contracts, and close sales.
- Skills Developed: Sales techniques, communication skills, product knowledge, and negotiation skills.
- Advancement: With experience and consistent performance, you can advance to senior sales representative or team lead roles.
6.2 Senior Sales Representative
As a senior sales representative, you take on more complex sales opportunities, mentor junior team members, and contribute to strategic sales planning.
- Responsibilities: Manage key accounts, develop sales strategies, mentor junior representatives, and exceed sales targets.
- Skills Developed: Strategic planning, leadership skills, advanced sales techniques, and client relationship management.
- Advancement: You can advance to sales team lead, sales manager, or account executive positions.
6.3 Sales Team Lead
A sales team lead is responsible for overseeing a team of sales representatives, providing guidance, and ensuring the team meets its sales goals.
- Responsibilities: Lead and motivate a sales team, provide training and coaching, monitor performance, and implement sales strategies.
- Skills Developed: Leadership, team management, performance monitoring, and strategic implementation.
- Advancement: You can advance to sales manager, regional sales manager, or sales director positions.
6.4 Sales Manager
As a sales manager, you manage multiple sales teams, develop sales plans, and ensure the overall sales targets of the organization are met.
- Responsibilities: Develop and implement sales strategies, manage sales budgets, oversee sales teams, and ensure sales targets are achieved.
- Skills Developed: Strategic planning, budget management, team leadership, and performance optimization.
- Advancement: You can advance to regional sales manager, sales director, or VP of sales positions.
6.5 Regional Sales Manager
A regional sales manager is responsible for overseeing sales operations in a specific geographic region, managing multiple sales teams, and driving revenue growth.
- Responsibilities: Manage regional sales teams, develop regional sales strategies, oversee sales budgets, and ensure regional sales targets are met.
- Skills Developed: Regional management, strategic planning, budget oversight, and team leadership.
- Advancement: You can advance to sales director or VP of sales positions.
6.6 Sales Director
As a sales director, you are responsible for the overall sales strategy and performance of the organization, working closely with executive leadership to drive revenue growth.
- Responsibilities: Develop and implement sales strategies, oversee sales operations, manage sales budgets, and ensure sales targets are achieved.
- Skills Developed: Strategic planning, sales operations, budget management, and executive leadership.
- Advancement: You can advance to VP of sales or executive leadership positions.
6.7 VP of Sales
The VP of sales is a key executive leadership role, responsible for setting the overall sales vision and strategy, managing sales teams, and driving revenue growth.
- Responsibilities: Set the sales vision and strategy, manage sales teams, oversee sales operations, and drive revenue growth.
- Skills Developed: Executive leadership, strategic planning, sales operations, and revenue growth management.
- Advancement: You can advance to executive leadership positions such as Chief Revenue Officer (CRO) or CEO.
6.8 Account Executive
Account executives focus on managing and growing relationships with key clients, ensuring customer satisfaction and driving repeat business.
- Responsibilities: Manage key client accounts, develop account strategies, ensure customer satisfaction, and drive repeat business.
- Skills Developed: Client relationship management, account strategy, customer service, and business development.
- Advancement: You can advance to senior account executive, account manager, or sales management positions.
6.9 Sales Operations Manager
Sales operations managers are responsible for streamlining sales processes, implementing sales technologies, and ensuring the sales team has the resources they need to succeed.
- Responsibilities: Streamline sales processes, implement sales technologies, manage sales data, and provide sales support.
- Skills Developed: Process optimization, technology implementation, data analysis, and sales support.
- Advancement: You can advance to sales operations director or sales leadership positions.
6.10 Training and Development Manager
Training and development managers are responsible for developing and delivering sales training programs, ensuring the sales team has the skills and knowledge they need to succeed.
- Responsibilities: Develop sales training programs, deliver training sessions, assess training needs, and evaluate training effectiveness.
- Skills Developed: Training development, facilitation, needs assessment, and evaluation.
- Advancement: You can advance to training director or HR leadership positions.
7. How Does Remote Work Impact Software Sales Careers?
Remote work has significantly transformed software sales, offering flexibility and access to a broader talent pool, while also presenting challenges in maintaining team cohesion and client relationships.
7.1 Increased Flexibility
Remote work offers software sales professionals increased flexibility, allowing them to manage their schedules and work from anywhere. According to a survey by FlexJobs, 80% of workers would be more loyal to their employer if they had flexible work options.
7.2 Expanded Talent Pool
Companies can hire software sales professionals from anywhere in the world, expanding their talent pool and access to specialized skills. A report by SHRM indicates that remote work can increase employee engagement and retention rates.
7.3 Enhanced Productivity
Many software sales professionals find that remote work enhances their productivity by reducing distractions and commuting time. According to a study by Stanford University, remote workers are 13% more productive than their in-office counterparts.
7.4 Improved Work-Life Balance
Remote work can improve work-life balance, allowing software sales professionals to spend more time with family and pursue personal interests. A survey by Deloitte found that 77% of employees believe that flexible work arrangements can improve their overall well-being.
7.5 Challenges in Communication
Remote work can present challenges in maintaining effective communication and collaboration among team members. Overcoming these challenges requires the use of technology and proactive communication strategies.
7.6 Maintaining Team Cohesion
Building and maintaining team cohesion can be difficult in a remote work environment. Companies must implement strategies to foster team spirit and camaraderie.
7.7 Client Relationship Management
Building and maintaining strong client relationships can be more challenging when working remotely. Software sales professionals must leverage technology to stay connected with clients.
7.8 Technological Requirements
Remote work requires access to reliable technology, including high-speed internet, video conferencing tools, and CRM software. Companies must ensure that remote employees have the necessary tools and resources to succeed.
7.9 Impact on Training and Onboarding
Training and onboarding new software sales professionals can be more complex in a remote work environment. Companies must develop effective virtual training programs to ensure new hires are properly prepared.
7.10 Adapting Sales Strategies
Software sales professionals must adapt their sales strategies to succeed in a remote work environment. This includes leveraging digital tools and techniques to engage with clients.
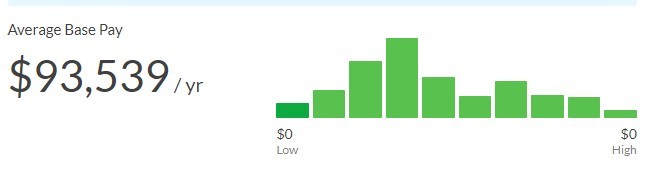 Software Sales Representative Salary
Software Sales Representative Salary
8. How Can CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN Help You In Your Automotive Career?
CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN can provide valuable support for your automotive career, especially if you are interested in remote diagnostic services and automotive repair technology.
8.1 Specialized Training Programs
CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN offers specialized training programs in remote diagnostics, automotive repair technology, and software applications, providing essential skills for modern automotive careers.
8.2 Hands-On Experience
The programs emphasize hands-on experience, allowing you to work with the latest diagnostic tools and software, enhancing your practical skills and employability.
8.3 Industry-Relevant Curriculum
The curriculum is designed in collaboration with industry experts, ensuring that the skills you learn are directly applicable to the current needs of the automotive industry.
8.4 Career Guidance and Placement
CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN provides career guidance and job placement assistance, helping you find employment opportunities in remote diagnostics, automotive repair, and related fields.
8.5 Networking Opportunities
You can connect with industry professionals, potential employers, and fellow students, expanding your professional network and opening doors to new opportunities.
8.6 Advanced Diagnostic Techniques
Learn advanced diagnostic techniques, including remote vehicle diagnostics, ECU programming, and fault code analysis, to excel in modern automotive repair.
8.7 Software Proficiency
Gain proficiency in using diagnostic software and tools, such as Autel, Snap-on, and Bosch, to enhance your efficiency and effectiveness in diagnosing and repairing vehicles remotely.
8.8 Remote Assistance Skills
Develop the skills to provide remote assistance to technicians in the field, troubleshooting complex issues and guiding them through repair procedures.
8.9 Automotive Cybersecurity
Understand the importance of automotive cybersecurity and learn how to protect vehicles from cyber threats, addressing a critical need in the modern automotive industry.
8.10 Business and Management Skills
Acquire business and management skills to operate your own remote diagnostic service or manage an automotive repair facility, enhancing your entrepreneurial capabilities.
9. What Are The Challenges In Software Sales?
Software sales comes with its own set of challenges, including intense competition, constant product updates, and the need to handle rejection, requiring resilience and adaptability.
9.1 Intense Competition
The software market is highly competitive, with numerous companies vying for the same clients. Standing out from the competition requires a strong value proposition and effective sales strategies.
9.2 Rapid Product Updates
Software products are constantly evolving, requiring sales professionals to stay updated with the latest features and updates. Continuous learning is essential for effectively selling software solutions.
9.3 Handling Rejection
Rejection is a common part of the sales process, and software sales professionals must develop resilience and learn from their failures. Maintaining a positive attitude and persistence is crucial for overcoming rejection.
9.4 Complex Sales Cycles
Software sales often involve complex sales cycles, with multiple stakeholders and decision-makers. Navigating these complex sales cycles requires patience, persistence, and strong relationship-building skills.
9.5 Building Trust with Clients
Building trust with clients is essential for long-term success in software sales. Demonstrating integrity, honesty, and a commitment to meeting client needs can help build trust and establish lasting relationships.
9.6 Maintaining Product Knowledge
Staying up-to-date with product knowledge is essential for effectively selling software solutions. Software sales professionals must dedicate time to learning about new features, updates, and industry trends.
9.7 Adapting to Market Changes
The software market is constantly changing, requiring sales professionals to adapt their strategies and approaches. Flexibility and a willingness to learn are crucial for staying ahead of the curve.
9.8 Overcoming Objections
Addressing client objections is a common part of the sales process. Software sales professionals must develop effective techniques for overcoming objections and persuading clients to purchase their solutions.
9.9 Managing Time Effectively
Software sales professionals must manage their time effectively to prioritize tasks, meet deadlines, and maximize productivity. Effective time management is essential for achieving sales targets and maintaining a healthy work-life balance.
9.10 Ethical Considerations
Maintaining ethical standards is crucial for building trust with clients and maintaining a positive reputation. Software sales professionals must adhere to ethical guidelines and avoid misleading or deceptive sales practices.
10. FAQ: Is Software Sales A Good Career?
10.1 Is software sales a lucrative career?
Yes, software sales offers high earning potential with attractive base salaries, commissions, and bonuses, providing opportunities for significant income growth.
10.2 What skills are essential for software sales?
Essential skills include technical knowledge, sales acumen, communication skills, interpersonal skills, and problem-solving abilities.
10.3 How stable is a career in software sales?
Software sales is a stable career choice due to the increasing demand for software solutions across industries, providing numerous job opportunities.
10.4 What are the daily responsibilities of a software sales professional?
Daily responsibilities include prospecting, client communication, product demonstrations, sales process management, and administrative tasks.
10.5 What career advancement opportunities are available in software sales?
Career advancement opportunities include sales representative, senior sales representative, sales team lead, sales manager, and VP of sales.
10.6 How does remote work impact software sales?
Remote work offers flexibility, expands the talent pool, and enhances productivity, but it also presents challenges in communication and team cohesion.
10.7 What are the challenges in software sales?
Challenges include intense competition, rapid product updates, handling rejection, and complex sales cycles.
10.8 How can I stay updated with the latest trends in software sales?
Stay updated by attending industry events, participating in training programs, and continuously researching market trends.
10.9 Is a specific degree required for software sales?
While not always required, a bachelor’s degree in business, marketing, or a related field can be beneficial.
10.10 How can CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN help me in my automotive career?
CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN offers specialized training programs in remote diagnostics, automotive repair technology, and software applications, providing essential skills for modern automotive careers.
In conclusion, software sales presents a promising career path with significant opportunities for financial success and personal growth. By developing the necessary skills, staying updated with industry trends, and leveraging resources like CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN, you can excel in this dynamic field and achieve your career goals. If you’re ready to elevate your skills and explore the world of remote automotive diagnostics, visit CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN today to learn more about our specialized training programs and unlock your potential in the automotive industry. Our address is 1700 W Irving Park Rd, Chicago, IL 60613, United States. You can also contact us via WhatsApp at +1 (641) 206-8880.