Are you curious about a Software Sales Career Progression and how to navigate it effectively? Software sales career progression offers incredible opportunities for motivated individuals to excel in a dynamic industry, and CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN provides the expertise you need to enhance your skills and advance your career. This article outlines the steps and strategies to achieve the best tech sales positions and accelerate career growth in salesforce development. We’ll delve into the details of each role, highlighting the key skills, responsibilities, and advancement opportunities within the IT sector.
Contents
- 1. Understanding the Software Sales Landscape
- 1.1. Key Skills for Success in Software Sales
- 1.2. The Growing Demand for Software Sales Professionals
- 2. Entry-Level Positions in Software Sales
- 2.1. Sales Development Representative (SDR)
- 2.2. Junior Account Executive
- 2.3. Comparing SDR and Junior Account Executive Roles
- 3. Mid-Level Positions in Software Sales
- 3.1. Account Executive (AE)
- 3.2. Sales Manager
- 3.3. Sales Engineer
- 3.4. Comparing Mid-Level Roles
- 4. Senior-Level Positions in Software Sales
- 4.1. VP of Sales
- 4.2. Director of Sales
- 4.3. Chief Revenue Officer (CRO)
- 4.4. Comparing Senior-Level Roles
- 5. Strategies for Career Advancement in Software Sales
- 5.1. Continuous Learning and Skill Development
- 5.2. Networking and Mentorship
- 5.3. Building a Strong Personal Brand
- 5.4. Setting and Achieving Goals
- 6. Case Studies of Successful Software Sales Professionals
- 6.1. Case Study 1: From SDR to VP of Sales
- 6.2. Case Study 2: From Sales Engineer to CRO
- 6.3. Case Study 3: Overcoming Challenges in Software Sales
- 7. The Role of CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN in Your Career Progression
- 7.1. Comprehensive Training Programs
- 7.2. Expert Instructors and Mentors
- 7.3. Networking Opportunities
- 7.4. Career Support Services
- 8. Future Trends in Software Sales
- 8.1. AI and Automation
- 8.2. Remote Selling
- 8.3. Customer-Centric Approach
- 8.4. Data-Driven Sales
- 9. Overcoming Common Challenges in Software Sales Career Progression
- 9.1. Dealing with Rejection
- 9.2. Staying Updated with Product Knowledge
- 9.3. Building and Maintaining Relationships
- 9.4. Time Management and Prioritization
1. Understanding the Software Sales Landscape
What exactly does a career in software sales entail, and what makes it such a promising field?
A career in software sales involves selling software products or services to businesses and individuals. According to a report by the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, sales roles, including those in software, are projected to grow in the coming years. This growth is driven by the increasing reliance on technology across all industries.
Software sales professionals are responsible for understanding their clients’ needs and demonstrating how their software solutions can address those needs. This often involves:
- Identifying potential clients: Researching and identifying businesses or individuals who could benefit from the software.
- Building relationships: Establishing and maintaining strong relationships with clients to understand their needs and challenges.
- Presenting solutions: Demonstrating how the software can solve the client’s problems through presentations and demos.
- Negotiating deals: Working with clients to reach mutually beneficial agreements.
- Closing sales: Finalizing sales agreements and ensuring client satisfaction.
- Providing ongoing support: Offering support and assistance to clients after the sale to ensure they continue to see value in the software.
1.1. Key Skills for Success in Software Sales
What are the essential skills that can help you thrive in a software sales career?
To succeed in software sales, several key skills are crucial. These include:
- Communication: The ability to articulate complex ideas clearly and persuasively is vital.
- Interpersonal Skills: Building rapport and maintaining relationships with clients is essential.
- Product Knowledge: A deep understanding of the software you are selling is necessary to answer client questions and address their concerns.
- Problem-Solving: Identifying client needs and providing effective solutions is key to closing deals.
- Negotiation: The ability to negotiate favorable terms with clients is essential for maximizing sales.
- Resilience: The ability to bounce back from rejection and stay motivated is important in this competitive field.
- Technical Aptitude: A basic understanding of technology and how software works is beneficial for explaining the technical aspects of the product.
- Time Management: Managing your time effectively to handle multiple clients and tasks is crucial for success.
These skills can be honed through training programs like those offered by CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN, which provides comprehensive courses designed to equip you with the tools and knowledge needed to excel in software sales.
1.2. The Growing Demand for Software Sales Professionals
Why is there such a high demand for skilled software sales professionals in today’s market?
The demand for software sales professionals is growing due to the increasing reliance on technology across all industries. According to a report by CompTIA, the IT sector is expected to continue growing, creating numerous opportunities for skilled sales professionals.
As businesses increasingly adopt software solutions to improve efficiency and productivity, the need for professionals who can effectively sell and support these solutions grows as well. This demand is particularly high in emerging technology areas such as cloud computing, artificial intelligence, and cybersecurity.
This demand translates to excellent career prospects and earning potential for those who possess the necessary skills and knowledge. By investing in training and development, you can position yourself to take advantage of these opportunities and build a successful career in software sales.
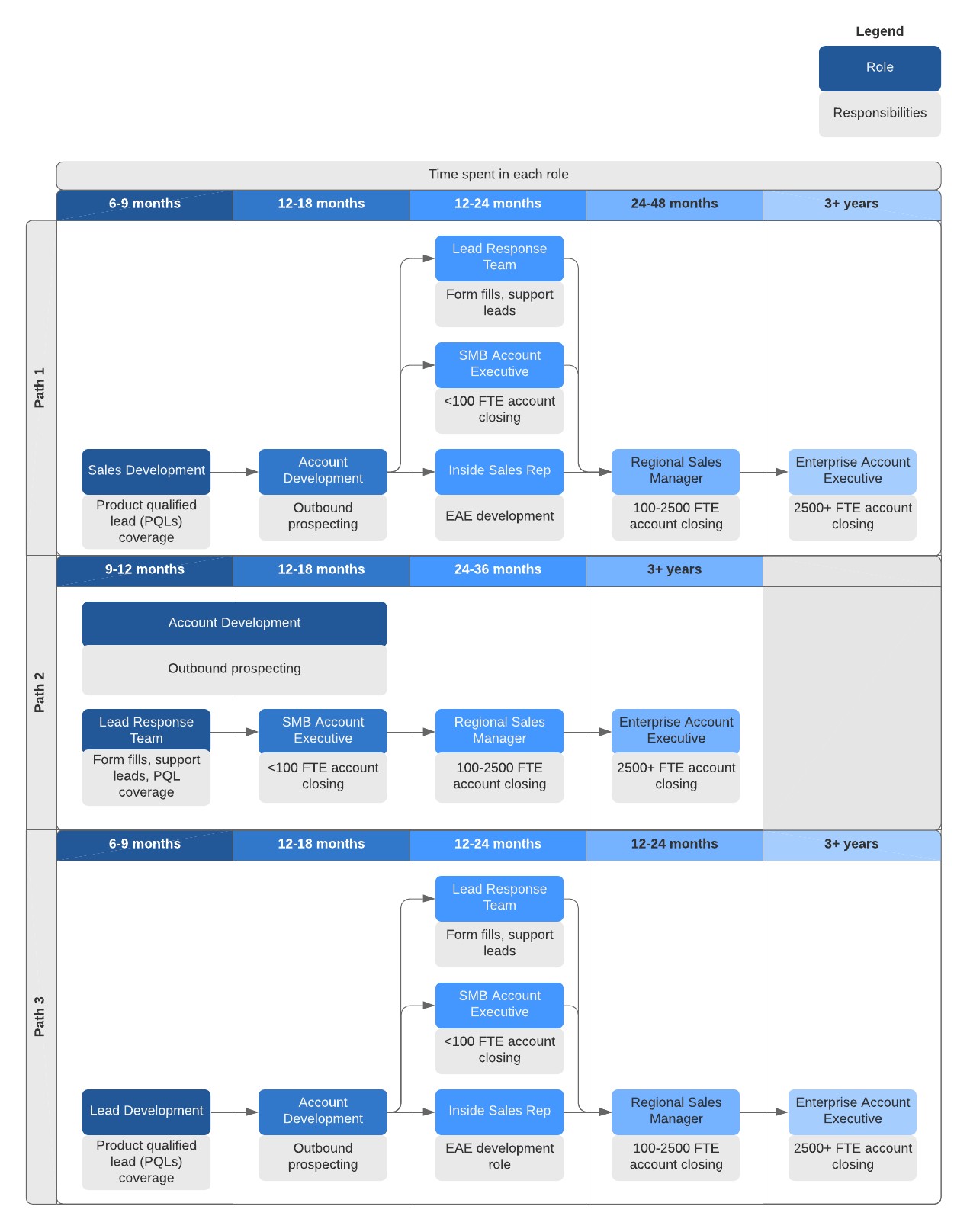 Sales Development Reps and Account Executives working together to achieve more deals
Sales Development Reps and Account Executives working together to achieve more deals
2. Entry-Level Positions in Software Sales
What are the typical entry-level roles in software sales, and what do they entail?
Entry-level positions in software sales are designed to introduce newcomers to the field and provide them with the foundational skills and knowledge needed to advance. Common entry-level roles include Sales Development Representative (SDR) and Junior Account Executive.
2.1. Sales Development Representative (SDR)
What does an SDR do, and what are the key responsibilities of this role?
A Sales Development Representative (SDR) is responsible for generating new leads and qualifying potential clients. According to The Bridge Group, SDRs play a crucial role in the sales process by identifying and nurturing leads that can be passed on to Account Executives.
The key responsibilities of an SDR include:
- Lead Generation: Identifying potential clients through various channels, such as online research, social media, and networking events.
- Cold Calling: Reaching out to potential clients via phone to introduce the software and gauge their interest.
- Email Marketing: Creating and sending targeted email campaigns to nurture leads and drive engagement.
- Qualifying Leads: Assessing the needs and requirements of potential clients to determine if they are a good fit for the software.
- Scheduling Meetings: Setting up meetings between qualified leads and Account Executives.
- Maintaining CRM: Keeping accurate records of all interactions with leads in the company’s Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system.
Example: An SDR might spend their day researching companies in the healthcare industry that could benefit from a new electronic health records (EHR) system. They would then reach out to these companies via phone and email to introduce the EHR system and schedule demos for interested prospects.
2.2. Junior Account Executive
What is the role of a Junior Account Executive, and how does it differ from that of an SDR?
A Junior Account Executive is responsible for managing the sales process from initial contact to closing the deal. Unlike SDRs, who focus on lead generation, Junior Account Executives work directly with qualified leads to understand their needs and present tailored solutions.
The key responsibilities of a Junior Account Executive include:
- Conducting Product Demos: Showcasing the features and benefits of the software through live demos.
- Understanding Client Needs: Conducting in-depth consultations with clients to understand their specific requirements and challenges.
- Developing Proposals: Creating customized proposals that outline how the software can address the client’s needs.
- Negotiating Terms: Working with clients to negotiate pricing and contract terms.
- Closing Deals: Finalizing sales agreements and ensuring client satisfaction.
- Building Relationships: Maintaining strong relationships with clients to ensure ongoing satisfaction and identify opportunities for upselling and cross-selling.
Example: A Junior Account Executive might work with a small business owner to implement a new accounting software system. They would conduct a demo of the software, understand the owner’s specific needs, develop a customized proposal, and negotiate the terms of the sale.
2.3. Comparing SDR and Junior Account Executive Roles
What are the key differences between these two entry-level positions?
| Feature | Sales Development Representative (SDR) | Junior Account Executive |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Lead Generation and Qualification | Sales and Closing |
| Responsibilities | Cold calling, email marketing, qualifying leads | Product demos, understanding client needs, negotiating terms |
| Interaction | Initial contact with potential clients | Direct management of sales process |
| Advancement | Opportunity to become an Account Executive | Opportunity to become a Senior Account Executive |
Understanding the differences between these roles can help you determine which path is the best fit for your skills and career goals. CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN offers tailored training programs for both SDRs and Junior Account Executives, providing you with the skills and knowledge needed to excel in your chosen role.
3. Mid-Level Positions in Software Sales
What are the common mid-level roles in software sales, and what kind of experience is typically required to attain them?
Mid-level positions in software sales require a proven track record of success and a deeper understanding of the sales process. Common mid-level roles include Account Executive, Sales Manager, and Sales Engineer.
3.1. Account Executive (AE)
What are the responsibilities of an Account Executive, and what skills are essential for success?
An Account Executive (AE) is responsible for managing the entire sales cycle, from prospecting to closing deals. According to HubSpot, Account Executives are crucial to the success of any growing organization.
The key responsibilities of an Account Executive include:
- Prospecting: Identifying and reaching out to potential clients who could benefit from the software.
- Building Relationships: Establishing and maintaining strong relationships with clients to understand their needs and challenges.
- Conducting Needs Assessments: Conducting in-depth consultations with clients to understand their specific requirements.
- Presenting Solutions: Demonstrating how the software can solve the client’s problems through presentations and demos.
- Negotiating Deals: Working with clients to reach mutually beneficial agreements.
- Closing Sales: Finalizing sales agreements and ensuring client satisfaction.
- Providing Ongoing Support: Offering support and assistance to clients after the sale to ensure they continue to see value in the software.
Skills for Success:
- Sales Acumen: A deep understanding of the sales process and the ability to effectively manage it.
- Communication Skills: The ability to articulate complex ideas clearly and persuasively.
- Interpersonal Skills: Building rapport and maintaining relationships with clients.
- Product Knowledge: A deep understanding of the software you are selling.
- Problem-Solving: Identifying client needs and providing effective solutions.
- Negotiation Skills: The ability to negotiate favorable terms with clients.
3.2. Sales Manager
What does a Sales Manager do, and how does this role contribute to the overall sales strategy?
A Sales Manager is responsible for overseeing and guiding a team of sales representatives. According to Salesforce, Sales Managers play a critical role in driving revenue and ensuring the success of the sales team.
The key responsibilities of a Sales Manager include:
- Team Leadership: Providing guidance, support, and motivation to the sales team.
- Setting Sales Targets: Establishing realistic and achievable sales targets for the team and individual representatives.
- Training and Development: Providing ongoing training and development opportunities to improve the skills and knowledge of the sales team.
- Monitoring Performance: Tracking and analyzing the performance of the sales team to identify areas for improvement.
- Coaching and Mentoring: Providing personalized coaching and mentoring to help sales representatives achieve their goals.
- Developing Sales Strategies: Working with senior management to develop and implement effective sales strategies.
- Reporting: Providing regular reports to senior management on the performance of the sales team.
3.3. Sales Engineer
What is the role of a Sales Engineer, and how does it bridge the gap between sales and technical expertise?
A Sales Engineer is responsible for providing technical expertise and support to the sales team. According to Gartner, Sales Engineers play a crucial role in helping clients understand the technical aspects of the software and how it can address their specific needs.
The key responsibilities of a Sales Engineer include:
- Technical Support: Providing technical support to the sales team during the sales process.
- Product Demonstrations: Conducting technical demonstrations of the software to showcase its capabilities.
- Needs Analysis: Working with clients to understand their technical requirements and challenges.
- Solution Design: Designing customized solutions that meet the client’s specific needs.
- Technical Documentation: Creating technical documentation to support the sales process.
- Training: Providing training to clients on how to use the software effectively.
- Troubleshooting: Troubleshooting technical issues that arise during the sales process.
3.4. Comparing Mid-Level Roles
What are the key differences between these three mid-level positions?
| Feature | Account Executive (AE) | Sales Manager | Sales Engineer |
|---|---|---|---|
| Focus | Sales and Closing | Team Leadership and Strategy | Technical Expertise and Support |
| Responsibilities | Prospecting, building relationships, negotiating deals | Team leadership, setting sales targets, training | Technical support, product demonstrations, solution design |
| Interaction | Direct management of sales process | Guiding and supporting sales team | Providing technical expertise |
| Skills | Sales acumen, communication, negotiation | Leadership, training, strategy | Technical knowledge, communication, problem-solving |
Each of these mid-level positions offers unique opportunities for growth and advancement. Choosing the right path depends on your skills, interests, and career goals. CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN provides advanced training programs for each of these roles, helping you develop the expertise needed to succeed.
 Illustration of pre-sales process steps
Illustration of pre-sales process steps
4. Senior-Level Positions in Software Sales
What are the top-tier roles in software sales, and what does it take to reach these heights?
Senior-level positions in software sales represent the pinnacle of career progression in this field. These roles require extensive experience, exceptional leadership skills, and a deep understanding of the software industry. Common senior-level roles include VP of Sales, Director of Sales, and Chief Revenue Officer (CRO).
4.1. VP of Sales
What are the responsibilities of a VP of Sales, and how does this role shape the overall sales strategy of the company?
A VP of Sales is responsible for overseeing the entire sales organization and driving revenue growth. According to LinkedIn, VP of Sales is a critical leadership role that requires a combination of strategic thinking, operational excellence, and people management skills.
The key responsibilities of a VP of Sales include:
- Developing Sales Strategy: Creating and implementing a comprehensive sales strategy that aligns with the company’s overall goals.
- Setting Sales Targets: Establishing ambitious but achievable sales targets for the organization.
- Building and Managing Sales Teams: Recruiting, training, and managing a high-performing sales team.
- Monitoring Performance: Tracking and analyzing sales performance to identify areas for improvement.
- Forecasting: Developing accurate sales forecasts to guide business decisions.
- Building Relationships: Building and maintaining strong relationships with key clients and partners.
- Representing the Company: Representing the company at industry events and conferences.
4.2. Director of Sales
What does a Director of Sales do, and how does this role support the VP of Sales in executing the sales strategy?
A Director of Sales is responsible for managing a specific region or product line within the sales organization. According to Glassdoor, Directors of Sales play a critical role in executing the sales strategy and achieving revenue targets.
The key responsibilities of a Director of Sales include:
- Managing Sales Teams: Managing and supporting a team of sales managers and representatives.
- Implementing Sales Strategies: Implementing the sales strategies developed by the VP of Sales.
- Monitoring Performance: Tracking and analyzing sales performance within their region or product line.
- Coaching and Mentoring: Providing coaching and mentoring to sales managers and representatives.
- Developing Sales Plans: Developing detailed sales plans for their region or product line.
- Building Relationships: Building and maintaining strong relationships with key clients and partners.
4.3. Chief Revenue Officer (CRO)
What are the responsibilities of a CRO, and how does this role integrate sales with other revenue-generating functions within the organization?
A Chief Revenue Officer (CRO) is responsible for overseeing all revenue-generating functions within the organization, including sales, marketing, and customer success. According to Forbes, CROs are becoming increasingly important as companies seek to align their revenue-generating efforts and drive growth.
The key responsibilities of a CRO include:
- Developing Revenue Strategy: Creating and implementing a comprehensive revenue strategy that aligns sales, marketing, and customer success.
- Setting Revenue Targets: Establishing ambitious but achievable revenue targets for the organization.
- Managing Revenue Teams: Managing and supporting the sales, marketing, and customer success teams.
- Monitoring Performance: Tracking and analyzing revenue performance across all functions.
- Optimizing Processes: Optimizing revenue-generating processes to improve efficiency and effectiveness.
- Building Relationships: Building and maintaining strong relationships with key clients and partners.
4.4. Comparing Senior-Level Roles
What are the key differences between these three senior-level positions?
| Feature | VP of Sales | Director of Sales | Chief Revenue Officer (CRO) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Focus | Overall Sales Strategy | Regional/Product Sales | Overall Revenue Generation |
| Responsibilities | Developing sales strategy, building sales teams | Managing sales teams, implementing strategies | Developing revenue strategy, managing revenue teams |
| Interaction | Overseeing entire sales organization | Managing specific sales teams | Integrating sales, marketing, and customer success |
| Skills | Strategic thinking, leadership, communication | Management, coaching, implementation | Strategic thinking, leadership, integration |
These senior-level positions represent the pinnacle of achievement in software sales. Reaching these heights requires a combination of experience, expertise, and leadership skills. CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN offers executive-level training programs designed to prepare you for these challenging and rewarding roles.
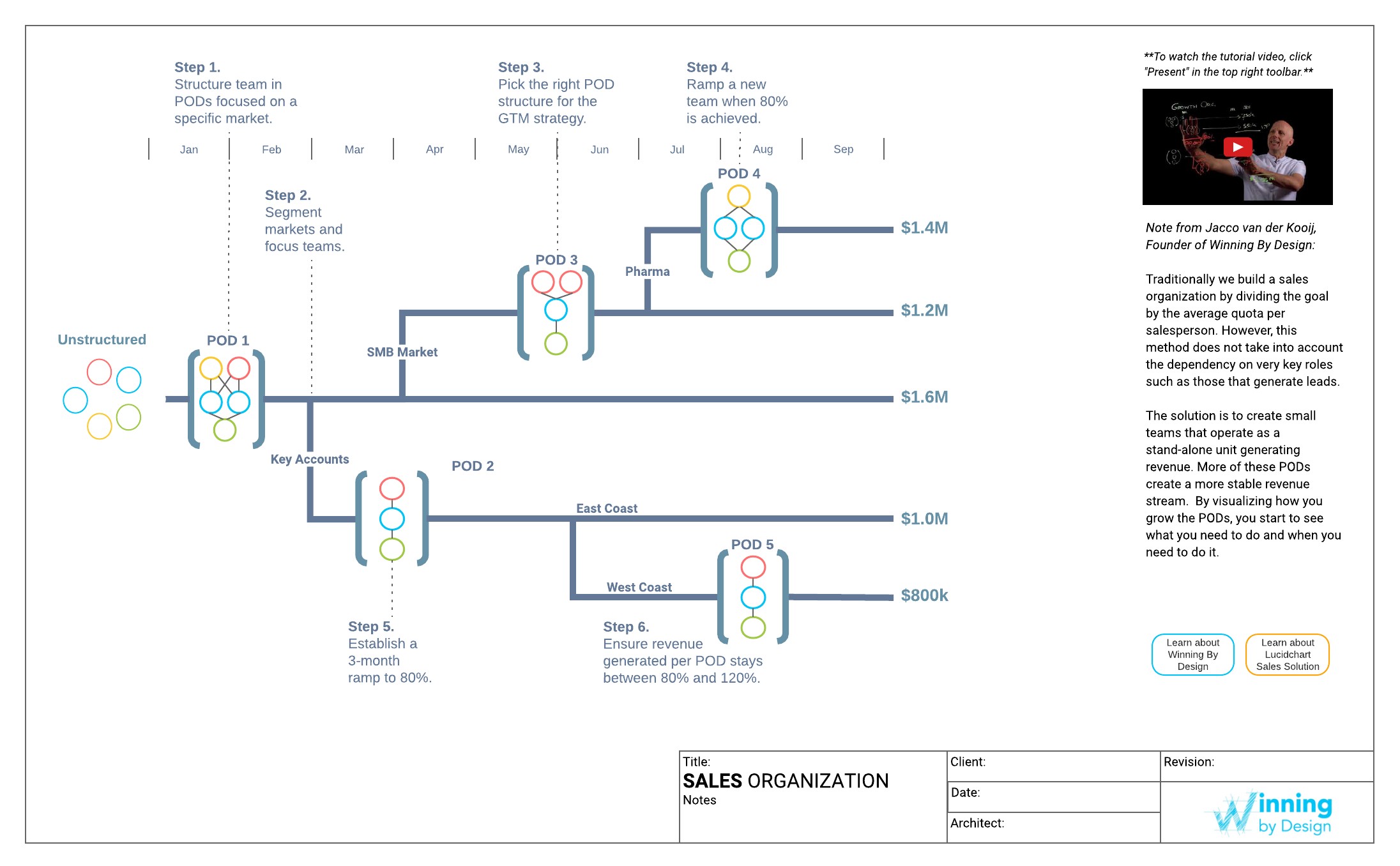 Illustration of sales organisation by Winning by Design
Illustration of sales organisation by Winning by Design
5. Strategies for Career Advancement in Software Sales
What steps can you take to accelerate your career progression in software sales?
Advancing your career in software sales requires a combination of skills development, strategic networking, and continuous learning. Here are some key strategies to help you climb the ladder:
5.1. Continuous Learning and Skill Development
How important is it to continuously update your skills and knowledge in the ever-evolving software industry?
Continuous learning and skill development are essential for staying ahead in the rapidly evolving software industry. According to a report by the Association for Talent Development (ATD), employees who engage in continuous learning are more productive, innovative, and engaged.
Here are some ways to stay current with the latest trends and technologies:
- Attend Industry Conferences: Participate in industry conferences and events to learn about the latest trends and network with other professionals.
- Take Online Courses: Enroll in online courses and certifications to develop new skills and deepen your knowledge.
- Read Industry Publications: Stay informed by reading industry publications, blogs, and articles.
- Join Professional Organizations: Join professional organizations to network with peers and access valuable resources.
CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN offers a wide range of training programs designed to help you develop the skills and knowledge needed to succeed in software sales. Our courses cover topics such as sales techniques, product knowledge, and leadership skills.
5.2. Networking and Mentorship
How can networking and mentorship opportunities contribute to your career growth?
Networking and mentorship can provide valuable insights, guidance, and opportunities for career advancement. According to a study by the Harvard Business Review, individuals who have mentors are more likely to be promoted and earn higher salaries.
Here are some ways to build your network and find a mentor:
- Attend Industry Events: Attend industry events and conferences to meet other professionals in your field.
- Join Online Communities: Join online communities and forums to connect with peers and experts.
- Seek Out Mentors: Identify experienced professionals who can provide guidance and support.
- Offer to Help Others: Offer to help others in your network to build goodwill and strengthen relationships.
5.3. Building a Strong Personal Brand
Why is it important to develop a strong personal brand, and how can you do it effectively?
Building a strong personal brand can help you stand out from the competition and attract new opportunities. According to Forbes, a strong personal brand can increase your visibility, credibility, and influence.
Here are some ways to build your personal brand:
- Define Your Unique Value Proposition: Identify what makes you unique and valuable to potential employers and clients.
- Create a Professional Online Presence: Develop a professional online presence on platforms such as LinkedIn and Twitter.
- Share Your Expertise: Share your expertise by writing articles, giving presentations, and participating in online discussions.
- Seek Out Opportunities to Lead: Seek out opportunities to lead projects and initiatives to demonstrate your leadership skills.
5.4. Setting and Achieving Goals
How can setting and achieving goals help you stay focused and motivated on your career path?
Setting and achieving goals can help you stay focused and motivated on your career path. According to a study by the University of California, individuals who set specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals are more likely to succeed.
Here are some tips for setting and achieving goals:
- Set SMART Goals: Set specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound goals.
- Break Down Goals: Break down large goals into smaller, more manageable tasks.
- Track Your Progress: Track your progress regularly to stay on track and identify areas for improvement.
- Reward Yourself: Reward yourself for achieving milestones to stay motivated.
By implementing these strategies, you can accelerate your career progression in software sales and achieve your professional goals. CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN is committed to providing you with the resources and support you need to succeed.
6. Case Studies of Successful Software Sales Professionals
Can you share some examples of individuals who have successfully navigated their career path in software sales?
Learning from the experiences of successful software sales professionals can provide valuable insights and inspiration. Here are a few case studies:
6.1. Case Study 1: From SDR to VP of Sales
Background:
- Name: John Smith
- Starting Role: Sales Development Representative (SDR)
- Current Role: VP of Sales
Career Path:
- Sales Development Representative (SDR): John started his career as an SDR, focusing on lead generation and qualification. He quickly excelled in this role by consistently exceeding his targets and demonstrating a strong understanding of the software.
- Account Executive (AE): After 18 months as an SDR, John was promoted to Account Executive. In this role, he managed the entire sales cycle, from prospecting to closing deals. He quickly established himself as a top performer by building strong relationships with clients and consistently exceeding his sales targets.
- Sales Manager: After three years as an AE, John was promoted to Sales Manager. In this role, he led a team of sales representatives, providing guidance, support, and motivation. He excelled as a Sales Manager by developing effective sales strategies and fostering a positive team environment.
- VP of Sales: After five years as a Sales Manager, John was promoted to VP of Sales. In this role, he is responsible for overseeing the entire sales organization and driving revenue growth. He has successfully implemented new sales strategies and built a high-performing sales team.
Key Takeaways:
- Continuous Learning: John consistently invested in his skills and knowledge, attending industry conferences and taking online courses.
- Strong Relationships: He built strong relationships with clients and colleagues, which helped him advance his career.
- Leadership Skills: He demonstrated strong leadership skills, which earned him promotions to management positions.
6.2. Case Study 2: From Sales Engineer to CRO
Background:
- Name: Jane Doe
- Starting Role: Sales Engineer
- Current Role: Chief Revenue Officer (CRO)
Career Path:
- Sales Engineer: Jane started her career as a Sales Engineer, providing technical expertise and support to the sales team. She quickly established herself as a valuable asset by demonstrating a deep understanding of the software and the ability to communicate complex technical concepts to clients.
- Account Executive (AE): After two years as a Sales Engineer, Jane transitioned to an Account Executive role. In this role, she leveraged her technical knowledge to build strong relationships with clients and close complex deals.
- Director of Sales: After four years as an AE, Jane was promoted to Director of Sales. In this role, she managed a team of sales representatives and was responsible for driving revenue growth within her region.
- Chief Revenue Officer (CRO): After six years as a Director of Sales, Jane was promoted to Chief Revenue Officer (CRO). In this role, she is responsible for overseeing all revenue-generating functions within the organization, including sales, marketing, and customer success.
Key Takeaways:
- Technical Expertise: Jane leveraged her technical expertise to build credibility with clients and close complex deals.
- Strategic Thinking: She demonstrated strategic thinking skills, which earned her promotions to leadership positions.
- Cross-Functional Collaboration: She fostered strong collaboration between sales, marketing, and customer success, which drove revenue growth.
6.3. Case Study 3: Overcoming Challenges in Software Sales
Background:
- Name: David Lee
- Starting Role: Junior Account Executive
- Current Role: Senior Account Executive
Challenges Faced:
- Initial Struggles: David initially struggled to meet his sales targets and faced rejection from potential clients.
- Lack of Confidence: He lacked confidence in his ability to close deals and felt overwhelmed by the complexity of the software.
- Competition: He faced intense competition from other sales representatives within his organization.
Strategies Used:
- Mentorship: David sought guidance from experienced sales professionals who provided him with valuable advice and support.
- Training: He enrolled in sales training programs to improve his sales techniques and product knowledge.
- Positive Mindset: He adopted a positive mindset and focused on building strong relationships with clients.
- Persistence: He remained persistent despite facing rejection and continued to work hard to achieve his goals.
Outcomes:
- Improved Performance: David’s sales performance improved significantly after implementing these strategies.
- Increased Confidence: He gained confidence in his ability to close deals and build strong relationships with clients.
- Career Advancement: He was promoted to Senior Account Executive and is now a top performer within his organization.
Key Takeaways:
- Seek Support: Don’t be afraid to seek guidance from mentors and peers.
- Invest in Training: Invest in sales training programs to improve your skills and knowledge.
- Maintain a Positive Mindset: Adopt a positive mindset and focus on building strong relationships with clients.
- Be Persistent: Remain persistent despite facing challenges and setbacks.
These case studies demonstrate that success in software sales requires a combination of skills, knowledge, and strategies. By learning from the experiences of others and investing in your own development, you can achieve your career goals. CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN is here to provide you with the training, resources, and support you need to succeed.
7. The Role of CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN in Your Career Progression
How can CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN help you achieve your career goals in software sales?
CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN is committed to providing you with the training, resources, and support you need to succeed in software sales. Our comprehensive programs are designed to equip you with the skills and knowledge required to excel at every stage of your career.
7.1. Comprehensive Training Programs
What types of training programs does CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN offer to support your career progression?
CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN offers a variety of training programs designed to support your career progression in software sales. Our programs cover a wide range of topics, including:
- Sales Techniques: Learn the latest sales techniques and strategies to improve your closing rate.
- Product Knowledge: Gain a deep understanding of the software you are selling.
- Negotiation Skills: Develop your negotiation skills to secure favorable terms with clients.
- Leadership Skills: Enhance your leadership skills to manage and motivate sales teams.
- Technical Expertise: Develop your technical expertise to provide effective support to the sales team.
Our training programs are designed to be interactive and engaging, with a focus on practical application. You will have the opportunity to practice your skills through simulations, role-playing exercises, and real-world case studies.
7.2. Expert Instructors and Mentors
Who are the instructors and mentors at CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN, and what experience do they bring to the table?
Our instructors and mentors are experienced software sales professionals who have a proven track record of success. They bring a wealth of knowledge and expertise to the table and are committed to helping you achieve your career goals.
Our instructors and mentors have held senior-level positions at leading software companies and have a deep understanding of the challenges and opportunities in the industry. They are passionate about sharing their knowledge and helping others succeed.
7.3. Networking Opportunities
How does CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN facilitate networking opportunities for its students and alumni?
CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN provides numerous networking opportunities for its students and alumni. We organize industry events, workshops, and conferences where you can connect with other professionals in your field.
We also have an active online community where you can network with peers, share ideas, and find job opportunities. Our networking events and online community provide valuable opportunities to build relationships and expand your professional network.
7.4. Career Support Services
What kind of career support services does CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN offer to help you find the right job and advance your career?
CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN offers a range of career support services to help you find the right job and advance your career. Our services include:
- Resume Review: We will review your resume and provide feedback to help you create a compelling and effective document.
- Interview Preparation: We will help you prepare for job interviews by conducting mock interviews and providing feedback on your performance.
- Job Placement Assistance: We will help you find job opportunities by connecting you with our network of employers.
- Career Coaching: We will provide personalized career coaching to help you develop a career plan and achieve your goals.
Our career support services are designed to provide you with the tools and resources you need to succeed in your job search and advance your career.
CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN is dedicated to helping you achieve your career goals in software sales. Contact us today to learn more about our training programs and career support services. Visit us at 1700 W Irving Park Rd, Chicago, IL 60613, United States, or reach out via WhatsApp at +1 (641) 206-8880. Explore our website at CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN.
8. Future Trends in Software Sales
What are some emerging trends in software sales, and how can you prepare for them?
The software sales landscape is constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements, changing customer expectations, and global economic factors. Here are some key trends to watch out for:
8.1. AI and Automation
How is AI and automation transforming the software sales process?
Artificial intelligence (AI) and automation are transforming the software sales process by streamlining tasks, improving efficiency, and enhancing customer experiences. According to a report by McKinsey, AI and automation can automate up to 30% of sales-related activities.
Here are some ways AI and automation are being used in software sales:
- Lead Generation: AI-powered tools can identify and qualify leads more efficiently.
- Personalized Communication: AI can personalize communication with clients based on their needs and preferences.
- Sales Forecasting: AI can improve the accuracy of sales forecasts by analyzing historical data and identifying patterns.
- Customer Service: AI-powered chatbots can provide instant customer service and support.
To prepare for this trend, you should develop your skills in data analysis, AI, and automation. CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN offers training programs on these topics to help you stay ahead of the curve.
8.2. Remote Selling
How is remote selling becoming more prevalent, and what skills are needed to succeed in this environment?
Remote selling has become increasingly prevalent, driven by the COVID-19 pandemic and the growing adoption of remote work. According to a report by Gartner, remote selling is expected to continue to grow in the coming years.
To succeed in remote selling, you need to develop skills in virtual communication, online presentations, and remote relationship building. You also need to be comfortable using technology and tools such as video conferencing, CRM systems, and collaboration platforms.
8.3. Customer-Centric Approach
Why is a customer-centric approach becoming more important in software sales?
A customer-centric approach is becoming more important in software sales as customers demand personalized experiences and tailored solutions. According to a report by Deloitte, customer-centric companies are more profitable and have higher customer satisfaction rates.
To adopt a customer-centric approach, you need to understand your customers’ needs and challenges, build strong relationships with them, and provide them with personalized solutions. You also need to be responsive to their feedback and continuously improve your products and services.
8.4. Data-Driven Sales
How is data being used to improve decision-making and drive sales performance?
Data is being used to improve decision-making and drive sales performance by providing insights into customer behavior, market trends, and sales effectiveness. According to a report by Forrester, data-driven companies are more likely to achieve their sales targets.
To leverage data effectively, you need to develop your skills in data analysis, data visualization, and data-driven decision-making. You also need to be familiar with tools and technologies such as CRM systems, business intelligence platforms, and data analytics software.
By staying informed about these emerging trends and developing the necessary skills, you can position yourself for success in the future of software sales. CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN is committed to providing you with the training and resources you need to thrive in this dynamic field.
9. Overcoming Common Challenges in Software Sales Career Progression
What are some typical challenges faced by software sales professionals, and how can they be overcome?
Navigating a career in software sales can present several challenges. Understanding these challenges and developing strategies to overcome them is crucial for success.
9.1. Dealing with Rejection
How can software sales professionals effectively handle rejection and maintain motivation?
Rejection is a common part of software sales. It’s essential to develop resilience and maintain a positive attitude.
Strategies:
- Reframe Rejection: View rejection as a learning opportunity rather than a personal failure. Analyze what went wrong and identify areas for improvement.
- Set Realistic Goals: Set achievable goals to maintain motivation and track progress.
- Celebrate Small Wins: Acknowledge and celebrate small achievements to boost morale.
- Seek Support: Connect with mentors or peers to discuss challenges and gain encouragement.
- Focus on the Process: Concentrate on improving your sales process rather than dwelling on individual outcomes.
9.2. Staying Updated with Product Knowledge
How can sales professionals keep up with rapidly changing software products and technologies?
The software industry is constantly evolving, making it crucial to stay updated with product knowledge.
Strategies:
- Continuous Learning: Dedicate time to learning about new products, features, and technologies.
- Attend Training Sessions: Participate in product training sessions offered by your company or industry experts.
- Read Industry Publications: Stay informed by reading industry blogs, articles, and newsletters.
- Hands-On Experience: Use the software products you sell to gain practical experience and understanding.
- Seek Feedback: Ask for feedback from colleagues and customers to identify areas for improvement.
9.3. Building and Maintaining Relationships
How can software sales professionals build and maintain strong relationships with clients?
Building strong relationships with clients is essential for long-term success in software sales.
Strategies:
- Active Listening: Listen attentively to understand clients’ needs and challenges.
- Personalized Communication: Tailor your communication to each client’s preferences and requirements.
- Follow-Up: Follow up regularly with clients to provide support and address any concerns.
- Be Responsive: Respond promptly to client inquiries and requests.
- Provide Value: Offer valuable insights, resources, and solutions to help clients achieve their goals.
9.4. Time Management and Prioritization
How can sales professionals effectively manage their time and prioritize tasks to maximize productivity?
Time management and prioritization are critical skills for software sales professionals who often juggle multiple clients and tasks.
Strategies:
- Prioritize Tasks: Identify the most important tasks and focus on completing them first.
