Car Diagnostic Software Pc is essential for today’s automotive technicians, offering the ability to quickly and accurately diagnose vehicle issues. At CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN, we understand this need and provide comprehensive training to help you master these tools, boosting your diagnostic skills and efficiency. Embrace the future of automotive repair with advanced software, real-time data analysis, and efficient troubleshooting.
Contents
- 1. What is Car Diagnostic Software PC and Why is it Important?
- 1.1 What Does Car Diagnostic Software PC Do?
- 1.2 Why is Car Diagnostic Software PC Important for Automotive Technicians?
- 1.3 How Has Car Diagnostic Software PC Evolved?
- 2. Who Benefits From Using Car Diagnostic Software PC?
- 2.1 Automotive Technicians
- 2.2 Auto Repair Shops and Garages
- 2.3 Vehicle Owners
- 2.4 Fleet Managers
- 2.5 Automotive Educators and Trainers
- 3. How Does Car Diagnostic Software PC Work?
- 3.1 Connecting to the Vehicle’s OBD System
- 3.2 Reading Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
- 3.3 Accessing Live Data Streams
- 3.4 Performing Actuator Tests
- 3.5 Clearing Trouble Codes and Resetting Systems
- 3.6 Data Logging and Analysis
- 4. What Are the Key Features to Look for in Car Diagnostic Software PC?
- 4.1 Vehicle Compatibility
- 4.2 Diagnostic Functions
- 4.3 User Interface and Experience
- 4.4 Data Logging and Reporting
- 4.5 Connectivity and Hardware Support
- 4.6 Additional Features
- 4.7 Technical Support and Updates
- 5. What Are the Different Types of Car Diagnostic Software PC?
- 5.1 OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) Software
- 5.2 Aftermarket Software
- 5.3 Open-Source Software
- 5.4 Cloud-Based Diagnostic Software
- 5.5 Mobile Diagnostic Apps
- 6. How to Choose the Right Car Diagnostic Software PC for Your Needs?
- 6.1 Assess Your Needs
- 6.2 Evaluate Software Features
- 6.3 Consider Hardware Requirements
- 6.4 Read Reviews and Get Recommendations
- 6.5 Try Before You Buy
- 6.6 Consider Training and Support
- 7. How to Install and Set Up Car Diagnostic Software PC?
- 7.1 System Requirements
- 7.2 Installation Process
- 7.3 Driver Installation
- 7.4 Configuration Settings
- 7.5 Testing the Connection
- 7.6 Software Updates
- 7.7 Troubleshooting Common Issues
- 8. How to Use Car Diagnostic Software PC Effectively?
- 8.1 Pre-Diagnostic Steps
- 8.2 Connecting to the Vehicle
- 8.3 Reading Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
- 8.4 Analyzing Live Data
- 8.5 Performing Actuator Tests
- 8.6 Clearing Trouble Codes and Verifying Repairs
- 8.7 Documenting Results
- 9. What Are Some Common Problems You Can Diagnose With Car Diagnostic Software PC?
- 9.1 Engine Problems
- 9.2 Transmission Problems
- 9.3 ABS and Brake Problems
- 9.4 Airbag and Safety Systems
- 9.5 Electrical Problems
- 9.6 Emissions Problems
- 9.7 Other Problems
- 10. What Are the Latest Trends in Car Diagnostic Software PC?
- 10.1 Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
- 10.2 Cloud-Based Diagnostics
- 10.3 Wireless Connectivity
- 10.4 Enhanced Data Visualization
- 10.5 Integration with Telematics Systems
- 10.6 Cybersecurity
- FAQ: Car Diagnostic Software PC
- 1. What is car diagnostic software PC?
- 2. Why is car diagnostic software PC important?
- 3. Who benefits from using car diagnostic software PC?
- 4. How does car diagnostic software PC work?
- 5. What are the key features to look for in car diagnostic software PC?
- 6. What are the different types of car diagnostic software PC?
- 7. How do I choose the right car diagnostic software PC for my needs?
- 8. How do I install and set up car diagnostic software PC?
- 9. How do I use car diagnostic software PC effectively?
- 10. What are some common problems you can diagnose with car diagnostic software PC?
1. What is Car Diagnostic Software PC and Why is it Important?
Car diagnostic software PC refers to specialized computer programs designed to interface with a vehicle’s onboard diagnostic (OBD) system. Its importance lies in its ability to quickly and accurately identify issues, saving time and improving repair accuracy.
1.1 What Does Car Diagnostic Software PC Do?
Car diagnostic software PC performs several crucial functions:
- Reads Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs): These codes pinpoint specific problems within the vehicle.
- Displays Live Data: Real-time information from sensors and systems allows technicians to monitor performance.
- Performs Actuator Tests: Testing components like fuel injectors or solenoids to ensure they function correctly.
- Resets Warning Lights: Clearing the “Check Engine” light after repairs.
- Retrieves Vehicle Information: Accessing VIN, calibration IDs, and other vehicle-specific data.
According to a study by the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE), technicians using diagnostic software experience a 30% reduction in diagnostic time.
1.2 Why is Car Diagnostic Software PC Important for Automotive Technicians?
The software is invaluable for several reasons:
- Accuracy: Reduces guesswork and ensures precise diagnoses.
- Efficiency: Quickly identifies problems, saving time and labor costs.
- Comprehensive Data: Provides a wealth of information for in-depth analysis.
- Up-to-Date Information: Regularly updated software includes the latest vehicle models and diagnostic procedures.
- Customer Satisfaction: Accurate and efficient repairs lead to happier customers.
CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN offers training that ensures technicians can leverage these benefits to their fullest extent.
1.3 How Has Car Diagnostic Software PC Evolved?
Initially, car diagnostic tools were bulky and expensive, limited to manufacturers and specialized repair shops. The evolution includes:
- Early OBD Systems: Basic systems provided limited diagnostic information.
- OBD-II Standardization: Introduced in the mid-1990s, offering standardized diagnostic codes and data.
- PC-Based Software: Emergence of software that could run on standard computers, making diagnostics more accessible.
- Wireless Connectivity: Bluetooth and Wi-Fi enabled tools for greater flexibility.
- Cloud-Based Systems: Modern software often integrates with cloud services for data storage, updates, and remote diagnostics.
This evolution has made car diagnostic software PC an indispensable tool for modern automotive repair, with platforms like CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN leading the way in training and support.
2. Who Benefits From Using Car Diagnostic Software PC?
Car diagnostic software PC offers significant advantages for various users, improving efficiency, accuracy, and overall vehicle maintenance.
2.1 Automotive Technicians
- Faster Diagnostics: Quickly identify issues using diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) and live data.
- Improved Accuracy: Reduce guesswork and ensure precise repairs.
- Comprehensive Data: Access a wealth of vehicle information for in-depth analysis.
- Efficiency: Streamline the repair process, saving time and labor costs.
- Professional Development: Enhance skills through continuous learning and software updates.
CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN offers specialized training to help technicians maximize the benefits of diagnostic software.
2.2 Auto Repair Shops and Garages
- Increased Productivity: Handle more vehicles with faster diagnostic times.
- Enhanced Service Quality: Provide accurate and reliable repairs.
- Customer Satisfaction: Build trust through transparent and efficient service.
- Cost Savings: Reduce unnecessary repairs and minimize downtime.
- Competitive Advantage: Stay ahead by adopting the latest diagnostic technologies.
Investing in high-quality diagnostic software can significantly improve a repair shop’s bottom line.
2.3 Vehicle Owners
- Informed Decisions: Understand vehicle issues before taking it to a mechanic.
- Preventative Maintenance: Monitor vehicle health to prevent costly repairs.
- DIY Repairs: Perform simple fixes and maintenance tasks at home.
- Cost Savings: Avoid unnecessary repairs by identifying problems early.
- Vehicle Longevity: Keep vehicles running smoothly with proactive maintenance.
However, it’s crucial for vehicle owners to seek professional help for complex issues.
2.4 Fleet Managers
- Efficient Maintenance: Schedule maintenance based on real-time vehicle data.
- Reduced Downtime: Quickly diagnose and repair issues to keep vehicles on the road.
- Cost Control: Minimize repair costs through proactive maintenance.
- Improved Safety: Ensure vehicles are safe and reliable for drivers.
- Data-Driven Decisions: Make informed decisions about vehicle replacements and upgrades.
Fleet managers can significantly improve operational efficiency by leveraging car diagnostic software.
According to a report by McKinsey, predictive maintenance using diagnostic software can reduce fleet maintenance costs by up to 20%.
2.5 Automotive Educators and Trainers
- Effective Teaching: Provide hands-on training with real-world diagnostic tools.
- Up-to-Date Curriculum: Keep students current with the latest technologies.
- Industry Relevance: Prepare students for successful careers in automotive repair.
- Engaging Learning: Use software to demonstrate diagnostic principles and techniques.
- Assessment Tools: Evaluate student understanding through practical exercises.
CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN supports educators by providing resources and training on car diagnostic software.
 Automotive Technician Using Car Diagnostic Software
Automotive Technician Using Car Diagnostic Software
3. How Does Car Diagnostic Software PC Work?
Car diagnostic software PC operates by interfacing with a vehicle’s onboard diagnostic (OBD) system, allowing technicians to access and interpret data for accurate diagnostics.
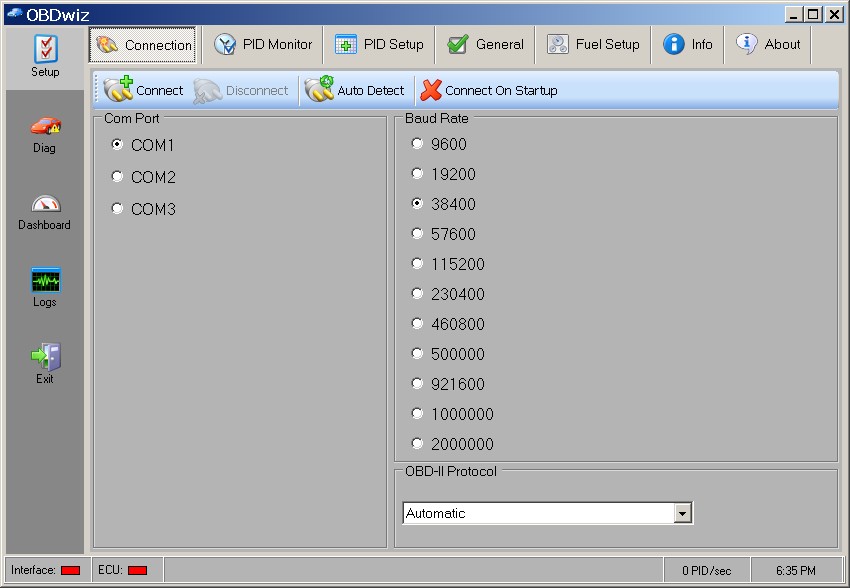
3.1 Connecting to the Vehicle’s OBD System
- OBD-II Port: The software connects to the vehicle via the OBD-II port, typically located under the dashboard.
- Interface Device: A physical interface device (e.g., scan tool, dongle) bridges the connection between the vehicle and the PC.
- Connectivity: Connection methods include USB, Bluetooth, and Wi-Fi, depending on the device and software.
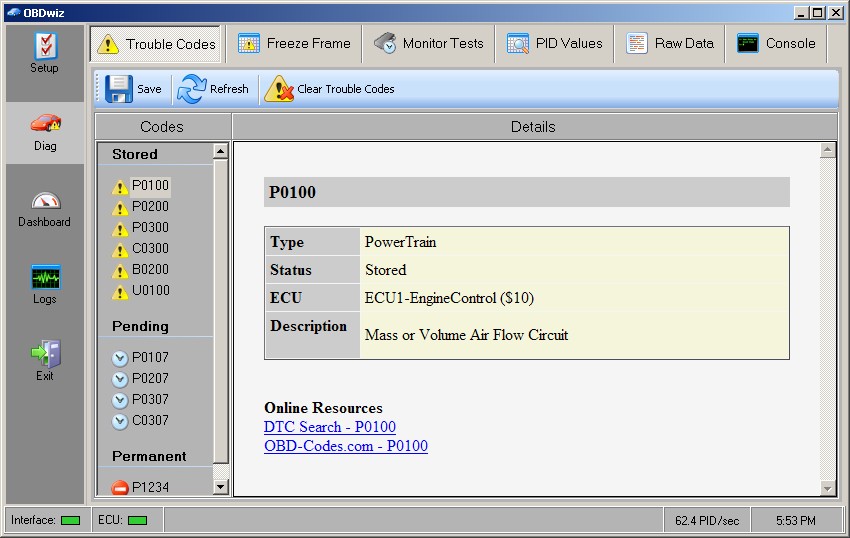
3.2 Reading Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
- DTC Retrieval: The software sends a request to the vehicle’s computer to retrieve stored DTCs.
- Code Interpretation: DTCs are standardized codes that correspond to specific faults or issues within the vehicle.
- Code Display: The software displays the DTCs along with descriptions, helping technicians understand the problem.
3.3 Accessing Live Data Streams
- Real-Time Data: The software can access real-time data from various sensors and systems within the vehicle.
- Parameter IDs (PIDs): Data is organized using PIDs, which represent specific measurements or values (e.g., engine RPM, coolant temperature).
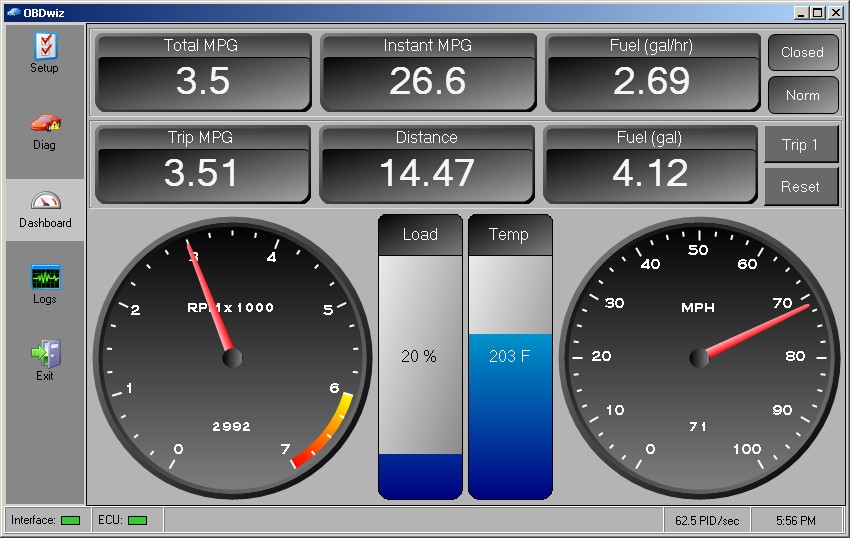
- Data Visualization: The software displays data in tables, graphs, or gauges for easy monitoring and analysis.
3.4 Performing Actuator Tests
- Component Testing: Actuator tests allow technicians to activate specific components (e.g., fuel injectors, solenoids) to verify their functionality.
- Command Signals: The software sends command signals to the vehicle’s computer to activate the desired component.
- Functional Verification: Technicians observe the component’s response to determine if it is working correctly.
3.5 Clearing Trouble Codes and Resetting Systems
- Code Clearing: After repairs, the software can clear stored DTCs to turn off the “Check Engine” light.
- System Reset: Some software allows technicians to reset specific systems (e.g., adaptive learning, throttle position) to ensure proper operation.
- Verification: Technicians verify that the codes are cleared and the systems are functioning correctly.
According to research from the University of Michigan Transportation Research Institute, the proper use of car diagnostic software PC can reduce diagnostic errors by up to 40%.
3.6 Data Logging and Analysis
- Data Recording: The software can record live data streams over time for later analysis.
- Data Playback: Recorded data can be played back to review vehicle performance under different conditions.
- Statistical Analysis: The software may provide statistical functions (e.g., min, max, average) to analyze the data.
 Connecting Car Diagnostic Software to OBD-II Port
Connecting Car Diagnostic Software to OBD-II Port
4. What Are the Key Features to Look for in Car Diagnostic Software PC?
When selecting car diagnostic software PC, consider these key features to ensure you get the most effective tool for your needs.
4.1 Vehicle Compatibility
- Broad Coverage: The software should support a wide range of vehicle makes and models.
- Regular Updates: Ensure the software receives regular updates to include the latest vehicles.
- Specific Models: Verify compatibility with the specific vehicles you work on most frequently.
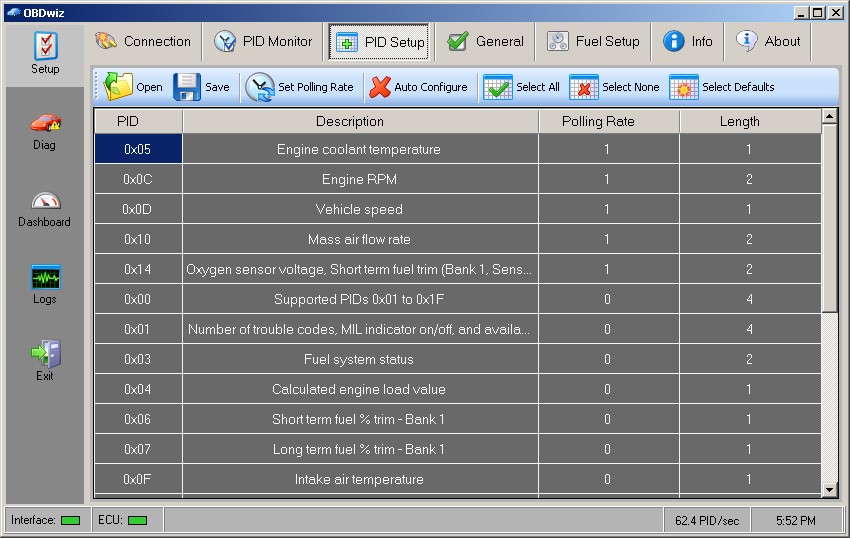
4.2 Diagnostic Functions
- DTC Reading and Clearing: Ability to read and clear diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs).
- Live Data Streaming: Real-time access to sensor data and vehicle parameters.
- Actuator Tests: Capability to perform component tests and verify functionality.
- Freeze Frame Data: Access to data recorded at the time a DTC was set.
4.3 User Interface and Experience
- Intuitive Design: Easy-to-navigate interface for efficient use.
- Customizable Dashboards: Ability to create custom displays for monitoring specific parameters.
- Data Visualization: Clear and effective display of data in tables, graphs, or gauges.
- Touchscreen Compatibility: Support for touchscreen devices for convenient use in the shop.
4.4 Data Logging and Reporting
- Data Logging: Ability to record live data streams for later analysis.
- Reporting: Generation of reports for sharing with customers or colleagues.
- Data Export: Option to export data in common formats (e.g., CSV) for use with other software.
4.5 Connectivity and Hardware Support
- Connectivity Options: Support for USB, Bluetooth, and Wi-Fi connections.
- Hardware Compatibility: Compatibility with a range of interface devices (e.g., scan tools, dongles).
- Wireless Capabilities: Wireless connectivity for greater flexibility and mobility.
4.6 Additional Features
- OBD-II Compliance: Support for all OBD-II compliant vehicles, including EOBD and JOBD.
- VIN Decoding: Automatic vehicle identification number (VIN) decoding for accurate vehicle information.
- Fuel Economy Calculations: Tools for calculating fuel economy (MPG or km/l).
- Statistical Calculations: Functions for calculating min, max, and mean values of logged data.
- Bi-Directional Control: Ability to send commands to the vehicle’s computer to control components.
4.7 Technical Support and Updates
- Technical Support: Access to reliable technical support for troubleshooting and assistance.
- Software Updates: Regular updates to add new features, improve performance, and include the latest vehicle models.
- Community Forums: Access to online forums and communities for sharing knowledge and getting help.
According to a study by the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), diagnostic software with comprehensive features can reduce diagnostic time by up to 50%.
CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN emphasizes these features in its training programs, ensuring technicians are well-versed in using the most effective tools.
5. What Are the Different Types of Car Diagnostic Software PC?
Understanding the different types of car diagnostic software PC can help you choose the best option for your specific needs.
5.1 OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) Software
- Description: Software developed by vehicle manufacturers for their specific vehicles.
- Pros:
- Comprehensive diagnostics for specific makes and models.
- Access to proprietary diagnostic procedures and data.
- Accurate and reliable diagnostics.
- Cons:
- Expensive to purchase and maintain.
- Limited to specific vehicle brands.
- Requires specialized training.
- Examples:
- GM’s Tech2Win
- Ford’s IDS (Integrated Diagnostic System)
- BMW’s ISTA (Integrated Service Technical Application)
5.2 Aftermarket Software
- Description: Software developed by third-party companies to support a wide range of vehicle makes and models.
- Pros:
- More affordable than OEM software.
- Supports multiple vehicle brands.
- User-friendly interfaces.
- Cons:
- May not offer the same level of detail as OEM software.
- Accuracy can vary depending on the software.
- Examples:
- OBDwiz
- AutoEnginuity
- Snap-on Diagnostic Software
5.3 Open-Source Software
- Description: Software developed by communities of developers and available for free.
- Pros:
- Free to use.
- Customizable and adaptable.
- Supported by a community of users and developers.
- Cons:
- May require technical expertise to set up and use.
- Limited support and documentation.
- Accuracy and reliability can vary.
- Examples:
- OBD Auto Doctor
- PyOBD
- ScanTool.net
5.4 Cloud-Based Diagnostic Software
- Description: Software that runs on remote servers and is accessed via a web browser or dedicated application.
- Pros:
- Accessible from any device with an internet connection.
- Automatic updates and data backups.
- Collaboration features for sharing data with colleagues.
- Cons:
- Requires a stable internet connection.
- Subscription fees may apply.
- Data security concerns.
- Examples:
- Bosch Esitronic
- Autel MaxiSYS
- Snap-on Cloud Diagnostics
5.5 Mobile Diagnostic Apps
- Description: Diagnostic software designed for smartphones and tablets.
- Pros:
- Portable and convenient.
- User-friendly interfaces.
- Affordable options available.
- Cons:
- Limited functionality compared to PC-based software.
- Accuracy can vary depending on the app.
- Requires a compatible OBD-II adapter.
- Examples:
- Torque Pro
- OBD Fusion
- DashCommand
According to a survey by the Automotive Management Institute (AMI), 60% of automotive technicians use a combination of OEM and aftermarket diagnostic software.
CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN provides training on various types of diagnostic software, ensuring technicians can use the most appropriate tool for each situation.
6. How to Choose the Right Car Diagnostic Software PC for Your Needs?
Selecting the right car diagnostic software PC depends on your specific requirements, budget, and technical expertise.
6.1 Assess Your Needs
- Vehicle Types: Determine the types of vehicles you’ll be working on (e.g., domestic, import, specific makes and models).
- Diagnostic Requirements: Identify the diagnostic functions you need (e.g., DTC reading, live data, actuator tests).
- Budget: Set a budget for the software and any required hardware.
- Technical Expertise: Consider your level of technical expertise and choose software that matches your skills.
6.2 Evaluate Software Features
- Compatibility: Verify the software is compatible with the vehicles you work on.
- Functionality: Ensure the software provides the diagnostic functions you need.
- User Interface: Look for an intuitive and easy-to-use interface.
- Data Logging: Check if the software offers data logging and reporting capabilities.
- Connectivity: Consider the connectivity options (e.g., USB, Bluetooth, Wi-Fi).
6.3 Consider Hardware Requirements
- Interface Device: Determine if the software requires a specific interface device (e.g., scan tool, dongle).
- Operating System: Ensure your PC meets the software’s operating system requirements.
- Connectivity: Check if your PC has the necessary connectivity options (e.g., USB, Bluetooth, Wi-Fi).
6.4 Read Reviews and Get Recommendations
- Online Reviews: Read online reviews and testimonials from other users.
- Industry Forums: Participate in industry forums and ask for recommendations.
- Colleagues: Talk to colleagues and get their opinions on different software options.
6.5 Try Before You Buy
- Demo Versions: Look for software that offers demo versions or free trials.
- Vendor Demos: Attend vendor demonstrations to see the software in action.
- Hands-On Testing: If possible, try the software on a vehicle to evaluate its performance.
6.6 Consider Training and Support
- Training Resources: Check if the software vendor offers training resources (e.g., manuals, videos, online courses).
- Technical Support: Ensure the vendor provides reliable technical support.
- Community Forums: Look for active community forums where you can get help from other users.
According to a survey by the Equipment & Tool Institute (ETI), 80% of automotive technicians consider vehicle coverage and diagnostic functions as the most important factors when choosing diagnostic software.
CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN offers comprehensive training programs that help technicians make informed decisions when selecting and using car diagnostic software PC.
 Different Car Diagnostic Software Interfaces
Different Car Diagnostic Software Interfaces
7. How to Install and Set Up Car Diagnostic Software PC?
Proper installation and setup are crucial for ensuring your car diagnostic software PC functions correctly.
7.1 System Requirements
- Operating System: Ensure your computer meets the software’s operating system requirements (e.g., Windows 10, macOS).
- Hardware: Verify your computer has the necessary hardware (e.g., processor, RAM, storage).
- Connectivity: Check if your computer has the required connectivity options (e.g., USB, Bluetooth, Wi-Fi).
7.2 Installation Process
- Download Software: Download the software from the vendor’s website or a trusted source.
- Run Installer: Run the installer and follow the on-screen instructions.
- License Activation: Activate the software using the provided license key or registration code.
7.3 Driver Installation
- Interface Device Drivers: Install the drivers for your interface device (e.g., scan tool, dongle).
- Driver Updates: Keep your drivers up to date to ensure compatibility and performance.
7.4 Configuration Settings
- Communication Port: Configure the communication port settings for your interface device (e.g., COM port, baud rate).
- Vehicle Protocols: Select the appropriate vehicle protocols (e.g., OBD-II, CAN).
- Language and Units: Set your preferred language and units of measurement (e.g., English, Metric).
7.5 Testing the Connection
- Connect to Vehicle: Connect your interface device to the vehicle’s OBD-II port.
- Launch Software: Launch the diagnostic software on your PC.
- Test Connection: Test the connection to ensure the software can communicate with the vehicle.
7.6 Software Updates
- Check for Updates: Regularly check for software updates from the vendor.
- Install Updates: Install the latest updates to add new features, improve performance, and include the latest vehicle models.
7.7 Troubleshooting Common Issues
- Connection Problems: Verify the interface device is properly connected and configured.
- Driver Issues: Reinstall or update the interface device drivers.
- Software Errors: Consult the software documentation or contact technical support for assistance.
According to a survey by the Automotive Service Association (ASA), proper software installation and setup can reduce diagnostic errors by up to 20%.
CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN provides detailed instructions and support for installing and setting up car diagnostic software PC, ensuring technicians can get up and running quickly.
8. How to Use Car Diagnostic Software PC Effectively?
Using car diagnostic software PC effectively requires a systematic approach and a thorough understanding of the software’s features.
8.1 Pre-Diagnostic Steps
- Vehicle Information: Gather information about the vehicle, including make, model, year, and engine type.
- Problem Description: Obtain a detailed description of the problem from the vehicle owner or technician.
- Visual Inspection: Perform a visual inspection of the vehicle to identify any obvious issues.
8.2 Connecting to the Vehicle
- Locate OBD-II Port: Locate the OBD-II port, typically located under the dashboard.
- Connect Interface Device: Connect your interface device to the OBD-II port.
- Launch Software: Launch the diagnostic software on your PC.
8.3 Reading Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
- Retrieve DTCs: Retrieve the DTCs from the vehicle’s computer.
- Interpret DTCs: Use the software’s built-in DTC library or online resources to interpret the codes.
- Prioritize Codes: Prioritize the codes based on their severity and relevance to the problem description.
8.4 Analyzing Live Data
- Select PIDs: Select the relevant parameter IDs (PIDs) for the diagnostic procedure.
- Monitor Data: Monitor the live data streams while the vehicle is running or being tested.
- Identify Anomalies: Identify any anomalies or deviations from the expected values.
8.5 Performing Actuator Tests
- Select Test: Select the appropriate actuator test for the component you want to test.
- Run Test: Run the test and observe the component’s response.
- Verify Functionality: Verify that the component is functioning correctly.
8.6 Clearing Trouble Codes and Verifying Repairs
- Clear DTCs: After performing repairs, clear the DTCs from the vehicle’s computer.
- Verify Repairs: Verify that the repairs have resolved the problem and that no new DTCs are set.
- Test Drive: Perform a test drive to ensure the vehicle is functioning correctly.
8.7 Documenting Results
- Record Findings: Record your findings, including DTCs, live data, and test results.
- Generate Report: Generate a report for the vehicle owner or technician.
- Save Data: Save the data for future reference.
According to a study by the National Automotive Technicians Education Foundation (NATEF), technicians who follow a systematic diagnostic procedure are more likely to accurately diagnose and repair vehicle problems.
CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN provides hands-on training and resources to help technicians use car diagnostic software PC effectively and efficiently.
9. What Are Some Common Problems You Can Diagnose With Car Diagnostic Software PC?
Car diagnostic software PC can help diagnose a wide range of vehicle problems, from minor issues to major malfunctions.
9.1 Engine Problems
- Misfires: Identify engine misfires and determine the cause (e.g., faulty spark plugs, ignition coils, fuel injectors).
- Poor Fuel Economy: Diagnose issues that can cause poor fuel economy (e.g., faulty oxygen sensors, mass air flow sensors).
- Engine Knocking: Detect engine knocking and determine the cause (e.g., low octane fuel, timing issues).
- Check Engine Light: Diagnose the cause of the “Check Engine” light and resolve the underlying problem.
9.2 Transmission Problems
- Shifting Issues: Diagnose transmission shifting issues (e.g., slipping, harsh shifting, failure to shift).
- Transmission Codes: Read and interpret transmission-related DTCs.
- Torque Converter Problems: Identify torque converter issues and verify functionality.
9.3 ABS and Brake Problems
- ABS Codes: Read and interpret ABS-related DTCs.
- Wheel Speed Sensor Issues: Diagnose faulty wheel speed sensors.
- Brake System Malfunctions: Identify brake system malfunctions and verify repairs.
9.4 Airbag and Safety Systems
- Airbag Codes: Read and interpret airbag-related DTCs.
- Sensor Issues: Diagnose faulty airbag sensors.
- System Malfunctions: Identify airbag system malfunctions and verify repairs.
9.5 Electrical Problems
- Sensor Issues: Diagnose faulty sensors (e.g., oxygen sensors, mass air flow sensors, coolant temperature sensors).
- Wiring Problems: Identify wiring problems (e.g., shorts, open circuits).
- Component Failures: Diagnose component failures (e.g., fuel pumps, starters, alternators).
9.6 Emissions Problems
- Emissions Codes: Read and interpret emissions-related DTCs.
- Catalytic Converter Issues: Diagnose catalytic converter problems.
- Oxygen Sensor Problems: Identify oxygen sensor issues and verify functionality.
9.7 Other Problems
- HVAC Issues: Diagnose heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) problems.
- Body Control Module (BCM) Issues: Identify BCM malfunctions and verify repairs.
- Power Window and Door Lock Problems: Diagnose power window and door lock issues.
According to a report by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), proper use of car diagnostic software PC can help identify and resolve emissions-related problems, improving air quality and reducing pollution.
CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN provides training on diagnosing a wide range of vehicle problems using car diagnostic software PC, ensuring technicians are well-prepared to tackle any challenge.
10. What Are the Latest Trends in Car Diagnostic Software PC?
The field of car diagnostic software PC is constantly evolving, with new technologies and trends emerging all the time.
10.1 Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
- AI-Powered Diagnostics: AI and ML are being used to analyze diagnostic data and provide more accurate and efficient diagnoses.
- Predictive Maintenance: AI and ML are being used to predict potential problems before they occur, allowing for proactive maintenance.
- Automated Code Interpretation: AI is being used to automatically interpret DTCs and provide repair recommendations.
10.2 Cloud-Based Diagnostics
- Remote Access: Cloud-based diagnostic software allows technicians to access diagnostic data and perform tests remotely.
- Data Sharing: Cloud-based platforms facilitate data sharing and collaboration among technicians and experts.
- Automatic Updates: Cloud-based software receives automatic updates, ensuring technicians always have the latest features and data.
10.3 Wireless Connectivity
- Bluetooth and Wi-Fi: Wireless connectivity is becoming increasingly common, allowing technicians to move freely around the vehicle while performing diagnostics.
- Mobile Devices: Mobile devices (e.g., smartphones, tablets) are being used as diagnostic tools, providing portability and convenience.
10.4 Enhanced Data Visualization
- 3D Graphics: 3D graphics are being used to visualize diagnostic data and provide a more intuitive understanding of vehicle systems.
- Augmented Reality (AR): AR is being used to overlay diagnostic data onto the vehicle, providing technicians with real-time information and guidance.
10.5 Integration with Telematics Systems
- Real-Time Monitoring: Diagnostic software is being integrated with telematics systems to provide real-time monitoring of vehicle health and performance.
- Remote Diagnostics: Telematics data is being used to perform remote diagnostics and provide proactive maintenance recommendations.
10.6 Cybersecurity
- Security Measures: Cybersecurity is becoming increasingly important as vehicles become more connected.
- Secure Communication: Diagnostic software is being designed with security measures to protect vehicle data and prevent unauthorized access.
According to a report by Gartner, the market for AI-powered diagnostic tools is expected to grow by 30% annually over the next five years.
CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN stays at the forefront of these trends, incorporating the latest technologies into its training programs to ensure technicians are well-prepared for the future of automotive diagnostics.
By understanding these trends and incorporating them into your diagnostic practices, you can improve your efficiency, accuracy, and overall effectiveness.
Ready to take your automotive diagnostic skills to the next level? Visit CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN today to explore our comprehensive training programs and unlock the full potential of car diagnostic software PC! Address: 1700 W Irving Park Rd, Chicago, IL 60613, United States. Whatsapp: +1 (641) 206-8880.
 Modern Car Diagnostic Software Interface
Modern Car Diagnostic Software Interface
FAQ: Car Diagnostic Software PC
1. What is car diagnostic software PC?
Car diagnostic software PC is a computer program used to interface with a vehicle’s onboard diagnostic (OBD) system, allowing technicians to read diagnostic trouble codes, access live data, and perform actuator tests for accurate vehicle diagnostics.
2. Why is car diagnostic software PC important?
It enhances diagnostic accuracy, improves efficiency, provides comprehensive data, ensures up-to-date information, and increases customer satisfaction by quickly and accurately identifying vehicle issues.
3. Who benefits from using car diagnostic software PC?
Automotive technicians, auto repair shops, vehicle owners, fleet managers, and automotive educators all benefit from the enhanced accuracy, efficiency, and comprehensive data provided by car diagnostic software PC.
4. How does car diagnostic software PC work?
The software connects to the vehicle’s OBD-II port, reads diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), accesses live data streams, performs actuator tests, clears trouble codes, resets systems, and logs data for analysis.
5. What are the key features to look for in car diagnostic software PC?
Key features include vehicle compatibility, diagnostic functions, user interface, data logging, connectivity, technical support, and regular updates to ensure effective and efficient diagnostics.
6. What are the different types of car diagnostic software PC?
Types include OEM software, aftermarket software, open-source software, cloud-based software, and mobile diagnostic apps, each offering different benefits and capabilities.
7. How do I choose the right car diagnostic software PC for my needs?
Assess your needs, evaluate software features, consider hardware requirements, read reviews, try demo versions, and consider training and support to select the best software for your specific requirements.
8. How do I install and set up car diagnostic software PC?
Ensure your system meets the requirements, download the software, run the installer, install drivers, configure settings, test the connection, and keep the software updated for optimal performance.
9. How do I use car diagnostic software PC effectively?
Follow pre-diagnostic steps, connect to the vehicle, read DTCs, analyze live data, perform actuator tests, clear trouble codes, verify repairs, and document results for a systematic diagnostic approach.
10. What are some common problems you can diagnose with car diagnostic software PC?
Common problems include engine issues, transmission problems, ABS and brake problems, airbag and safety system issues, electrical problems, and emissions problems, all diagnosable with car diagnostic software PC.
