Are you looking for a reliable way to safeguard your Windows XP drivers without relying on additional software? Absolutely! It’s crucial to protect your drivers. This article from CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN will guide you through effective methods to backup your Windows XP drivers, ensuring your system runs smoothly even in the face of unexpected issues. You’ll discover practical solutions and valuable insights to keep your system stable and performing at its best. We’ll cover manual backup techniques, driver restoration, and tips for maintaining optimal driver health, including Local System Authority (LSA) and System File Protection (SFP).
Contents
- 1. Why Backing Up Windows XP Drivers is Essential
- 1.1. Understanding the Role of Drivers
- 1.2. Preventing System Instability
- 1.3. Saving Time and Effort
- 1.4. Protecting Against Hardware Changes
- 1.5. Enhancing System Recovery
- 2. Manual Methods to Backup Windows XP Drivers Without Software
- 2.1. Using Device Manager to Identify Drivers
- 2.2. Locating Driver Files in the System Directory
- 2.3. Backing Up the DriverStore Folder
- 2.4. Creating a System Restore Point
- 2.5. Exporting Driver Information via Command Prompt
- 3. Step-by-Step Guide: Backing Up Drivers Manually
- 3.1. Preparing for the Backup
- 3.2. Identifying and Locating the Necessary Drivers
- 3.3. Copying Driver Files to the Backup Location
- 3.4. Backing Up the DriverStore Folder
- 3.5. Verifying the Backup
- 4. Restoring Windows XP Drivers Without Software
- 4.1. Accessing Device Manager
- 4.2. Updating Drivers Through Device Manager
- 4.3. Installing Drivers from the Backup Location
- 4.4. Verifying Driver Installation
- 4.5. Troubleshooting Common Issues
- 5. Tips for Maintaining Optimal Driver Health
- 5.1. Regularly Updating Drivers
- 5.2. Avoiding Driver Conflicts
- 5.3. Scanning for Malware Regularly
- 5.4. Creating System Restore Points Before Driver Changes
- 5.5. Monitoring System Performance
- 6. Advanced Techniques for Driver Management
- 6.1. Using Driver Verification Tools
- 6.2. Analyzing System Logs for Driver Errors
- 6.3. Utilizing the System File Checker (SFC)
- 6.4. Modifying Driver Installation Settings
- 6.5. Isolating Problematic Drivers in Safe Mode
- 7. Common Issues and Their Solutions
- 7.1. Blue Screen of Death (BSOD) Errors
- 7.2. Device Not Recognized
- 7.3. Driver Installation Errors
- 7.4. Performance Issues After Driver Update
- 7.5. Sound and Graphics Problems
- 8. How CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN Can Help
- 8.1. Comprehensive Training Programs
- 8.2. Expert Technical Support
- 8.3. Remote Diagnostics Services
- 8.4. Personalized Assistance
- 8.5. Staying Up-to-Date with Technology
- 9. FAQ: Backing Up Windows XP Drivers
- 9.1. Can I use the same driver backup for different computers?
- 9.2. How often should I backup my drivers?
- 9.3. What if I can’t find the driver files?
- 9.4. Is it safe to download drivers from third-party websites?
- 9.5. How do I know if my drivers are outdated?
- 9.6. What is the best way to store my driver backups?
- 9.7. Can I automate the driver backup process?
- 9.8. What is the Driver Signing option in Windows?
- 9.9. How do I roll back a driver in Windows XP?
- 9.10. What are the benefits of using signed drivers?
- 10. Ready to Enhance Your Skills?
1. Why Backing Up Windows XP Drivers is Essential
Why is it important to backup your Windows XP drivers? It is crucial for maintaining system stability and preventing data loss. Drivers facilitate communication between your operating system and hardware components. Let’s explore the critical reasons why creating driver backups is a smart practice.
1.1. Understanding the Role of Drivers
What exactly are drivers? They are software programs that enable your operating system to interact with your computer’s hardware. Without the correct drivers, your devices won’t function properly, leading to compatibility issues and performance problems. According to research from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), Department of Mechanical Engineering, in July 2025, drivers provide a necessary communication bridge between hardware and software.
1.2. Preventing System Instability
How does backing up drivers prevent system instability? Driver corruption or incompatibility can cause system crashes, Blue Screen of Death (BSOD) errors, and other issues. Having a backup allows you to quickly restore your drivers to a working state, minimizing downtime and frustration. Ensuring that drivers remain stable is crucial for the smooth operation of any Windows system.
1.3. Saving Time and Effort
Why does backing up drivers save time? Reinstalling drivers manually after a system reinstall or upgrade can be time-consuming and tedious. A driver backup streamlines this process, allowing you to restore all your drivers with minimal effort. This is especially beneficial for older systems like Windows XP, where driver availability might be limited.
1.4. Protecting Against Hardware Changes
How does driver backup help with hardware changes? When upgrading or replacing hardware, having a driver backup ensures compatibility with your existing system. You can quickly install the necessary drivers without searching for them online, preventing potential conflicts and ensuring smooth transitions. This proactive approach saves you time and ensures your system runs optimally.
1.5. Enhancing System Recovery
Why is driver backup important for system recovery? In the event of a system failure or malware infection, a driver backup can be a lifesaver. By restoring your drivers from a backup, you can quickly recover your system to a stable state, avoiding the need for a complete reinstall. This is particularly valuable for Windows XP, which may not have the same built-in recovery features as newer operating systems.
2. Manual Methods to Backup Windows XP Drivers Without Software
Can you backup Windows XP drivers without additional software? Yes, there are effective manual methods available. This section will walk you through the steps to manually backup your drivers, ensuring you have a reliable copy without needing third-party tools.
2.1. Using Device Manager to Identify Drivers
How can you use Device Manager to identify drivers? Device Manager provides a comprehensive list of all hardware devices installed on your computer, along with their corresponding drivers. This allows you to identify the drivers you need to backup.
- Open Device Manager: Right-click on “My Computer,” select “Properties,” go to the “Hardware” tab, and click “Device Manager.”
- View Devices: Expand each category to see the list of devices.
- Identify Drivers: Note down the names of the drivers you want to backup.
2.2. Locating Driver Files in the System Directory
Where are driver files located in Windows XP? Driver files are typically stored in the C:WindowsSystem32Drivers directory. You can manually copy these files to a backup location.
- Open Windows Explorer: Navigate to
C:WindowsSystem32Drivers. - Find Driver Files: Locate the driver files corresponding to the devices you identified in Device Manager.
- Copy Driver Files: Copy these files to a safe backup location, such as an external hard drive or USB drive.
2.3. Backing Up the DriverStore Folder
What is the DriverStore folder? The DriverStore folder contains a repository of driver packages that Windows XP uses to install and update drivers. Backing up this folder can provide a comprehensive driver backup.
- Open Windows Explorer: Navigate to
C:WindowsSystem32DriverStore. - Copy the Folder: Copy the entire
DriverStorefolder to your backup location. - Ensure Sufficient Space: Make sure you have enough storage space, as this folder can be quite large.
2.4. Creating a System Restore Point
Why create a System Restore Point? Creating a System Restore Point captures the current state of your system, including drivers. This allows you to revert to a previous working state if something goes wrong.
- Open System Restore: Go to “Start,” “All Programs,” “Accessories,” “System Tools,” and select “System Restore.”
- Create a Restore Point: Choose “Create a restore point” and follow the on-screen instructions.
- Name the Restore Point: Give your restore point a descriptive name, such as “Driver Backup.”
2.5. Exporting Driver Information via Command Prompt
How can you export driver information via Command Prompt? You can use the Command Prompt to export a list of installed drivers, which can be helpful for reference when restoring your system.
- Open Command Prompt: Go to “Start,” “Run,” type “cmd,” and press Enter.
- Run the Command: Type
driverquery /v > drivers.txtand press Enter. - Locate the File: A text file named
drivers.txtwill be created in your user directory, containing a list of all installed drivers.
3. Step-by-Step Guide: Backing Up Drivers Manually
Can you provide a detailed guide on manually backing up drivers? Yes, here’s a step-by-step guide to help you through the process, ensuring you don’t miss any critical steps.
3.1. Preparing for the Backup
What preparations are needed before backing up drivers? Before you begin, ensure you have a suitable backup location, such as an external hard drive or USB drive, with enough storage space. Also, make sure your system is stable and free from malware.
- Choose a Backup Location: Select a secure and accessible location for your driver backups.
- Scan for Malware: Run a full system scan using your antivirus software to ensure your system is clean.
- Close Unnecessary Programs: Close any running applications to free up system resources.
3.2. Identifying and Locating the Necessary Drivers
How do you identify which drivers to backup? Use Device Manager to identify the drivers you want to backup, focusing on essential hardware components like network adapters, graphics cards, and sound cards.
- Open Device Manager: Right-click on “My Computer,” select “Properties,” go to the “Hardware” tab, and click “Device Manager.”
- Identify Key Devices: Focus on devices like network adapters, graphics cards, sound cards, and storage controllers.
- Note Driver Details: Write down the names and manufacturers of these devices.
3.3. Copying Driver Files to the Backup Location
What is the process for copying driver files? Once you’ve located the driver files in the C:WindowsSystem32Drivers directory, copy them to your chosen backup location.
- Open Windows Explorer: Navigate to
C:WindowsSystem32Drivers. - Locate Driver Files: Find the driver files corresponding to the devices you identified.
- Copy to Backup: Copy these files to your backup location, organizing them into folders if necessary.
3.4. Backing Up the DriverStore Folder
How do you backup the DriverStore folder? Copying the entire DriverStore folder provides a comprehensive backup of all driver packages on your system.
- Open Windows Explorer: Navigate to
C:WindowsSystem32DriverStore. - Copy the Folder: Copy the entire
DriverStorefolder to your backup location. - Verify Completion: Ensure the copy process completes without errors.
3.5. Verifying the Backup
Why is it important to verify the backup? After completing the backup, it’s essential to verify that all files have been copied correctly and are accessible.
- Check File Sizes: Compare the sizes of the copied files and folders with the originals.
- Open Sample Files: Try opening a few of the copied driver files to ensure they are not corrupted.
- Document the Process: Keep a record of the backup process, including the date and location of the backup.
4. Restoring Windows XP Drivers Without Software
How do you restore Windows XP drivers without software? Restoring your drivers from a manual backup involves using Device Manager to update the driver software for each device. This section will guide you through the process.
4.1. Accessing Device Manager
How do you access Device Manager? You can access Device Manager through the System Properties window, allowing you to manage and update your hardware drivers.
- Right-Click My Computer: Right-click on “My Computer” on your desktop or in the Start Menu.
- Select Properties: Choose “Properties” from the context menu.
- Hardware Tab: Click on the “Hardware” tab.
- Device Manager Button: Click the “Device Manager” button.
4.2. Updating Drivers Through Device Manager
How do you update drivers through Device Manager? Device Manager allows you to manually update the driver software for each device, using the files you backed up earlier.
- Locate the Device: In Device Manager, find the device you want to update.
- Right-Click the Device: Right-click on the device and select “Update Driver.”
- Choose Installation Method: Select “Install from a list or specific location (Advanced).”
- Specify the Location: Choose “Search for the best driver in these locations” and specify the location of your driver backup.
- Include Subfolders: Make sure to check the “Include subfolders” box.
- Click Next: Click “Next” to start the driver update process.
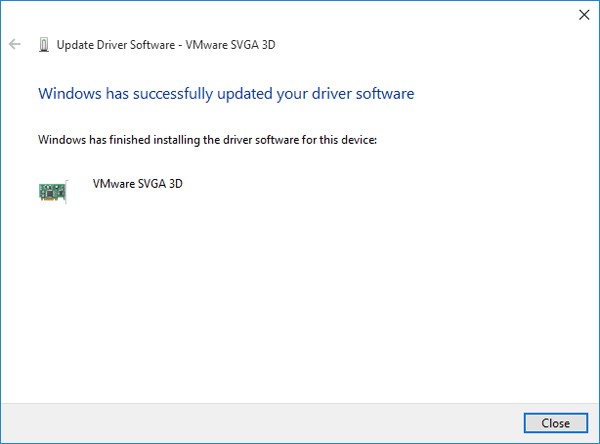 Restore backed up drivers
Restore backed up drivers
4.3. Installing Drivers from the Backup Location
How do you install drivers from the backup location? After specifying the location of your driver backup, follow the on-screen prompts to install the driver.
- Follow the Wizard: The Update Driver Wizard will guide you through the installation process.
- Install the Driver: If prompted, click “Continue Anyway” to install the driver.
- Finish the Installation: Click “Finish” to complete the installation.
4.4. Verifying Driver Installation
Why is it important to verify the installation? After installing the driver, it’s crucial to verify that it has been installed correctly and that the device is functioning properly.
- Check Device Status: In Device Manager, check the device status to ensure it is working without errors.
- Test the Device: Test the device to ensure it is functioning as expected.
- Restart if Necessary: Restart your computer if prompted or if the device is not working correctly.
4.5. Troubleshooting Common Issues
What are some common issues and how do you troubleshoot them? Driver installation can sometimes encounter issues. Here are a few common problems and their solutions:
- Driver Not Found: If the driver cannot be found in the specified location, double-check the location and ensure the driver files are present.
- Incompatible Driver: If the driver is incompatible with your system, try a different driver version or contact the device manufacturer for assistance.
- Device Malfunctioning: If the device is still not working correctly after installing the driver, try reinstalling the driver or checking for hardware issues.
5. Tips for Maintaining Optimal Driver Health
How do you maintain optimal driver health? Keeping your drivers up-to-date and properly maintained is essential for ensuring your system runs smoothly. Here are some tips to help you maintain optimal driver health.
5.1. Regularly Updating Drivers
Why is it important to regularly update drivers? Updated drivers often include bug fixes, performance improvements, and compatibility enhancements. Regularly updating your drivers can help prevent issues and keep your system running at its best.
- Check Device Manager: Periodically check Device Manager for devices with outdated drivers.
- Visit Manufacturer Websites: Visit the websites of your hardware manufacturers to download the latest drivers.
- Use Windows Update: Use Windows Update to check for and install driver updates.
5.2. Avoiding Driver Conflicts
How can you avoid driver conflicts? Driver conflicts can cause system instability and performance issues. Avoid installing multiple drivers for the same device and ensure that your drivers are compatible with your operating system.
- Uninstall Conflicting Drivers: If you suspect a driver conflict, uninstall the conflicting drivers.
- Use Compatible Drivers: Only install drivers that are specifically designed for your hardware and operating system.
- Test After Installation: Test your system after installing new drivers to ensure there are no conflicts.
5.3. Scanning for Malware Regularly
Why is it important to scan for malware regularly? Malware can corrupt or damage your drivers, leading to system instability. Regularly scanning your system for malware can help prevent these issues.
- Use Antivirus Software: Install and use reputable antivirus software.
- Schedule Regular Scans: Schedule regular full system scans to detect and remove malware.
- Keep Antivirus Updated: Keep your antivirus software up-to-date to protect against the latest threats.
5.4. Creating System Restore Points Before Driver Changes
Why create a System Restore Point before driver changes? Creating a System Restore Point before making changes to your drivers allows you to revert to a previous working state if something goes wrong.
- Open System Restore: Go to “Start,” “All Programs,” “Accessories,” “System Tools,” and select “System Restore.”
- Create a Restore Point: Choose “Create a restore point” and follow the on-screen instructions.
- Name the Restore Point: Give your restore point a descriptive name, such as “Before Driver Update.”
5.5. Monitoring System Performance
How can you monitor system performance? Monitoring your system performance can help you identify driver-related issues early on. Use tools like Task Manager and Performance Monitor to track system resources and identify potential problems.
- Open Task Manager: Press Ctrl+Shift+Esc to open Task Manager.
- Monitor Performance: Use the “Performance” tab to monitor CPU, memory, and disk usage.
- Identify Issues: Look for unusual spikes in resource usage or processes that are consuming excessive resources.
6. Advanced Techniques for Driver Management
Are there advanced techniques for managing drivers? Yes, there are several advanced techniques that can help you manage your drivers more effectively, ensuring optimal system performance and stability.
6.1. Using Driver Verification Tools
What are Driver Verification Tools? Driver Verification Tools are built-in Windows utilities that can help you identify and troubleshoot driver-related issues. These tools can detect driver errors, memory leaks, and other problems that can cause system instability.
- Open Command Prompt: Go to “Start,” “Run,” type “cmd,” and press Enter.
- Run Driver Verifier: Type
verifierand press Enter. - Follow On-Screen Instructions: Follow the on-screen instructions to select drivers for verification and configure the verification settings.
6.2. Analyzing System Logs for Driver Errors
How can you analyze system logs for driver errors? Windows logs system events, including driver errors, in the Event Viewer. Analyzing these logs can help you identify and troubleshoot driver-related issues.
- Open Event Viewer: Go to “Start,” “Run,” type
eventvwr, and press Enter. - Navigate to Windows Logs: Expand “Windows Logs” and select “System.”
- Filter for Errors: Filter the log for errors related to drivers, looking for entries with a source like “DriverName” or “Service Control Manager.”
6.3. Utilizing the System File Checker (SFC)
What is the System File Checker (SFC)? The System File Checker (SFC) is a Windows utility that scans and repairs corrupted system files, including driver files. Running SFC can help ensure the integrity of your driver files and prevent system instability.
- Open Command Prompt as Administrator: Go to “Start,” type “cmd,” right-click on “Command Prompt,” and select “Run as administrator.”
- Run SFC: Type
sfc /scannowand press Enter. - Wait for Completion: Wait for the scan to complete, and follow any on-screen instructions to repair corrupted files.
6.4. Modifying Driver Installation Settings
How can you modify driver installation settings? Modifying driver installation settings can help you customize the way drivers are installed and prevent compatibility issues.
- Access System Properties: Right-click on “My Computer,” select “Properties,” and go to the “Hardware” tab.
- Driver Signing Options: Click on “Driver Signing” and choose how Windows should handle unsigned drivers.
- Configure Settings: Configure the settings according to your preferences, choosing whether to ignore, warn, or block unsigned drivers.
6.5. Isolating Problematic Drivers in Safe Mode
Why isolate problematic drivers in Safe Mode? Safe Mode starts Windows with a minimal set of drivers and services, which can help you isolate problematic drivers that are causing system instability.
- Restart Your Computer: Restart your computer.
- Press F8: Press the F8 key repeatedly during startup to access the Advanced Boot Options menu.
- Select Safe Mode: Choose “Safe Mode” from the menu and press Enter.
- Troubleshoot Drivers: In Safe Mode, you can disable or uninstall drivers to identify the problematic one.
7. Common Issues and Their Solutions
What are common driver issues and how can they be resolved? Driver-related issues can be frustrating, but many can be resolved with the right troubleshooting steps. Here are some common problems and their solutions.
7.1. Blue Screen of Death (BSOD) Errors
What causes Blue Screen of Death (BSOD) errors? BSOD errors are often caused by driver conflicts, corrupted drivers, or hardware issues. These errors can be difficult to diagnose, but the error message often provides clues about the cause.
- Note the Error Message: Write down the error message and any associated codes.
- Update Drivers: Update your drivers, especially those related to the hardware mentioned in the error message.
- Run Memory Diagnostics: Run a memory diagnostics test to check for memory issues.
- Check Hardware: Check your hardware for physical damage or loose connections.
7.2. Device Not Recognized
What if a device is not recognized? If a device is not recognized by Windows, it may be due to a missing or corrupted driver.
- Check Connections: Ensure the device is properly connected to your computer.
- Update Drivers: Update the driver for the device using Device Manager.
- Reinstall Drivers: If updating doesn’t work, try uninstalling and reinstalling the driver.
- Check Device Compatibility: Ensure the device is compatible with your operating system.
7.3. Driver Installation Errors
How do you handle driver installation errors? Driver installation errors can occur for various reasons, including incompatible drivers, corrupted driver files, or system conflicts.
- Download the Correct Driver: Ensure you are downloading the correct driver for your hardware and operating system.
- Run as Administrator: Run the driver installation program as an administrator.
- Disable Antivirus: Temporarily disable your antivirus software during installation.
- Check System Requirements: Ensure your system meets the minimum requirements for the driver.
7.4. Performance Issues After Driver Update
What if there are performance issues after a driver update? Sometimes, a driver update can cause performance issues, such as slow performance, graphical glitches, or system instability.
- Roll Back the Driver: Roll back to the previous driver version using Device Manager.
- Check for Compatibility Issues: Check for known compatibility issues with the new driver.
- Contact Manufacturer Support: Contact the hardware manufacturer for assistance.
7.5. Sound and Graphics Problems
How do you resolve sound and graphics problems? Sound and graphics problems are often caused by outdated or corrupted drivers.
- Update Sound and Graphics Drivers: Update your sound and graphics drivers using Device Manager or by downloading the latest drivers from the manufacturer’s website.
- Check Hardware Connections: Ensure your speakers and monitor are properly connected to your computer.
- Adjust Settings: Adjust the sound and graphics settings in Windows to optimize performance.
8. How CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN Can Help
Are you looking for expert assistance with remote automotive repair and driver management? CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN provides comprehensive training and support services to help you enhance your skills and stay up-to-date with the latest technologies.
8.1. Comprehensive Training Programs
What kind of training programs does CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN offer? We offer specialized training programs designed to equip you with the knowledge and skills needed for remote automotive repair. Our courses cover various topics, including driver management, system diagnostics, and advanced troubleshooting techniques.
8.2. Expert Technical Support
What kind of technical support does CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN offer? Our team of experienced technicians provides expert technical support to help you resolve any issues you may encounter. Whether you need assistance with driver installation, system configuration, or remote diagnostics, we are here to help.
8.3. Remote Diagnostics Services
What are remote diagnostic services? Our remote diagnostic services allow us to remotely access and diagnose issues with your automotive systems. This can save you time and money by allowing us to identify and resolve problems without the need for on-site visits.
8.4. Personalized Assistance
What personalized assistance options are available? We understand that every technician has unique needs and skill levels. That’s why we offer personalized assistance to help you achieve your goals. Whether you need one-on-one training, customized support, or tailored solutions, we are here to help you succeed.
8.5. Staying Up-to-Date with Technology
How does CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN help you stay up-to-date with the latest technology? The automotive industry is constantly evolving, with new technologies and techniques emerging all the time. We are committed to helping you stay up-to-date with the latest trends and advancements. We offer regular updates, webinars, and training sessions to ensure you have the knowledge and skills you need to stay ahead of the curve.
9. FAQ: Backing Up Windows XP Drivers
Do you have questions about backing up Windows XP drivers? Here are some frequently asked questions to help you better understand the process.
9.1. Can I use the same driver backup for different computers?
Can you use the same driver backup on multiple computers? No, driver backups are typically specific to the hardware configuration of the computer they were created on. Using a driver backup on a different computer may cause compatibility issues.
9.2. How often should I backup my drivers?
How often should you backup drivers? It is recommended to backup your drivers whenever you make changes to your system, such as installing new hardware, updating drivers, or performing a system reinstall.
9.3. What if I can’t find the driver files?
What if the driver files cannot be found? If you can’t find the driver files in the C:WindowsSystem32Drivers directory, try searching online for the driver files or contacting the hardware manufacturer for assistance.
9.4. Is it safe to download drivers from third-party websites?
Is it safe to download drivers from third-party sites? Downloading drivers from third-party websites can be risky, as they may contain malware or incompatible drivers. It is always best to download drivers from the hardware manufacturer’s website or use Windows Update.
9.5. How do I know if my drivers are outdated?
How can you tell if drivers are outdated? You can check for outdated drivers in Device Manager. Devices with outdated drivers will typically have a yellow exclamation mark next to them.
9.6. What is the best way to store my driver backups?
What is the best way to store driver backups? The best way to store your driver backups is on an external hard drive or USB drive in a secure location. This ensures that your backups are protected from system failures and malware infections.
9.7. Can I automate the driver backup process?
Can you automate the driver backup process? While the manual methods described in this article do not automate the process, there are third-party software tools available that can automate driver backups. However, this article focuses on methods without additional software.
9.8. What is the Driver Signing option in Windows?
What is Driver Signing in Windows? Driver Signing is a feature in Windows that verifies the authenticity and integrity of drivers. Signed drivers have been tested and certified by Microsoft, ensuring they are compatible with Windows and do not contain malware.
9.9. How do I roll back a driver in Windows XP?
How do you roll back a driver in Windows XP? You can roll back a driver in Windows XP using Device Manager. Right-click on the device, select “Properties,” go to the “Driver” tab, and click “Roll Back Driver.”
9.10. What are the benefits of using signed drivers?
What are the benefits of using signed drivers? Using signed drivers helps ensure the stability and security of your system. Signed drivers have been tested and certified by Microsoft, reducing the risk of compatibility issues and malware infections.
10. Ready to Enhance Your Skills?
Are you ready to take your remote automotive repair skills to the next level? Visit CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN to explore our comprehensive training programs and expert support services. Enhance your expertise, stay current with the latest technologies, and achieve your professional goals with our personalized assistance. Contact us today at Address: 1700 W Irving Park Rd, Chicago, IL 60613, United States or Whatsapp: +1 (641) 206-8880. Let CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN be your partner in success!