Want to enhance your skills in automotive repair and learn about remote repair services in the USA? Blocking software using Windows 7 Firewall is a fundamental skill for maintaining network security, and CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN can help you master it! Discover how to protect your systems effectively with our comprehensive training and support, focusing on critical security practices. Explore our hands-on workshops and expert guidance to keep your network safe.
Contents
- 1. Understanding the Basics of Windows Firewall
- 2. Step-by-Step Guide to Blocking Software with Windows 7 Firewall
- 2.1. Enabling Windows Firewall Service
- 2.2. Opening Advanced Firewall Settings
- 2.3. Creating a New Inbound Rule
- 2.4. Specifying the Program Path
- 2.5. Choosing the Action: Block the Connection
- 2.6. Selecting Network Profiles
- 2.7. Naming and Describing the Rule
- 2.8. Creating a New Outbound Rule
- 3. Advanced Firewall Techniques
- 4. Troubleshooting Common Firewall Issues
- 5. Keeping Your Firewall Up-to-Date
- 6. The Role of Firewalls in Automotive Repair Cybersecurity
- 7. Alternative Firewall Solutions for Enhanced Security
- 8. Best Practices for Firewall Management
- 9. The Future of Automotive Cybersecurity and Firewalls
- 10. Getting Started with Automotive Repair Training at CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN
- FAQ: Blocking Software Using Windows 7 Firewall
1. Understanding the Basics of Windows Firewall
What is Windows Firewall and why is it important?
Windows Firewall is a built-in security system in Windows operating systems designed to monitor and control network traffic, preventing unauthorized access to your computer. According to Microsoft, enabling your firewall helps protect your computer by blocking potentially malicious traffic. It acts as a barrier between your computer and the outside world, examining incoming and outgoing network traffic and blocking anything that doesn’t meet its defined security rules.
Why should automotive technicians care about firewalls?
In the modern automotive industry, vehicles are increasingly connected to networks for diagnostics, software updates, and remote services. Technicians need to ensure that these connections are secure to prevent unauthorized access or malicious attacks that could compromise vehicle systems or customer data. Firewalls provide a critical layer of defense against such threats. CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN emphasizes the importance of cybersecurity in automotive repair, providing training to help technicians protect their systems and customer data.
What are the benefits of using Windows Firewall?
- Protection against unauthorized access: Windows Firewall blocks unauthorized attempts to access your computer, preventing hackers and malicious software from gaining control.
- Control over network traffic: You can define rules to control which programs are allowed to send and receive data over the network, reducing the risk of malware infections.
- Improved system performance: By blocking unnecessary network traffic, Windows Firewall can help improve your computer’s performance and prevent it from being slowed down by malicious activity.
- Ease of use: Windows Firewall is easy to configure and manage, making it accessible to users with varying levels of technical expertise.
How does Windows Firewall work?
Windows Firewall operates by inspecting network packets as they attempt to enter or leave your computer. Each packet is compared against a set of rules defined in the firewall’s configuration. If a packet matches a rule, the firewall takes the action specified in the rule, such as allowing or blocking the connection. This process helps prevent unauthorized access and malicious activity from affecting your system. The firewall uses protocols and port numbers to analyze network traffic, allowing specific types of communication while blocking others.
 Windows Firewall settings
Windows Firewall settings
2. Step-by-Step Guide to Blocking Software with Windows 7 Firewall
How do I access Windows Firewall settings in Windows 7?
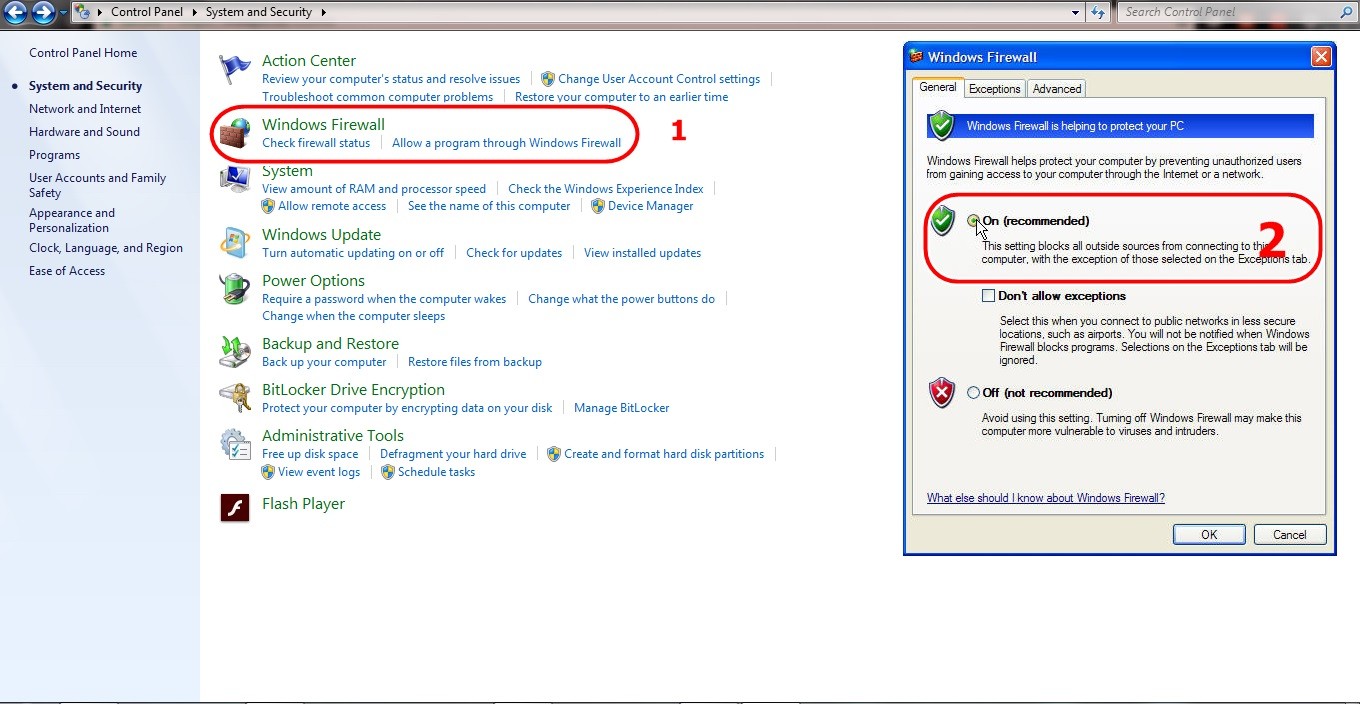
To access Windows Firewall settings in Windows 7, click the Start button, then go to Control Panel. Select “System and Security,” and then click on “Windows Firewall.” From here, you can view the current firewall status, change settings, and configure advanced options. According to Microsoft’s support documentation, the Windows Firewall control panel allows you to customize your firewall settings to suit your specific needs.
What are inbound and outbound rules in Windows Firewall?
Inbound rules control incoming network traffic, while outbound rules control outgoing traffic. To effectively block software, you typically need to create both inbound and outbound rules. Inbound rules prevent unauthorized connections to the software on your computer, while outbound rules prevent the software from sending data to external servers. Understanding the difference between inbound and outbound rules is crucial for maintaining network security, as emphasized in CompTIA Security+ certification training.
2.1. Enabling Windows Firewall Service
How do I ensure the Windows Firewall service is running?
First, make sure the Windows Firewall service is active. Go to Control Panel – System and Security – Windows Firewall. Ensure that you have selected On (recommended) to activate Windows Firewall.
Why is it important to ensure the Windows Firewall service is running?
If the Windows Firewall service is not running, your computer is vulnerable to unauthorized access and malicious attacks. The firewall acts as a gatekeeper, monitoring network traffic and blocking anything that doesn’t meet its defined security rules. Without the firewall running, your computer is essentially defenseless against external threats. According to the SANS Institute, a properly configured and running firewall is a critical component of any network security strategy.
What steps can I take to troubleshoot if the Windows Firewall service is not running?
- Check the Services Panel: Press
Windows Key + R, typeservices.msc, and press Enter. Locate the “Windows Firewall” service in the list. - Start the Service: If the service is stopped, right-click on it and select “Start.”
- Set Startup Type: Right-click on the service, select “Properties,” and ensure the “Startup type” is set to “Automatic.” This ensures the service starts automatically when Windows starts.
- Check Dependencies: In the service properties, check the “Dependencies” tab to see if any other services are required for Windows Firewall to run. Ensure those services are also running.
- Run System File Checker: Open Command Prompt as an administrator and run
sfc /scannowto check for and repair any corrupted system files that may be preventing the service from running.
2.2. Opening Advanced Firewall Settings
How do I open the “Windows Firewall with Advanced Security” panel?
Go to Control Panel – System and Security – Windows Firewall – Advanced Settings. A security window will appear, allowing you to configure firewall rules. This panel provides granular control over network traffic, allowing you to create custom rules to allow or block specific programs and services. According to NIST’s guidelines on firewall security, advanced settings provide the flexibility needed to protect complex network environments.
What options are available in the Advanced Security panel?
- Inbound Rules: Define rules for incoming network connections to your computer.
- Outbound Rules: Define rules for outgoing network connections from your computer.
- Connection Security Rules: Configure secure communication channels between computers using IPsec.
- Monitoring: View firewall activity and statistics, including blocked connections and active rules.
- Customization: Configure advanced settings such as logging, default behaviors, and IPsec settings.
2.3. Creating a New Inbound Rule
How do I create a new inbound rule to block a program?
In the “Windows Firewall with Advanced Security” window, select “Inbound Rules” on the left panel. Then, choose “New Rule…” from the “Action” menu on the right panel. This will open the “New Inbound Rule Wizard,” which guides you through the process of creating a new firewall rule. Creating a new rule allows you to specify the program, ports, and protocols to block, providing precise control over network traffic.
What options do I have when creating a new inbound rule?
- Rule Type: Choose whether to create a rule for a specific program, port, predefined service, or custom configuration.
- Program: Specify the exact program you want to block by browsing to its executable file.
- Protocol and Ports: Define the specific protocols (e.g., TCP, UDP) and ports to block for the selected program.
- Action: Choose whether to allow or block the connection.
- Profile: Select the network profiles (Domain, Private, Public) to which the rule applies.
- Name: Give the rule a descriptive name and add an optional description for future reference.
2.4. Specifying the Program Path
How do I specify the program path for the inbound rule?
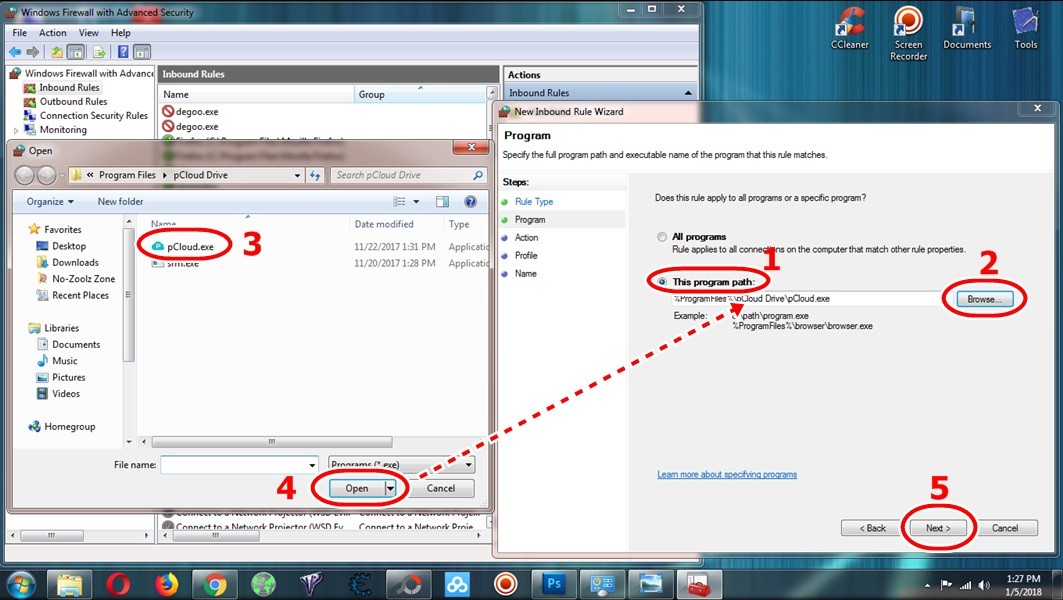
In the “New Inbound Rule Wizard,” select “Program” and click “Next.” Then, choose “This program path:” and browse to the location of the software you want to block. The standard installation path for Windows programs is typically “C:/Program Files.” Select the program’s executable file and click “Open,” then “Next.” Specifying the exact program path ensures that the firewall rule only affects the intended software.
What should I do if I can’t find the program in the default “Program Files” folder?
If you can’t find the program in the default “Program Files” folder, it may be installed in a different location. Check the following:
- Program’s Shortcut: Right-click on the program’s shortcut on your desktop or in the Start Menu and select “Properties.” The “Target” field will show the program’s installation path.
- Program’s Installation Folder: If you know the program’s name, search for it in File Explorer to locate its installation folder.
- Custom Installation: During installation, the program may have been installed in a custom location. Check your installation records or contact the software vendor for assistance.
 Specifying the program path
Specifying the program path
2.5. Choosing the Action: Block the Connection
How do I block the connection for the specified program?
After specifying the program path, you will be presented with options to allow or block the connection. Select “Block the connection” to prevent the program from sending or receiving data over the network. Blocking the connection effectively disables the program’s ability to communicate with external servers, protecting your system from potential threats. According to cybersecurity experts at Carnegie Mellon University, blocking unnecessary network connections is a key strategy for reducing your attack surface.
What are the implications of blocking a program’s connection?
Blocking a program’s connection can have various implications, depending on the software’s functionality:
- Limited Functionality: The program may not be able to access online features, such as updates, cloud storage, or online multiplayer modes.
- Error Messages: The program may display error messages indicating that it cannot connect to the internet or a specific server.
- Program Instability: In some cases, blocking a program’s connection can cause it to become unstable or crash.
- Security Enhancement: Blocking malicious or unnecessary connections can enhance your system’s security and prevent unauthorized data transfer.
2.6. Selecting Network Profiles
Which network profiles should I select for the rule to apply to?
Select all available options: “Domain,” “Private,” and “Public.” This ensures that the rule applies regardless of the network you are connected to. Applying the rule to all network profiles provides comprehensive protection, whether you are connected to a home network, a public Wi-Fi hotspot, or a corporate domain. According to network security best practices, consistent security policies should be applied across all network environments.
What are the differences between Domain, Private, and Public network profiles?
- Domain: Typically used in corporate environments where computers are part of a domain network managed by a central server. Domain networks often have strict security policies and authentication requirements.
- Private: Used for home or small business networks where you trust the devices and users connected to the network. Private networks usually have less restrictive security settings compared to domain networks.
- Public: Used for public Wi-Fi hotspots in coffee shops, airports, or other public places where you do not trust the devices and users connected to the network. Public networks require the most restrictive security settings to protect your data from potential threats.
2.7. Naming and Describing the Rule
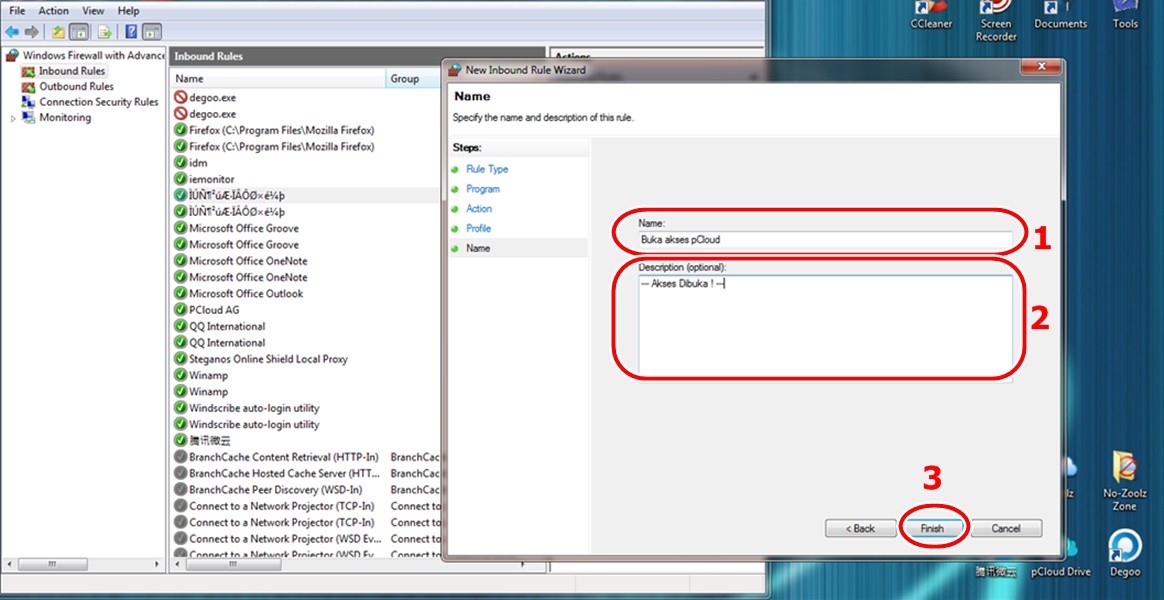
How do I name and describe the rule?
Create a name and description for the rule. The name and description can be arbitrary, but it’s best to provide something descriptive so you can easily identify the rule later. After naming the rule, click “Finish.” Providing a clear and descriptive name and description helps you manage and maintain your firewall rules effectively. According to IT governance guidelines, proper documentation is essential for managing complex security configurations.
What are some best practices for naming and describing firewall rules?
- Descriptive Name: Use a name that clearly identifies the program or service being blocked, such as “Block [Program Name] Inbound.”
- Detailed Description: Provide a brief explanation of the rule’s purpose, such as “Blocks inbound connections for [Program Name] to prevent unauthorized access.”
- Consistent Naming Convention: Use a consistent naming convention for all your firewall rules to make them easier to manage and understand.
- Date of Creation: Include the date the rule was created or last modified in the description to track changes over time.
 Naming the firewall rule
Naming the firewall rule
2.8. Creating a New Outbound Rule
Do I need to create an outbound rule as well?
Yes, for comprehensive protection, create an outbound rule for the same program by repeating steps 5-9. This prevents the program from sending data to external servers. Creating both inbound and outbound rules ensures that the program cannot communicate over the network in either direction. According to the Center for Internet Security (CIS), a layered security approach is essential for protecting against cyber threats.
What are the key differences between creating inbound and outbound rules?
- Direction of Traffic: Inbound rules control incoming network traffic, while outbound rules control outgoing network traffic.
- Purpose: Inbound rules prevent unauthorized connections to your computer, while outbound rules prevent programs from sending data to external servers without your permission.
- Configuration: The steps for creating inbound and outbound rules are similar, but you need to select the appropriate options based on the direction of traffic you want to control.
3. Advanced Firewall Techniques
How can I block specific ports or protocols using Windows Firewall?
In the “New Inbound Rule Wizard,” select “Port” instead of “Program.” Then, specify the protocol (TCP or UDP) and the port numbers you want to block. This allows you to block specific types of network traffic, regardless of the program sending or receiving it. Blocking specific ports and protocols can be useful for preventing certain types of attacks or for restricting access to specific services. According to the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF), understanding network protocols and ports is essential for effective network security.
What are some common ports that should be blocked for security reasons?
- Port 21: FTP (File Transfer Protocol) – Often used for unencrypted file transfers, making it vulnerable to eavesdropping.
- Port 23: Telnet – Provides unencrypted command-line access to remote servers, posing a significant security risk.
- Port 25: SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) – Used for sending email, but can be exploited by spammers and malware distributors.
- Port 135: RPC (Remote Procedure Call) – Used by Windows for inter-process communication, but can be exploited by attackers to gain control of your system.
- Port 445: SMB (Server Message Block) – Used for file sharing and printer sharing on Windows networks, but can be exploited by malware to spread across the network.
How can I create a custom rule to block all traffic from a specific IP address?
In the “New Inbound Rule Wizard,” select “Custom” and click “Next.” Then, specify the IP address you want to block in the “Scope” settings. This allows you to block all network traffic from a specific source, regardless of the program or port being used. Blocking traffic from known malicious IP addresses is a proactive measure to protect your system from potential attacks. According to the FBI’s Internet Crime Complaint Center (IC3), blocking known malicious IP addresses can significantly reduce your risk of becoming a victim of cybercrime.
4. Troubleshooting Common Firewall Issues
What should I do if blocking a program causes unexpected issues?
If blocking a program causes unexpected issues, you can temporarily disable the firewall rule to see if it resolves the problem. If disabling the rule fixes the issue, you may need to adjust the rule’s settings to allow specific types of traffic required by the program. Troubleshooting firewall issues often involves trial and error, as well as careful analysis of network traffic and program behavior. According to Microsoft’s support forums, many firewall issues can be resolved by adjusting rule settings or creating exceptions for specific programs or services.
What are some common causes of firewall-related issues?
- Incorrect Rule Settings: Incorrectly configured firewall rules can block legitimate traffic, causing programs to malfunction.
- Conflicting Rules: Conflicting firewall rules can cause unexpected behavior, as the firewall may not know which rule to apply.
- Software Updates: Software updates can sometimes change the way a program interacts with the network, requiring adjustments to firewall rules.
- Malware Infections: Malware can sometimes modify firewall settings to allow unauthorized access to your system.
How can I diagnose firewall issues using the Windows Firewall log?
The Windows Firewall log records all firewall activity, including blocked and allowed connections. You can use the log to diagnose firewall issues by examining the entries related to the program or service that is experiencing problems. The log can provide valuable information about the source and destination of blocked traffic, as well as the firewall rules that are being applied. According to the National Security Agency (NSA), analyzing firewall logs is an essential step in identifying and responding to security incidents.
To enable and view the Windows Firewall log:
- Enable Logging: Open “Windows Firewall with Advanced Security,” right-click on “Windows Firewall with Advanced Security” in the left pane, and select “Properties.”
- Logging Settings: In the “Properties” window, go to the “General” tab and click “Customize” under “Logging.” Specify the file path, size limit, and other logging settings.
- View the Log: The firewall log is stored in the specified file path and can be viewed using a text editor or a log analysis tool.
5. Keeping Your Firewall Up-to-Date
Why is it important to keep my Windows Firewall up-to-date?
Keeping your Windows Firewall up-to-date ensures that you have the latest security patches and protection against emerging threats. Microsoft regularly releases updates to Windows Firewall to address newly discovered vulnerabilities and improve its effectiveness. Failing to keep your firewall up-to-date can leave your system vulnerable to attack. According to the U.S. Department of Homeland Security, keeping your software up-to-date is one of the most important steps you can take to protect your computer from cyber threats.
How can I ensure that my Windows Firewall is always up-to-date?
Windows Firewall updates are typically included in Windows Update, so make sure that you have automatic updates enabled. This ensures that your firewall is always running the latest version and has the most up-to-date protection against emerging threats. Enabling automatic updates is a simple but effective way to maintain your system’s security. According to the SANS Institute, automatic updates are a critical component of any patch management strategy.
What are the potential risks of not updating my Windows Firewall?
- Vulnerability to Exploits: Outdated firewalls may have known vulnerabilities that attackers can exploit to gain unauthorized access to your system.
- Lack of Protection: Outdated firewalls may not be able to protect against the latest threats, as they may not have the necessary signatures or detection mechanisms.
- Compliance Issues: In some industries, failing to keep your firewall up-to-date may result in non-compliance with regulatory requirements.
6. The Role of Firewalls in Automotive Repair Cybersecurity
How can firewalls protect automotive repair shops from cyber threats?
Firewalls can protect automotive repair shops from cyber threats by preventing unauthorized access to their networks and systems. This can help prevent data breaches, malware infections, and other cyberattacks that could disrupt operations and compromise customer data. In the automotive industry, cybersecurity is becoming increasingly important as vehicles become more connected and reliant on software. According to a report by IBM, the automotive industry is one of the most targeted sectors for cyberattacks.
What types of cyber threats are automotive repair shops vulnerable to?
- Data Breaches: Cybercriminals may attempt to steal customer data, such as credit card numbers, addresses, and vehicle information.
- Malware Infections: Malware, such as ransomware, can encrypt critical data and systems, preventing technicians from accessing them.
- Remote Access Attacks: Attackers may attempt to gain remote access to vehicle systems, allowing them to control or manipulate vehicle functions.
- Denial-of-Service Attacks: Attackers may flood the repair shop’s network with traffic, preventing technicians from accessing online resources and tools.
How can CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN help automotive technicians improve their cybersecurity skills?
CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN offers specialized training courses on automotive cybersecurity, teaching technicians how to protect their systems and customer data from cyber threats. Our courses cover topics such as firewall configuration, network security, malware prevention, and incident response. By completing our training, technicians can gain the skills and knowledge they need to defend against cyberattacks and maintain a secure automotive repair environment. Contact us at Address: 1700 W Irving Park Rd, Chicago, IL 60613, United States. Whatsapp: +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit our website at CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN.
7. Alternative Firewall Solutions for Enhanced Security
Are there alternatives to Windows Firewall that offer enhanced security features?
Yes, several third-party firewall solutions offer enhanced security features compared to Windows Firewall. These solutions often include advanced features such as intrusion detection, application control, and cloud-based threat intelligence. While Windows Firewall provides a basic level of protection, third-party firewalls offer more comprehensive security for users with higher security needs. According to a study by AV-Comparatives, third-party firewalls often provide better protection against malware and other threats than built-in firewalls.
What are some popular third-party firewall solutions?
- Comodo Firewall: A free firewall solution that offers advanced features such as application control, virtual desktop, and cloud-based whitelisting.
- ZoneAlarm Free Firewall: A popular firewall solution that provides robust protection against inbound and outbound threats, as well as identity theft protection.
- GlassWire: A user-friendly firewall solution that visualizes network activity, allowing you to easily identify and block suspicious connections.
- Norton Smart Firewall: A paid firewall solution that offers advanced features such as intrusion prevention, exploit blocking, and botnet protection.
What factors should I consider when choosing a firewall solution?
- Security Features: Consider the types of threats the firewall protects against and the advanced features it offers, such as intrusion detection and application control.
- Ease of Use: Choose a firewall solution that is easy to configure and manage, even for users with limited technical expertise.
- Performance: Ensure that the firewall does not significantly impact your system’s performance, as some firewalls can consume a lot of resources.
- Cost: Consider the cost of the firewall solution, as some firewalls are free while others require a paid subscription.
8. Best Practices for Firewall Management
How often should I review and update my firewall rules?
You should review and update your firewall rules regularly, at least every six months, to ensure that they are still effective and relevant. As your software and network environment change, you may need to adjust your firewall rules to maintain optimal security. Regularly reviewing and updating your firewall rules is a proactive way to protect your system from emerging threats. According to the SANS Institute, regular security assessments are essential for maintaining a strong security posture.
What are some best practices for managing firewall rules?
- Document Your Rules: Keep a record of all your firewall rules, including their purpose, the programs and ports they affect, and the date they were created or last modified.
- Use Descriptive Names: Use descriptive names for your firewall rules so you can easily identify them later.
- Test Your Rules: After creating or modifying a firewall rule, test it to ensure that it is working as expected.
- Remove Unnecessary Rules: Remove any firewall rules that are no longer needed, as they can create unnecessary complexity and potential security risks.
How can I use group policy to manage firewalls on multiple computers?
Group policy allows you to centrally manage firewall settings on multiple computers in a domain environment. This can help ensure that all computers have the same firewall configuration and are protected against cyber threats. Using group policy to manage firewalls is a best practice for organizations with a large number of computers. According to Microsoft’s documentation, group policy provides a powerful and efficient way to manage security settings across an entire network.
To use group policy to manage firewalls:
- Open Group Policy Management Console: Open the Group Policy Management Console (GPMC) on a domain controller.
- Create or Edit a GPO: Create a new Group Policy Object (GPO) or edit an existing GPO that applies to the computers you want to manage.
- Firewall Settings: In the GPO, navigate to “Computer Configuration” -> “Policies” -> “Windows Settings” -> “Security Settings” -> “Windows Firewall with Advanced Security.”
- Configure Firewall Rules: Configure the firewall rules you want to apply to the computers, such as inbound and outbound rules, connection security rules, and logging settings.
- Apply the GPO: Link the GPO to the appropriate organizational unit (OU) containing the computers you want to manage.
9. The Future of Automotive Cybersecurity and Firewalls
How will automotive cybersecurity evolve in the future?
Automotive cybersecurity will continue to evolve as vehicles become more connected and autonomous. Future vehicles will require more sophisticated security measures to protect against a wider range of cyber threats. This will include advanced firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and other security technologies. According to a report by McKinsey & Company, cybersecurity will be a key differentiator for automotive manufacturers in the future.
What role will firewalls play in the future of automotive cybersecurity?
Firewalls will continue to play a critical role in the future of automotive cybersecurity by preventing unauthorized access to vehicle systems. Future firewalls will need to be more intelligent and adaptive, capable of detecting and blocking new and emerging threats in real time. They will also need to be integrated with other security systems, such as intrusion detection and prevention systems, to provide a comprehensive defense against cyberattacks. According to a report by the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA), firewalls are an essential component of a layered security approach for protecting vehicle systems.
What are some emerging trends in firewall technology?
- Next-Generation Firewalls (NGFWs): NGFWs offer advanced features such as intrusion detection, application control, and cloud-based threat intelligence.
- Software-Defined Firewalls (SDFWs): SDFWs are virtualized firewalls that can be deployed in cloud environments and managed centrally.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) Firewalls: AI firewalls use machine learning algorithms to detect and block new and emerging threats in real time.
10. Getting Started with Automotive Repair Training at CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN
Why should I choose CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN for automotive repair training?
CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN offers comprehensive training programs designed to equip automotive technicians with the skills and knowledge they need to succeed in today’s rapidly evolving industry. Our courses cover a wide range of topics, including firewall configuration, network security, malware prevention, and incident response. By completing our training, technicians can gain the skills and knowledge they need to defend against cyberattacks and maintain a secure automotive repair environment. Our programs are designed to meet the specific needs of the automotive industry, providing technicians with the most relevant and up-to-date training available.
What types of training programs does CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN offer?
We offer a variety of training programs to suit different skill levels and career goals, including:
- Basic Automotive Repair: Covers the fundamentals of automotive repair, including engine repair, brakes, suspension, and electrical systems.
- Advanced Diagnostics: Focuses on advanced diagnostic techniques, including the use of scan tools, oscilloscopes, and other diagnostic equipment.
- Automotive Cybersecurity: Teaches technicians how to protect their systems and customer data from cyber threats.
- Remote Repair Services: Provides training on how to perform remote diagnostics and repairs using the latest technology and tools.
How can I enroll in a training program at CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN?
Enrolling in a training program at CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN is easy. Simply visit our website at CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN or contact us at Address: 1700 W Irving Park Rd, Chicago, IL 60613, United States. Whatsapp: +1 (641) 206-8880 to speak with one of our training advisors. We can help you choose the right program for your needs and guide you through the enrollment process.
Ready to take your automotive repair skills to the next level? Visit CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN today to explore our training programs and discover how we can help you achieve your career goals. Protect your systems and customer data with our specialized training in automotive cybersecurity. Contact us now and start your journey towards becoming a certified automotive cybersecurity expert. Boost your skills and safeguard your future with CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN! Learn more about automotive diagnostics, repair techniques, and network protection.
FAQ: Blocking Software Using Windows 7 Firewall
-
Q1: What is a firewall and why is it important for my computer?
A1: A firewall is a security system that monitors and controls incoming and outgoing network traffic, preventing unauthorized access. It’s essential for protecting your computer from hackers and malicious software by creating a barrier that examines network traffic and blocks anything that doesn’t meet its security rules.
-
Q2: How do I access Windows Firewall settings in Windows 7?
A2: You can access Windows Firewall settings by clicking the Start button, going to Control Panel, selecting “System and Security,” and then clicking on “Windows Firewall.” This allows you to view the current firewall status and configure settings.
-
Q3: What is the difference between inbound and outbound rules in Windows Firewall?
A3: Inbound rules control incoming network traffic to your computer, while outbound rules control outgoing traffic from your computer. Blocking software often requires both types of rules to prevent unauthorized connections and data transfer.
-
Q4: How do I create a new inbound rule to block a program in Windows Firewall?
A4: To create a new inbound rule, open “Windows Firewall with Advanced Security,” select “Inbound Rules,” choose “New Rule…” from the “Action” menu, select “Program,” specify the program path, choose “Block the connection,” select network profiles, and name the rule.
-
Q5: What should I do if I can’t find the program in the default “Program Files” folder when creating a firewall rule?
A5: If you can’t find the program in the default “Program Files” folder, check the program’s shortcut properties for the installation path or search for the program’s installation folder in File Explorer.
-
Q6: Is it necessary to create an outbound rule in addition to an inbound rule when blocking software with Windows Firewall?
A6: Yes, creating both inbound and outbound rules provides comprehensive protection by preventing the program from both receiving and sending data over the network, enhancing your system’s security.
-
Q7: How can I block specific ports or protocols using Windows Firewall?
A7: In the “New Inbound Rule Wizard,” select “Port” instead of “Program,” and then specify the protocol (TCP or UDP) and the port numbers you want to block. This blocks specific types of network traffic.
-
Q8: What should I do if blocking a program with Windows Firewall causes unexpected issues or errors?
A8: If blocking a program causes issues, temporarily disable the firewall rule to see if it resolves the problem. If so, adjust the rule’s settings to allow specific types of traffic required by the program.
-
Q9: How often should I review and update my firewall rules to maintain effective security?
A9: You should review and update your firewall rules regularly, at least every six months, to ensure they are still effective and relevant, especially as software and network environments change.
-
Q10: Are there alternative firewall solutions to Windows Firewall that offer enhanced security features?
A10: Yes, several third-party firewall solutions offer enhanced security features such as intrusion detection, application control, and cloud-based threat intelligence, providing more comprehensive security for users with higher security needs.