Are you looking for a way to recover an unallocated partition without software? CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN is here to guide you through the process of partition recovery, data security, and remote technical support. You can explore various methods, understand potential risks, and discover how CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN’s training and services can help you enhance your skills and ensure data integrity with disk management.
Contents
- 1. Understanding Unallocated Partitions
- 1.1. Causes of Unallocated Partitions
- 1.2. Risks of Ignoring Unallocated Partitions
- 2. Methods to Recover Unallocated Partitions Without Software
- 2.1. Using Disk Management
- 2.2. Extending an Existing Partition
- 2.3. Using Command Prompt (Diskpart)
- 3. Potential Risks and How to Avoid Them
- 3.1. Data Loss
- 3.2. System Instability
- 3.3. Incorrect Partitioning
- 4. When to Seek Professional Help
- 4.1. Complex Data Loss Scenarios
- 4.2. Lack of Technical Expertise
- 4.3. Hardware Issues
- 5. How CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN Can Help
- 5.1. Training Courses
- 5.2. Remote Technical Support
- 5.3. Benefits of Using Our Services
- 6. Best Practices for Partition Management
- 6.1. Regular Backups
- 6.2. Disk Health Monitoring
- 6.3. Avoiding Partitioning Errors
- 7. Understanding File Systems
- 7.1. NTFS (New Technology File System)
- 7.2. FAT32 (File Allocation Table 32)
- 7.3. exFAT (Extended File Allocation Table)
- 8. Advanced Partitioning Techniques
- 8.1. RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks)
- 8.2. Dynamic Disks
- 8.3. GPT (GUID Partition Table)
- 9. Common Partitioning Mistakes to Avoid
- 9.1. Deleting the Wrong Partition
- 9.2. Formatting the Wrong Partition
- 9.3. Running Out of Space on a Partition
- 10. FAQs About Unallocated Partitions
- 10.1. What is an unallocated partition?
- 10.2. How do I create a new partition from unallocated space?
- 10.3. How do I extend an existing partition to include unallocated space?
- 10.4. Can I recover data from an unallocated partition?
- 10.5. What is Disk Management?
- 10.6. What is Diskpart?
- 10.7. What are the risks of modifying partitions?
- 10.8. When should I seek professional help for partition recovery?
- 10.9. What is a file system?
- 10.10. How can CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN help with partition management?
1. Understanding Unallocated Partitions
What does having unallocated partitions even mean? An unallocated partition is a section of a hard drive or storage device that does not belong to any partition. This means that the space is not in use and cannot be used to store data until it is allocated to a partition.
1.1. Causes of Unallocated Partitions
What causes an unallocated partition to appear on your hard drive? There are several reasons why a partition might become unallocated. Here are some common causes:
- Partition Deletion: When a partition is deleted, the space it occupied becomes unallocated.
- Partition Corruption: If a partition’s file system becomes corrupted, the operating system may no longer recognize it, marking it as unallocated.
- Resizing Errors: Errors during partition resizing operations can sometimes lead to unallocated space.
- Disk Initialization Issues: Problems during the initialization of a new hard drive can result in the entire disk being shown as unallocated.
1.2. Risks of Ignoring Unallocated Partitions
What are the risks of leaving unallocated partitions as they are? Ignoring unallocated partitions can lead to inefficient use of storage space and potential data loss.
- Wasted Storage Space: Unallocated space is essentially wasted storage that could be used to store files and applications.
- Data Recovery Challenges: If important data was previously stored on the unallocated partition, recovering it can be challenging without specialized tools or expertise.
- System Instability: In some cases, unallocated space can contribute to system instability or errors, especially if it results from partition corruption.
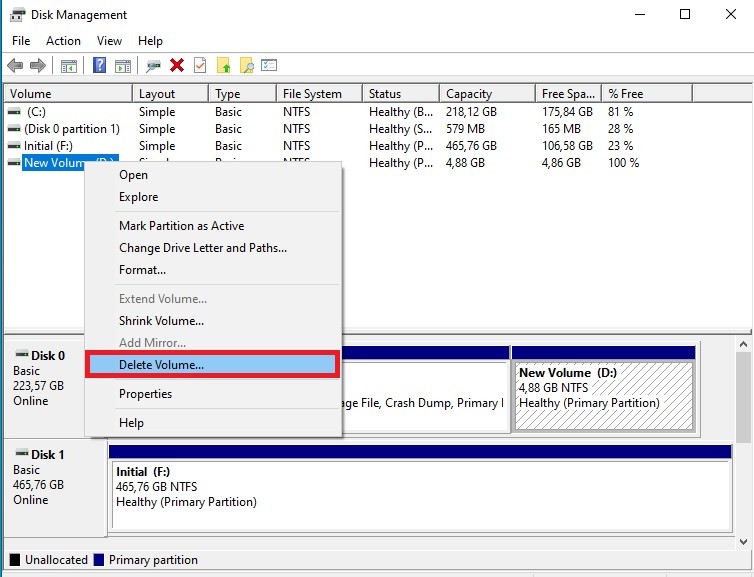 Unallocated partition in Disk Management
Unallocated partition in Disk Management
2. Methods to Recover Unallocated Partitions Without Software
Is there any way to recover unallocated partitions without software? Yes, you can use built-in Windows tools to recover unallocated partitions.
2.1. Using Disk Management
How can I use Disk Management to recover unallocated partitions? Disk Management is a built-in Windows utility that allows you to manage your hard drives and partitions. You can use it to create new partitions from unallocated space or extend existing partitions to include unallocated space. Here’s how:
- Open Disk Management:
- Press
Windows + Xand select “Disk Management” from the menu. - Alternatively, search for “Disk Management” in the Start menu and open it.
- Press
- Locate the Unallocated Space:
- In the Disk Management window, find the unallocated space. It will be labeled as “Unallocated.”
- Create a New Partition:
- Right-click on the unallocated space and select “New Simple Volume.”
- The New Simple Volume Wizard will appear. Click “Next” to continue.
- Specify the Volume Size:
- Enter the size of the new partition you want to create. By default, it will use the entire unallocated space. Click “Next.”
- Assign a Drive Letter:
- Choose a drive letter for the new partition from the dropdown menu. Click “Next.”
- Format the Partition:
- Select a file system (NTFS is recommended for Windows).
- Enter a volume label (name) for the partition.
- Check the “Perform a quick format” box.
- Click “Next.”
- Complete the Wizard:
- Review the settings and click “Finish” to create the partition.
2.2. Extending an Existing Partition
How can I extend an existing partition to include unallocated space? If you have an existing partition that you want to expand, you can extend it to include the unallocated space. Here’s how:
- Open Disk Management:
- Press
Windows + Xand select “Disk Management.”
- Press
- Locate the Partition to Extend:
- Find the partition you want to extend and the adjacent unallocated space. The unallocated space must be directly to the right of the partition you want to extend.
- Extend the Volume:
- Right-click on the partition you want to extend and select “Extend Volume.”
- The Extend Volume Wizard will appear. Click “Next” to continue.
- Select the Disk:
- In the “Select Disks” window, the unallocated space should be automatically selected. If not, select it.
- Click “Next.”
- Complete the Wizard:
- Review the settings and click “Finish” to extend the partition.
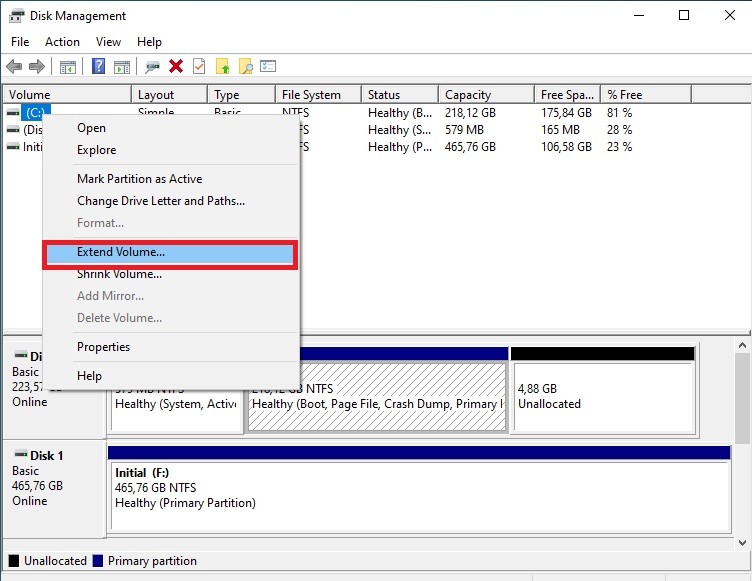 Extend Volume option in Disk Management
Extend Volume option in Disk Management
2.3. Using Command Prompt (Diskpart)
Can I use Command Prompt to recover unallocated partitions? Yes, Command Prompt, specifically using the Diskpart utility, can be used to manage partitions. This method is more advanced but can be useful if Disk Management is not working correctly.
- Open Command Prompt as Administrator:
- Search for “Command Prompt” in the Start menu.
- Right-click on “Command Prompt” and select “Run as administrator.”
- Start Diskpart:
- Type
diskpartand press Enter.
- Type
- List Disks:
- Type
list diskand press Enter. This will show all the disks on your system.
- Type
- Select the Disk:
- Identify the disk containing the unallocated space. Type
select disk X(replaceXwith the disk number) and press Enter.
- Identify the disk containing the unallocated space. Type
- List Partitions:
- Type
list partitionand press Enter. This will show all the partitions on the selected disk.
- Type
- Create a New Partition (if needed):
- If you want to create a new partition, type
create partition primary size=Y(replaceYwith the size in MB) and press Enter.
- If you want to create a new partition, type
- Select the New Partition:
- Type
select partition Z(replaceZwith the partition number) and press Enter.
- Type
- Format the Partition:
- Type
format fs=ntfs quickand press Enter to format the partition with the NTFS file system.
- Type
- Assign a Drive Letter:
- Type
assign letter=W(replaceWwith the desired drive letter) and press Enter.
- Type
- Exit Diskpart:
- Type
exitand press Enter to exit Diskpart. - Type
exitagain to close Command Prompt.
- Type
3. Potential Risks and How to Avoid Them
Are there any risks involved in recovering unallocated partitions? Yes, there are potential risks when working with disk partitions.
3.1. Data Loss
What is the risk of data loss during partition recovery? The most significant risk is data loss. Incorrectly deleting or formatting a partition can result in permanent data loss.
- Backup Your Data: Always back up your important data before attempting any partition recovery operations.
- Double-Check Commands: When using Command Prompt, double-check your commands to ensure you are targeting the correct disk and partition.
- Use Reliable Methods: Stick to well-documented and reliable methods for partition recovery.
3.2. System Instability
Can partition recovery cause system instability? Incorrect partition operations can lead to system instability, especially if you accidentally modify system partitions.
- Avoid Modifying System Partitions: Be extremely cautious when working with partitions that contain the operating system or boot files.
- Follow Instructions Carefully: Follow instructions carefully and avoid making assumptions.
- Restart After Changes: After making changes to partitions, restart your computer to ensure the changes are applied correctly.
3.3. Incorrect Partitioning
What happens if I partition the disk incorrectly? Incorrect partitioning can lead to inefficient use of storage space and difficulty managing your files.
- Plan Your Partitions: Before creating or modifying partitions, plan how you want to organize your data.
- Use Appropriate Sizes: Choose appropriate sizes for your partitions based on your storage needs.
- Consider Partition Types: Understand the different types of partitions (primary, extended, logical) and choose the appropriate type for your needs.
4. When to Seek Professional Help
When is it necessary to get help from a professional? Sometimes, the do-it-yourself methods are not enough, especially if the data is critical or the situation is complex.
4.1. Complex Data Loss Scenarios
When should I seek professional help for complex data loss? If you have experienced significant data loss or partition corruption, it’s best to seek professional help.
- Severe Corruption: If the partition is severely corrupted, professional data recovery services may be necessary.
- Physical Damage: If the hard drive has physical damage, such as clicking sounds or not spinning, do not attempt to repair it yourself.
- Critical Data: If the data on the partition is critical and irreplaceable, it’s worth the investment to hire a professional.
4.2. Lack of Technical Expertise
When should I seek professional help if I don’t have technical expertise? If you are not comfortable using command-line tools or working with disk partitions, it’s best to seek professional help.
- Unfamiliarity with Tools: If you are not familiar with Disk Management or Command Prompt, you may accidentally make mistakes that lead to data loss.
- Fear of Making Mistakes: If you are afraid of making mistakes, it’s better to let a professional handle the recovery process.
- Time Constraints: If you don’t have the time to troubleshoot and recover the partition yourself, a professional can do it for you more quickly.
4.3. Hardware Issues
When should I seek professional help if I suspect hardware issues? If you suspect that there is a hardware issue with your hard drive, such as physical damage or failure, it’s important to seek professional help.
- Unusual Noises: If the hard drive is making unusual noises, such as clicking or grinding, it may be failing.
- Drive Not Recognized: If the hard drive is not recognized by your computer, it may have a hardware issue.
- Overheating: If the hard drive is overheating, it may be a sign of a hardware problem.
5. How CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN Can Help
What are the benefits of CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN? CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN offers comprehensive training and remote technical support to help you manage and recover partitions effectively.
5.1. Training Courses
What kind of training courses does CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN offer? CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN provides specialized training courses designed to enhance your skills in diagnosing and repairing automotive issues remotely.
- Advanced Diagnostic Techniques: Learn how to use advanced diagnostic tools and software to identify and resolve complex automotive problems.
- Remote Repair Procedures: Master the techniques for performing remote repairs, including software updates, module programming, and system calibrations.
- Data Recovery and Management: Gain expertise in recovering lost or corrupted data from automotive systems and managing storage efficiently.
5.2. Remote Technical Support
What kind of remote technical support does CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN offer? CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN offers remote technical support for automotive diagnostics and repairs.
- Expert Assistance: Access expert technicians who can provide guidance and support for diagnosing and resolving automotive issues remotely.
- Real-Time Solutions: Receive real-time solutions and step-by-step instructions to help you perform repairs efficiently.
- Troubleshooting Support: Get assistance with troubleshooting complex problems and identifying the root cause of automotive issues.
 Disk Management Interface
Disk Management Interface
5.3. Benefits of Using Our Services
What are the benefits of using CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN’s services? Using CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN provides numerous advantages for automotive professionals.
- Enhanced Skills: Improve your diagnostic and repair skills through specialized training courses.
- Efficient Problem Solving: Resolve automotive issues quickly and efficiently with remote technical support.
- Cost Savings: Reduce the need for expensive on-site repairs by utilizing remote repair services.
- Increased Productivity: Enhance your productivity by accessing expert assistance and real-time solutions.
- Professional Growth: Advance your career by gaining expertise in remote automotive diagnostics and repairs.
6. Best Practices for Partition Management
What are some best practices for partition management? Proper partition management is crucial for maintaining the health and performance of your storage devices.
6.1. Regular Backups
How often should I back up my data? Regularly backing up your data is essential to protect against data loss.
- Schedule Regular Backups: Create a schedule for backing up your data, such as daily, weekly, or monthly, depending on your needs.
- Use Multiple Backup Methods: Use a combination of backup methods, such as local backups and cloud backups, to ensure redundancy.
- Verify Backups: Regularly verify your backups to ensure they are working correctly and that you can restore your data if needed.
6.2. Disk Health Monitoring
How can I monitor the health of my disk? Monitoring the health of your disk can help you identify potential problems before they lead to data loss.
- Use Disk Monitoring Tools: Use disk monitoring tools to track the health of your hard drives, such as CrystalDiskInfo or HD Tune.
- Check SMART Status: Check the SMART (Self-Monitoring, Analysis and Reporting Technology) status of your hard drives to identify potential issues.
- Monitor Performance: Monitor the performance of your hard drives to identify any slowdowns or errors.
6.3. Avoiding Partitioning Errors
How can I avoid partitioning errors? Avoiding partitioning errors can help you prevent data loss and system instability.
- Plan Your Partitions: Before creating or modifying partitions, plan how you want to organize your data.
- Follow Instructions Carefully: Follow instructions carefully and avoid making assumptions.
- Double-Check Commands: When using Command Prompt, double-check your commands to ensure you are targeting the correct disk and partition.
- Use Reliable Tools: Use reliable partitioning tools, such as Disk Management or Partition Wizard, to minimize the risk of errors.
7. Understanding File Systems
What is a file system and why is it important? A file system is a method of organizing and storing files on a storage device. Choosing the right file system is important for compatibility and performance.
7.1. NTFS (New Technology File System)
What is NTFS and when should I use it? NTFS is the standard file system used by Windows operating systems.
- Compatibility: Fully compatible with Windows and supports advanced features such as file permissions and encryption.
- Large File Support: Supports large files and partitions, making it suitable for modern storage devices.
- Recommended for Windows: Recommended for use on Windows systems, especially for the system partition.
7.2. FAT32 (File Allocation Table 32)
What is FAT32 and when should I use it? FAT32 is an older file system that is compatible with a wide range of operating systems.
- Compatibility: Compatible with Windows, macOS, and Linux, as well as older devices such as digital cameras and USB drives.
- Limited File Size: Has a maximum file size limit of 4GB, which can be a limitation for modern storage needs.
- Suitable for Small Drives: Suitable for small USB drives and devices that need to be compatible with older operating systems.
7.3. exFAT (Extended File Allocation Table)
What is exFAT and when should I use it? exFAT is a file system designed for flash storage devices such as USB drives and SD cards.
- Large File Support: Supports large files and partitions, making it suitable for high-capacity storage devices.
- Compatibility: Compatible with Windows and macOS, with limited support on older operating systems.
- Recommended for Flash Drives: Recommended for use on USB drives and SD cards that need to store large files.
8. Advanced Partitioning Techniques
What are some advanced partitioning techniques? Advanced partitioning techniques can help you optimize your storage space and improve system performance.
8.1. RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks)
What is RAID and how does it work? RAID is a technology that combines multiple physical hard drives into a single logical unit to improve performance and/or provide redundancy.
- RAID 0 (Striping): Improves performance by spreading data across multiple drives, but provides no redundancy.
- RAID 1 (Mirroring): Provides redundancy by duplicating data on multiple drives, but reduces usable storage space.
- RAID 5 (Striping with Parity): Provides both performance and redundancy by striping data across multiple drives and using parity information to recover from drive failures.
- RAID 10 (Mirroring and Striping): Combines the benefits of RAID 1 and RAID 0, providing both performance and redundancy.
8.2. Dynamic Disks
What are dynamic disks and how do they differ from basic disks? Dynamic disks are a type of disk management that allows for more flexible partition management.
- Flexibility: Dynamic disks allow you to create volumes that span multiple physical disks and to resize volumes without restarting your computer.
- Compatibility: Dynamic disks are only compatible with Windows operating systems.
- Complex Management: Dynamic disks can be more complex to manage than basic disks.
8.3. GPT (GUID Partition Table)
What is GPT and why is it important? GPT is a modern partitioning scheme that is used on most new computers.
- Large Partition Support: GPT supports partitions larger than 2TB, which is a limitation of the older MBR (Master Boot Record) partitioning scheme.
- Compatibility: GPT is compatible with UEFI (Unified Extensible Firmware Interface) BIOS, which is used on most new computers.
- Reliability: GPT is more reliable than MBR because it stores multiple copies of the partition table on the disk.
9. Common Partitioning Mistakes to Avoid
What are some common partitioning mistakes to avoid? Avoiding common partitioning mistakes can help you prevent data loss and system instability.
9.1. Deleting the Wrong Partition
How can I avoid deleting the wrong partition? Deleting the wrong partition can result in permanent data loss.
- Double-Check the Partition: Before deleting a partition, double-check that you have selected the correct partition.
- Backup Your Data: Always back up your data before deleting a partition.
- Use Descriptive Labels: Use descriptive labels for your partitions to help you identify them easily.
9.2. Formatting the Wrong Partition
How can I avoid formatting the wrong partition? Formatting the wrong partition can result in permanent data loss.
- Double-Check the Partition: Before formatting a partition, double-check that you have selected the correct partition.
- Backup Your Data: Always back up your data before formatting a partition.
- Use Descriptive Labels: Use descriptive labels for your partitions to help you identify them easily.
9.3. Running Out of Space on a Partition
What should I do if I run out of space on a partition? Running out of space on a partition can lead to performance problems and errors.
- Monitor Disk Space: Regularly monitor the amount of free space on your partitions.
- Delete Unnecessary Files: Delete unnecessary files to free up disk space.
- Move Files to Another Partition: Move files to another partition to free up disk space.
- Extend the Partition: Extend the partition to include unallocated space or another partition.
10. FAQs About Unallocated Partitions
10.1. What is an unallocated partition?
An unallocated partition is a section of a hard drive or storage device that does not belong to any partition and cannot be used to store data until it is allocated.
10.2. How do I create a new partition from unallocated space?
To create a new partition from unallocated space, use Disk Management in Windows. Right-click on the unallocated space, select “New Simple Volume,” and follow the wizard to create a new partition.
10.3. How do I extend an existing partition to include unallocated space?
To extend an existing partition, the unallocated space must be directly to the right of the partition. Right-click on the partition, select “Extend Volume,” and follow the wizard to extend the partition.
10.4. Can I recover data from an unallocated partition?
Yes, you can recover data from an unallocated partition using data recovery software or professional data recovery services. However, the chances of successful recovery depend on whether the space has been overwritten.
10.5. What is Disk Management?
Disk Management is a built-in Windows utility that allows you to manage your hard drives and partitions, including creating, deleting, and formatting partitions.
10.6. What is Diskpart?
Diskpart is a command-line utility in Windows that allows you to manage disks and partitions. It is more advanced than Disk Management but can be useful for complex tasks.
10.7. What are the risks of modifying partitions?
The risks of modifying partitions include data loss, system instability, and incorrect partitioning. Always back up your data before making changes.
10.8. When should I seek professional help for partition recovery?
Seek professional help if you have experienced significant data loss, partition corruption, or hardware issues, or if you are not comfortable using command-line tools.
10.9. What is a file system?
A file system is a method of organizing and storing files on a storage device. Common file systems include NTFS, FAT32, and exFAT.
10.10. How can CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN help with partition management?
CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN offers training courses and remote technical support to help you manage and recover partitions effectively, ensuring data integrity and efficient storage management.
By understanding these methods, potential risks, and best practices, you can effectively manage and recover unallocated partitions without additional software. For comprehensive training and expert support, visit CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN, contact us at Address: 1700 W Irving Park Rd, Chicago, IL 60613, United States, Whatsapp: +1 (641) 206-8880, and explore our services to enhance your skills in automotive diagnostics and repairs. Act now to ensure your data is safe and your systems are running efficiently.