Is it possible to convert a logical partition to primary without the need for third-party tools? Yes, it is! At CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN, we provide expert insights and solutions for all your automotive repair and technology needs. Dive in to discover efficient methods and best practices for managing your disk partitions, enhancing your system performance and stability. Discover innovative solutions to troubleshoot system issues and maximize hard drive efficiency.
Contents
- Understanding Partition Types
- 1. What are Primary and Logical Partitions?
- 2. Why Convert a Partition?
- 3. What are the Limitations of Partitioning?
- Methods to Convert Logical to Primary Partition
- 4. Using Disk Management in Windows
- 5. Using Command Prompt (Diskpart)
- 6. Converting to GPT to Avoid Logical Partitions
- Understanding the Technical Aspects
- 7. MBR vs. GPT: A Detailed Comparison
- 8. File System Considerations
- 9. Troubleshooting Common Issues
- 10. Advanced Partitioning Techniques
- Leveraging CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN for Advanced Automotive Solutions
- 11. Why Choose CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN?
- 12. Remote Diagnostic Services
- 13. Enhancing Skills with CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN Training Programs
- 14. Benefits of Remote Automotive Services
- 15. Success Stories from Our Clients
- Additional Tips and Considerations
- 16. Best Practices for Disk Partitioning
- 17. When to Seek Professional Help
- 18. Future Trends in Disk Management
- 19. Tools for Monitoring Disk Health
- 20. Understanding Drive Letters
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- 21. Can I convert a logical partition to primary without losing data?
- 22. What is the difference between primary and logical partitions?
- 23. How many primary partitions can I have on a GPT disk?
- 24. What is the best file system for a primary partition?
- 25. Can I use Disk Management to convert a disk from MBR to GPT?
- 26. Is it safe to use third-party software to convert partitions?
- 27. What should I do if my system won’t boot after converting partitions?
- 28. How do I create a primary partition using Diskpart?
- 29. What is the purpose of an extended partition?
- 30. What are the advantages of using GPT over MBR?
- Conclusion
Understanding Partition Types
1. What are Primary and Logical Partitions?
Primary partitions are essential for operating systems because they can be booted directly. Logical partitions, on the other hand, reside within an extended partition and are used to organize data. Primary partitions are limited to four on a single hard drive, while logical partitions offer more flexibility within an extended partition.
2. Why Convert a Partition?
Converting a partition might be necessary for various reasons:
- Operating System Requirements: Some operating systems require a primary partition for installation.
- Booting Issues: To resolve booting problems, you might need to convert a logical partition to primary.
- Partition Limits: If you’ve reached the limit of primary partitions, converting a logical drive can free up space.
- Flexibility: Managing space between partitions for better organization and resource allocation.
3. What are the Limitations of Partitioning?
Partitioning limitations depend on the disk’s partitioning scheme:
- MBR (Master Boot Record):
- Limited to four primary partitions.
- If more partitions are needed, one primary partition can be designated as an extended partition, housing multiple logical partitions.
- Maximum disk size of 2TB.
- GPT (GUID Partition Table):
- Supports up to 128 primary partitions in most systems.
- No need for extended or logical partitions.
- Supports disk sizes larger than 2TB.
Methods to Convert Logical to Primary Partition
4. Using Disk Management in Windows
Disk Management is a built-in Windows utility that allows you to manage your hard drives and partitions. While it doesn’t directly convert a logical partition to primary without data loss, you can achieve the desired outcome through a series of steps.
-
Back Up Your Data:
- Before making any changes, back up all important data from the logical partition you intend to convert. This precaution ensures no data loss during the process.
-
Delete the Logical Partition:
- Open Disk Management by pressing
Windows + R, typingdiskmgmt.msc, and pressing Enter. - Locate the logical partition you want to convert.
- Right-click on the partition and select “Delete Volume.”
- Confirm the deletion. The space will now be marked as “Unallocated.”
 Delete Volume Option
Delete Volume Option- Alt: Context menu in Disk Management showing the ‘Delete Volume’ option for a selected partition, indicating the step to remove the logical partition to prepare for conversion.
- Open Disk Management by pressing
-
Delete the Extended Partition:
- The logical partition resides within an extended partition. After deleting the logical partition, you need to delete the extended partition as well.
- Right-click on the extended partition (it will be the container of the unallocated space) and select “Delete Partition.”
- Confirm the deletion. The space will now be entirely unallocated.
-
Create a New Primary Partition:
- Right-click on the unallocated space and select “New Simple Volume.”
- The New Simple Volume Wizard will appear. Click “Next.”
- Specify the size of the partition. You can use the entire unallocated space or allocate a portion of it. Click “Next.”
- Assign a drive letter to the new partition. Click “Next.”
- Choose a file system (NTFS is recommended) and provide a volume label. Check the “Perform a quick format” box. Click “Next.”
- Review your settings and click “Finish.”
-
Restore Your Data:
- After creating the new primary partition, restore your backed-up data to the partition.
5. Using Command Prompt (Diskpart)
Diskpart is a powerful command-line utility for managing disks, partitions, and volumes. It offers more control than Disk Management but requires careful attention to avoid data loss.
- Back Up Your Data:
- As with any partition modification, back up all critical data from the logical partition.
- Open Command Prompt as Administrator:
- Type
cmdin the Windows search bar. - Right-click on “Command Prompt” and select “Run as administrator.”
- Type
- Start Diskpart:
- In the Command Prompt window, type
diskpartand press Enter. - Diskpart will launch, and the prompt will change to
DISKPART>.
- In the Command Prompt window, type
- List Disks:
- Type
list diskand press Enter. This command displays all disks on your system. Note the disk number containing the logical partition you want to convert.
- Type
- Select the Disk:
- Type
select disk X, replacingXwith the disk number you noted in the previous step. For example, if the disk number is 1, typeselect disk 1.
- Type
- List Partitions:
- Type
list partitionand press Enter. This command lists all partitions on the selected disk. Identify the logical partition you want to convert.
- Type
- Select the Logical Partition:
- Type
select partition Y, replacingYwith the partition number of the logical partition. For example, if the partition number is 3, typeselect partition 3.
- Type
- Delete the Logical Partition:
- Type
delete partitionand press Enter. This command deletes the selected logical partition.
- Type
- Delete the Extended Partition:
- Type
select partition Z, replacingZwith the partition number of the extended partition. - Type
delete partitionand press Enter. This command deletes the selected extended partition.
- Type
- Create a New Primary Partition:
- Type
create partition primaryand press Enter. This command creates a new primary partition using the unallocated space.
- Type
- Select the New Partition:
- Type
select partition 1and press Enter.
- Type
- Format the Partition:
- Type
format fs=ntfs quickand press Enter. This command formats the new primary partition with the NTFS file system using a quick format.
- Type
- Assign a Drive Letter:
- Type
assign letter=W, replacingWwith the desired drive letter. For example, typeassign letter=Eto assign the letter E to the partition.
- Type
- Exit Diskpart:
- Type
exitand press Enter to exit Diskpart. - Type
exitagain to close the Command Prompt.
- Type
- Restore Your Data:
- Restore the backed-up data to the newly created primary partition.
6. Converting to GPT to Avoid Logical Partitions
If your system supports UEFI, converting your disk to GPT (GUID Partition Table) can eliminate the need for extended and logical partitions altogether. GPT supports up to 128 primary partitions and is required for disks larger than 2TB.
- Check if Your System Uses UEFI:
- Press
Windows + R, typemsinfo32, and press Enter. - In the System Information window, look for “BIOS Mode.” If it says “UEFI,” your system supports UEFI.
- Press
- Back Up Your Data:
- Converting to GPT will erase all data on the disk, so backing up is essential.
- Convert to GPT using Diskpart:
- Open Command Prompt as an administrator.
- Type
diskpartand press Enter. - Type
list diskand press Enter to list all disks. - Type
select disk X(replaceXwith the disk number). - Type
cleanand press Enter (this will erase all data on the disk). - Type
convert gptand press Enter. - Type
exitand press Enter to exit Diskpart.
- Create New Partitions:
- Open Disk Management.
- Right-click on the unallocated space and select “New Simple Volume” to create primary partitions.
- Restore Your Data:
- Restore the backed-up data to the new primary partitions.
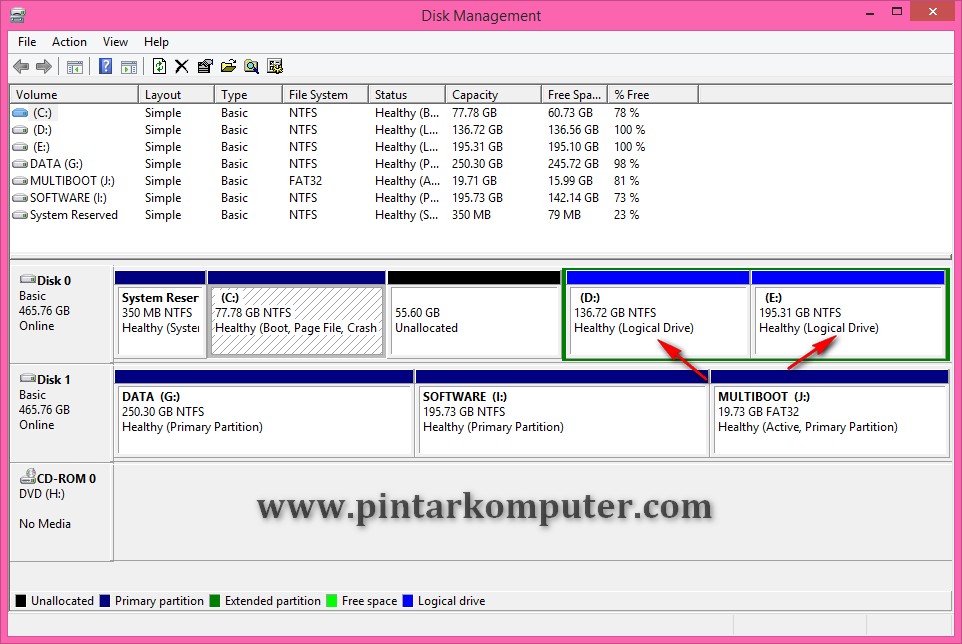 Disk Management Interface
Disk Management Interface
Alt: A screenshot of Windows Disk Management showing different partition types, including primary and logical drives, highlighting the disk management interface.
Understanding the Technical Aspects
7. MBR vs. GPT: A Detailed Comparison
Understanding the differences between MBR and GPT is crucial for effective disk management.
| Feature | MBR (Master Boot Record) | GPT (GUID Partition Table) |
|---|---|---|
| Maximum Partitions | 4 Primary or 3 Primary + 1 Extended (containing logical drives) | Up to 128 Primary Partitions |
| Maximum Disk Size | 2TB | 9.4ZB (Zettabytes) |
| BIOS/UEFI | BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) | UEFI (Unified Extensible Firmware Interface) |
| Data Storage | Boot code and partition table in the first sector | Partition table and boot data stored in multiple locations, providing redundancy and better data integrity |
| Compatibility | Compatible with older systems | Requires UEFI-based systems for booting |
| Partition Structure | Less flexible, limited to primary and logical partitions | More flexible, supports numerous primary partitions |
8. File System Considerations
The file system you choose for your partition affects how data is stored and accessed. Here’s a brief overview of common file systems:
- NTFS (New Technology File System): The standard file system for Windows. It supports large file sizes, file permissions, and data encryption.
- FAT32 (File Allocation Table 32): Compatible with many operating systems but has a 4GB file size limit.
- exFAT (Extended File Allocation Table): Designed for flash drives and external storage. It supports large file sizes and is compatible with both Windows and macOS.
9. Troubleshooting Common Issues
- Issue: Cannot delete a partition.
- Solution: Ensure no programs are running from the partition. Use Diskpart to force deletion if necessary.
- Issue: Diskpart “clean” command fails.
- Solution: Verify you have administrator privileges. Check if the disk is write-protected and remove write protection if necessary.
- Issue: System won’t boot after conversion.
- Solution: Ensure your BIOS/UEFI settings are correctly configured to boot from the new partition. For GPT disks, make sure UEFI mode is enabled.
10. Advanced Partitioning Techniques
- Partition Alignment: Aligning partitions can improve performance, especially on SSDs. Most modern operating systems automatically handle partition alignment.
- RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks): Combining multiple physical disks into one logical unit for redundancy or performance.
- Dynamic Disks: A Windows feature that allows for spanned, striped, and mirrored volumes. Dynamic disks are less portable than basic disks and may not be compatible with other operating systems.
Leveraging CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN for Advanced Automotive Solutions
11. Why Choose CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN?
At CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN, we understand the challenges faced by automotive technicians and garage owners. Our platform is designed to provide expert training, remote support, and cutting-edge solutions to enhance your skills and service offerings.
- Expert Training: Access comprehensive courses on automotive diagnostics, repair techniques, and advanced technologies.
- Remote Support: Get real-time assistance from experienced technicians to troubleshoot complex issues.
- Latest Technologies: Stay updated with the latest advancements in automotive technology and repair methods.
12. Remote Diagnostic Services
Our remote diagnostic services provide you with the capability to diagnose and repair vehicles from a distance, saving time and resources. With state-of-the-art equipment and experienced technicians, we offer:
- Remote Vehicle Diagnostics: Accurate identification of vehicle issues without the need for physical inspection.
- Software Updates and Programming: Remote installation of software updates and programming to ensure optimal vehicle performance.
- Real-time Troubleshooting: Immediate support to resolve technical issues as they arise.
13. Enhancing Skills with CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN Training Programs
Our training programs are designed to elevate your expertise in automotive repair. Whether you’re a new technician or an experienced professional, we have courses to meet your needs:
- Basic Automotive Repair: Foundational knowledge for new technicians.
- Advanced Diagnostics: Techniques for diagnosing complex vehicle issues.
- Remote Repair Technologies: Training on using remote diagnostic tools and software.
14. Benefits of Remote Automotive Services
- Cost Savings: Reduce the need for expensive equipment and on-site technicians.
- Time Efficiency: Diagnose and repair vehicles faster, increasing your service throughput.
- Expert Access: Tap into the knowledge of experienced technicians without geographical limitations.
- Customer Satisfaction: Provide quicker and more efficient service to your customers.
15. Success Stories from Our Clients
Many automotive shops have already benefited from our training and remote support services. Here are a few examples:
- Case Study 1: A small auto repair shop in Chicago increased its diagnostic accuracy by 40% after implementing our remote diagnostic services.
- Case Study 2: A technician in Los Angeles completed our advanced diagnostics course and successfully resolved a complex engine issue remotely, saving the client thousands of dollars.
- Case Study 3: A garage owner in New York improved customer satisfaction by offering faster and more efficient remote repair services.
Additional Tips and Considerations
16. Best Practices for Disk Partitioning
- Plan Ahead: Before partitioning, consider how you will use the disk space. Allocate enough space for the operating system, applications, and data.
- Regular Backups: Implement a regular backup strategy to protect against data loss.
- Use Descriptive Labels: Label your partitions clearly to avoid confusion.
- Keep System Partitions Separate: Store your operating system and applications on separate partitions for better organization and system stability.
17. When to Seek Professional Help
If you’re not comfortable modifying partitions yourself, seek help from a professional. Incorrect partitioning can lead to data loss or system instability. Professionals have the tools and expertise to perform these tasks safely and efficiently.
18. Future Trends in Disk Management
- Cloud Storage Integration: Seamless integration of cloud storage with local partitions.
- AI-Powered Partitioning Tools: Intelligent tools that automatically optimize partition sizes and configurations.
- Advanced Data Recovery Techniques: More sophisticated methods for recovering data from damaged or corrupted partitions.
19. Tools for Monitoring Disk Health
Regularly monitoring the health of your hard drives can help prevent data loss. Here are some tools for monitoring disk health:
- CrystalDiskInfo: A free tool that displays detailed information about your hard drives, including temperature, health status, and SMART attributes.
- HD Tune: A benchmarking and diagnostic tool for hard drives.
- Windows Performance Monitor: A built-in Windows tool that allows you to monitor disk performance and identify potential issues.
20. Understanding Drive Letters
Drive letters are used to identify partitions and volumes in Windows. Here are some tips for managing drive letters:
- Assign Meaningful Letters: Choose drive letters that make sense for your partitions (e.g., C for the system drive, D for data).
- Avoid Conflicts: Ensure no two partitions have the same drive letter.
- Change Drive Letters: You can change drive letters using Disk Management if needed.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
21. Can I convert a logical partition to primary without losing data?
No, directly converting a logical partition to a primary partition without data loss using built-in Windows tools isn’t possible. You need to back up the data, delete the partition, and create a new primary partition.
22. What is the difference between primary and logical partitions?
Primary partitions can be directly booted and are limited to four per disk in MBR systems, while logical partitions reside within an extended partition and are used to organize data.
23. How many primary partitions can I have on a GPT disk?
GPT disks support up to 128 primary partitions, eliminating the need for extended or logical partitions.
24. What is the best file system for a primary partition?
NTFS is generally the best file system for primary partitions on Windows due to its support for large file sizes, file permissions, and data encryption.
25. Can I use Disk Management to convert a disk from MBR to GPT?
Yes, but you must first delete all partitions on the disk. Back up your data before converting.
26. Is it safe to use third-party software to convert partitions?
While some third-party software can convert partitions without data loss, it’s always safer to back up your data before using any partitioning tool.
27. What should I do if my system won’t boot after converting partitions?
Ensure your BIOS/UEFI settings are correctly configured to boot from the new partition. For GPT disks, make sure UEFI mode is enabled.
28. How do I create a primary partition using Diskpart?
Open Command Prompt as administrator, type diskpart, select the disk, and then use the command create partition primary.
29. What is the purpose of an extended partition?
An extended partition is a special type of primary partition that can contain multiple logical partitions, allowing you to bypass the four-partition limit of MBR disks.
30. What are the advantages of using GPT over MBR?
GPT supports larger disk sizes (over 2TB), allows for more primary partitions (up to 128), and provides better data integrity through redundant storage of partition information.
Conclusion
Understanding how to manage disk partitions is essential for optimizing your system’s performance and ensuring data integrity. While converting a logical partition to primary without software requires a few steps, it is a manageable task with the right knowledge and precautions. At CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN, we provide the expertise and resources you need to excel in automotive technology and repair. Enhance your skills with our training programs and leverage our remote diagnostic services to stay ahead in the industry.
Ready to take your automotive repair skills to the next level? Visit CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN today to explore our training programs and remote support services. Contact us at Whatsapp: +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit our location at 1700 W Irving Park Rd, Chicago, IL 60613, United States. Unlock your potential with CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN and drive your career forward!