Embarking on a career path in software sales opens doors to substantial earning potential and the opportunity to be at the forefront of technological advancements. At CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN, we recognize the increasing demand for skilled professionals in this field. Let’s explore how you can kickstart or elevate your journey in software sales, focusing on essential career growth, available sales roles, and career advancement in this thriving industry. This career guide will give you an idea of the best software sales jobs.
Contents
- 1. Understanding the Software Sales Landscape
- 1.1. What Exactly Does Software Sales Entail?
- 1.2. Key Responsibilities in Software Sales
- 1.3. The Growing Importance of Software Sales in the Tech Industry
- 2. Exploring Different Sales Positions: Which Role Suits You?
- 2.1. Sales Development Representative (SDR): Your Entry Point
- 2.2. Outside Sales Representative: The Independent Player
- 2.3. Account Executive (AE): The Deal Closer
- 2.4. Post-Sales Account Manager: Ensuring Customer Success
- 2.5. Sales Manager: Leading the Team
- 2.6. VP of Sales: Setting the Strategy
- 2.7. Sales Operations: Supporting the Sales Force
- 2.8. Sales Engineer: The Technical Expert
- 3. Essential Skills for Success in Software Sales
- 3.1. Technical Proficiency: Understanding the Product
- 3.2. Sales Acumen: Mastering the Art of the Deal
- 3.3. Personal Attributes: The Soft Skills That Matter
- 3.4. Training and Certifications: Enhancing Your Expertise
- 4. Navigating the Career Path: Advancement Opportunities
- 4.1. From SDR to AE: Making the Jump
- 4.2. Climbing the Ladder: AE to Sales Manager
- 4.3. The Executive Level: VP of Sales and Beyond
- 4.4. Lateral Moves: Expanding Your Horizons
- 5. Maximizing Your Earning Potential: Salary and Compensation
- 5.1. Understanding Base Salary vs. Commission
- 5.2. Factors Influencing Salary
- 5.3. Negotiating Your Salary
- 5.4. Benefits and Perks
- 6. The Role of Technology in Modern Software Sales
- 6.1. CRM Systems: Managing Customer Relationships
- 6.2. Sales Automation Tools: Streamlining the Sales Process
- 6.3. Data Analytics: Making Informed Decisions
- 6.4. Remote Sales Tools: Adapting to the New Normal
- 7. Finding the Right Company: Where to Start Your Career
- 7.1. Startups vs. Established Companies
- 7.2. Company Culture
- 7.3. Growth Opportunities
- 7.4. Industry and Market
- 7.5. Researching Companies
- 8. The Future of Software Sales: Trends and Predictions
- 8.1. AI and Automation
- 8.2. Data-Driven Sales
- 8.3. Remote Selling
- 8.4. Customer Experience
- 8.5. The Rise of SaaS
- 9. CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN: Your Partner in Career Development
- 9.1. Specialized Training Programs
- 9.2. Remote Diagnostic Services
- 9.3. Career Resources and Support
- 9.4. Community and Networking
- 10. FAQs: Your Questions Answered About a Software Sales Career
- 10.1. Is a career in software sales right for me?
- 10.2. What education or experience is required to get into software sales?
- 10.3. What are the typical hours for a software sales professional?
- 10.4. How can I improve my chances of getting hired in software sales?
- 10.5. What are the biggest challenges in software sales?
- 10.6. What are the best resources for learning more about software sales?
- 10.7. How important is networking in software sales?
- 10.8. What is the best way to stay motivated in software sales?
- 10.9. How do I handle rejection in software sales?
- 10.10. What is the future outlook for software sales careers?
1. Understanding the Software Sales Landscape
Software sales involves selling software products or services to businesses and individuals. It’s about understanding customer needs and offering solutions that improve their operations. According to a report by Grand View Research, the global software market is expected to reach $816.51 billion by 2028, growing at a CAGR of 11.7%. This growth underscores the increasing demand for software sales professionals.
1.1. What Exactly Does Software Sales Entail?
Software sales isn’t just about pushing products; it’s about understanding your client’s problems and showing them how your software can solve them. Top salespeople are more like consultants, offering the best solutions for their clients. As explained in “The SaaS Sales Process” by Lucidchart, the best software sales professionals are advocates, acting on behalf of both their company and their clients to find the perfect solution.
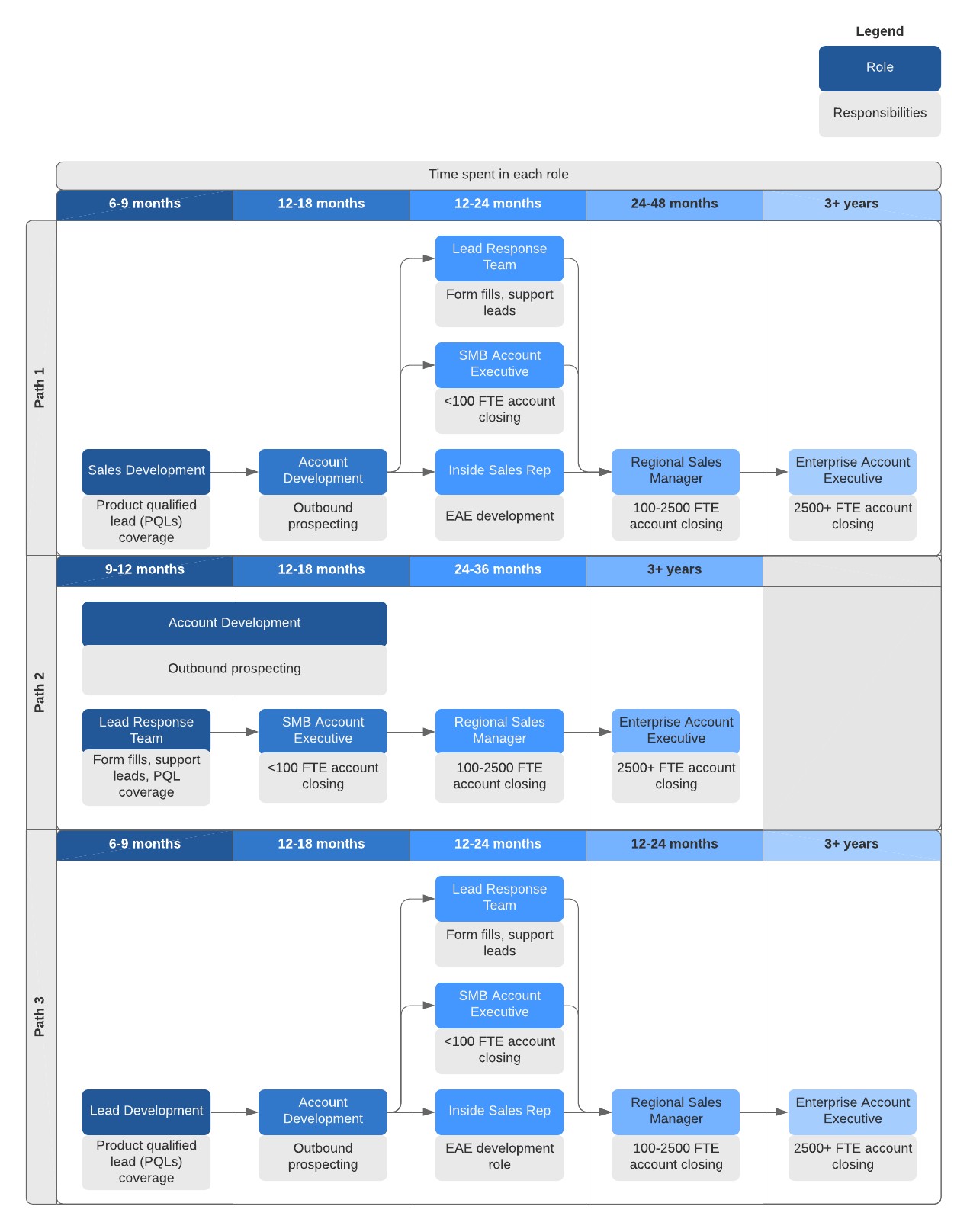 software sales career path
software sales career path
Alt: An informative software sales career path diagram showcasing various roles such as Sales Development Rep, Account Executive, and VP of Sales, illustrating career progression and opportunities for advancement.
1.2. Key Responsibilities in Software Sales
The main goal in software sales is to provide clients with the tech they need to solve problems. This involves:
- Identifying Potential Clients: Finding businesses or individuals who could benefit from your software.
- Understanding Client Needs: Learning about their challenges and goals.
- Presenting Solutions: Showing how your software can meet their specific needs.
- Closing Deals: Negotiating and finalizing sales agreements.
- Building Relationships: Maintaining ongoing relationships with clients to ensure satisfaction and identify future opportunities.
1.3. The Growing Importance of Software Sales in the Tech Industry
The tech industry is booming, and software sales is at the heart of it. As more businesses rely on software to streamline operations and gain a competitive edge, the demand for skilled sales professionals will only increase.
2. Exploring Different Sales Positions: Which Role Suits You?
The field of software sales offers a range of positions, each with unique responsibilities and career paths. Understanding these roles can help you find the best fit for your skills and goals.
2.1. Sales Development Representative (SDR): Your Entry Point
What They Do: SDRs are the first point of contact, reaching out to potential clients through cold calls and emails. Their main goal is to create opportunities for Account Executives (AEs) to close deals.
Average Salary: According to The Bridge Group, SDRs typically earn a base salary of around $48,000, with total compensation reaching about $75,000.
Pros:
- Great way to break into sales.
- Opportunity to learn the basics of sales and customer engagement.
Cons:
- Lower base pay compared to other sales roles.
- Heavy reliance on cold outreach can be challenging.
Career Path: SDRs can advance to become AEs or sales managers.
2.2. Outside Sales Representative: The Independent Player
What They Do: Outside sales reps build relationships in markets outside the company’s main office. They often work independently, managing their schedules and client interactions.
Pros:
- High degree of independence and flexibility.
- Opportunity to build relationships in diverse markets.
Cons:
- Can be isolating due to remote work.
- Requires strong self-discipline and motivation.
Career Path: Outside sales reps can transition to AEs or sales management roles.
2.3. Account Executive (AE): The Deal Closer
What They Do: AEs are central to closing deals, working directly with potential clients to understand their needs and present tailored solutions.
Average Salary: The Bridge Group reports that AEs have an average base salary of $62,000, with on-target earnings of around $126,000.
Pros:
- Good starting salary with significant earning potential through commissions.
- Opportunity to develop strong sales and negotiation skills.
Cons:
- Success depends on the quality of the product or service.
- Income can be variable due to commission-based pay.
Career Path: Successful AEs can move into sales management or even VP of Sales positions.
2.4. Post-Sales Account Manager: Ensuring Customer Success
What They Do: Post-sales account managers maintain client relationships after a deal is closed, focusing on contract renewals, upselling, and ensuring customer satisfaction.
Pros:
- Wide range of responsibilities, including relationship management and technical support.
- Higher average starting salary compared to AEs or SDRs.
Cons:
- Lower cap on earnings compared to direct sales roles.
- Requires a blend of sales and customer service skills.
Career Path: Post-sales account managers can advance to sales management or VP positions.
2.5. Sales Manager: Leading the Team
What They Do: Sales managers lead and train sales teams, monitor progress, and report to the VP of Sales.
Salary: Sales managers typically earn a base salary between $89,000 and $95,000, with on-target earnings ranging from $127,000 to $147,000.
Pros:
- Great starting salary with excellent earning potential through commissions.
- Opportunity to develop leadership and strategic skills.
Cons:
- Less direct client interaction.
- Focus on team oversight and performance management.
Career Path: Sales managers can advance to sales leadership roles, such as VP or Head of Sales.
2.6. VP of Sales: Setting the Strategy
What They Do: As an executive, the VP of Sales is responsible for the company’s overall sales strategy, working closely with marketing to align sales and marketing efforts.
Pros:
- High earning potential with significant commission-based upside.
- Opportunity to influence the company’s direction and growth.
Cons:
- High level of responsibility and pressure to meet sales targets.
- Can be subject to turnover if sales targets are not met.
Career Path: VPs of Sales can transition to other executive positions, such as CFO or CEO.
2.7. Sales Operations: Supporting the Sales Force
What They Do: Sales operations professionals support sales teams by providing marketing materials, evaluating processes, and reporting to sales leadership.
Pros:
- Great starting salary.
- Opportunity to work behind the scenes and improve sales efficiency.
Cons:
- Limited opportunity for commission-based earnings.
- Less direct impact on sales outcomes.
Career Path: Experienced sales operations leaders can advance to sales leadership roles, such as VP of Sales.
2.8. Sales Engineer: The Technical Expert
What They Do: Sales engineers provide technical expertise during the sales process, answering complex questions and demonstrating the capabilities of the software.
Pros:
- High earning potential, comparable to software engineers.
- Opportunity to combine technical skills with sales acumen.
Cons:
- Not all companies offer commissions to sales engineers.
- Requires a deep understanding of both the software and the sales process.
Career Path: Sales engineers can become AEs, sales managers, or even executives like CTOs or CEOs.
Each of these positions plays a crucial role in the software sales ecosystem, offering diverse opportunities for individuals with different skills and career aspirations.
3. Essential Skills for Success in Software Sales
To excel in software sales, you need a combination of technical knowledge, sales skills, and personal attributes.
3.1. Technical Proficiency: Understanding the Product
A solid understanding of the software you’re selling is crucial. This includes:
- Software Features: Knowing the ins and outs of the software’s functionality.
- Technical Specifications: Understanding the technical requirements and limitations.
- Industry Trends: Staying up-to-date with the latest developments in the software industry.
3.2. Sales Acumen: Mastering the Art of the Deal
Effective sales skills are essential for closing deals and building relationships. Key skills include:
- Communication: Clearly and persuasively conveying information.
- Negotiation: Finding mutually beneficial agreements.
- Presentation: Delivering compelling presentations.
- Relationship Building: Establishing and maintaining strong client relationships.
3.3. Personal Attributes: The Soft Skills That Matter
Beyond technical and sales skills, certain personal attributes can significantly impact your success. These include:
- Resilience: Bouncing back from setbacks and rejections.
- Empathy: Understanding and relating to customer needs.
- Problem-Solving: Identifying and addressing customer challenges.
- Adaptability: Adjusting to changing market conditions and customer demands.
- Self-Motivation: Staying driven and focused on achieving goals.
3.4. Training and Certifications: Enhancing Your Expertise
Investing in training and certifications can significantly enhance your skills and credibility. Consider these options:
- Sales Training Programs: Programs like Sandler Training and SPIN Selling can improve your sales techniques.
- Software-Specific Certifications: Certifications related to the software you’re selling can demonstrate your expertise.
- Online Courses: Platforms like Coursera and Udemy offer courses on sales, marketing, and technology.
By developing these essential skills and attributes, you can position yourself for success in the competitive field of software sales.
 pre-sales process
pre-sales process
Alt: A detailed flowchart illustrating the pre-sales process, emphasizing the critical steps and skills needed for success in software sales, such as lead generation, qualification, and presentation.
4. Navigating the Career Path: Advancement Opportunities
Software sales offers a clear path for career advancement, with opportunities to move into leadership roles and increase your earning potential.
4.1. From SDR to AE: Making the Jump
Moving from an SDR to an AE is a common first step in software sales. To make this jump, focus on:
- Exceeding Targets: Consistently meeting or exceeding your SDR targets.
- Developing Sales Skills: Honing your communication, negotiation, and closing skills.
- Building Relationships: Networking with AEs and sales managers to learn from their experiences.
4.2. Climbing the Ladder: AE to Sales Manager
Advancing from an AE to a sales manager requires demonstrating leadership potential and a track record of success. To achieve this, focus on:
- Consistently Achieving Sales Targets: Demonstrating your ability to close deals and generate revenue.
- Mentoring Junior Salespeople: Helping new team members succeed and improve their performance.
- Developing Strategic Thinking: Understanding market trends and developing effective sales strategies.
4.3. The Executive Level: VP of Sales and Beyond
Reaching the VP of Sales level requires a combination of sales expertise, leadership skills, and strategic vision. To get there, focus on:
- Driving Revenue Growth: Consistently exceeding sales targets and driving overall revenue growth.
- Building and Leading High-Performing Teams: Creating a positive and productive sales culture.
- Developing and Implementing Sales Strategies: Creating effective sales strategies that align with the company’s goals.
4.4. Lateral Moves: Expanding Your Horizons
In addition to upward mobility, software sales offers opportunities for lateral moves into other areas of the business. These moves can broaden your skill set and provide new career opportunities. Examples include:
- Marketing: Leveraging your sales experience to develop effective marketing campaigns.
- Product Management: Using your customer insights to help shape the development of new software products.
- Customer Success: Ensuring customer satisfaction and driving customer loyalty.
By strategically planning your career and continuously developing your skills, you can navigate the Career Path In Software Sales and achieve your professional goals.
5. Maximizing Your Earning Potential: Salary and Compensation
One of the biggest draws of a career in software sales is the potential for high earnings.
5.1. Understanding Base Salary vs. Commission
Software sales compensation typically includes a base salary and commission. The base salary provides a stable income, while commission allows you to earn more based on your sales performance.
5.2. Factors Influencing Salary
Several factors can influence your salary in software sales, including:
- Experience: More experience typically leads to higher salaries.
- Location: Salaries can vary depending on the cost of living and demand for sales professionals in your area.
- Company Size: Larger companies often pay higher salaries than smaller companies.
- Industry: Some industries, such as enterprise software, may offer higher salaries than others.
5.3. Negotiating Your Salary
When negotiating your salary, it’s important to:
- Research Industry Standards: Understand the average salary for your role and experience level in your location.
- Highlight Your Accomplishments: Showcase your past successes and the value you can bring to the company.
- Be Confident: Know your worth and be prepared to walk away if the offer is not acceptable.
5.4. Benefits and Perks
In addition to salary and commission, many companies offer benefits and perks, such as:
- Health Insurance: Medical, dental, and vision coverage.
- Paid Time Off: Vacation, sick leave, and holidays.
- Retirement Plans: 401(k) or other retirement savings plans.
- Stock Options: The opportunity to purchase company stock at a discounted price.
- Professional Development: Training and development opportunities.
By understanding the factors that influence salary and negotiating effectively, you can maximize your earning potential in software sales.
6. The Role of Technology in Modern Software Sales
Technology plays a vital role in modern software sales, enabling sales professionals to be more efficient, effective, and data-driven.
6.1. CRM Systems: Managing Customer Relationships
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems are essential tools for managing customer interactions and tracking sales progress. Popular CRM systems include:
- Salesforce: A leading CRM platform with a wide range of features for sales, marketing, and customer service.
- Microsoft Dynamics 365: A comprehensive CRM solution that integrates with other Microsoft products.
- HubSpot CRM: A free CRM platform that is popular with small and medium-sized businesses.
6.2. Sales Automation Tools: Streamlining the Sales Process
Sales automation tools can help streamline the sales process by automating repetitive tasks, such as:
- Lead Generation: Tools like LinkedIn Sales Navigator and ZoomInfo can help you find and qualify leads.
- Email Marketing: Platforms like Mailchimp and Constant Contact can automate email campaigns and track engagement.
- Sales Intelligence: Tools like Gong and Chorus.ai can record and analyze sales calls to provide insights and improve performance.
6.3. Data Analytics: Making Informed Decisions
Data analytics tools can help you make informed decisions by providing insights into sales trends, customer behavior, and market opportunities. Key tools include:
- Tableau: A powerful data visualization tool that can help you create dashboards and reports.
- Google Analytics: A web analytics service that can track website traffic and user behavior.
- Excel: A versatile spreadsheet program that can be used for data analysis and reporting.
6.4. Remote Sales Tools: Adapting to the New Normal
With the rise of remote work, remote sales tools have become essential for connecting with customers and closing deals. These tools include:
- Video Conferencing: Platforms like Zoom and Microsoft Teams enable virtual meetings and presentations.
- Screen Sharing: Tools like GoToMeeting and TeamViewer allow you to share your screen and demonstrate software features remotely.
- Collaboration Tools: Platforms like Slack and Trello facilitate team communication and collaboration.
By leveraging these technologies, you can enhance your productivity, improve your sales performance, and adapt to the changing landscape of software sales.
7. Finding the Right Company: Where to Start Your Career
Choosing the right company can be crucial for your success and career growth in software sales.
7.1. Startups vs. Established Companies
- Startups: Offer a fast-paced, dynamic environment with opportunities to make a significant impact. However, they may also be more risky and less stable than established companies.
- Established Companies: Provide more stability, resources, and structure, but may also be less flexible and innovative than startups.
7.2. Company Culture
A positive and supportive company culture can significantly impact your job satisfaction and career growth. Consider factors such as:
- Values: Does the company’s values align with your own?
- Leadership: Are the company’s leaders supportive and inspiring?
- Teamwork: Does the company foster a collaborative and supportive team environment?
- Work-Life Balance: Does the company prioritize work-life balance?
7.3. Growth Opportunities
Look for companies that offer opportunities for professional development and career advancement. Consider factors such as:
- Training Programs: Does the company offer training programs to help you develop your skills?
- Mentorship Programs: Does the company offer mentorship programs to help you learn from experienced sales professionals?
- Career Paths: Does the company have clear career paths and opportunities for advancement?
7.4. Industry and Market
Choose a company in an industry and market that you are passionate about and believe in. This will make it easier to stay motivated and engaged in your work.
7.5. Researching Companies
Before applying for a job, take the time to research companies and learn about their culture, values, and opportunities. Use resources such as:
- Company Websites: Visit the company’s website to learn about their mission, values, and products.
- LinkedIn: Research the company’s employees and learn about their experiences.
- Glassdoor: Read reviews from current and former employees.
By carefully considering these factors and researching companies thoroughly, you can find the right company to start or advance your career in software sales.
Alt: An illustrative sales organization chart from Winning by Design, highlighting various roles within a sales team, emphasizing the importance of structure and career progression in software sales.
8. The Future of Software Sales: Trends and Predictions
The field of software sales is constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements and changing customer expectations.
8.1. AI and Automation
Artificial intelligence (AI) and automation are transforming the sales process by automating tasks, improving lead generation, and personalizing customer interactions. According to a report by McKinsey, AI could increase sales productivity by up to 30%.
8.2. Data-Driven Sales
Data-driven sales is becoming increasingly important, as sales professionals leverage data analytics to identify opportunities, personalize their approach, and improve their performance.
8.3. Remote Selling
Remote selling is here to stay, as more companies embrace remote work and customers become more comfortable with virtual interactions. This requires sales professionals to develop strong remote communication and collaboration skills.
8.4. Customer Experience
Customer experience is becoming a key differentiator in the software industry, as customers demand personalized, seamless, and value-driven interactions. Sales professionals need to focus on building relationships and delivering exceptional customer service.
8.5. The Rise of SaaS
The Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) model continues to dominate the software industry, requiring sales professionals to understand the nuances of selling subscription-based software and managing recurring revenue streams.
By staying abreast of these trends and adapting to the changing landscape of software sales, you can position yourself for success in the future.
9. CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN: Your Partner in Career Development
At CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN, we understand the importance of staying ahead in the rapidly evolving automotive technology landscape. We offer specialized training and services designed to help you excel in your career.
9.1. Specialized Training Programs
Our training programs focus on the latest technologies and techniques in automotive diagnostics and repair, including remote solutions. These programs provide you with the skills and knowledge you need to succeed in today’s market.
9.2. Remote Diagnostic Services
We offer remote diagnostic services that allow you to troubleshoot and repair vehicles from anywhere in the world. This can help you expand your service offerings and reach new customers.
9.3. Career Resources and Support
We provide career resources and support to help you find the right job and advance in your career. This includes resume writing assistance, interview coaching, and job placement services.
9.4. Community and Networking
Join our community of automotive professionals to connect with peers, share knowledge, and learn about new opportunities.
Contact us today at +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit our website at CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN to learn more about how we can help you achieve your career goals. Our address is 1700 W Irving Park Rd, Chicago, IL 60613, United States.
10. FAQs: Your Questions Answered About a Software Sales Career
Here are some frequently asked questions about a career in software sales:
10.1. Is a career in software sales right for me?
If you enjoy working with people, solving problems, and have a passion for technology, a career in software sales may be a good fit.
10.2. What education or experience is required to get into software sales?
While a bachelor’s degree can be helpful, it’s not always required. Experience in sales, customer service, or technology can also be valuable.
10.3. What are the typical hours for a software sales professional?
The hours can vary depending on the role and company, but typically involve a standard workweek with some evenings and weekends required.
10.4. How can I improve my chances of getting hired in software sales?
Focus on developing your sales skills, networking with industry professionals, and tailoring your resume and cover letter to the specific job.
10.5. What are the biggest challenges in software sales?
Some of the biggest challenges include dealing with rejection, staying up-to-date with technology, and managing customer expectations.
10.6. What are the best resources for learning more about software sales?
Consider industry publications, online courses, and networking events. CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN also offers specialized training programs.
10.7. How important is networking in software sales?
Networking is crucial for building relationships, finding new opportunities, and staying informed about industry trends.
10.8. What is the best way to stay motivated in software sales?
Set clear goals, celebrate successes, and focus on the positive impact you’re making for your customers.
10.9. How do I handle rejection in software sales?
View rejection as a learning opportunity, stay positive, and focus on improving your approach.
10.10. What is the future outlook for software sales careers?
The future outlook for software sales careers is bright, with continued growth expected in the software industry.
A career path in software sales offers a rewarding and challenging opportunity to be at the forefront of technology and drive business growth. With the right skills, knowledge, and dedication, you can achieve success and make a significant impact in this dynamic field. Consider enhancing your expertise with CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN and unlock your full potential.
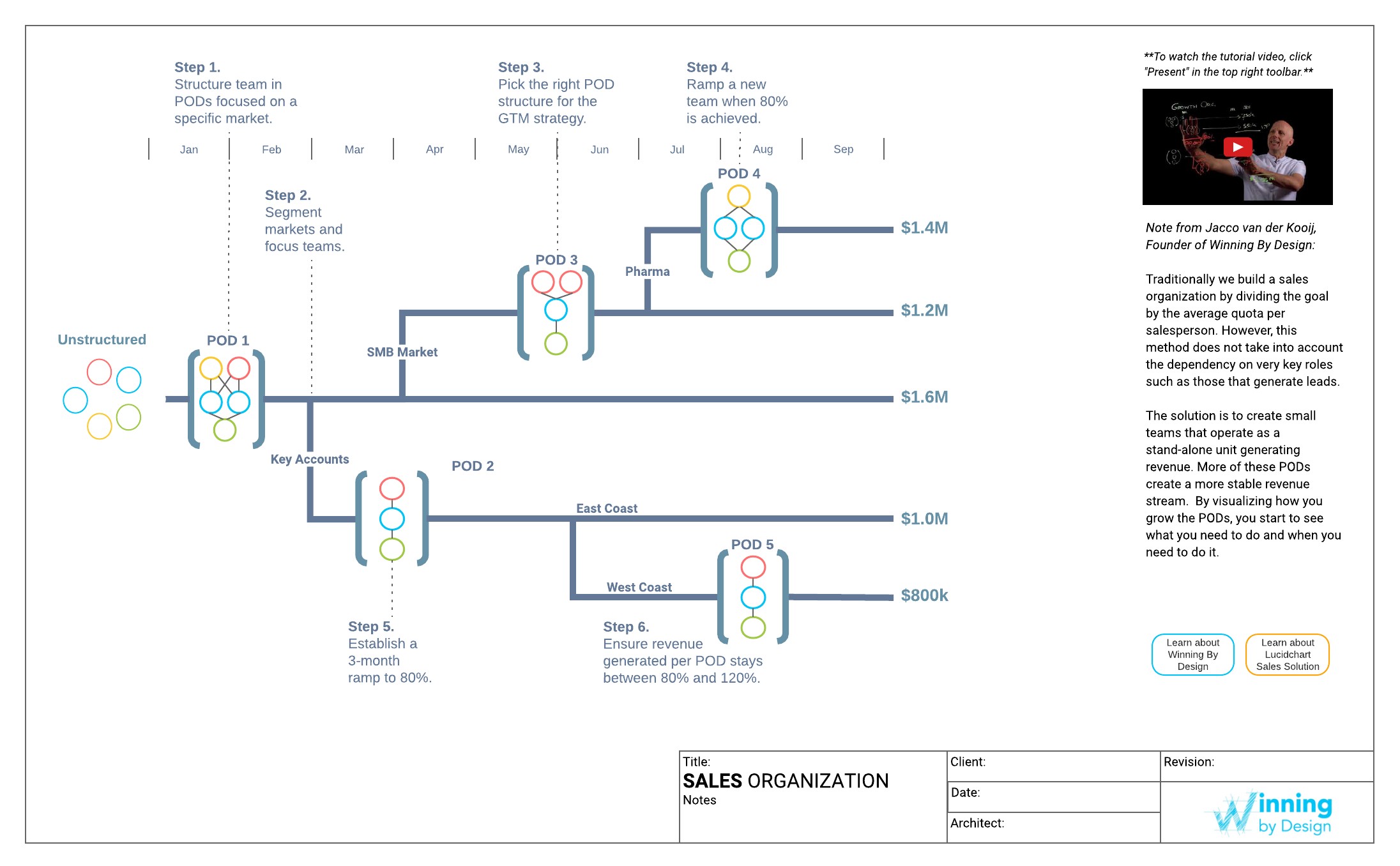 Sales Organization
Sales Organization