Cars Use A Ton Of Software, and this reliance is only increasing as vehicles become more technologically advanced, requiring specialized expertise. At CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN, we offer comprehensive training to help you master the intricacies of modern automotive technology and remote diagnostics. With the surge in automotive software, mastering vehicle tech and diagnostics is crucial for repair professionals.
Contents
- 1. Why Do Cars Use A Ton Of Software? The Software Defined Vehicle Explained
- 1.1 What Roles Does Software Play in Modern Vehicles?
- 1.2 How Has Software Content in Cars Changed Over Time?
- 2. What Are The Key Software Components in Cars?
- 2.1 How Do Operating Systems Manage Vehicle Functions?
- 2.2 What Is The Role of Middleware in Automotive Systems?
- 3. How Does Software Impact Vehicle Performance and Efficiency?
- 3.1 How Does Software Optimize Engine Performance?
- 3.2 What Role Does Software Play in Electric Vehicle Efficiency?
- 4. What Are Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems (ADAS) and How Do They Rely On Software?
- 4.1 What Types of Sensors Do ADAS Use and How Is Data Processed?
- 4.2 How Does ADAS Software Enhance Vehicle Safety?
- 5. What Is The Future Of Automotive Software?
- 5.1 How Will Over-The-Air (OTA) Updates Change Vehicle Maintenance?
- 5.2 What Role Will Artificial Intelligence (AI) Play in Future Vehicles?
- 6. What Are The Challenges of Managing Software in Cars?
- 6.1 How Can Automotive Cybersecurity Threats Be Addressed?
- 6.2 What Are The Best Practices for Automotive Software Development?
- 7. What Skills Are Needed to Work with Automotive Software?
- 7.1 What Training and Certifications Are Available for Automotive Software Professionals?
- 7.2 How Can CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN Help You Enhance Your Skills?
- 8. What Tools Are Used For Automotive Software Development And Diagnostics?
- 8.1 What Are The Latest Diagnostic Scanners and Their Capabilities?
- 8.2 How Is Simulation Software Used in Automotive Development?
- 9. How Do Cars Use A Ton Of Software to Facilitate Remote Diagnostics?
- 9.1 What Are The Benefits of Remote Automotive Diagnostics?
- 9.2 How Does CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN Support Remote Diagnostics?
- 10. What Are Examples of Companies That Use Software for Remote Car Repair?
- 10.1 How Does Tesla Use Software For Remote Vehicle Repair and Maintenance?
- 10.2 What Remote Car Repair Services Are Offered by Bosch?
- FAQ: Cars Use a Ton of Software
- 1. Why do cars use a ton of software?
- 2. What are the key software components in modern vehicles?
- 3. How does software impact vehicle performance and efficiency?
- 4. What are Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems (ADAS) and how do they rely on software?
- 5. What is the future of automotive software?
- 6. How can Over-The-Air (OTA) updates change vehicle maintenance?
- 7. What skills are needed to work with automotive software?
- 8. What tools are used for automotive software development and diagnostics?
- 9. How do cars use a ton of software to facilitate remote diagnostics?
- 10. How does CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN support remote diagnostics?
1. Why Do Cars Use A Ton Of Software? The Software Defined Vehicle Explained
Cars use a ton of software because modern vehicles are increasingly becoming “software-defined,” which allows for enhanced functionality, improved performance, and advanced features. As vehicles evolve, software becomes integral to almost every aspect of their operation.
Expanding on this, the software manages a wide array of systems, from engine control and transmission to infotainment and safety features. According to a 2023 McKinsey report, software can account for up to 90% of new vehicle innovation. This includes advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) and autonomous driving functionalities. These complex systems require millions of lines of code, transforming the automotive industry by allowing vehicles to adapt and improve over time through software updates.
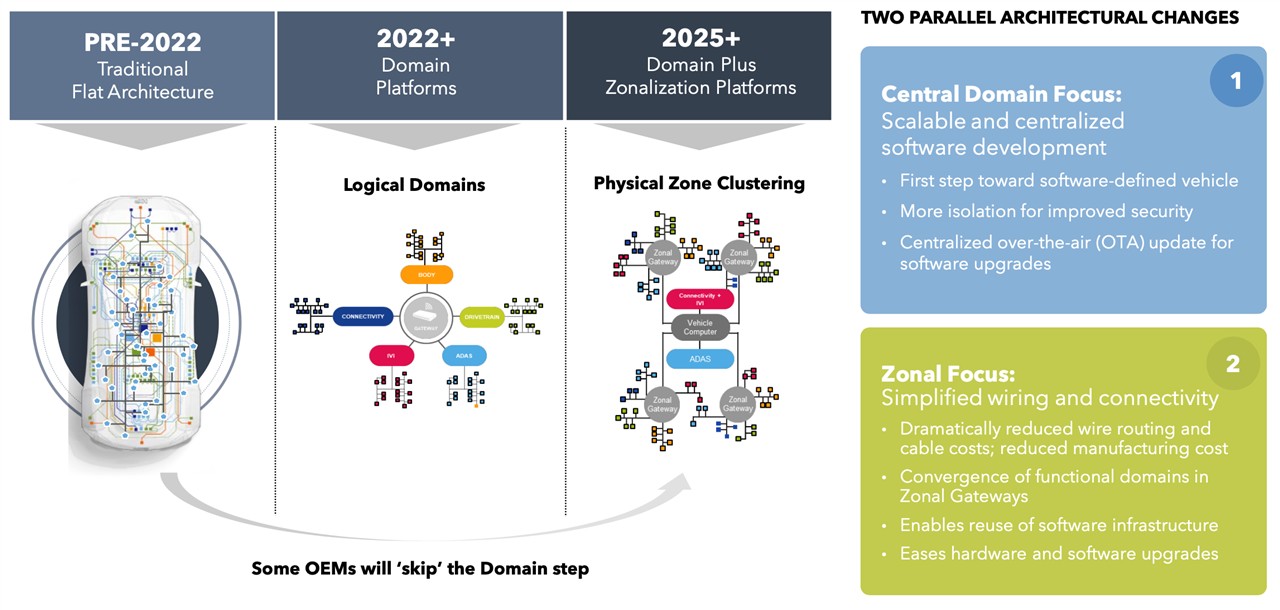 ECU-Based Architecture
ECU-Based Architecture
1.1 What Roles Does Software Play in Modern Vehicles?
Software plays several crucial roles in modern vehicles, including controlling critical systems, enhancing the driver experience, and enabling advanced features. Software in cars isn’t just for entertainment; it’s fundamental to how vehicles operate and interact with the world around them.
- Engine and Powertrain Management: Software optimizes engine performance, fuel efficiency, and emissions, ensuring the vehicle runs smoothly and efficiently.
- Safety Systems: Advanced safety features like anti-lock braking systems (ABS), electronic stability control (ESC), and airbag deployment rely heavily on software to detect and respond to potential hazards.
- Infotainment and Connectivity: Modern infotainment systems offer navigation, media playback, smartphone integration, and internet connectivity, all powered by complex software.
- Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems (ADAS): Features such as adaptive cruise control, lane departure warning, and automatic emergency braking use sensors and software algorithms to enhance safety and convenience.
- Autonomous Driving: Self-driving cars depend on sophisticated software to perceive their environment, make decisions, and control the vehicle without human intervention.
1.2 How Has Software Content in Cars Changed Over Time?
The amount of software in cars has increased dramatically over time, driven by advancements in technology and growing consumer demand for enhanced features. Historically, vehicles had minimal software, primarily limited to basic engine control.
Today, cars can contain over 100 million lines of code, a figure that continues to grow. According to a study by Deloitte in 2024, the increasing complexity of automotive software reflects the industry’s shift towards electric vehicles, autonomous driving, and connected car services. This exponential growth necessitates advanced skills in software development and automotive diagnostics.
2. What Are The Key Software Components in Cars?
Key software components in cars include operating systems, middleware, application software, and communication protocols, each playing a critical role in vehicle functionality. Understanding these components is essential for anyone involved in automotive repair and diagnostics.
- Operating Systems (OS): The OS manages the hardware resources of the vehicle’s computer systems, providing a platform for other software to run. Examples include QNX, Linux, and Automotive Grade Linux (AGL).
- Middleware: This software layer facilitates communication between different software components and hardware devices. It handles tasks like data management, security, and network connectivity.
- Application Software: These are the programs that provide specific functionalities, such as engine control, infotainment, ADAS, and autonomous driving.
- Communication Protocols: These protocols enable different electronic control units (ECUs) within the vehicle to communicate with each other. Examples include CAN, LIN, and Ethernet.
2.1 How Do Operating Systems Manage Vehicle Functions?
Operating systems manage vehicle functions by providing a stable and reliable platform for software applications to run, ensuring real-time performance and security. They are the backbone of the software-defined vehicle.
According to a white paper from BlackBerry QNX, real-time operating systems (RTOS) are crucial for applications requiring immediate responses, such as airbag deployment and braking systems. These OSs manage tasks, allocate resources, and ensure that critical functions are executed without delay.
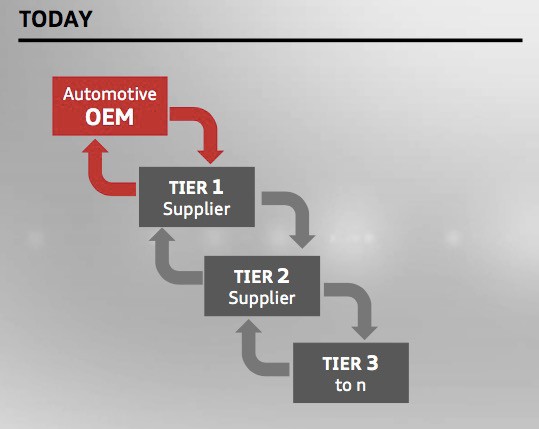 Automobile Industry Tiers
Automobile Industry Tiers
2.2 What Is The Role of Middleware in Automotive Systems?
The role of middleware in automotive systems is to facilitate seamless communication and data exchange between different software components and hardware devices, which is essential for integrating complex systems.
Middleware solutions like AUTOSAR (Automotive Open System Architecture) provide a standardized platform for developing and integrating automotive software. According to Bosch, AUTOSAR enables OEMs and suppliers to collaborate more effectively, reduce development costs, and improve software quality. This standardized approach is critical for managing the complexity of modern vehicle systems.
3. How Does Software Impact Vehicle Performance and Efficiency?
Software significantly impacts vehicle performance and efficiency by optimizing engine operations, managing energy consumption, and enhancing aerodynamics. Advanced algorithms and control systems enable vehicles to achieve better fuel economy, lower emissions, and improved handling.
- Engine Control: Software optimizes fuel injection, ignition timing, and valve control to maximize engine power and efficiency while minimizing emissions.
- Transmission Control: Software manages gear shifting and torque distribution to ensure smooth and efficient power delivery.
- Energy Management: In electric vehicles, software controls battery charging, power distribution, and regenerative braking to maximize range and efficiency.
- Aerodynamics: Software adjusts vehicle components like active grilles and rear spoilers to reduce drag and improve fuel economy.
3.1 How Does Software Optimize Engine Performance?
Software optimizes engine performance by precisely controlling various parameters such as fuel injection, ignition timing, and air-fuel mixture, leading to improved power, efficiency, and reduced emissions.
According to research from the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), advanced engine control algorithms can significantly improve fuel economy and reduce emissions. These algorithms use real-time data from sensors to adjust engine parameters dynamically, ensuring optimal performance under varying driving conditions.
3.2 What Role Does Software Play in Electric Vehicle Efficiency?
Software plays a crucial role in electric vehicle efficiency by managing battery performance, optimizing energy consumption, and controlling regenerative braking, thereby extending the vehicle’s range and overall efficiency.
A study by the U.S. Department of Energy found that advanced software algorithms can improve EV range by up to 20%. These algorithms monitor battery health, optimize charging strategies, and manage power distribution to maximize efficiency. Regenerative braking, controlled by software, captures kinetic energy during deceleration and converts it back into electricity, further enhancing efficiency.
4. What Are Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems (ADAS) and How Do They Rely On Software?
Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems (ADAS) are sophisticated safety features that use software to enhance driver awareness, prevent accidents, and even automate certain driving tasks. These systems rely heavily on software for sensor data processing, decision-making, and vehicle control.
- Adaptive Cruise Control (ACC): Maintains a safe following distance by automatically adjusting the vehicle’s speed based on traffic conditions.
- Lane Departure Warning (LDW): Alerts the driver if the vehicle begins to drift out of its lane.
- Automatic Emergency Braking (AEB): Detects potential collisions and automatically applies the brakes to prevent or mitigate the impact.
- Blind Spot Monitoring (BSM): Alerts the driver to vehicles in their blind spots.
- Parking Assistance: Helps the driver park the vehicle by providing guidance and even automating the steering.
4.1 What Types of Sensors Do ADAS Use and How Is Data Processed?
ADAS use a variety of sensors, including cameras, radar, and lidar, to gather data about the vehicle’s surroundings; this data is then processed by sophisticated software algorithms to make informed decisions and control the vehicle.
According to a report by the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA), sensor fusion is a critical aspect of ADAS. Sensor fusion involves combining data from multiple sensors to create a more accurate and comprehensive understanding of the vehicle’s environment. Software algorithms filter noise, correct errors, and interpret the data to identify objects, predict their behavior, and initiate appropriate actions.
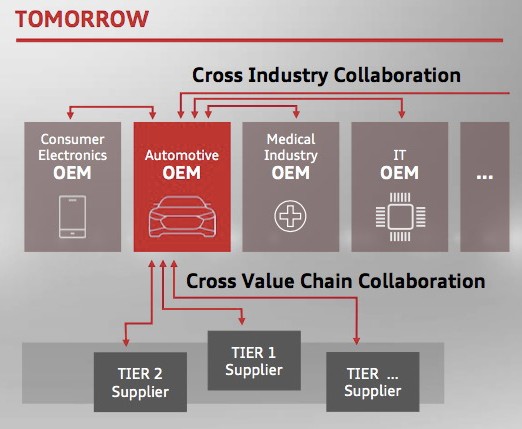 Automobile Industry Tiers Today
Automobile Industry Tiers Today
4.2 How Does ADAS Software Enhance Vehicle Safety?
ADAS software enhances vehicle safety by providing real-time alerts, automated interventions, and improved driver awareness, which helps prevent accidents and reduce the severity of collisions.
Research from the Insurance Institute for Highway Safety (IIHS) has shown that ADAS features like AEB and LDW can significantly reduce crash rates. AEB systems, for example, have been found to reduce rear-end collisions by up to 50%. By continuously monitoring the vehicle’s surroundings and providing timely warnings or automated assistance, ADAS software helps drivers avoid dangerous situations and stay safe on the road.
5. What Is The Future Of Automotive Software?
The future of automotive software involves greater autonomy, enhanced connectivity, and personalized experiences, which will transform how we interact with vehicles. Software updates and advanced AI will continuously improve vehicle capabilities, leading to safer, more efficient, and more enjoyable driving experiences.
- Autonomous Driving: Self-driving cars will become more prevalent, relying on advanced software to navigate roads, make decisions, and transport passengers without human intervention.
- Connectivity: Vehicles will be seamlessly connected to the internet, enabling over-the-air updates, remote diagnostics, and access to cloud-based services.
- Personalization: Software will tailor the driving experience to individual preferences, adjusting settings like seat position, climate control, and infotainment based on driver profiles.
- Electrification: Software will play an increasingly important role in managing the performance and efficiency of electric vehicles, optimizing battery usage, and enabling advanced charging capabilities.
5.1 How Will Over-The-Air (OTA) Updates Change Vehicle Maintenance?
Over-The-Air (OTA) updates will revolutionize vehicle maintenance by allowing manufacturers to remotely update software, fix bugs, and add new features without requiring a visit to the service center, which saves time and enhances vehicle performance.
According to a report by IHS Markit, OTA updates will become increasingly common in the automotive industry, with a growing number of vehicles equipped with the necessary hardware and software infrastructure. OTA updates enable manufacturers to address security vulnerabilities, improve system performance, and deploy new features quickly and efficiently, ensuring that vehicles remain up-to-date throughout their lifespan.
5.2 What Role Will Artificial Intelligence (AI) Play in Future Vehicles?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) will play a pivotal role in future vehicles by enabling advanced automation, personalized experiences, and predictive maintenance, enhancing safety, efficiency, and overall driver satisfaction.
A study by NVIDIA highlights the transformative potential of AI in the automotive industry. AI algorithms will power self-driving capabilities, analyze sensor data to detect potential hazards, and optimize vehicle performance based on real-time conditions. AI will also enable personalized features like voice-activated assistants, adaptive interfaces, and predictive maintenance, which alerts drivers to potential issues before they escalate.
6. What Are The Challenges of Managing Software in Cars?
Managing software in cars presents several challenges, including complexity, security, and the need for continuous updates. Ensuring that software is reliable, secure, and up-to-date requires advanced skills and robust processes.
- Complexity: Modern vehicles contain millions of lines of code, making software development and maintenance highly complex.
- Security: Automotive software is vulnerable to cyberattacks, which could compromise vehicle safety and security.
- Updates: Keeping software up-to-date requires Over-The-Air (OTA) update capabilities and robust update management processes.
- Reliability: Automotive software must be highly reliable to ensure the safe and reliable operation of the vehicle.
- Integration: Integrating software from different suppliers and ensuring compatibility can be challenging.
6.1 How Can Automotive Cybersecurity Threats Be Addressed?
Automotive cybersecurity threats can be addressed through robust security measures, including encryption, intrusion detection systems, and secure Over-The-Air (OTA) update mechanisms. These measures protect vehicle systems from unauthorized access and cyberattacks.
According to a report by the Automotive Information Sharing and Analysis Center (Auto-ISAC), collaboration and information sharing are essential for addressing automotive cybersecurity threats. Auto-ISAC provides a platform for automakers, suppliers, and security experts to share threat intelligence, best practices, and security solutions. Implementing strong security measures and staying informed about emerging threats can help protect vehicles from cyberattacks.
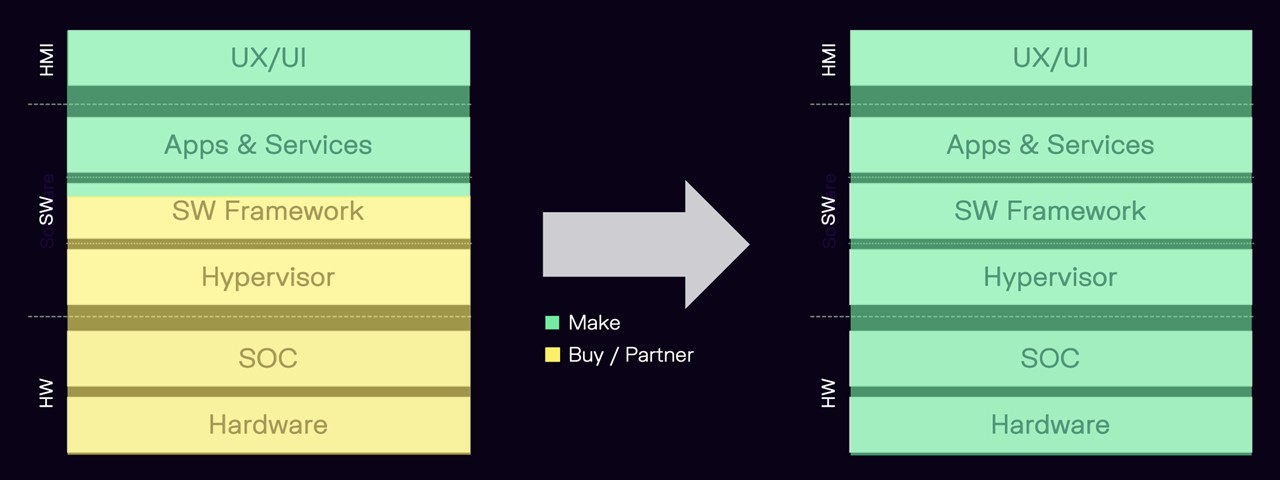 Automotive Stack
Automotive Stack
6.2 What Are The Best Practices for Automotive Software Development?
Best practices for automotive software development include following industry standards, using modular design principles, and implementing rigorous testing and validation processes. These practices ensure that software is reliable, secure, and compliant with safety requirements.
The Automotive Open System Architecture (AUTOSAR) provides a standardized framework for developing automotive software. According to Elektrobit, following AUTOSAR principles can improve software quality, reduce development costs, and facilitate collaboration between OEMs and suppliers. Modular design, which involves breaking down software into smaller, independent components, can improve maintainability and reusability. Rigorous testing and validation processes are essential for identifying and fixing defects before software is deployed in vehicles.
7. What Skills Are Needed to Work with Automotive Software?
Working with automotive software requires a combination of technical skills, including programming, software engineering, and automotive diagnostics. Professionals in this field must also possess a strong understanding of vehicle systems and safety requirements.
- Programming Languages: Proficiency in languages like C, C++, and Python is essential for developing and maintaining automotive software.
- Software Engineering: Skills in software design, testing, and project management are needed to manage the complexity of automotive software projects.
- Automotive Diagnostics: Knowledge of vehicle systems, diagnostic tools, and troubleshooting techniques is crucial for identifying and resolving software-related issues.
- Cybersecurity: Understanding cybersecurity principles and best practices is essential for protecting automotive software from cyberattacks.
- Standards and Regulations: Familiarity with industry standards like AUTOSAR and safety regulations like ISO 26262 is necessary for developing compliant software.
7.1 What Training and Certifications Are Available for Automotive Software Professionals?
Various training programs and certifications are available for automotive software professionals, including courses in software engineering, automotive diagnostics, and cybersecurity. These programs provide the skills and knowledge needed to succeed in this rapidly evolving field.
CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN offers specialized training programs in automotive software diagnostics and remote repair, equipping professionals with the latest skills and knowledge. Additionally, organizations like SAE International and IEEE offer certifications in automotive engineering and software development. These certifications validate your expertise and demonstrate your commitment to professional development.
7.2 How Can CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN Help You Enhance Your Skills?
CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN can help you enhance your skills by providing comprehensive training programs, hands-on experience, and expert guidance in automotive software diagnostics and remote repair. Our courses are designed to equip you with the latest knowledge and practical skills needed to excel in this field.
Our training programs cover a wide range of topics, including vehicle systems, software diagnostics, remote repair techniques, and cybersecurity. We offer hands-on experience with industry-standard diagnostic tools and equipment, allowing you to apply your knowledge in a real-world setting. Our expert instructors provide personalized guidance and support, helping you develop the skills and confidence to tackle complex automotive software challenges.
8. What Tools Are Used For Automotive Software Development And Diagnostics?
Various tools are used for automotive software development and diagnostics, including integrated development environments (IDEs), diagnostic scanners, and simulation software. These tools enable engineers and technicians to develop, test, and troubleshoot automotive software efficiently.
- Integrated Development Environments (IDEs): Software development tools like Eclipse and Visual Studio provide a platform for writing, compiling, and debugging automotive software.
- Diagnostic Scanners: Tools like Bosch ESI[tronic] and Snap-on Modis Edge allow technicians to diagnose and troubleshoot vehicle systems by reading diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) and monitoring sensor data.
- Simulation Software: Programs like MATLAB and Simulink enable engineers to simulate and test automotive software in a virtual environment before deploying it in a vehicle.
- Bus Analyzers: Tools like CANalyzer and Busmaster are used to monitor and analyze communication traffic on vehicle networks like CAN and Ethernet.
- Calibration Tools: Software like ETAS INCA allows engineers to calibrate engine control units (ECUs) and optimize vehicle performance.
8.1 What Are The Latest Diagnostic Scanners and Their Capabilities?
The latest diagnostic scanners offer advanced capabilities, including wireless connectivity, cloud-based data analysis, and enhanced diagnostic coverage for a wide range of vehicle makes and models. These scanners enable technicians to diagnose and repair vehicles more efficiently.
According to a review by Auto Service Professional, the latest diagnostic scanners offer features like remote diagnostics, which allows technicians to access vehicle data and perform diagnostic tests from a remote location. Cloud-based data analysis provides access to a vast library of diagnostic information and repair procedures, helping technicians troubleshoot complex issues. Enhanced diagnostic coverage ensures that scanners can support the latest vehicle technologies and systems.
8.2 How Is Simulation Software Used in Automotive Development?
Simulation software is used in automotive development to create virtual models of vehicle systems, allowing engineers to test and validate software designs before they are implemented in physical prototypes. This helps identify and fix defects early in the development process, saving time and reducing costs.
A study by the Engineering Simulation Community highlights the benefits of using simulation software in automotive development. Simulation tools like MATLAB and Simulink enable engineers to model vehicle dynamics, engine performance, and control systems. By simulating different scenarios and conditions, engineers can optimize software designs, improve vehicle performance, and ensure safety and reliability.
9. How Do Cars Use A Ton Of Software to Facilitate Remote Diagnostics?
Cars use a ton of software to facilitate remote diagnostics by enabling technicians to access vehicle data, perform diagnostic tests, and troubleshoot issues from a remote location. This capability is crucial for providing efficient and cost-effective repair services.
- Remote Access: Software allows technicians to remotely connect to a vehicle’s diagnostic port and access real-time data about its systems and components.
- Data Analysis: Diagnostic software analyzes vehicle data to identify potential issues and provide technicians with insights into the root cause of problems.
- Troubleshooting: Remote diagnostics enables technicians to perform tests, run diagnostics, and troubleshoot issues without being physically present at the vehicle.
- Software Updates: Remote software updates allow technicians to update vehicle software and fix bugs without requiring a visit to the service center.
9.1 What Are The Benefits of Remote Automotive Diagnostics?
The benefits of remote automotive diagnostics include reduced downtime, lower repair costs, and improved customer satisfaction. Remote diagnostics enables technicians to diagnose and resolve issues quickly, without requiring the vehicle to be transported to a service center.
According to a survey by AAA, remote diagnostics can reduce vehicle downtime by up to 50%. By diagnosing issues remotely, technicians can identify the necessary repairs and order parts in advance, minimizing the time the vehicle spends in the shop. Remote diagnostics also reduces repair costs by eliminating the need for towing and reducing diagnostic labor time.
9.2 How Does CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN Support Remote Diagnostics?
CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN supports remote diagnostics by providing specialized training programs, advanced diagnostic tools, and expert technical support. Our programs are designed to equip technicians with the skills and knowledge needed to perform remote diagnostics effectively.
Our training programs cover a wide range of topics, including remote access techniques, data analysis methods, and troubleshooting strategies. We offer hands-on experience with industry-standard diagnostic tools and equipment, allowing technicians to apply their knowledge in a real-world setting. Our expert technical support team is available to provide guidance and assistance, helping technicians resolve complex diagnostic issues remotely.
10. What Are Examples of Companies That Use Software for Remote Car Repair?
Examples of companies that use software for remote car repair include Tesla, Bosch, and several independent service providers. These companies leverage advanced software and connectivity to provide remote diagnostic and repair services.
- Tesla: Uses Over-The-Air (OTA) updates to fix software bugs, improve vehicle performance, and add new features remotely.
- Bosch: Offers remote diagnostic solutions for vehicle manufacturers and service providers, enabling technicians to diagnose and troubleshoot issues remotely.
- Independent Service Providers: Companies like CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN provide remote diagnostic and repair services for a wide range of vehicle makes and models.
10.1 How Does Tesla Use Software For Remote Vehicle Repair and Maintenance?
Tesla uses software for remote vehicle repair and maintenance through Over-The-Air (OTA) updates, remote diagnostics, and mobile service appointments. These capabilities allow Tesla to address many issues without requiring customers to visit a service center.
According to Tesla’s website, OTA updates can fix software bugs, improve vehicle performance, and add new features. Remote diagnostics enables Tesla technicians to monitor vehicle systems, identify potential issues, and schedule service appointments proactively. Mobile service appointments allow technicians to perform minor repairs and maintenance tasks at the customer’s location, further reducing downtime and improving customer satisfaction.
10.2 What Remote Car Repair Services Are Offered by Bosch?
Bosch offers a range of remote car repair services, including remote diagnostics, software updates, and technical support. These services are designed to help vehicle manufacturers and service providers diagnose and resolve issues quickly and efficiently.
Bosch’s remote diagnostic solutions enable technicians to access vehicle data, perform diagnostic tests, and troubleshoot issues remotely. Software updates can be deployed Over-The-Air (OTA), allowing manufacturers to fix bugs and improve vehicle performance without requiring a visit to the service center. Bosch also provides technical support to help technicians resolve complex diagnostic issues and perform remote repairs effectively.
Ready to take your automotive repair skills to the next level? Visit CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN today to explore our comprehensive training programs and discover how you can master the art of remote diagnostics and vehicle technology. Contact us at Address: 1700 W Irving Park Rd, Chicago, IL 60613, United States or WhatsApp: +1 (641) 206-8880. Let us help you stay ahead in the rapidly evolving world of automotive technology.
FAQ: Cars Use a Ton of Software
1. Why do cars use a ton of software?
Cars use a ton of software to manage complex systems, enhance performance, enable advanced features like ADAS, and facilitate connectivity.
2. What are the key software components in modern vehicles?
Key components include operating systems, middleware, application software, and communication protocols.
3. How does software impact vehicle performance and efficiency?
Software optimizes engine operations, manages energy consumption, and enhances aerodynamics for better fuel economy and lower emissions.
4. What are Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems (ADAS) and how do they rely on software?
ADAS are safety features that use software to enhance driver awareness, prevent accidents, and automate driving tasks through sensor data processing and decision-making.
5. What is the future of automotive software?
The future includes greater autonomy, enhanced connectivity, personalized experiences, and continuous improvements through software updates and AI.
6. How can Over-The-Air (OTA) updates change vehicle maintenance?
OTA updates allow manufacturers to remotely update software, fix bugs, and add new features without requiring a visit to a service center.
7. What skills are needed to work with automotive software?
Skills include programming, software engineering, automotive diagnostics, cybersecurity, and knowledge of industry standards.
8. What tools are used for automotive software development and diagnostics?
Tools include IDEs, diagnostic scanners, simulation software, bus analyzers, and calibration tools.
9. How do cars use a ton of software to facilitate remote diagnostics?
Software enables technicians to access vehicle data, perform diagnostic tests, and troubleshoot issues from a remote location.
10. How does CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN support remote diagnostics?
CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN provides specialized training programs, advanced diagnostic tools, and expert technical support for remote diagnostics.