Catia Car Software is indeed a top-tier solution for automotive design, offering a robust set of tools and capabilities tailored to the industry’s specific needs. At CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN, we recognize the importance of mastering such advanced software to excel in modern automotive repair and design. CATIA enables engineers and designers to create, simulate, and analyze complex automotive designs, improving product development and overall performance; this will enhance your remote repair abilities. Learning CATIA can open doors to numerous opportunities in the automotive industry, from design to manufacturing.
Contents
- 1. What Exactly is CATIA Car Software and How Is It Used?
- 1.1 Design and Styling
- 1.2 Engineering and Simulation
- 1.3 Manufacturing and Tooling
- 1.4 Collaboration and Data Management
- 1.5 Key Benefits of CATIA Car Software
- 2. What Are The Key Features of CATIA Car Software?
- 2.1 Advanced Surface Modeling
- 2.2 Parametric Design
- 2.3 Simulation and Analysis
- 2.4 Manufacturing Tools
- 2.5 Collaboration and Data Management Tools
- 2.6 Summary Table of Key Features
- 3. What Are The Benefits of Using CATIA Car Software?
- 3.1 Enhanced Design Quality
- 3.2 Improved Engineering Accuracy
- 3.3 Streamlined Manufacturing
- 3.4 Enhanced Collaboration
- 3.5 Reduced Time-to-Market
- 3.6 Summary of Benefits Table
- 4. Who Uses CATIA Car Software?
- 4.1 Automotive Designers
- 4.2 Automotive Engineers
- 4.3 Manufacturing Specialists
- 4.4 Project Managers
- 4.5 Table of CATIA Users and Their Roles
- 5. How to Learn CATIA Car Software Effectively?
- 5.1 Formal Training Courses
- 5.2 Online Resources
- 5.3 Hands-On Practice
- 5.4 Collaboration and Networking
- 5.5 Continuous Learning
- 5.6 Summary Table of Learning Strategies
- 6. CATIA Car Software and Remote Automotive Repair
- 6.1 Detailed 3D Models for Remote Diagnosis
- 6.2 Simulation for Troubleshooting
- 6.3 Collaboration and Communication
- 6.4 Improving Efficiency and Reducing Downtime
- 6.5 Table Summarizing CATIA’s Role in Remote Repair
- 7. Examples of CATIA Car Software in Automotive Companies
- 7.1 General Motors
- 7.2 Ford Motor Company
- 7.3 BMW Group
- 7.4 Toyota Motor Corporation
- 7.5 Table of Automotive Companies Using CATIA
- 8. What Are The Alternatives To CATIA Car Software?
- 8.1 Siemens NX
- 8.2 Autodesk AutoCAD
- 8.3 SolidWorks
- 8.4 PTC Creo
- 8.5 Table of Alternatives to CATIA
1. What Exactly is CATIA Car Software and How Is It Used?
CATIA car software is a comprehensive Computer-Aided Design (CAD), Computer-Aided Engineering (CAE), and Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAM) suite used extensively in the automotive industry for designing, analyzing, and manufacturing vehicles. It’s a leading tool that enables automotive engineers and designers to create everything from initial concept sketches to fully detailed 3D models, simulate vehicle performance, and prepare designs for manufacturing.
1.1 Design and Styling
CATIA empowers designers to create innovative and aesthetically pleasing car designs. According to Dassault Systèmes, the makers of CATIA, its Class-A surfacing tools allow for the creation of high-quality surfaces that meet the stringent requirements of automotive styling. This includes:
- Conceptual Design: Initial sketches and ideation.
- Surface Modeling: Creating smooth, aesthetically pleasing surfaces.
- Detailed Design: Adding intricate details to the design.
1.2 Engineering and Simulation
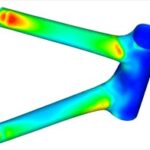
Engineers use CATIA to simulate and analyze various aspects of vehicle performance, ensuring structural integrity and safety. A study by the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) highlights the use of CATIA for finite element analysis (FEA) to optimize vehicle structures for crashworthiness. This involves:
- Structural Analysis: Evaluating the strength and durability of components.
- Crash Simulation: Simulating crash scenarios to improve safety.
- Fluid Dynamics: Analyzing airflow and aerodynamics.
1.3 Manufacturing and Tooling
CATIA facilitates the creation of manufacturing plans and tooling designs, ensuring efficient production processes. Research from the University of Michigan’s Automotive Engineering Department emphasizes the role of CATIA in creating precise tooling for automotive parts. This includes:
- Tool Design: Designing molds, dies, and fixtures.
- NC Programming: Generating numerical control programs for manufacturing machines.
- Assembly Planning: Planning the sequence of assembly operations.
1.4 Collaboration and Data Management
CATIA enables seamless collaboration among design, engineering, and manufacturing teams through robust data management capabilities. A report by the Automotive Industry Action Group (AIAG) underscores the importance of integrated data management for reducing errors and improving time-to-market.
- Product Lifecycle Management (PLM): Managing all aspects of a product’s lifecycle from concept to disposal.
- Data Exchange: Facilitating the exchange of design data with suppliers and partners.
- Version Control: Managing different versions of designs and ensuring traceability.
1.5 Key Benefits of CATIA Car Software
Here’s a quick look at the main advantages:
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Enhanced Design Quality | Enables the creation of innovative and aesthetically pleasing designs with precise surface modeling. |
| Improved Engineering Accuracy | Allows for detailed simulation and analysis, ensuring structural integrity and safety through tools like FEA and crash simulation. |
| Streamlined Manufacturing | Facilitates the creation of efficient manufacturing plans and tooling designs, optimizing production processes. |
| Better Collaboration | Supports seamless collaboration among design, engineering, and manufacturing teams with robust data management and PLM capabilities. |
| Reduced Time-to-Market | Helps reduce errors and accelerate the product development cycle through integrated data management and efficient design processes. |
| Compliance | Ensures designs meet industry standards and regulations, incorporating quality requirements and facilitating compliance checks. |
| Customization | Provides tools for customizing and automating design processes, allowing for tailored solutions that fit specific needs and improve overall efficiency. |
| Innovation | Empowers designers and engineers to explore new ideas and push the boundaries of automotive design, fostering innovation and competitive advantage. |
| Cost Reduction | Optimizes designs for cost-effectiveness, reduces material usage, and streamlines manufacturing processes, leading to significant cost savings. |
| Lifecycle Management | Manages all aspects of a product’s lifecycle, from initial concept to disposal, ensuring long-term sustainability and efficiency. |
2. What Are The Key Features of CATIA Car Software?
CATIA car software boasts a wide array of features that cater to the diverse needs of automotive design, engineering, and manufacturing. These features are designed to enhance collaboration, improve efficiency, and ensure the highest standards of quality.
2.1 Advanced Surface Modeling
CATIA provides powerful tools for creating and manipulating complex surfaces, essential for automotive design. According to a study in the International Journal of Vehicle Design, CATIA’s surface modeling capabilities enable designers to achieve the desired aesthetic and aerodynamic properties.
- Class-A Surfacing: Creating high-quality surfaces with precise control over curvature and tangency.
- Freeform Modeling: Allowing designers to sculpt and shape surfaces intuitively.
- Reverse Engineering: Converting scanned data into usable surface models.
2.2 Parametric Design
Parametric design allows engineers to create models that can be easily modified by changing parameters. Research from the University of Stuttgart highlights the use of parametric design in CATIA for optimizing vehicle components.
- Feature-Based Modeling: Creating models using features that can be easily modified.
- Design Tables: Managing different configurations of a design.
- Knowledge-Based Engineering: Automating design tasks based on predefined rules and knowledge.
2.3 Simulation and Analysis
CATIA offers a comprehensive suite of tools for simulating and analyzing vehicle performance. An article in Automotive Engineering International discusses how CATIA is used for simulating crash tests and optimizing vehicle safety.
- Finite Element Analysis (FEA): Analyzing the structural behavior of components under various loads.
- Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD): Simulating airflow around the vehicle to optimize aerodynamics.
- Multi-Body Simulation: Analyzing the dynamic behavior of vehicle systems.
2.4 Manufacturing Tools
CATIA provides tools for designing manufacturing processes and creating numerical control (NC) programs. A study by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) emphasizes the importance of integrated CAD/CAM systems for efficient manufacturing.
- Tool Design: Designing molds, dies, and fixtures for manufacturing.
- NC Programming: Generating toolpaths for CNC machines.
- Robotics Simulation: Simulating robot movements for automated manufacturing processes.
2.5 Collaboration and Data Management Tools
CATIA facilitates collaboration among design, engineering, and manufacturing teams through robust data management capabilities. A report by the Product Development and Management Association (PDMA) highlights the benefits of PLM systems for improving product development processes.
- Product Lifecycle Management (PLM): Managing all aspects of a product’s lifecycle.
- Data Exchange: Supporting various data exchange formats such as STEP and IGES.
- Version Control: Managing different versions of designs and ensuring traceability.
2.6 Summary Table of Key Features
| Feature | Description | Automotive Application |
|---|---|---|
| Advanced Surface Modeling | Creation of high-quality, precise surfaces with curvature control. | Designing exterior body panels, ensuring aesthetic appeal and aerodynamic efficiency. |
| Parametric Design | Model modification through parameter changes, feature-based modeling. | Optimizing component dimensions, managing design configurations for different vehicle models. |
| Simulation and Analysis | Analyzing structural behavior, airflow, and dynamic systems. | Evaluating crashworthiness, optimizing aerodynamics, and analyzing suspension system performance. |
| Manufacturing Tools | Designing tooling, creating NC programs, and simulating robotic movements. | Designing molds for plastic parts, generating toolpaths for machining components, and simulating assembly line operations. |
| Collaboration and Data Management | Managing product lifecycle, supporting data exchange, and controlling versions. | Facilitating data sharing between design and manufacturing teams, managing design changes, and tracking product development progress. |
| Reverse Engineering | Converting scanned data into usable surface models for redesign. | Redesigning legacy parts, creating CAD models from physical prototypes for improvement. |
| Knowledge-Based Engineering | Automating design tasks based on predefined rules. | Automating the design of standard components, ensuring compliance with engineering standards. |
3. What Are The Benefits of Using CATIA Car Software?
Using CATIA car software offers numerous benefits to automotive manufacturers and engineers, enhancing design quality, improving engineering accuracy, and streamlining manufacturing processes. These advantages lead to increased efficiency, reduced costs, and faster time-to-market.
3.1 Enhanced Design Quality
CATIA enables designers to create innovative and aesthetically pleasing car designs with precise surface modeling. According to a study by the College for Creative Studies, CATIA’s advanced surfacing tools allow for the creation of high-quality surfaces that meet the stringent requirements of automotive styling.
- Improved Aesthetics: Creating visually appealing designs that attract customers.
- Aerodynamic Optimization: Designing vehicles with low drag coefficients to improve fuel efficiency.
- Ergonomic Design: Ensuring comfortable and user-friendly interior designs.
3.2 Improved Engineering Accuracy
CATIA allows for detailed simulation and analysis, ensuring structural integrity and safety. Research from the Insurance Institute for Highway Safety (IIHS) highlights the use of CATIA for finite element analysis (FEA) to optimize vehicle structures for crashworthiness.
- Structural Integrity: Evaluating the strength and durability of components.
- Safety Performance: Simulating crash scenarios to improve safety.
- Performance Optimization: Analyzing and optimizing vehicle performance characteristics.
3.3 Streamlined Manufacturing
CATIA facilitates the creation of efficient manufacturing plans and tooling designs, optimizing production processes. A report by the Automotive Industry Action Group (AIAG) underscores the importance of integrated CAD/CAM systems for reducing errors and improving time-to-market.
- Efficient Tooling: Designing molds, dies, and fixtures that minimize material waste.
- Optimized NC Programming: Generating efficient toolpaths for CNC machines.
- Effective Assembly Planning: Planning the sequence of assembly operations to minimize production time.
3.4 Enhanced Collaboration
CATIA enables seamless collaboration among design, engineering, and manufacturing teams through robust data management capabilities. A study by the National Center for Manufacturing Sciences (NCMS) highlights the benefits of PLM systems for improving collaboration and reducing errors.
- Improved Communication: Facilitating clear communication between different departments.
- Data Sharing: Ensuring that all stakeholders have access to the latest design data.
- Concurrent Engineering: Allowing teams to work on different aspects of the design simultaneously.
3.5 Reduced Time-to-Market
By streamlining the design and manufacturing processes, CATIA helps reduce the time it takes to bring a new vehicle to market. A report by McKinsey & Company emphasizes the importance of speed-to-market in the automotive industry.
- Faster Design Cycles: Reducing the time it takes to create and refine designs.
- Efficient Manufacturing Planning: Streamlining the manufacturing process to minimize production time.
- Quick Design Changes: Facilitating rapid design changes to respond to market demands.
3.6 Summary of Benefits Table
| Benefit | Description | Impact on Automotive Industry |
|---|---|---|
| Enhanced Design Quality | Creation of innovative and aesthetically pleasing designs, optimized for aerodynamics and ergonomics. | Attracts customers with visually appealing vehicles, improves fuel efficiency, and enhances user experience. |
| Improved Engineering Accuracy | Detailed simulation and analysis ensuring structural integrity, safety, and performance optimization. | Enhances vehicle safety, improves durability, and optimizes performance characteristics. |
| Streamlined Manufacturing | Efficient tooling designs, optimized NC programming, and effective assembly planning. | Minimizes material waste, reduces production time, and improves overall manufacturing efficiency. |
| Enhanced Collaboration | Improved communication, data sharing, and concurrent engineering among design, engineering, and manufacturing teams. | Facilitates clear communication, ensures access to the latest data, and allows simultaneous work on different aspects. |
| Reduced Time-to-Market | Faster design cycles, efficient manufacturing planning, and quick design changes. | Reduces time to bring new vehicles to market, enabling faster response to market demands. |
| Cost Reduction | Optimized material usage, reduced errors, and improved efficiency in design and manufacturing processes. | Lowers production costs, minimizes waste, and enhances profitability. |
| Innovation | Enables the exploration of new ideas, fostering innovation in design and engineering. | Promotes the development of cutting-edge technologies and designs. |
4. Who Uses CATIA Car Software?
CATIA car software is used by a wide range of professionals within the automotive industry, from designers and engineers to manufacturing specialists and project managers. Its comprehensive suite of tools and capabilities makes it an indispensable asset for various roles in vehicle development and production.
4.1 Automotive Designers
Automotive designers use CATIA to create the aesthetic and ergonomic aspects of vehicle designs. According to the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), CATIA’s surface modeling tools are essential for creating visually appealing and aerodynamically efficient designs.
- Exterior Designers: Focus on the outer appearance of the vehicle, creating visually appealing designs that meet aerodynamic requirements.
- Interior Designers: Design the interior of the vehicle, ensuring comfort, functionality, and aesthetic appeal.
- Styling Designers: Work on the overall style and appearance of the vehicle, ensuring it aligns with the brand’s identity.
4.2 Automotive Engineers
Automotive engineers use CATIA to analyze and optimize the performance, safety, and structural integrity of vehicle components. A study by the University of Michigan’s Automotive Engineering Department highlights the use of CATIA for finite element analysis (FEA) to optimize vehicle structures.
- Structural Engineers: Analyze the structural integrity of vehicle components, ensuring they can withstand various loads and stresses.
- Safety Engineers: Simulate crash scenarios and optimize vehicle structures to improve safety performance.
- Performance Engineers: Analyze and optimize vehicle performance characteristics such as fuel efficiency, handling, and acceleration.
4.3 Manufacturing Specialists
Manufacturing specialists use CATIA to plan and optimize manufacturing processes, create tooling designs, and generate numerical control (NC) programs. A report by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) emphasizes the importance of integrated CAD/CAM systems for efficient manufacturing.
- Tooling Engineers: Design molds, dies, and fixtures used in the manufacturing process.
- NC Programmers: Generate toolpaths for CNC machines, ensuring efficient and accurate machining of components.
- Manufacturing Planners: Plan the sequence of manufacturing operations, optimizing production time and minimizing waste.
4.4 Project Managers
Project managers use CATIA to manage the entire product development lifecycle, from initial concept to final production. A study by the Product Development and Management Association (PDMA) highlights the benefits of PLM systems for improving project management and reducing time-to-market.
- Product Managers: Oversee the development of new vehicles, ensuring they meet market demands and customer expectations.
- Engineering Managers: Manage engineering teams, ensuring projects are completed on time and within budget.
- Program Managers: Coordinate multiple projects, ensuring they align with the overall business strategy.
4.5 Table of CATIA Users and Their Roles
| User Group | Role | CATIA Application |
|---|---|---|
| Automotive Designers | Create aesthetic and ergonomic vehicle designs. | Use surface modeling tools to design exterior and interior components, ensuring visual appeal and aerodynamic efficiency. |
| Automotive Engineers | Analyze and optimize vehicle performance, safety, and structural integrity. | Use FEA to analyze structural integrity, simulate crash scenarios to improve safety, and optimize performance characteristics like fuel efficiency. |
| Manufacturing Specialists | Plan and optimize manufacturing processes, create tooling designs, and generate NC programs. | Design molds, dies, and fixtures for manufacturing, generate toolpaths for CNC machines, and plan the sequence of manufacturing operations to optimize production time. |
| Project Managers | Manage the entire product development lifecycle from concept to production. | Use PLM systems to manage project timelines, budgets, and resources, ensuring projects are completed on time and within budget. |
| Quality Control Engineers | Ensure designs meet industry standards and regulations. | Use CATIA to check designs for compliance with industry standards, conduct quality inspections, and identify potential issues. |
| Research and Development Teams | Develop new technologies and innovations in automotive design. | Use CATIA to explore new design concepts, simulate advanced technologies, and develop innovative solutions for improving vehicle performance and efficiency. |
5. How to Learn CATIA Car Software Effectively?
Learning CATIA car software effectively requires a combination of formal training, hands-on practice, and continuous learning. Whether you’re a student, a working professional, or simply someone interested in automotive design, there are several strategies you can employ to master CATIA.
5.1 Formal Training Courses
Enrolling in formal training courses is one of the most effective ways to learn CATIA. These courses are typically offered by educational institutions, training centers, and Dassault Systèmes authorized partners.
- Educational Institutions: Universities and colleges often offer courses in CAD and CAE that cover CATIA. For example, the University of Michigan offers courses in automotive engineering that include CATIA training.
- Training Centers: Specialized training centers provide intensive courses focused specifically on CATIA. These centers often offer certifications upon completion of the course.
- Dassault Systèmes Training: Dassault Systèmes, the maker of CATIA, offers a range of training programs designed to help users master the software. These programs include online courses, instructor-led training, and customized training solutions.
5.2 Online Resources
Numerous online resources are available to help you learn CATIA at your own pace. These resources include tutorials, videos, and online communities where you can ask questions and get help from experienced users.
- YouTube Tutorials: Many experienced CATIA users upload tutorials on YouTube, covering a wide range of topics from basic modeling to advanced simulation techniques.
- Online Courses: Platforms like Coursera, Udemy, and edX offer CATIA courses taught by industry experts. These courses often include hands-on exercises and projects.
- Online Communities: Forums and online communities dedicated to CATIA provide a platform for users to share knowledge, ask questions, and collaborate on projects.
5.3 Hands-On Practice
Hands-on practice is essential for mastering CATIA. The more you use the software, the more comfortable you will become with its features and capabilities.
- Personal Projects: Work on personal projects that challenge you to use CATIA in different ways. For example, you could try modeling a car, designing a mechanical component, or simulating a structural analysis.
- Internships: Internships in automotive companies provide valuable experience using CATIA in a real-world setting. You’ll have the opportunity to work on actual projects and learn from experienced professionals.
- Practice Exercises: Complete practice exercises and tutorials to reinforce what you have learned. Many online resources offer practice exercises that you can use to test your knowledge and skills.
5.4 Collaboration and Networking
Collaborating with other CATIA users and networking with professionals in the automotive industry can provide valuable learning opportunities.
- Join User Groups: Join CATIA user groups to connect with other users, share knowledge, and learn about new features and techniques.
- Attend Industry Events: Attend industry events such as conferences and trade shows to network with professionals in the automotive industry and learn about the latest trends and technologies.
- Participate in Online Communities: Participate in online communities to ask questions, share your knowledge, and collaborate on projects.
5.5 Continuous Learning
CATIA is a constantly evolving software, so it’s important to stay up-to-date with the latest features and techniques.
- Read Documentation: Read the official CATIA documentation to learn about new features and capabilities.
- Follow Industry Blogs: Follow industry blogs and publications to stay informed about the latest trends and technologies in automotive design and engineering.
- Take Advanced Courses: Take advanced courses to learn about specialized topics such as advanced surface modeling, simulation, and manufacturing.
5.6 Summary Table of Learning Strategies
| Strategy | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Formal Training Courses | Enrolling in courses offered by educational institutions, training centers, or Dassault Systèmes. | Structured learning, expert instruction, certifications, and in-depth knowledge of CATIA features. |
| Online Resources | Utilizing online tutorials, videos, and communities to learn at your own pace. | Flexible learning schedule, access to a wide range of topics, cost-effective, and community support. |
| Hands-On Practice | Working on personal projects, internships, and practice exercises. | Real-world experience, practical skills development, enhanced problem-solving abilities, and application of theoretical knowledge. |
| Collaboration and Networking | Joining user groups, attending industry events, and participating in online communities. | Knowledge sharing, networking opportunities, exposure to new ideas, and collaboration on projects. |
| Continuous Learning | Reading documentation, following industry blogs, and taking advanced courses. | Staying up-to-date with the latest features and techniques, expanding knowledge in specialized areas, and enhancing professional development. |
| Mentorship | Seeking guidance from experienced CATIA users or professionals in the automotive industry. | Personalized advice, career guidance, insights into industry practices, and accelerated learning through direct interaction with experts. |
6. CATIA Car Software and Remote Automotive Repair
CATIA car software, while primarily used for design and engineering, plays a crucial role in enabling and enhancing remote automotive repair services. By providing detailed 3D models and simulations, CATIA allows remote technicians to diagnose and guide repairs with greater precision and efficiency.
6.1 Detailed 3D Models for Remote Diagnosis
CATIA’s detailed 3D models provide remote technicians with a comprehensive view of vehicle components and systems. This allows them to identify potential issues and guide on-site technicians through the repair process with greater accuracy.
- Visualizing Complex Systems: CATIA models enable technicians to visualize complex systems such as engines, transmissions, and electrical systems, making it easier to diagnose problems remotely.
- Identifying Component Locations: Technicians can quickly identify the location of specific components within the vehicle, reducing the time it takes to diagnose and repair issues.
- Guiding Repair Procedures: Remote technicians can use CATIA models to guide on-site technicians through repair procedures, ensuring that repairs are performed correctly and efficiently.
6.2 Simulation for Troubleshooting
CATIA’s simulation capabilities allow remote technicians to simulate various scenarios and troubleshoot problems remotely. This can be particularly useful for diagnosing intermittent issues or complex system failures.
- Simulating System Behavior: Technicians can simulate the behavior of vehicle systems under different conditions, helping them to identify the root cause of problems.
- Testing Repair Solutions: Remote technicians can test potential repair solutions in a virtual environment before implementing them on the actual vehicle, reducing the risk of further damage or complications.
- Analyzing Data Remotely: CATIA allows technicians to analyze data collected from vehicle sensors and diagnostic tools remotely, helping them to identify potential issues and monitor the effectiveness of repairs.
6.3 Collaboration and Communication
CATIA facilitates collaboration and communication between remote technicians and on-site personnel, ensuring that repairs are performed efficiently and effectively.
- Real-Time Communication: Remote technicians can communicate with on-site personnel in real-time using video conferencing and screen sharing tools, allowing them to provide guidance and support throughout the repair process.
- Data Sharing: CATIA allows technicians to share design data, diagnostic information, and repair procedures with on-site personnel, ensuring that everyone has access to the latest information.
- Remote Assistance: Remote technicians can use CATIA to provide remote assistance to on-site personnel, guiding them through complex repair procedures and troubleshooting problems.
6.4 Improving Efficiency and Reducing Downtime
By enabling remote diagnosis and repair, CATIA helps improve efficiency and reduce downtime for automotive repair services.
- Faster Diagnosis: Remote technicians can diagnose problems more quickly and accurately, reducing the time it takes to identify and resolve issues.
- Reduced Travel Costs: Remote repair services eliminate the need for technicians to travel to the vehicle location, reducing travel costs and improving efficiency.
- Increased Productivity: Remote technicians can support multiple on-site teams simultaneously, increasing productivity and improving overall efficiency.
6.5 Table Summarizing CATIA’s Role in Remote Repair
| Application | Description | Benefits for Remote Repair |
|---|---|---|
| Detailed 3D Models | Provides comprehensive views of vehicle components and systems. | Enables accurate remote diagnosis, quick identification of component locations, and guidance on repair procedures. |
| Simulation Capabilities | Allows remote technicians to simulate scenarios and troubleshoot problems remotely. | Facilitates diagnosis of intermittent issues, testing of repair solutions in a virtual environment, and remote analysis of vehicle data. |
| Collaboration and Communication | Facilitates real-time communication, data sharing, and remote assistance. | Ensures efficient and effective collaboration between remote and on-site personnel, providing guidance and support throughout the repair process. |
| Efficiency and Downtime Reduction | Improves diagnostic speed, reduces travel costs, and increases productivity. | Reduces time to identify and resolve issues, eliminates travel expenses, and allows remote technicians to support multiple on-site teams. |
| Training and Education | Used in training programs to educate technicians on vehicle systems and repair procedures. | Enhances the skills of remote technicians, ensuring they are proficient in diagnosing and resolving issues remotely. |
7. Examples of CATIA Car Software in Automotive Companies
Many leading automotive companies worldwide use CATIA car software to design, engineer, and manufacture their vehicles. These companies leverage CATIA’s advanced capabilities to improve design quality, enhance engineering accuracy, and streamline manufacturing processes. Here are some notable examples:
7.1 General Motors
General Motors (GM) uses CATIA extensively for vehicle design, engineering, and manufacturing. According to a case study by Dassault Systèmes, GM uses CATIA to create detailed 3D models of its vehicles, simulate crash tests, and optimize manufacturing processes.
- Vehicle Design: GM designers use CATIA to create innovative and aesthetically pleasing designs for their vehicles.
- Engineering Analysis: GM engineers use CATIA to analyze the structural integrity and safety performance of vehicle components.
- Manufacturing Planning: GM manufacturing specialists use CATIA to plan and optimize manufacturing processes, reducing production time and minimizing waste.
7.2 Ford Motor Company
Ford Motor Company uses CATIA to design and engineer its vehicles, focusing on improving fuel efficiency, safety, and performance. An article in Automotive Engineering International highlights Ford’s use of CATIA for computational fluid dynamics (CFD) to optimize vehicle aerodynamics.
- Aerodynamic Design: Ford engineers use CATIA to simulate airflow around vehicles and optimize designs for improved fuel efficiency.
- Structural Analysis: Ford engineers use CATIA to analyze the structural integrity of vehicle components and ensure they can withstand various loads and stresses.
- Virtual Prototyping: Ford uses CATIA to create virtual prototypes of vehicles, allowing them to test and refine designs before building physical prototypes.
7.3 BMW Group
BMW Group uses CATIA to design and engineer its vehicles, focusing on innovation and performance. According to a report by the BMW Group, CATIA is used to create detailed 3D models of vehicle components, simulate crash tests, and optimize manufacturing processes.
- Design Innovation: BMW designers use CATIA to create innovative and aesthetically pleasing designs for their vehicles, incorporating cutting-edge technologies and materials.
- Performance Optimization: BMW engineers use CATIA to optimize vehicle performance characteristics such as handling, acceleration, and braking.
- Manufacturing Efficiency: BMW manufacturing specialists use CATIA to plan and optimize manufacturing processes, reducing production time and minimizing waste.
7.4 Toyota Motor Corporation
Toyota Motor Corporation uses CATIA to design and engineer its vehicles, focusing on quality, reliability, and efficiency. According to a case study by Toyota, CATIA is used to create detailed 3D models of vehicle components, simulate crash tests, and optimize manufacturing processes.
- Quality Assurance: Toyota engineers use CATIA to check designs for compliance with industry standards and regulations, ensuring the highest levels of quality and reliability.
- Efficiency Optimization: Toyota engineers use CATIA to optimize vehicle designs for improved fuel efficiency, reducing emissions and minimizing environmental impact.
- Manufacturing Excellence: Toyota manufacturing specialists use CATIA to plan and optimize manufacturing processes, ensuring efficient and cost-effective production.
7.5 Table of Automotive Companies Using CATIA
| Company | CATIA Application | Benefits Achieved |
|---|---|---|
| General Motors | Vehicle design, engineering analysis, manufacturing planning. | Improved design quality, enhanced safety performance, and streamlined manufacturing processes. |
| Ford Motor Company | Aerodynamic design, structural analysis, virtual prototyping. | Enhanced fuel efficiency, improved structural integrity, and reduced time-to-market. |
| BMW Group | Design innovation, performance optimization, manufacturing efficiency. | Innovative designs, optimized performance characteristics, and efficient manufacturing processes. |
| Toyota Motor Corporation | Quality assurance, efficiency optimization, manufacturing excellence. | High levels of quality and reliability, improved fuel efficiency, and cost-effective production. |
| Tesla | Electric vehicle design, battery system engineering, manufacturing process optimization. | Accelerated innovation, improved battery performance, and streamlined production of electric vehicles. |
8. What Are The Alternatives To CATIA Car Software?
While CATIA car software is a leading solution for automotive design, engineering, and manufacturing, several alternatives offer similar capabilities and benefits. These alternatives cater to different needs, budgets, and preferences, providing automotive companies with a range of options for their CAD, CAE, and CAM requirements.
8.1 Siemens NX
Siemens NX is a comprehensive CAD/CAM/CAE software suite used in various industries, including automotive. It offers advanced modeling, simulation, and manufacturing capabilities, making it a strong competitor to CATIA. According to Siemens, NX enables companies to streamline product development processes and reduce time-to-market.
- Advanced Modeling: NX provides powerful tools for creating and manipulating complex 3D models, including parametric modeling, direct modeling, and surface modeling.
- Simulation and Analysis: NX offers a comprehensive suite of simulation tools for analyzing structural behavior, thermal performance, and fluid dynamics.
- Manufacturing Solutions: NX provides tools for designing manufacturing processes, creating tooling designs, and generating numerical control (NC) programs.
8.2 Autodesk AutoCAD
Autodesk AutoCAD is a widely used CAD software known for its versatility and ease of use. While not specifically designed for the automotive industry, AutoCAD can be used for various automotive design and drafting tasks. According to Autodesk, AutoCAD is used by millions of professionals worldwide for creating precise 2D and 3D drawings.
- 2D Drafting: AutoCAD provides tools for creating precise 2D drawings, including floor plans, elevations, and sections.
- 3D Modeling: AutoCAD offers basic 3D modeling capabilities, allowing users to create simple 3D models of vehicle components.
- Customization: AutoCAD can be customized with add-ons and extensions to meet the specific needs of automotive designers and engineers.
8.3 SolidWorks
SolidWorks is a popular 3D CAD software known for its ease of use and comprehensive feature set. It is widely used in the automotive industry for designing and engineering vehicle components, tooling, and manufacturing equipment. According to Dassault Systèmes, SolidWorks enables companies to accelerate product development and improve quality.
- 3D CAD: SolidWorks provides powerful tools for creating and manipulating complex 3D models, including parametric modeling, direct modeling, and surface modeling.
- Simulation: SolidWorks offers simulation tools for analyzing structural behavior, thermal performance, and fluid dynamics.
- Manufacturing: SolidWorks provides tools for designing manufacturing processes, creating tooling designs, and generating numerical control (NC) programs.
8.4 PTC Creo
PTC Creo is a CAD/CAM/CAE software suite used in various industries, including automotive. It offers advanced modeling, simulation, and manufacturing capabilities, making it a strong competitor to CATIA. According to PTC, Creo enables companies to design, analyze, and manufacture products faster and more efficiently.
- Parametric Modeling: Creo provides powerful tools for creating and manipulating complex 3D models using parametric modeling techniques.
- Simulation and Analysis: Creo offers a comprehensive suite of simulation tools for analyzing structural behavior, thermal performance, and fluid dynamics.
- Manufacturing Solutions: Creo provides tools for designing manufacturing processes, creating tooling designs, and generating numerical control (NC) programs.
8.5 Table of Alternatives to CATIA
| Software | Description | Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|