Data software tools for healthcare OpenEpi are invaluable for those aiming to enhance their auto repair skills and explore remote diagnostics in the US. At CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN, we provide the resources and training necessary to master these essential instruments. Discover how to leverage data software and epidemiological tools to excel in remote vehicle diagnostics, enhancing your expertise in vehicle maintenance, and staying competitive in the automotive repair industry.
Contents
- 1. What is OpenEpi and Why is it Important for Healthcare Data Analysis?
- 2. What are the Key Features of OpenEpi that Make it Useful for Epidemiological Analysis?
- Key Features of OpenEpi:
- 3. How Can OpenEpi be Used to Analyze and Interpret Healthcare Data Effectively?
- Steps to Effectively Use OpenEpi for Healthcare Data Analysis:
- 4. What Types of Statistical Analyses Can be Performed Using OpenEpi?
- Comprehensive List of Statistical Analyses in OpenEpi:
- 5. What are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Using OpenEpi for Healthcare Data Analysis?
- Advantages of Using OpenEpi:
- Disadvantages of Using OpenEpi:
- 6. How Does OpenEpi Compare to Other Statistical Software Packages Used in Healthcare?
- Comparison of OpenEpi with Other Statistical Software Packages:
- Summary Table:
- 7. What Specific Healthcare Scenarios Would Benefit Most from Using OpenEpi?
- Specific Healthcare Scenarios Benefiting from OpenEpi:
- 8. Are There any Limitations to Consider When Using OpenEpi in Healthcare Data Analysis?
- Key Limitations to Consider When Using OpenEpi:
- 9. How Can I Get Started with Using OpenEpi for Analyzing Healthcare Data?
- Step-by-Step Guide to Getting Started with OpenEpi:
- 10. Where Can I Find Resources and Training Materials for Learning to Use OpenEpi Effectively?
- Comprehensive List of Resources and Training Materials for OpenEpi:
1. What is OpenEpi and Why is it Important for Healthcare Data Analysis?
OpenEpi is a free, web-based, open-source software used for epidemiological statistics, making it invaluable for healthcare data analysis. OpenEpi is a suite of programs intended for use in public health and medicine. It provides a number of epidemiological and statistical tools for summary data. The importance of OpenEpi lies in its accessibility and utility for training and practice in public health.
- Accessibility: OpenEpi is free and web-based, removing financial and hardware barriers to access.
- Ease of Use: The program is designed to be user-friendly, requiring no programming experience.
- Comprehensive Tools: OpenEpi provides a range of statistical and epidemiological tools, including confidence intervals, two-by-two tables, and sample size calculations.
- Educational Value: It is utilized in various universities for teaching epidemiology.
- Global Impact: OpenEpi has a broad reach, with users in over 160 countries.
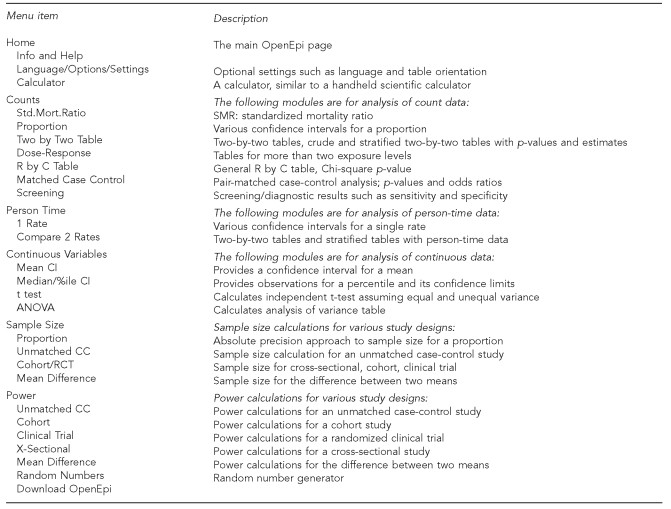
2. What are the Key Features of OpenEpi that Make it Useful for Epidemiological Analysis?
OpenEpi boasts key features that greatly aid epidemiological analysis, including a range of statistical calculations and tools for data interpretation. These features empower healthcare professionals and researchers to efficiently analyze data and derive meaningful insights.
Key Features of OpenEpi:
-
Confidence Intervals: OpenEpi offers various confidence intervals for proportions, rates, standard mortality ratio, mean, median, and percentiles. These calculations help in assessing the reliability of statistical estimates.
-
Two-by-Two Tables: It handles both crude and stratified two-by-two tables for count and rate data, which are essential for analyzing associations between exposures and outcomes.
-
Matched Case-Control Analysis: This feature supports matched case-control studies, a critical design for investigating disease outbreaks and risk factors.
-
Test for Trend: OpenEpi includes a test for trend with count data, valuable for examining dose-response relationships.
-
Independent t-test and ANOVA: These statistical tests help compare means across different groups, facilitating the identification of significant differences.
-
Diagnostic and Screening Test Analyses: OpenEpi supports diagnostic and screening test analyses with Receiving Operator Characteristic (ROC) curves, crucial for evaluating the performance of diagnostic tests.
-
Sample Size and Power Calculations: The software assists in sample size determination for various study designs (proportions, cross-sectional surveys, case-control, cohort, randomized controlled trials) and power calculations for proportions and comparisons of two means, ensuring studies are adequately powered.
-
Random Number Generator: A random number generator is included for randomization in clinical trials and other research designs.
-
Etiologic and Prevented Fraction Estimates: OpenEpi provides estimates for the etiologic or prevented fraction in the population and exposed, with confidence intervals, based on risk, odds, or rate data.
-
Odds Ratio Calculations: The software calculates the cross-product and maximum likelihood odds ratio estimates, along with mid-p and exact p-values and confidence limits for the odds ratio.
-
Rate Ratios and Rate Differences: Calculations of rate ratios and rate differences with confidence intervals and statistical tests are included, essential for analyzing incidence data.
-
Mantel-Haenszel Estimates: For stratified two-by-two tables with count data, OpenEpi provides Mantel-Haenszel and precision-based estimates of the risk ratio and odds ratio.
-
Adjusted Risk Difference: It includes a precision-based adjusted risk difference, aiding in understanding the impact of exposures on health outcomes.
-
Tests for Interaction: OpenEpi offers tests for interaction for the risk ratio, odds ratio, and risk difference, helping to identify effect modification.
-
Confidence Limit Methods: It provides four different confidence limit methods for the odds ratio, enhancing the robustness of the analysis.
 OpenEpiMenu
OpenEpiMenu
3. How Can OpenEpi be Used to Analyze and Interpret Healthcare Data Effectively?
OpenEpi can be effectively used to analyze and interpret healthcare data through its comprehensive suite of statistical tools. By leveraging these features, healthcare professionals can gain valuable insights into disease patterns, risk factors, and the effectiveness of interventions.
Steps to Effectively Use OpenEpi for Healthcare Data Analysis:
-
Data Entry and Preparation:
- Start by entering your healthcare data into OpenEpi. Ensure that the data is properly formatted and cleaned. This may involve checking for missing values, correcting errors, and categorizing variables appropriately.
-
Descriptive Statistics:
- Use OpenEpi to calculate descriptive statistics such as means, medians, standard deviations, and percentiles. These statistics provide a basic understanding of the distribution of your data.
-
Two-by-Two Table Analysis:
- For categorical data, use two-by-two tables to analyze the relationship between exposures and outcomes. OpenEpi can calculate risk ratios, odds ratios, and their confidence intervals, helping you assess the strength of associations.
-
Stratified Analysis:
- If you suspect confounding, perform stratified analysis using OpenEpi. This involves dividing your data into subgroups based on a potential confounder and then analyzing the relationship between exposure and outcome within each subgroup.
-
Test for Trend:
- If you have ordinal data (e.g., disease severity), use the test for trend to determine if there is a dose-response relationship.
-
Confidence Intervals:
- Calculate confidence intervals for your estimates to assess the precision of your results. OpenEpi provides various methods for calculating confidence intervals, allowing you to choose the most appropriate one for your data.
-
Diagnostic Test Evaluation:
- If you are evaluating a diagnostic test, use OpenEpi to calculate sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, and negative predictive value. You can also generate ROC curves to assess the overall performance of the test.
-
Sample Size and Power Calculations:
- Before conducting a study, use OpenEpi to perform sample size and power calculations. This will help you determine the number of participants needed to detect a statistically significant effect.
-
Interpretation of Results:
- Carefully interpret the results of your analysis. Consider the limitations of your data and the potential for bias. Draw conclusions that are supported by the evidence.
-
Visualization:
- Create graphs and charts to visualize your data. OpenEpi does not have extensive visualization capabilities, so you may need to use other software for this purpose.
-
Documentation:
- Document your analysis thoroughly. This includes describing your data sources, methods, and results. Good documentation is essential for reproducibility and transparency.
-
Continuous Learning:
- Stay updated with the latest features and updates of OpenEpi. As an open-source tool, it evolves over time, and new functionalities may be added.
 OpenEpi
OpenEpi
- Stay updated with the latest features and updates of OpenEpi. As an open-source tool, it evolves over time, and new functionalities may be added.
4. What Types of Statistical Analyses Can be Performed Using OpenEpi?
OpenEpi supports a wide array of statistical analyses that are crucial for epidemiological and public health research. These analyses range from basic descriptive statistics to more advanced methods for assessing associations and making inferences.
Comprehensive List of Statistical Analyses in OpenEpi:
-
Descriptive Statistics:
- Measures of Central Tendency: Mean, median, mode.
- Measures of Dispersion: Standard deviation, variance, range, interquartile range.
- Frequencies and Proportions: For categorical variables.
-
Confidence Intervals:
- For Proportions: Wilson score interval, Clopper-Pearson interval.
- For Means: t-intervals.
- For Rates: Based on Poisson distribution.
- For Standardized Mortality Ratio (SMR).
-
Two-by-Two Table Analysis:
- Crude and Stratified Tables: For count and rate data.
- Risk Ratio (RR): With confidence intervals.
- Odds Ratio (OR): With confidence intervals (cross-product, maximum likelihood).
- Rate Ratio and Rate Difference: With confidence intervals and statistical tests.
- Etiologic and Prevented Fraction: In the population and exposed.
- p-values: Mid-p, exact p-values.
-
Matched Case-Control Analysis:
- McNemar’s Test: For paired categorical data.
- Conditional Logistic Regression: For more complex models.
-
Test for Trend:
- Cochran-Armitage Test: For trend in proportions.
- Mantel Extension Test: For ordinal data.
-
Independent t-test and One-Way ANOVA:
- t-test: For comparing means of two independent groups.
- ANOVA: For comparing means of more than two independent groups.
- Post-hoc Tests: For pairwise comparisons (e.g., Tukey’s HSD).
-
Diagnostic and Screening Test Analyses:
- Sensitivity, Specificity, Positive Predictive Value (PPV), Negative Predictive Value (NPV).
- Likelihood Ratios: Positive and negative likelihood ratios.
- ROC Curves: Analysis of test performance.
-
Sample Size and Power Calculations:
- For Proportions: Cross-sectional surveys, unmatched case-control, cohort studies, randomized controlled trials.
- For Means: Comparison of two means.
-
Mantel-Haenszel Statistics:
- Adjusted Risk Ratio and Odds Ratio: For stratified data.
- Tests for Interaction: For effect modification.
-
Regression Analysis (Prototype Modules):
- Logistic Regression: For binary outcomes.
- Survival Analysis: For time-to-event data (available in prototype).
-
Other Statistical Tools:
- Random Number Generator.
- Chi-Square Test: For categorical data.
- Fisher’s Exact Test: For small sample sizes in two-by-two tables.
- Standardized Mortality Ratio (SMR): For comparing mortality rates.
5. What are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Using OpenEpi for Healthcare Data Analysis?
When considering OpenEpi for healthcare data analysis, it is crucial to weigh its advantages and disadvantages. OpenEpi is a free, web-based, open-source statistical software designed for use in public health and medicine.
Advantages of Using OpenEpi:
-
Cost-Effective:
- Free of Charge: One of the most significant advantages is that OpenEpi is completely free, making it accessible to users who may not have the budget for commercial software like SAS or SPSS.
-
Accessibility:
- Web-Based: As a web-based tool, OpenEpi can be accessed from any computer with an internet connection. This eliminates the need for installation and allows for easy collaboration among users in different locations.
-
Ease of Use:
- User-Friendly Interface: OpenEpi is designed to be user-friendly, with a straightforward interface that is easy to navigate, even for those with limited statistical experience.
- No Programming Required: Users can perform analyses without needing to write code, making it accessible to a broader audience.
-
Comprehensive Statistical Tools:
- Wide Range of Analyses: OpenEpi offers a variety of statistical tests and functions, including descriptive statistics, confidence intervals, two-by-two tables, stratified analysis, and sample size calculations.
-
Educational Value:
- Training and Teaching: OpenEpi is widely used in educational settings for teaching epidemiology and biostatistics. Its simplicity and accessibility make it an excellent tool for students.
-
Open Source:
- Customizable: As an open-source software, OpenEpi can be customized and modified to meet specific needs. The source code is freely available, allowing developers to contribute to its improvement.
-
Cross-Platform Compatibility:
- Operating System Independent: OpenEpi is compatible with various operating systems, including Windows, macOS, and Linux, as long as the user has a web browser.
Disadvantages of Using OpenEpi:
-
Limited Advanced Features:
- Basic Analyses: OpenEpi primarily focuses on basic epidemiological and statistical analyses. It may not be suitable for complex statistical modeling or advanced data manipulation.
-
No Data Management Capabilities:
- Data Input: OpenEpi lacks robust data management capabilities. Users may need to prepare and clean their data in other software (e.g., Excel) before importing it into OpenEpi.
-
No Automation or Scripting:
- Repetitive Tasks: OpenEpi does not support scripting or automation of analyses, which can be time-consuming if you need to perform the same analysis on multiple datasets.
-
Web-Based Limitations:
- Internet Dependency: As a web-based tool, OpenEpi requires an internet connection to function. This can be a limitation in areas with poor or unreliable internet access.
- Security Concerns: Web-based applications may raise security concerns, especially when dealing with sensitive healthcare data.
-
Limited Visualization:
- Basic Graphics: OpenEpi offers limited graphical capabilities for visualizing data. Users may need to export their results to other software for creating more sophisticated charts and graphs.
-
Support and Updates:
- Community Support: While OpenEpi is open-source, support is primarily community-based, which may not be as responsive or comprehensive as commercial software support.
- Infrequent Updates: Updates and new features may be less frequent compared to commercial software, as development depends on volunteer efforts.
-
Not Suitable for Large Datasets:
- Performance: OpenEpi may not perform as efficiently with very large datasets compared to desktop-based statistical software.
6. How Does OpenEpi Compare to Other Statistical Software Packages Used in Healthcare?
OpenEpi offers a unique position in the landscape of statistical software used in healthcare, particularly when compared to other popular packages like SAS, SPSS, and R. Each of these tools has its own strengths and weaknesses, making them suitable for different types of users and analytical tasks.
Comparison of OpenEpi with Other Statistical Software Packages:
-
OpenEpi:
- Cost: Free
- Accessibility: Web-based
- Ease of Use: Very user-friendly, no programming required
- Statistical Capabilities: Basic epidemiological and statistical analyses
- Data Management: Limited
- Visualization: Basic
- Best For: Students, public health practitioners in low-resource settings, quick and simple analyses
-
SAS (Statistical Analysis System):
- Cost: Expensive (commercial license)
- Accessibility: Desktop-based
- Ease of Use: Requires programming knowledge (SAS language)
- Statistical Capabilities: Comprehensive, advanced statistical modeling, and machine learning
- Data Management: Excellent, can handle large and complex datasets
- Visualization: Good, with advanced graphics options
- Best For: Large organizations, complex statistical analyses, data mining, and predictive modeling
-
SPSS (Statistical Package for the Social Sciences):
- Cost: Moderate (commercial license)
- Accessibility: Desktop-based
- Ease of Use: User-friendly interface, but some programming knowledge is helpful (syntax)
- Statistical Capabilities: Wide range of statistical analyses, commonly used in social sciences and healthcare
- Data Management: Good, with data transformation and cleaning tools
- Visualization: Good, with a variety of chart types
- Best For: Researchers, academics, and analysts in social sciences and healthcare for statistical analysis and reporting
-
R:
- Cost: Free (open source)
- Accessibility: Desktop-based
- Ease of Use: Requires programming knowledge (R language)
- Statistical Capabilities: Highly comprehensive, with a vast library of packages for specialized analyses
- Data Management: Flexible, but requires coding skills
- Visualization: Excellent, with highly customizable graphics
- Best For: Statisticians, data scientists, and researchers who need advanced statistical modeling, data visualization, and custom analyses
Summary Table:
| Feature | OpenEpi | SAS | SPSS | R |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cost | Free | Expensive | Moderate | Free |
| Accessibility | Web-based | Desktop-based | Desktop-based | Desktop-based |
| Ease of Use | Very User-Friendly | Requires Programming | User-Friendly/Syntax | Requires Programming |
| Statistical Capabilities | Basic | Comprehensive | Wide Range | Highly Comprehensive |
| Data Management | Limited | Excellent | Good | Flexible |
| Visualization | Basic | Good | Good | Excellent |
| Best For | Students/Low-Resource | Large Organizations | Researchers/Academics | Statisticians/Scientists |
7. What Specific Healthcare Scenarios Would Benefit Most from Using OpenEpi?
OpenEpi is particularly beneficial in a variety of healthcare scenarios, especially where resources are limited, and quick, accessible statistical analysis is needed. Its user-friendly interface and web-based accessibility make it a valuable tool for healthcare professionals in diverse settings.
Specific Healthcare Scenarios Benefiting from OpenEpi:
-
Outbreak Investigations:
- Scenario: Investigating a sudden increase in cases of a disease in a community.
- How OpenEpi Helps: OpenEpi can quickly analyze case data, calculate attack rates, and identify potential risk factors through two-by-two table analysis and stratified analysis. Its ease of use allows public health officials to respond rapidly.
-
Community Health Assessments:
- Scenario: Conducting a survey to assess the health needs and behaviors of a local population.
- How OpenEpi Helps: OpenEpi can analyze survey data to calculate prevalence rates of health conditions, identify health disparities, and prioritize interventions. Its sample size calculation tools are useful for planning the survey.
-
Evaluating Screening Programs:
- Scenario: Assessing the effectiveness of a screening program for a disease like breast cancer or diabetes.
- How OpenEpi Helps: OpenEpi can calculate sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, and negative predictive value to evaluate the performance of the screening test. ROC curve analysis can help optimize screening thresholds.
-
Monitoring and Evaluation of Interventions:
- Scenario: Evaluating the impact of a public health intervention, such as a smoking cessation program.
- How OpenEpi Helps: OpenEpi can compare outcomes between intervention and control groups using t-tests or chi-square tests. It can also calculate risk ratios or odds ratios to measure the effect of the intervention.
-
Health Education and Training:
- Scenario: Teaching epidemiology and biostatistics to students or training healthcare workers.
- How OpenEpi Helps: OpenEpi’s user-friendly interface and web-based accessibility make it an excellent tool for hands-on training. Students can easily perform statistical analyses and focus on interpreting the results.
-
Research in Low-Resource Settings:
- Scenario: Conducting health research in areas with limited access to resources and technology.
- How OpenEpi Helps: OpenEpi’s free cost and minimal system requirements make it accessible in low-resource settings. It can be used to analyze data from surveys, observational studies, and small-scale interventions.
-
Infectious Disease Surveillance:
- Scenario: Monitoring the incidence and prevalence of infectious diseases.
- How OpenEpi Helps: OpenEpi can analyze surveillance data to identify trends, detect outbreaks, and evaluate the impact of control measures. Its ability to calculate confidence intervals for rates and proportions is particularly useful.
-
Occupational Health Studies:
- Scenario: Investigating the relationship between workplace exposures and health outcomes.
- How OpenEpi Helps: OpenEpi can analyze data from occupational health studies to calculate risk ratios or odds ratios for specific exposures. Stratified analysis can help control for confounding factors.
8. Are There any Limitations to Consider When Using OpenEpi in Healthcare Data Analysis?
While OpenEpi is a valuable tool for healthcare data analysis, it’s essential to be aware of its limitations to ensure appropriate use and interpretation of results. These limitations primarily stem from its focus on basic epidemiological and statistical analyses and its web-based nature.
Key Limitations to Consider When Using OpenEpi:
-
Limited Advanced Statistical Capabilities:
- Complex Modeling: OpenEpi is not designed for complex statistical modeling, such as multivariate regression, time series analysis, or advanced survival analysis. For these types of analyses, more sophisticated software like SAS, SPSS, or R would be more appropriate.
-
Data Management Constraints:
- Data Cleaning and Transformation: OpenEpi lacks robust data management features. Users may need to rely on other software (e.g., Excel) for data cleaning, transformation, and manipulation before importing data into OpenEpi.
-
Visualization Limitations:
- Basic Graphics: OpenEpi’s graphical capabilities are limited. It can produce basic charts and graphs, but users who need more sophisticated visualizations may need to export data to other software like R, Python, or Tableau.
-
Web-Based Dependency:
- Internet Connection: As a web-based tool, OpenEpi requires a stable internet connection, which may be a limitation in areas with poor or unreliable internet access.
- Data Security: Users should be cautious when using OpenEpi with sensitive healthcare data, as web-based applications may pose security risks.
-
No Automation or Scripting:
- Repetitive Tasks: OpenEpi does not support scripting or automation, which can be time-consuming when performing the same analysis on multiple datasets.
-
Support and Updates:
- Community Support: Support for OpenEpi is primarily community-based, which may not be as responsive or comprehensive as commercial software support.
- Infrequent Updates: Updates and new features may be less frequent compared to commercial software, as development depends on volunteer efforts.
-
Large Dataset Performance:
- Processing Speed: OpenEpi may not perform as efficiently with very large datasets compared to desktop-based statistical software.
-
Lack of Integration with Other Tools:
- Data Transfer: OpenEpi does not seamlessly integrate with other healthcare data systems or electronic health records (EHRs). Data transfer may require manual export and import processes.
-
Limited Customization:
- Flexibility: While OpenEpi is open-source, customization options may be limited compared to software like R, which allows users to create custom functions and packages.
9. How Can I Get Started with Using OpenEpi for Analyzing Healthcare Data?
Getting started with OpenEpi for analyzing healthcare data is straightforward, thanks to its user-friendly interface and web-based accessibility. Follow these steps to begin using OpenEpi effectively:
Step-by-Step Guide to Getting Started with OpenEpi:
-
Access OpenEpi:
- Website: Open your web browser and go to the OpenEpi website (www.openepi.com).
-
Explore the Interface:
- Main Menu: Familiarize yourself with the main menu, which includes options for various statistical analyses such as “Proportions,” “Two by Two Table,” “Means,” and “Sample Size.”
- Navigation: Click on each menu item to see the available tools and options.
-
Choose a Module:
- Select Analysis: Based on your research question and data, select the appropriate module for analysis. For example, if you want to analyze the association between two categorical variables, choose the “Two by Two Table” module.
-
Enter Data:
- Data Entry: Enter your data into the provided fields. OpenEpi typically requires you to enter summary data (e.g., counts, means, standard deviations) rather than raw data.
- Data Format: Ensure your data is in the correct format. For example, for a two-by-two table, you will need to enter the counts for each cell.
-
Run the Analysis:
- Calculate Results: After entering your data, click the “Calculate” or “Submit” button to run the analysis.
- View Results: OpenEpi will display the results of the analysis, including statistical measures, confidence intervals, and p-values.
-
Interpret Results:
- Understand Output: Carefully review the output and interpret the results in the context of your research question.
- Statistical Significance: Pay attention to p-values and confidence intervals to assess the statistical significance of your findings.
-
Explore Examples and Documentation:
- Examples: Many OpenEpi modules include example datasets that you can use to practice and understand how the tool works.
- Documentation: Refer to the OpenEpi documentation for detailed explanations of the statistical methods used and guidance on interpreting the results.
-
Practice with Sample Datasets:
- Download Data: Download sample datasets from the OpenEpi website or other sources and use them to practice performing different types of analyses.
-
Seek Additional Resources:
- Online Tutorials: Look for online tutorials, webinars, and training materials on using OpenEpi.
- Community Forums: Participate in online forums and communities where you can ask questions and share your experiences with other OpenEpi users.
-
Validate Your Results:
- Compare with Other Tools: If possible, compare your results with those obtained from other statistical software packages to ensure accuracy.
-
Stay Updated:
- Check for Updates: Regularly check the OpenEpi website for updates and new features.
- Learn New Methods: As you become more comfortable with OpenEpi, explore more advanced modules and statistical methods.
10. Where Can I Find Resources and Training Materials for Learning to Use OpenEpi Effectively?
To effectively learn and use OpenEpi, a variety of resources and training materials are available. These resources cater to different learning styles and levels of expertise, ensuring users can maximize their understanding and application of OpenEpi in healthcare data analysis.
Comprehensive List of Resources and Training Materials for OpenEpi:
-
OpenEpi Official Website:
- Website: www.openepi.com
- Content: The official website is the primary source for all things OpenEpi. It includes:
- Software Download: Access to the latest version of the OpenEpi software.
- Documentation: Detailed documentation explaining the features, functions, and statistical methods used in OpenEpi.
- Examples: Sample datasets and examples demonstrating how to use OpenEpi for different types of analyses.
- Tutorials: Basic tutorials and guides on getting started with OpenEpi.
-
Online Tutorials and Guides:
- YouTube: Search for “OpenEpi tutorial” on YouTube to find video tutorials created by experts and users.
- Websites and Blogs: Many websites and blogs offer step-by-step guides and tutorials on using OpenEpi. Look for resources from universities, public health organizations, and statistical consultants.
-
Academic Courses and Workshops:
- Universities and Colleges: Many universities and colleges offer courses and workshops on epidemiology and biostatistics that include instruction on using OpenEpi.
- Public Health Organizations: Public health organizations such as the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and the World Health Organization (WHO) may offer training programs that include OpenEpi.
-
Books and Manuals:
- Statistical Textbooks: Some statistical textbooks include sections on using OpenEpi for specific types of analyses.
- OpenEpi Manuals: Look for user manuals and guides specifically designed for OpenEpi.
-
Online Forums and Communities:
- Statistical Forums: Participate in online forums and communities dedicated to statistics and data analysis. These forums are a great place to ask questions, share your experiences, and learn from other users.
- ResearchGate and LinkedIn: Use platforms like ResearchGate and LinkedIn to connect with other OpenEpi users and experts.
-
Conference Presentations and Workshops:
- Public Health Conferences: Attend public health conferences and workshops where OpenEpi is presented or discussed. These events offer opportunities to learn from experts and network with other users.
-
Training Datasets:
- Practice Datasets: Use publicly available datasets to practice using OpenEpi. Websites like Kaggle and the UCI Machine Learning Repository offer a wide variety of datasets that can be used for training purposes.
-
Personalized Training:
- Statistical Consultants: Hire a statistical consultant to provide personalized training and support on using OpenEpi.
- One-on-One Tutoring: Consider one-on-one tutoring from an experienced OpenEpi user.
Eager to enhance your expertise in auto repair and diagnostics? Explore the advanced training programs at CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN. Our comprehensive courses are designed to equip you with the latest skills and knowledge in remote vehicle diagnostics. Contact us today at Address: 1700 W Irving Park Rd, Chicago, IL 60613, United States, WhatsApp: +1 (641) 206-8880, or visit our Website: CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN to discover how we can help you excel in the rapidly evolving field of automotive repair.
