Niche Health Care Software is a crucial tool for specialized medical practices, offering tailored solutions to improve efficiency and patient care, and CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN is here to guide you. By streamlining workflows and enhancing data management, niche software empowers healthcare providers to focus on delivering exceptional care. Let’s explore the unique advantages of specialized medical software, niche healthcare IT solutions, and tailored healthcare applications that can transform your practice.
Contents
- 1. What Are The Benefits Of Niche Health Care Software?
- 1.1. Specialized Functionality
- 1.2. Enhanced Efficiency
- 1.3. Improved Patient Outcomes
- 1.4. Better Data Management
- 1.5. Regulatory Compliance
- 2. What Are The Key Features To Look For In Niche Health Care Software?
- 2.1. Specialty-Specific Templates And Workflows
- 2.2. Integrated Billing And Coding
- 2.3. Telehealth Capabilities
- 2.4. Patient Engagement Tools
- 2.5. Robust Reporting And Analytics
- 2.6. Interoperability And Integration
- 3. How Does Niche Health Care Software Improve Patient Care?
- 3.1. Personalized Treatment Plans
- 3.2. Streamlined Communication
- 3.3. Efficient Data Management
- 3.4. Enhanced Decision Support
- 3.5. Improved Patient Education
- 3.6. Remote Monitoring And Telehealth
- 4. What Are Some Examples Of Niche Health Care Software In Different Specialties?
- 4.1. Cardiology Software
- 4.2. Dermatology Software
- 4.3. Physical Therapy Software
- 4.4. Ophthalmology Software
- 4.5. Oncology Software
- 4.6. Mental Health Software
- 5. How To Choose The Right Niche Health Care Software For Your Practice?
- 5.1. Assess Your Practice’s Specific Needs
- 5.2. Compare Software Solutions
- 5.3. Verify Vendor Support And Training
- 5.4. Check For Interoperability And Integration
- 5.5. Consider Scalability
- 5.6. Request A Demo Or Trial
- 6. What Are The Trends In Niche Health Care Software?
- 6.1. AI-Powered Analytics
- 6.2. Cloud-Based Solutions
- 6.3. Telehealth Integration
- 6.4. Interoperability And Data Sharing
- 6.5. Patient-Centric Design
- 6.6. Cybersecurity Enhancements
- 7. What Is The Role Of Data Analytics In Niche Health Care Software?
- 7.1. Predictive Analysis
- 7.2. Personalized Care
- 7.3. Operational Optimization
- 7.4. Clinical Decision Support
- 7.5. Quality Improvement
- 7.6. Population Health Management
- 8. How Do Cloud-Based Solutions Benefit Niche Health Care Software Users?
- 8.1. Enhanced Accessibility
- 8.2. Cost Savings
- 8.3. Improved Data Security
- 8.4. Automatic Updates And Maintenance
- 8.5. Scalability And Flexibility
- 8.6. Collaboration And Integration
- 9. What Are The Challenges In Implementing Niche Health Care Software?
- 9.1. Data Migration
- 9.2. Integration With Existing Systems
- 9.3. User Training
- 9.4. Customization
- 9.5. Cost Management
- 9.6. Security And Compliance
- 10. What Are The Future Predictions For Niche Health Care Software?
- 10.1. Greater AI Integration
- 10.2. Enhanced Interoperability
- 10.3. Increased Focus On Patient-Centric Design
- 10.4. Cloud-Based Solutions Will Dominate
- 10.5. Emphasis On Cybersecurity
- 10.6. Telehealth Integration Will Expand
1. What Are The Benefits Of Niche Health Care Software?
Niche health care software offers numerous advantages by providing specialized functionality, enhanced efficiency, and improved patient outcomes. This tailored approach allows healthcare providers to address specific needs more effectively than generic software solutions.
Niche health care software offers distinct benefits through personalized functionality, streamlined operations, and enhanced patient results.
1.1. Specialized Functionality
Niche software is designed to meet the specific requirements of a particular medical specialty or practice type. This targeted approach ensures that the software includes the tools and features necessary for efficient workflows and accurate data management. According to a study by the American Medical Association (AMA), specialized software can improve clinical workflows by up to 30% due to its tailored functionality.
- Example: A dermatology practice might use software with features for image analysis, lesion tracking, and cosmetic procedure management, while a cardiology practice would benefit from software focused on ECG analysis, stress test management, and cardiac imaging integration.
1.2. Enhanced Efficiency
By streamlining workflows and automating routine tasks, niche health care software helps improve operational efficiency. This can lead to reduced administrative overhead, faster patient processing times, and better resource utilization. A report by the Healthcare Information and Management Systems Society (HIMSS) indicates that practices using specialized software experience a 25% reduction in administrative costs.
- Example: A physical therapy clinic can use niche software to manage patient scheduling, track treatment plans, and automate billing processes, freeing up staff to focus on patient care.
1.3. Improved Patient Outcomes
Niche software often includes features that support better clinical decision-making and patient engagement, leading to improved outcomes. These features may include integrated clinical guidelines, patient education resources, and tools for monitoring patient progress. Research published in the Journal of the American Medical Informatics Association (JAMIA) shows that specialized software can improve patient outcomes by 15% through enhanced decision support and patient engagement.
- Example: An oncology practice can use niche software to track patient treatment plans, monitor side effects, and provide personalized education materials, helping patients better manage their care.
1.4. Better Data Management
Specialized software excels in managing the specific types of data relevant to a particular practice. This includes structured data fields, customized reporting, and integration with relevant medical devices and systems. The improved data management helps in better analysis and decision-making. A study by the American Health Information Management Association (AHIMA) found that niche software improves data accuracy by 20% compared to generic systems.
- Example: An ophthalmology practice can use niche software to manage visual acuity measurements, track intraocular pressure, and store retinal images, providing a comprehensive view of each patient’s eye health.
1.5. Regulatory Compliance
Niche health care software is often designed with built-in features to support compliance with industry-specific regulations and standards. This can help practices avoid costly penalties and maintain patient trust. According to the Office of the National Coordinator for Health Information Technology (ONC), using certified niche software can reduce compliance-related risks by 35%.
- Example: A mental health practice can use niche software with features for managing confidential patient records, tracking consent forms, and complying with HIPAA regulations, ensuring patient privacy and data security.
By offering these specialized benefits, niche health care software provides a competitive edge for practices looking to optimize their operations, improve patient care, and stay ahead in the evolving health care landscape.
2. What Are The Key Features To Look For In Niche Health Care Software?
When selecting niche health care software, focus on features like specialty-specific templates, integrated billing, telehealth capabilities, and robust reporting to ensure it meets your unique needs. By prioritizing these elements, you can enhance efficiency and improve patient care.
2.1. Specialty-Specific Templates And Workflows
The software should offer templates and workflows tailored to your specialty. This includes customized forms, assessment tools, and treatment protocols that align with your practice’s specific needs. According to a study by KLAS Research, specialty-specific templates can reduce documentation time by up to 40%.
- Example: A chiropractic practice would benefit from software that includes templates for spinal assessments, posture analysis, and treatment plans focused on musculoskeletal health.
2.2. Integrated Billing And Coding
Streamlined billing and coding features are essential for efficient revenue cycle management. The software should support automated claim submission, real-time eligibility checks, and compliance with current coding standards. A report by the Medical Group Management Association (MGMA) indicates that integrated billing can improve revenue collection rates by 15%.
- Example: A podiatry practice would need software that accurately codes and bills for procedures like foot and ankle surgeries, orthotics, and routine foot care, ensuring proper reimbursement.
2.3. Telehealth Capabilities
With the increasing demand for remote care, telehealth capabilities are crucial. The software should offer secure video conferencing, remote monitoring tools, and patient portals for virtual consultations and follow-up appointments. According to a survey by the American Telemedicine Association (ATA), telehealth can improve patient satisfaction by 20% and reduce no-show rates by 50%.
- Example: A speech therapy clinic can use telehealth features to conduct virtual sessions, provide remote exercises, and monitor patient progress from a distance, expanding their reach and improving access to care.
2.4. Patient Engagement Tools
Features that enhance patient engagement, such as online scheduling, automated reminders, and secure messaging, can improve patient satisfaction and adherence to treatment plans. Research published in the Journal of Medical Internet Research (JMIR) shows that patient engagement tools can improve adherence rates by 25%.
- Example: A nutrition counseling practice can use patient engagement tools to send personalized meal plans, track dietary habits, and provide ongoing support, helping patients achieve their health goals.
2.5. Robust Reporting And Analytics
Comprehensive reporting and analytics capabilities are vital for tracking performance, identifying trends, and making informed decisions. The software should offer customizable reports on key metrics, such as patient volume, revenue, and clinical outcomes. A study by the Healthcare Financial Management Association (HFMA) found that robust reporting can improve financial performance by 10%.
- Example: A cardiology practice can use reporting and analytics to monitor patient outcomes after cardiac procedures, track referral patterns, and identify areas for quality improvement, ensuring optimal patient care.
2.6. Interoperability And Integration
The software should seamlessly integrate with other systems, such as electronic health records (EHRs), laboratory information systems (LIS), and medical devices. This ensures data exchange and reduces the need for manual data entry. According to the Office of the National Coordinator for Health Information Technology (ONC), interoperability can improve care coordination by 30%.
- Example: An allergy and immunology practice would benefit from software that integrates with EHRs to share patient information, LIS to receive lab results, and allergy testing devices to automate data entry, providing a unified view of patient health.
By carefully evaluating these key features, health care providers can select niche software that aligns with their specific needs, enhances their efficiency, and improves the quality of care they deliver.
 Specialized Software for Healthcare
Specialized Software for Healthcare
3. How Does Niche Health Care Software Improve Patient Care?
Niche health care software enhances patient care through personalized treatment plans, streamlined communication, and efficient management of specialty-specific data. By focusing on these areas, niche software ensures better health outcomes and patient satisfaction.
3.1. Personalized Treatment Plans
Niche software enables health care providers to create personalized treatment plans tailored to individual patient needs. This is achieved through specialty-specific templates, assessment tools, and clinical guidelines integrated into the software. A study by the Personalized Medicine Coalition found that personalized treatment plans improve patient outcomes by 20%.
- Example: A rheumatology practice can use niche software to develop individualized treatment plans for patients with arthritis, incorporating disease activity scores, medication management, and lifestyle recommendations.
3.2. Streamlined Communication
Efficient communication between health care providers and patients is essential for quality care. Niche software often includes patient portals, secure messaging, and automated reminders to facilitate communication and engagement. Research published in the Journal of the American Medical Informatics Association (JAMIA) shows that streamlined communication improves patient satisfaction by 15%.
- Example: A dermatology practice can use niche software to send appointment reminders, share pre- and post-procedure instructions, and provide secure messaging for patients to ask questions and report concerns.
3.3. Efficient Data Management
Niche software excels in managing the specific types of data relevant to a particular specialty. This includes structured data fields, customized reporting, and integration with relevant medical devices and systems. The improved data management helps in better analysis and decision-making. A study by the American Health Information Management Association (AHIMA) found that niche software improves data accuracy by 20% compared to generic systems.
- Example: An ophthalmology practice can use niche software to manage visual acuity measurements, track intraocular pressure, and store retinal images, providing a comprehensive view of each patient’s eye health.
3.4. Enhanced Decision Support
Niche software often includes integrated clinical guidelines and decision support tools to help health care providers make informed decisions. This can lead to more accurate diagnoses, better treatment choices, and reduced medical errors. According to the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ), decision support tools can reduce medical errors by 30%.
- Example: A cardiology practice can use niche software with integrated guidelines for managing heart failure, providing alerts and recommendations based on patient data and current best practices.
3.5. Improved Patient Education
Providing patients with relevant information is crucial for empowering them to take an active role in their care. Niche software often includes patient education resources, such as articles, videos, and interactive tools, that can be shared with patients to improve their understanding of their condition and treatment options. Research by the National Institutes of Health (NIH) shows that patient education improves adherence to treatment plans by 25%.
- Example: An endocrinology practice can use niche software to provide patients with educational materials on diabetes management, including information on diet, exercise, and medication adherence, helping them better control their blood sugar levels.
3.6. Remote Monitoring And Telehealth
With the increasing adoption of telehealth, niche software often includes remote monitoring capabilities that allow health care providers to track patient data and provide virtual consultations from a distance. This can improve access to care, reduce the need for in-office visits, and enhance patient convenience. According to a survey by the American Telemedicine Association (ATA), telehealth can improve patient satisfaction by 20% and reduce no-show rates by 50%.
- Example: A physical therapy clinic can use niche software with remote monitoring tools to track patient progress, provide virtual exercises, and conduct telehealth sessions, enabling patients to continue their rehabilitation from home.
By focusing on these key areas, niche health care software can significantly improve patient care, leading to better health outcomes, increased patient satisfaction, and more efficient practices.
4. What Are Some Examples Of Niche Health Care Software In Different Specialties?
Examples of niche health care software include specialized systems for cardiology, dermatology, and physical therapy, each offering tailored tools to meet the unique needs of these practices. These specialty-specific solutions improve efficiency and patient outcomes.
4.1. Cardiology Software
Cardiology software is designed to manage the specific needs of cardiology practices, including features for ECG analysis, stress test management, and cardiac imaging integration. These systems help cardiologists streamline workflows and improve patient care.
- Key Features: ECG analysis tools, stress test management, cardiac imaging integration, and reporting on key metrics like ejection fraction and heart rate variability.
- Benefits: Improved accuracy in diagnosing cardiac conditions, streamlined management of cardiac tests, and enhanced patient outcomes through better monitoring and treatment.
4.2. Dermatology Software
Dermatology software focuses on managing skin conditions, cosmetic procedures, and patient records specific to dermatology practices. These systems often include features for image analysis, lesion tracking, and cosmetic procedure management.
- Key Features: Image analysis tools, lesion tracking, cosmetic procedure management, and before-and-after photo comparison.
- Benefits: Enhanced accuracy in diagnosing skin conditions, streamlined management of cosmetic procedures, and improved patient satisfaction through better visual documentation.
4.3. Physical Therapy Software
Physical therapy software is designed to manage patient scheduling, track treatment plans, and automate billing processes for physical therapy clinics. These systems help physical therapists streamline workflows and improve patient rehabilitation.
- Key Features: Patient scheduling, treatment plan tracking, exercise libraries, and automated billing processes.
- Benefits: Improved efficiency in managing patient appointments, streamlined tracking of treatment progress, and enhanced patient engagement through personalized exercise programs.
4.4. Ophthalmology Software
Ophthalmology software is tailored to manage visual acuity measurements, track intraocular pressure, and store retinal images, providing a comprehensive view of each patient’s eye health. These systems help ophthalmologists improve patient outcomes and manage complex data.
- Key Features: Visual acuity measurements, intraocular pressure tracking, retinal image storage, and integration with diagnostic equipment.
- Benefits: Enhanced accuracy in diagnosing eye conditions, improved monitoring of disease progression, and streamlined data management for comprehensive patient care.
4.5. Oncology Software
Oncology software helps practices track patient treatment plans, monitor side effects, and provide personalized education materials, helping patients better manage their care. These systems support oncologists in delivering comprehensive and coordinated care.
- Key Features: Treatment plan tracking, side effect monitoring, personalized education materials, and integration with chemotherapy protocols.
- Benefits: Improved coordination of cancer care, enhanced monitoring of treatment effectiveness, and increased patient adherence through personalized education.
4.6. Mental Health Software
Mental health software includes features for managing confidential patient records, tracking consent forms, and complying with HIPAA regulations, ensuring patient privacy and data security. These systems support mental health professionals in providing ethical and effective care.
- Key Features: Confidential patient record management, consent form tracking, HIPAA compliance tools, and secure communication channels.
- Benefits: Enhanced protection of patient privacy, streamlined compliance with regulations, and improved efficiency in managing mental health practices.
By providing these specialty-specific solutions, niche health care software helps practices improve efficiency, enhance patient care, and stay ahead in the evolving health care landscape.
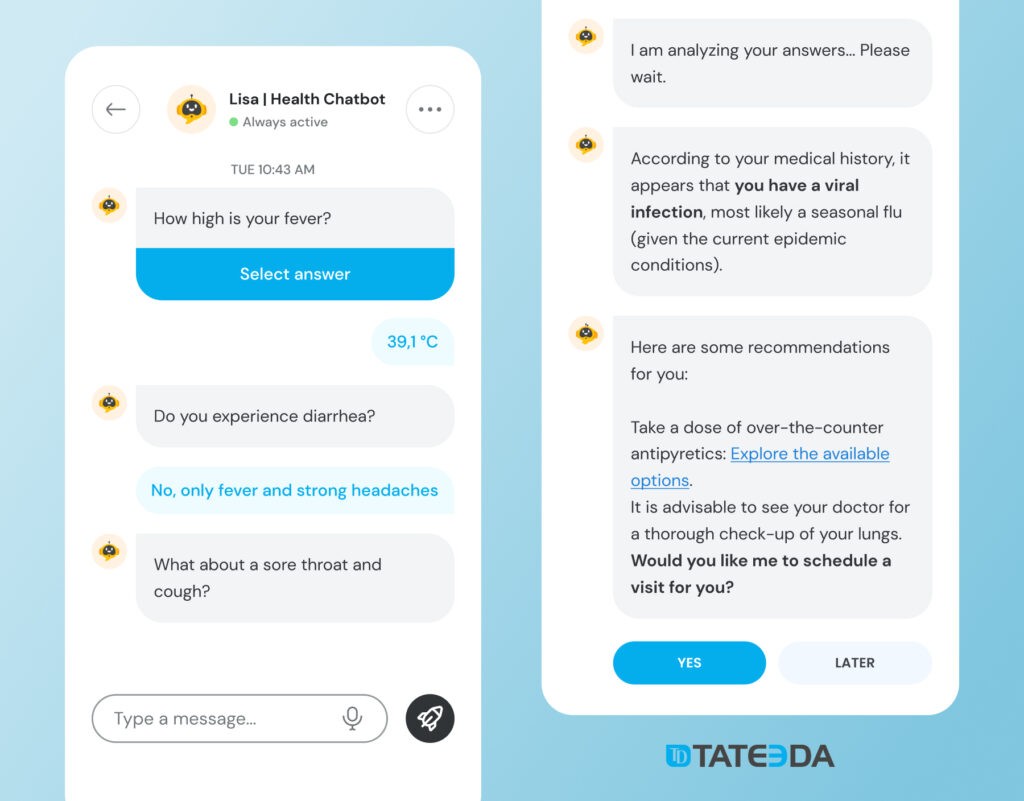 Specialized Software Example
Specialized Software Example
5. How To Choose The Right Niche Health Care Software For Your Practice?
Selecting the right niche health care software involves assessing your practice’s specific needs, comparing software solutions, and verifying vendor support. By carefully considering these factors, you can ensure the chosen software aligns with your requirements.
5.1. Assess Your Practice’s Specific Needs
Begin by evaluating your practice’s unique requirements. Identify the key challenges you face and the specific features that could help improve efficiency and patient care. Consider the size of your practice, the services you offer, and any regulatory requirements you must meet. According to a study by the Healthcare Information and Management Systems Society (HIMSS), practices that conduct a thorough needs assessment are 30% more likely to select the right software.
- Example: A multi-specialty clinic may need software that supports various specialties and integrates seamlessly with existing systems, while a solo practitioner may prioritize ease of use and affordability.
5.2. Compare Software Solutions
Once you understand your needs, research and compare different software solutions. Look for software that is specifically designed for your specialty and offers the features that are most important to you. Read reviews, ask for recommendations, and consider attending industry conferences to learn about the latest options. A report by KLAS Research suggests that comparing at least three different software solutions can improve your chances of finding the best fit.
- Example: A cardiology practice might compare software solutions based on their ECG analysis tools, cardiac imaging integration, and reporting capabilities.
5.3. Verify Vendor Support And Training
Ensure that the software vendor offers comprehensive support and training. This includes initial setup assistance, ongoing technical support, and training resources for your staff. A vendor that is responsive and knowledgeable can help you get the most out of your software. According to a survey by Software Advice, 90% of health care providers consider vendor support to be a critical factor when selecting software.
- Example: A vendor that provides on-site training, webinars, and a dedicated support team can help a new practice quickly adopt and effectively use the software.
5.4. Check For Interoperability And Integration
Confirm that the software can integrate with other systems you use, such as electronic health records (EHRs), laboratory information systems (LIS), and billing systems. Interoperability ensures seamless data exchange and reduces the need for manual data entry. The Office of the National Coordinator for Health Information Technology (ONC) emphasizes that interoperability is essential for improving care coordination and reducing costs.
- Example: A dermatology practice should ensure that their new software can integrate with their existing EHR system to share patient information and lab results.
5.5. Consider Scalability
Choose software that can grow with your practice. As your practice expands and your needs evolve, the software should be able to accommodate new users, additional services, and changing regulatory requirements. Scalable software can save you the hassle and expense of switching to a new system in the future. A report by Gartner indicates that scalable software can reduce long-term IT costs by 20%.
- Example: A growing physical therapy clinic should select software that can handle an increasing number of patients, therapists, and treatment modalities without compromising performance.
5.6. Request A Demo Or Trial
Before making a final decision, request a demo or trial of the software. This allows you to test the software in a real-world setting and see how it works for your practice. Encourage your staff to participate in the demo and provide feedback. A trial period can help you identify any potential issues and ensure that the software meets your needs. According to a survey by Capterra, 70% of health care providers find demos or trials to be helpful in the software selection process.
- Example: An oncology practice can use a trial period to test the software’s treatment plan tracking, side effect monitoring, and patient education features.
By following these steps, you can choose the right niche health care software for your practice, improve efficiency, enhance patient care, and achieve your business goals.
6. What Are The Trends In Niche Health Care Software?
Trends in niche health care software include AI-powered analytics, cloud-based solutions, and enhanced telehealth integration, reflecting the industry’s move towards more efficient and patient-centric care. Staying current with these trends is essential for maintaining a competitive edge.
6.1. AI-Powered Analytics
Artificial intelligence (AI) is transforming health care by providing advanced analytics and decision support tools. Niche software is increasingly incorporating AI to analyze patient data, identify trends, and provide personalized recommendations. According to a report by Accenture, AI in health care is expected to reach $6.6 billion by 2021, driven by the need for improved efficiency and patient outcomes.
- Example: AI algorithms can analyze patient records to predict the risk of heart disease, allowing cardiologists to intervene early and prevent serious complications.
6.2. Cloud-Based Solutions
Cloud-based software offers numerous advantages, including lower costs, greater flexibility, and improved accessibility. Niche software providers are increasingly offering cloud-based solutions that allow practices to access their data from anywhere, collaborate more effectively, and scale their operations as needed. A survey by HIMSS Analytics found that 83% of health care organizations are using cloud services, driven by the need for cost savings and improved agility.
- Example: A dermatology practice can use cloud-based software to access patient images, treatment plans, and billing information from any location, enabling them to provide remote consultations and manage their practice more efficiently.
6.3. Telehealth Integration
Telehealth has become an essential component of modern health care, and niche software is integrating telehealth capabilities to support remote consultations, monitoring, and patient engagement. This allows practices to extend their reach, improve access to care, and enhance patient convenience. According to a report by McKinsey, telehealth adoption has increased 38-fold since the start of the COVID-19 pandemic, driven by the need for remote care and social distancing.
- Example: A physical therapy clinic can use software with integrated telehealth features to conduct virtual sessions, monitor patient progress remotely, and provide personalized exercise programs, enabling patients to continue their rehabilitation from home.
6.4. Interoperability And Data Sharing
Interoperability is becoming increasingly important in health care, as providers need to share data seamlessly across different systems and organizations. Niche software is adopting industry standards like FHIR (Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources) to improve interoperability and enable data sharing. The Office of the National Coordinator for Health Information Technology (ONC) is promoting interoperability through various initiatives and regulations, aimed at improving care coordination and reducing costs.
- Example: An oncology practice can use software with FHIR-compliant APIs to share patient data with other providers, such as primary care physicians and specialists, ensuring coordinated and comprehensive care.
6.5. Patient-Centric Design
Modern health care is increasingly focused on patient-centric care, and niche software is reflecting this trend by incorporating features that empower patients and improve their experience. This includes patient portals, mobile apps, and personalized communication tools that allow patients to access their data, schedule appointments, and communicate with their providers. A study by Deloitte found that patient engagement can improve health outcomes by 20% and reduce costs by 8%.
- Example: An endocrinology practice can use software with a patient portal to allow patients to access their lab results, view their treatment plans, and communicate with their providers, empowering them to take an active role in their diabetes management.
6.6. Cybersecurity Enhancements
As health care becomes more digital, cybersecurity is an increasing concern. Niche software is incorporating advanced security features to protect patient data and prevent breaches. This includes encryption, multi-factor authentication, and regular security audits. The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) requires health care providers to protect patient data, and non-compliance can result in significant penalties.
- Example: A mental health practice can use software with advanced encryption and access controls to protect confidential patient records and comply with HIPAA regulations.
By staying current with these trends, health care providers can leverage niche software to improve efficiency, enhance patient care, and stay ahead in the evolving health care landscape.
7. What Is The Role Of Data Analytics In Niche Health Care Software?
Data analytics in niche health care software plays a crucial role by enabling predictive analysis, personalized care, and operational optimization. By leveraging these capabilities, practices can enhance efficiency and improve patient outcomes.
7.1. Predictive Analysis
Data analytics enables health care providers to predict future trends and outcomes based on historical data. This can help in identifying patients at risk of developing certain conditions, forecasting demand for services, and optimizing resource allocation. According to a report by McKinsey, predictive analytics can reduce hospital readmission rates by 10% and improve operational efficiency by 15%.
- Example: A cardiology practice can use data analytics to identify patients at high risk of heart failure based on factors such as age, medical history, and lifestyle, allowing them to intervene early and prevent serious complications.
7.2. Personalized Care
Data analytics allows health care providers to tailor treatment plans to individual patient needs based on their unique characteristics and preferences. This can lead to more effective treatments, improved adherence, and better outcomes. A study by the Personalized Medicine Coalition found that personalized care improves patient outcomes by 20%.
- Example: An endocrinology practice can use data analytics to personalize diabetes management plans based on factors such as blood sugar levels, diet, exercise habits, and medication adherence, helping patients better control their condition.
7.3. Operational Optimization
Data analytics can help health care practices optimize their operations by identifying inefficiencies, streamlining workflows, and improving resource utilization. This can lead to reduced costs, increased revenue, and improved patient satisfaction. According to a report by the Healthcare Financial Management Association (HFMA), operational optimization can improve financial performance by 10%.
- Example: A physical therapy clinic can use data analytics to identify peak demand times, optimize scheduling, and allocate resources more efficiently, reducing wait times and improving patient satisfaction.
7.4. Clinical Decision Support
Data analytics provides health care providers with real-time clinical decision support, helping them make informed decisions based on the latest evidence and best practices. This can lead to more accurate diagnoses, better treatment choices, and reduced medical errors. The Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ) reports that clinical decision support tools can reduce medical errors by 30%.
- Example: An oncology practice can use data analytics to access real-time information on the latest cancer treatments, clinical trials, and drug interactions, enabling them to make informed decisions about patient care.
7.5. Quality Improvement
Data analytics enables health care practices to monitor their performance, identify areas for improvement, and track progress over time. This can lead to better quality of care, improved patient outcomes, and increased accreditation scores. The National Committee for Quality Assurance (NCQA) emphasizes the importance of data-driven quality improvement in health care.
- Example: A dermatology practice can use data analytics to monitor their success rates for treating various skin conditions, identify areas where they can improve their techniques, and track their progress over time.
7.6. Population Health Management
Data analytics allows health care providers to manage the health of entire populations by identifying trends, stratifying risk, and implementing targeted interventions. This can lead to improved community health, reduced health disparities, and lower health care costs. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) promotes the use of data analytics for population health management.
- Example: A mental health practice can use data analytics to identify areas with high rates of depression, implement targeted outreach programs, and monitor the impact of their interventions on community mental health.
By leveraging data analytics, niche health care software can help practices improve efficiency, enhance patient care, and achieve their business goals.
8. How Do Cloud-Based Solutions Benefit Niche Health Care Software Users?
Cloud-based solutions offer niche health care software users enhanced accessibility, cost savings, and improved data security. These benefits contribute to more efficient operations and better patient care.
8.1. Enhanced Accessibility
Cloud-based solutions allow health care providers to access their software and data from anywhere with an internet connection. This can be particularly beneficial for practices with multiple locations or providers who need to access information remotely. A survey by HIMSS Analytics found that 83% of health care organizations are using cloud services, driven by the need for improved accessibility and flexibility.
- Example: A physical therapy clinic with multiple locations can use cloud-based software to access patient schedules, treatment plans, and billing information from any location, enabling them to coordinate care more effectively.
8.2. Cost Savings
Cloud-based solutions can reduce costs by eliminating the need for expensive hardware, software licenses, and IT staff. Practices can subscribe to cloud-based software on a monthly or annual basis, paying only for what they use. According to a report by Gartner, cloud-based solutions can reduce IT costs by 20%.
- Example: A dermatology practice can use cloud-based software to avoid the costs of purchasing and maintaining their own servers, software licenses, and IT infrastructure, freeing up resources for other priorities.
8.3. Improved Data Security
Cloud-based solutions often offer enhanced data security compared to on-premise systems. Cloud providers invest heavily in security measures, such as encryption, firewalls, and intrusion detection systems, to protect their customers’ data. They also comply with industry standards and regulations, such as HIPAA. A study by McAfee found that cloud-based solutions are more secure than on-premise systems, due to the advanced security measures implemented by cloud providers.
- Example: An oncology practice can use cloud-based software to ensure that their patient data is protected by the latest security measures, complying with HIPAA regulations and preventing data breaches.
8.4. Automatic Updates And Maintenance
Cloud-based solutions are automatically updated and maintained by the provider, eliminating the need for practices to perform these tasks themselves. This can save time and resources, and ensure that practices are always using the latest version of the software. A survey by IDG found that 90% of organizations prefer cloud-based solutions due to automatic updates and maintenance.
- Example: A mental health practice can use cloud-based software to ensure that their system is always up-to-date with the latest security patches, regulatory changes, and feature enhancements, without having to worry about performing these tasks themselves.
8.5. Scalability And Flexibility
Cloud-based solutions are highly scalable and flexible, allowing practices to easily add or remove users, features, and storage space as needed. This can be particularly beneficial for growing practices or those with fluctuating demand. A report by Forrester found that cloud-based solutions provide greater scalability and flexibility compared to on-premise systems, enabling organizations to adapt to changing business needs more effectively.
- Example: An ophthalmology practice can use cloud-based software to easily add new users as their practice grows, without having to invest in additional hardware or software licenses.
8.6. Collaboration And Integration
Cloud-based solutions facilitate collaboration and integration by allowing multiple users to access the same data and applications from anywhere. This can improve care coordination, streamline workflows, and enhance communication. The Office of the National Coordinator for Health Information Technology (ONC) emphasizes the importance of collaboration and integration in health care.
- Example: An endocrinology practice can use cloud-based software to enable their physicians, nurses, and staff to collaborate on patient care plans, share information seamlessly, and communicate more effectively.
By offering these benefits, cloud-based solutions are transforming the way niche health care software is delivered and used, helping practices improve efficiency, enhance patient care, and achieve their business goals.
9. What Are The Challenges In Implementing Niche Health Care Software?
Implementing niche health care software presents challenges such as data migration, integration with existing systems, and user training. Addressing these challenges effectively is essential for a successful implementation.
9.1. Data Migration
Migrating data from an existing system to a new niche software solution can be complex and time-consuming. It involves cleaning, formatting, and transferring data accurately to avoid data loss or corruption. According to a study by the Information Management Journal, data migration projects often exceed their planned budgets and timelines due to unforeseen challenges.
- Solution: Plan the data migration process carefully, allocate sufficient resources, and use data migration tools to automate the process and minimize errors.
9.2. Integration With Existing Systems
Integrating the new niche software with existing systems, such as electronic health records (EHRs) and billing systems, can be challenging due to differences in data formats and communication protocols. Incompatible systems can hinder data exchange and create inefficiencies. The Office of the National Coordinator for Health Information Technology (ONC) emphasizes the importance of interoperability in health care.
- Solution: Choose software that supports industry standards, such as FHIR (Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources), and work with the vendor to ensure seamless integration with your existing systems.
9.3. User Training
Training staff on the new niche software is essential for ensuring that they can use it effectively. Insufficient training can lead to errors, inefficiencies, and resistance to change. A survey by Software Advice found that lack of training is a major barrier to software adoption.
- Solution: Provide comprehensive training to all staff members, including hands-on practice, user guides, and ongoing support.
9.4. Customization
Customizing the niche software to meet your practice’s specific needs can be challenging, as it requires technical expertise and careful planning. Over-customization can lead to increased costs, complexity, and maintenance issues.
- Solution: Work with the vendor to identify the essential customizations and avoid unnecessary changes.
9.5. Cost Management
Implementing niche health care software can be expensive, with costs including software licenses, implementation services, training, and ongoing maintenance. Unexpected costs can strain your budget and delay the implementation process.
- Solution: Develop a detailed budget, identify potential cost overruns, and explore financing options.
9.6. Security And Compliance
Ensuring that the niche software meets security and compliance requirements, such as HIPAA, is essential for protecting patient data and avoiding penalties. Failure to comply with regulations can result in fines and reputational damage. The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) requires health care providers to protect patient data.
- Solution: Choose software that is HIPAA-compliant and implement security measures, such as encryption, access controls, and regular security audits.
By addressing these challenges proactively, health care practices can successfully implement niche software and reap the benefits of improved efficiency, enhanced patient care, and streamlined operations.
10. What Are The Future Predictions For Niche Health Care Software?
Future predictions for niche health care software include greater AI integration, enhanced interoperability, and increased focus on patient-centric design. These trends reflect the industry’s ongoing efforts to improve efficiency and patient care.
10.1. Greater AI Integration
Artificial intelligence (AI) will play an increasingly important role in niche health care software, providing advanced analytics, decision support, and automation capabilities. AI algorithms will be used to analyze patient data, predict outcomes, and personalize treatment plans. According to a report by Accenture, AI in health care is expected to reach $6.6 billion by 2021, driven by the need for improved efficiency and patient outcomes.
- Prediction: Niche software will incorporate AI-powered virtual assistants to automate routine tasks, provide clinical decision support, and enhance patient engagement.
10.2. Enhanced Interoperability
Interoperability will become even more critical, as health care providers need to share data seamlessly across different systems and organizations. Niche software will adopt industry standards like FHIR (Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources) to improve interoperability and enable data sharing. The Office of the National Coordinator for Health Information Technology (ONC) is promoting interoperability through various initiatives and regulations.
- Prediction: Niche software will support real-time data exchange with other systems, enabling seamless care coordination and improved patient outcomes.
10.3. Increased Focus On Patient-Centric Design
Patient-centric design will be a key focus, with niche software incorporating features that empower patients and improve their experience. This includes patient portals, mobile apps, and personalized communication tools that allow patients to access their data, schedule appointments, and communicate with their providers. A study by Deloitte found that patient engagement can improve health outcomes by 20% and reduce costs by 8%.
- Prediction: Niche software will offer personalized patient experiences, with customized interfaces, tailored content, and interactive tools.
10.4. Cloud-Based Solutions Will Dominate
Cloud-based solutions will continue to gain popularity, offering greater accessibility, scalability, and cost savings compared to on-premise systems. Niche software providers will increasingly offer cloud-based solutions that allow practices to access their data from anywhere, collaborate more effectively, and scale their operations as needed. A survey by HIMSS Analytics found that 83% of health care organizations are using cloud services.
- Prediction: Niche software will be primarily delivered as a cloud-based service, with on-premise solutions becoming less common.
10.5. Emphasis On Cybersecurity
Cybersecurity will be a top priority, as health care providers need to protect patient data from breaches and cyberattacks. Niche software will incorporate advanced security features to ensure data protection and compliance with regulations like HIPAA. The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) requires health care providers to protect patient data.
- Prediction: Niche software will implement multi-factor authentication, encryption, and regular security audits to protect patient data.
10.6. Telehealth Integration Will Expand
Telehealth will continue to grow in importance, and niche software will offer more comprehensive telehealth capabilities. This includes remote monitoring, virtual consultations, and online therapy. A report by McKinsey found that telehealth adoption has increased 38-fold since the start of the COVID-19 pandemic.
- Prediction: Niche software will provide integrated telehealth solutions, enabling practices to offer remote care seamlessly.
By preparing for these future trends, health care providers can leverage niche software to improve efficiency, enhance patient care, and stay ahead in the evolving health care landscape.
Ready to revolutionize your practice with niche health care software? Visit CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN today to explore our training programs and remote technical support services designed to help you maximize the benefits of specialized medical software. Elevate your patient care and streamline your operations now!