Are you a software engineer looking for a change? At CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN, we understand that the tech field is vast and your skills are transferable. There are several alternative career paths after software engineering where your technical expertise can shine, offering diverse opportunities and growth. Explore these options to find a career that better aligns with your passions, like a role in the automotive repair industry which can benefit greatly from your skills in remote diagnostics.
Contents
- 1. Why Consider Other Career Paths After Software Engineering?
- 2. Customer-Facing Roles
- 2.1. Developer Relations, Advocacy, or Evangelism
- 2.2. Developer Marketing
- 2.3. Sales Engineer
- 2.4. Technical Recruiter
- 3. Product Roles
- 3.1. Quality Assurance or Test Engineer
- 3.2. Business Analyst
- 3.3. Project Manager
- 3.4. Scrum Master
- 3.5. Product Manager
- 3.6. Designer
- 3.7. No or Low-Code Developer
- 4. Support Roles
- 4.1. Sysadmin or DevOps Engineer
- 4.2. Database Administrator
- 4.3. Site Reliability Engineer
- 4.4. Technical or Customer Support
- 5. Teaching and Writing Roles
- 5.1. Technical Writer
- 5.2. Teacher
- 5.3. Trainer
- 6. Analytical Roles
- 6.1. Data Scientist or Engineer
- 6.2. Security Analyst
- 6.3. R&D
- 7. Independence and Flexibility
- 7.1. Freelancer or Consultant
- 7.2. Startup Founder
- 8. CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN: Bridging Tech Skills to Automotive Repair
- 8.1. Leveraging Software Engineering Skills in Automotive Repair
- 8.2. Training Programs at CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN
- 8.3. Benefits of Training with CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN
- 8.4. Success Stories
- 8.5. Call to Action
- 9. FAQ About Other Career Paths After Software Engineering
Discover various options, including developer relations, technical writing, and product management, all requiring software engineering skills. CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN can help bridge your tech background to other sectors through specialized remote repair diagnostic training.
1. Why Consider Other Career Paths After Software Engineering?
Software engineering is a demanding field, and it’s not uncommon to find yourself seeking alternative career paths. There are numerous reasons why you might consider a change.
- Burnout: The high-pressure environment and long hours can lead to burnout.
- Changing Interests: Your interests might evolve, leading you to explore other fields.
- Better Work-Life Balance: Some roles offer a more sustainable work-life balance.
- Desire for More Interaction: Some engineers prefer roles with more human interaction.
- Career Growth: Opportunities for advancement might be limited in your current role.
- Financial Concerns: Some alternative paths may offer better financial prospects.
- Location Preferences: Certain careers might allow you to live in your preferred location.
Making a career change can be daunting, but recognizing the reasons behind your desire for a change is the first step toward finding a more fulfilling career path.
2. Customer-Facing Roles
If you enjoy interacting with people and want a career that combines your technical skills with customer engagement, customer-facing roles can be an excellent fit. Here are several options to explore.
2.1. Developer Relations, Advocacy, or Evangelism
Developer relations roles involve building relationships with developers who use your company’s software. This field is experiencing rapid growth as companies recognize the importance of engaging with their developer communities.
- Responsibilities: Creating demo applications, writing blog posts, speaking at conferences, and managing social media.
- Skills Needed: Strong communication, technical expertise, and community-building skills.
- How to Get Started: Engage with developer communities, contribute to open-source projects, and build a personal brand.
- Companies to Consider: Large tech companies like Google, Amazon, and Microsoft often hire developer relations professionals.
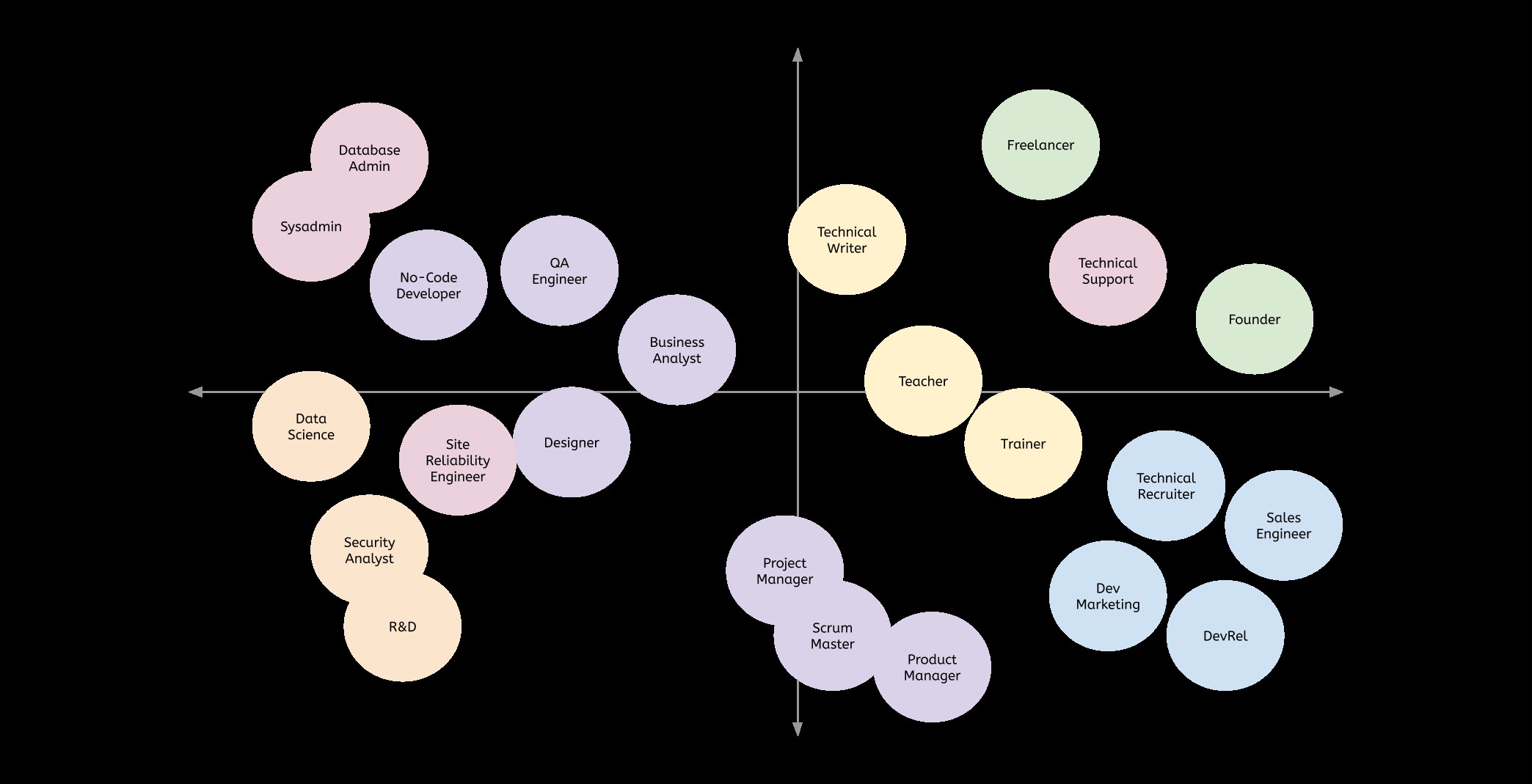 Developer relations is one of other career paths after software engineering
Developer relations is one of other career paths after software engineering
2.2. Developer Marketing
Developer marketing focuses on promoting software products and services to developers. This requires a deep understanding of the developer mindset and the ability to communicate technical value effectively.
- Responsibilities: Creating marketing content, running campaigns, and analyzing marketing data.
- Skills Needed: Marketing knowledge, technical background, and communication skills.
- How to Get Started: Learn online marketing skills such as SEO, content marketing, and social media marketing.
- Resources: SlashData offers valuable content on developer marketing, including a comprehensive guide.
2.3. Sales Engineer
Sales engineers combine technical expertise with sales skills to help customers find the right solutions. This role involves understanding customer needs and demonstrating how software products can meet those needs.
- Responsibilities: Providing technical demonstrations, answering technical questions, and building relationships with customers.
- Skills Needed: Technical knowledge, sales skills, and communication abilities.
- How to Get Started: Develop your sales skills and technical knowledge through courses and on-the-job training.
- Resources: Hubspot provides an excellent introduction to the skills and resources needed to become a sales engineer.
2.4. Technical Recruiter
Technical recruiters find and hire talented software engineers. With a background in software development, you’ll have a unique advantage in understanding the skills and qualifications needed for these roles.
- Responsibilities: Sourcing candidates, conducting interviews, and managing the hiring process.
- Skills Needed: Technical knowledge, communication skills, and networking abilities.
- How to Get Started: Look for entry-level recruiting jobs at reputable firms and build your network.
- Considerations: Check company reviews on Glassdoor to ensure you’re joining a high-quality firm.
3. Product Roles
If you prefer to stay involved in product development but want to move away from coding, product roles offer a variety of opportunities. These roles require close collaboration with engineers and a deep understanding of the product development process.
3.1. Quality Assurance or Test Engineer
Quality assurance (QA) and test engineers ensure that software products meet quality standards before they are released. This involves both manual testing and automated testing.
- Responsibilities: Writing test plans, executing tests, and reporting defects.
- Skills Needed: Attention to detail, analytical skills, and coding abilities (for automated testing).
- How to Get Started: Learn testing methodologies and tools, and gain experience through internships or entry-level roles.
- Key Differences: QA focuses on preventing defects, while testing focuses on finding defects.
3.2. Business Analyst
Business analysts bridge the gap between business needs and technical solutions. They work with stakeholders to understand requirements and translate them into actionable plans for the development team.
- Responsibilities: Gathering requirements, analyzing data, and creating reports.
- Skills Needed: Analytical skills, communication skills, and business knowledge.
- How to Get Started: Take online courses to develop a basic understanding of business analysis.
3.3. Project Manager
Project managers oversee the planning, execution, and completion of projects. They ensure that projects are delivered on time, within budget, and to the required quality standards.
- Responsibilities: Defining project scope, managing resources, and tracking progress.
- Skills Needed: Organization skills, communication skills, and leadership abilities.
- How to Get Started: Gain experience managing projects in your current role and consider pursuing project management certifications.
3.4. Scrum Master
Scrum Masters facilitate Agile development processes and help teams adhere to Scrum principles. They remove obstacles and ensure that the team can work effectively.
- Responsibilities: Facilitating Scrum ceremonies, coaching the team, and removing impediments.
- Skills Needed: Knowledge of Agile methodologies, communication skills, and leadership abilities.
- How to Get Started: Take a Scrum Master certification course and gain experience working in Agile teams.
- Agile Best Practices: Understanding and implementing Agile best practices is crucial for success.
3.5. Product Manager
Product managers define the vision, strategy, and roadmap for a product. They work with cross-functional teams to ensure that the product meets customer needs and business goals.
- Responsibilities: Conducting market research, defining product features, and prioritizing development efforts.
- Skills Needed: Strategic thinking, analytical skills, and communication abilities.
- How to Get Started: Start with smaller parts of a product or as a project manager to gain experience.
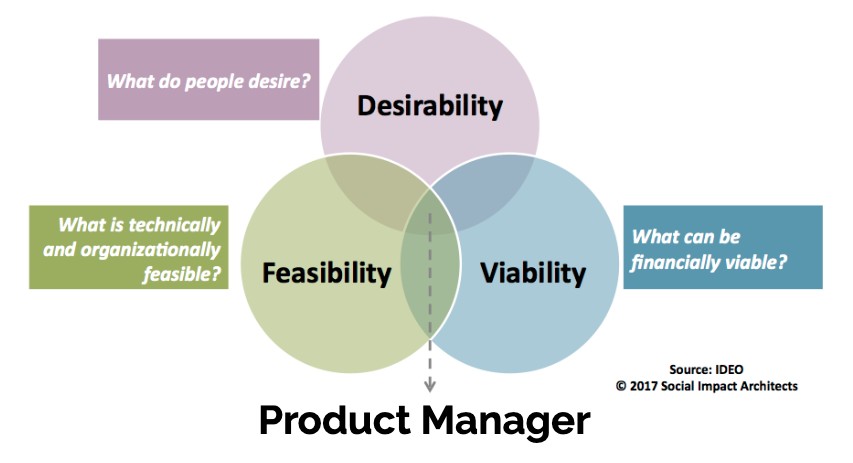 Product managers are the key of other career paths after software engineering
Product managers are the key of other career paths after software engineering
3.6. Designer
Designers focus on the user interface (UI) and user experience (UX) of software products. Combining coding skills with design expertise can make you a highly valuable asset to any team.
- Responsibilities: Creating wireframes, mockups, and prototypes.
- Skills Needed: Design skills, technical knowledge, and creativity.
- How to Get Started: Take design courses, build a portfolio, and practice creating interactive mockups.
- Portfolio Platforms: Dribbble is a popular platform for showcasing design work.
3.7. No or Low-Code Developer
No-code and low-code development tools allow you to build applications quickly without writing extensive code. This field is growing rapidly and offers opportunities for those who want to create software without being traditional developers.
- Responsibilities: Building applications using no-code or low-code platforms.
- Skills Needed: Problem-solving skills, technical aptitude, and familiarity with no-code tools.
- How to Get Started: Explore no-code platforms like Makerpad and No Code Jobs to find opportunities and training resources.
- Benefits: Rapid application development and reduced reliance on traditional coding.
4. Support Roles
Support roles are essential for maintaining the infrastructure and operations of software companies. These roles often require technical skills and a problem-solving mindset.
4.1. Sysadmin or DevOps Engineer
Sysadmins and DevOps engineers manage and maintain servers, networks, and systems. They ensure that the infrastructure is reliable, secure, and efficient.
- Responsibilities: Configuring servers, automating tasks, and monitoring system performance.
- Skills Needed: Knowledge of operating systems, networking, and automation tools.
- How to Get Started: Gain experience with Linux, cloud platforms, and scripting languages.
- Automation Tools: Terraform and Kubernetes are popular tools in this field.
4.2. Database Administrator
Database administrators (DBAs) manage and maintain databases, ensuring their security, performance, and availability. This role requires a deep understanding of database technologies and best practices.
- Responsibilities: Configuring databases, optimizing performance, and ensuring data security.
- Skills Needed: Knowledge of SQL and NoSQL databases, security best practices, and scripting skills.
- How to Get Started: Learn about database technologies and practice optimizing databases.
- Large Datasets: Kaggle offers large datasets to practice with.
4.3. Site Reliability Engineer
Site Reliability Engineers (SREs) focus on ensuring the reliability and availability of systems. They respond to incidents, troubleshoot issues, and implement solutions to prevent future problems.
- Responsibilities: Monitoring systems, responding to incidents, and automating tasks.
- Skills Needed: Problem-solving skills, technical knowledge, and communication abilities.
- How to Get Started: Gain experience with system monitoring, incident response, and automation.
- Unusual Problems: This role involves solving a wide range of unusual problems.
4.4. Technical or Customer Support
Technical and customer support roles involve helping customers resolve technical issues and answering questions about software products. This role requires patience, empathy, and strong communication skills.
- Responsibilities: Answering customer inquiries, troubleshooting technical issues, and providing solutions.
- Skills Needed: Technical knowledge, communication skills, and patience.
- How to Get Started: Gain experience in customer service and technical support.
- Interacting with Customers: This role involves interacting with customers who may be frustrated.
5. Teaching and Writing Roles
If you enjoy sharing your knowledge and helping others learn, teaching and writing roles can be a rewarding career path. These roles allow you to leverage your technical expertise to educate and inform others.
5.1. Technical Writer
Technical writers create documentation, tutorials, and other content to help users understand and use software products. This role requires strong writing skills and the ability to explain complex topics clearly and concisely.
- Responsibilities: Writing documentation, creating tutorials, and editing content.
- Skills Needed: Writing skills, technical knowledge, and organizational abilities.
- How to Get Started: Start writing for community programs and build a portfolio.
- Paid Community Writing Programs: These programs offer opportunities to get paid for your writing.
 Teaching roles for software developers are one of other career paths after software engineering
Teaching roles for software developers are one of other career paths after software engineering
5.2. Teacher
Teaching roles involve educating students about software development and related topics. You can teach at coding bootcamps, colleges, high schools, or online platforms.
- Responsibilities: Preparing lessons, delivering instruction, and assessing student learning.
- Skills Needed: Technical knowledge, communication skills, and patience.
- How to Get Started: Gain teaching experience and build your subject matter expertise.
- Online Platforms: Egghead.io, Teachable, and Educative are platforms for creating and selling online courses.
5.3. Trainer
Trainers provide hands-on training for specialized software to corporate clients. This role requires strong technical knowledge, communication skills, and the ability to deliver engaging presentations.
- Responsibilities: Delivering training sessions, creating training materials, and assessing participant learning.
- Skills Needed: Technical knowledge, communication skills, and presentation skills.
- How to Get Started: Gain experience delivering training and build your subject matter expertise.
- Corporate Training: This often pays better than teaching but can be more sales-driven.
6. Analytical Roles
Analytical roles involve using data and analysis to solve business problems. These roles require strong analytical skills, attention to detail, and the ability to communicate insights effectively.
6.1. Data Scientist or Engineer
Data scientists and engineers use large datasets to help businesses make better decisions. Data engineers focus on data ingestion and organization, while data scientists design experiments and algorithms.
- Responsibilities: Analyzing data, building models, and creating reports.
- Skills Needed: Knowledge of statistics, machine learning, and programming languages.
- How to Get Started: Take courses in data science and gain experience working with data.
- Machine Learning: This is a huge field with roots in math, software engineering, and statistics.
6.2. Security Analyst
Security analysts identify and address security vulnerabilities in software systems. This role requires a mix of technical, compliance, business, and risk assessment skills.
- Responsibilities: Conducting security assessments, identifying vulnerabilities, and recommending solutions.
- Skills Needed: Technical knowledge, analytical skills, and communication abilities.
- How to Get Started: Gain experience in security testing and learn about security best practices.
- Information Security: Check out the many paths you can take in information security.
6.3. R&D
Research and development (R&D) roles involve conducting experiments and developing new technologies. These roles require creativity, problem-solving skills, and a deep understanding of technology.
- Responsibilities: Conducting research, developing prototypes, and testing new technologies.
- Skills Needed: Technical knowledge, creativity, and problem-solving skills.
- How to Get Started: Gain experience in research and development and build your technical expertise.
- Ethical Hackers: Some companies hire ethical hackers to help round out the team.
7. Independence and Flexibility
If you value independence and flexibility in your career, consider roles that allow you to work on your own terms. These roles require strong self-discipline and the ability to manage your time effectively.
7.1. Freelancer or Consultant
Freelancers and consultants work independently, providing their services to clients on a contract basis. This allows you to set your own hours, choose your projects, and work from anywhere.
- Responsibilities: Providing technical services to clients.
- Skills Needed: Technical knowledge, communication skills, and business acumen.
- How to Get Started: Build a portfolio, network with potential clients, and use platforms like Upwork or Toptal.
- Referrals: These are great because the client comes to you based on a trusted relationship.
7.2. Startup Founder
Starting your own company can be a challenging but rewarding career path. As a founder, you’ll have the opportunity to build something from scratch and make a real impact on the world.
- Responsibilities: Developing a business plan, building a team, and raising capital.
- Skills Needed: Leadership skills, business acumen, and technical knowledge.
- How to Get Started: Develop a business idea, create a plan, and find co-founders.
- Outside of Regular Working Hours: You may be able to start a company outside of your regular working hours.
8. CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN: Bridging Tech Skills to Automotive Repair
At CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN, we recognize the value of your software engineering skills and offer specialized training to bridge your expertise to the automotive repair industry. Our remote repair diagnostic training can leverage your technical background to excel in this growing field.
8.1. Leveraging Software Engineering Skills in Automotive Repair
Your background in software engineering can be a significant asset in the automotive repair industry. Modern vehicles are increasingly complex, relying on sophisticated software and electronic systems.
- Remote Diagnostics: Use your technical skills to diagnose and repair vehicles remotely.
- Software Updates: Apply your knowledge of software development to update vehicle systems.
- Data Analysis: Analyze vehicle data to identify and resolve issues.
- Automation: Develop automation scripts to streamline repair processes.
8.2. Training Programs at CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN
CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN offers comprehensive training programs designed to equip you with the skills and knowledge needed to succeed in the automotive repair industry.
- Remote Diagnostic Training: Learn how to diagnose and repair vehicles remotely using advanced tools and techniques.
- Software Integration Training: Understand how to integrate software updates and modifications into vehicle systems.
- Data Analysis Training: Develop your data analysis skills to identify and resolve vehicle issues.
- Hands-On Experience: Gain practical experience through hands-on training sessions.
 Teaching roles for software developers are one of other career paths after software engineering
Teaching roles for software developers are one of other career paths after software engineering
8.3. Benefits of Training with CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN
Training with CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN offers several benefits that can help you transition your software engineering skills into a rewarding career in automotive repair.
- Expert Instruction: Learn from experienced instructors who are experts in the field.
- Cutting-Edge Technology: Work with the latest tools and technologies used in automotive repair.
- Career Opportunities: Open doors to a wide range of career opportunities in the automotive industry.
- Remote Work: Many automotive repair roles offer the flexibility to work remotely.
- Growing Demand: The demand for skilled automotive technicians is growing, ensuring job security.
8.4. Success Stories
Many software engineers have successfully transitioned their skills to the automotive repair industry through training programs at CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN.
- John Doe: A former software engineer now working as a remote diagnostic technician, leveraging his technical skills to solve complex vehicle issues.
- Jane Smith: A former developer who now specializes in software updates and integration for automotive systems.
- Mike Johnson: A data analyst who uses his skills to analyze vehicle data and improve performance.
8.5. Call to Action
Ready to explore a new career path in automotive repair? Visit CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN today to learn more about our training programs and how we can help you transition your software engineering skills into a rewarding career in the automotive industry. Contact us at Address: 1700 W Irving Park Rd, Chicago, IL 60613, United States. Whatsapp: +1 (641) 206-8880. Website: CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN.
9. FAQ About Other Career Paths After Software Engineering
9.1. What are some common career paths for former software engineers?
Former software engineers often transition into roles such as developer relations, technical writing, product management, data science, and security analysis. These roles leverage their technical skills in different capacities.
9.2. How can I leverage my software engineering skills in a new career?
Your software engineering skills are valuable in many fields. You can use your problem-solving abilities, technical knowledge, and analytical skills to excel in various roles.
9.3. What skills are most transferable from software engineering to other fields?
Key transferable skills include problem-solving, analytical thinking, attention to detail, communication, and project management.
9.4. How can I prepare for a career change from software engineering?
To prepare for a career change, identify your interests, assess your skills, gain relevant experience, and network with professionals in your desired field.
9.5. Are there any certifications that can help me transition to a new career?
Certifications in project management, data science, security analysis, and other fields can enhance your credibility and demonstrate your knowledge.
9.6. What is the demand for professionals in these alternative career paths?
Many alternative career paths, such as data science, security analysis, and developer relations, are in high demand, offering excellent job opportunities.
9.7. How can CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN help me transition to the automotive repair industry?
CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN offers specialized training programs that leverage your software engineering skills to excel in the automotive repair industry, particularly in remote diagnostics.
9.8. What are the benefits of working in the automotive repair industry?
The automotive repair industry offers job security, opportunities for remote work, and the chance to work with cutting-edge technology.
9.9. Can I work remotely in the automotive repair industry?
Yes, many roles in the automotive repair industry, such as remote diagnostic technician, offer the flexibility to work remotely.
9.10. How can I learn more about career opportunities in the automotive repair industry?
Visit CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN to explore our training programs and learn about career opportunities in the automotive repair industry. Contact us at Address: 1700 W Irving Park Rd, Chicago, IL 60613, United States. Whatsapp: +1 (641) 206-8880. Website: CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN.
Transitioning from software engineering to a new career path can be a fulfilling journey. By identifying your interests, leveraging your skills, and pursuing relevant training, you can find a career that better aligns with your passions and goals.