Considering a Software Sales Career? This dynamic field offers incredible earning potential and career advancement opportunities, especially within the automotive repair industry. At CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN, we equip you with the skills and knowledge needed to excel in this lucrative area, focusing on remote diagnostic and repair solutions. Unlock your potential in tech sales, software sales jobs, and SaaS sales with our specialized training programs, giving you the edge in today’s competitive market.
Contents
- 1. What is a Software Sales Career?
- 1.1. Why is Software Sales Important in the Automotive Repair Industry?
- 1.2. How Has Technology Changed Software Sales?
- 2. Different Types of Software Sales Positions
- 2.1. Sales Development Representative (SDR)
- 2.2. Account Executive (AE)
- 2.3. Outside Sales Representative
- 2.4. Post-Sales Account Manager
- 2.5. Sales Manager
- 2.6. VP of Sales
- 2.7. Sales Operations
- 2.8. Sales Engineer
- 2.9. How to Choose the Right Sales Role for You
- 3. Essential Skills for a Software Sales Career
- 3.1. How to Improve Your Communication Skills
- 3.2. Developing Technical Knowledge
- 4. Building a Software Sales Career in the Automotive Repair Industry
- 4.1. Understanding the Needs of Automotive Repair Shops
- 4.2. Tailoring Your Sales Approach for the Automotive Industry
- 5. Leveraging CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN for Career Advancement
1. What is a Software Sales Career?
A software sales career involves selling software products or services to businesses or individuals. It is a dynamic field where professionals act as advocates, understanding client needs and providing tailored technological solutions.
The core of a software sales career lies in offering potential clients technology that solves their problems. These sales professionals need to deeply understand their client’s needs and match them with appropriate software solutions. According to a report by Gartner, the software industry is continuously growing, with a projected global revenue of $620 billion in 2024, emphasizing the importance of skilled sales professionals in this sector.
1.1. Why is Software Sales Important in the Automotive Repair Industry?
In the automotive repair industry, software sales is crucial for providing remote diagnostic and repair solutions. These solutions enable technicians to diagnose and fix vehicles from a distance, saving time and resources.
Software sales plays a pivotal role in the automotive repair sector by offering cutting-edge remote diagnostic and repair solutions. According to a study by Grand View Research, the automotive diagnostic scan tools market is expected to reach $8.1 billion by 2027, highlighting the increasing reliance on software solutions for vehicle maintenance and repair. At CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN, we focus on equipping professionals with the skills to effectively sell and implement these advanced technologies.
1.2. How Has Technology Changed Software Sales?
Technology has significantly transformed software sales, with the rise of SaaS models, remote communication tools, and data-driven sales strategies. These advancements enable more efficient and personalized sales processes.
The digital era has revolutionized software sales, ushering in SaaS models, remote communication tools, and data-driven strategies. According to Salesforce, companies using AI-powered sales tools have seen a 50% increase in leads and appointments. Our training at CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN integrates these technological advancements, providing you with the skills to leverage these tools effectively and stay ahead in the competitive sales landscape.
2. Different Types of Software Sales Positions
The software sales field offers various roles, each with unique responsibilities and opportunities for growth. Understanding these roles is essential for charting a successful career path.
The software sales sector is diverse, offering roles from entry-level to executive positions. Each role requires a specific skill set and offers unique opportunities for growth and advancement. Below is an overview of common software sales positions, including their responsibilities, average salaries, and potential career trajectories.
2.1. Sales Development Representative (SDR)
Sales Development Representatives (SDRs) focus on generating new leads through cold calling and outreach. Their primary goal is to set up meetings between potential clients and account executives.
Description: SDRs are responsible for identifying and qualifying leads, often through cold outreach. They play a critical role in building the sales pipeline.
Average Base Salary: $48,000
Average Total Compensation: $75,000
Pros: Entry point into sales with opportunities to learn sales techniques and product knowledge.
Cons: Lower starting pay and higher pressure to meet quotas.
Opportunities for Advancement: SDR to Account Executive (AE) or Sales Manager.
According to data from The Bridge Group, SDRs who consistently meet or exceed their quotas are more likely to advance to AE roles within 12-18 months.
2.2. Account Executive (AE)
Account Executives (AEs) manage client relationships and close deals. They are central to driving revenue growth by understanding client needs and offering tailored software solutions.
Description: AEs are responsible for managing relationships with potential clients and closing deals. They need to have a deep understanding of the software product and the client’s needs.
Average Base Salary: $62,000
Average On-Target Earnings (OTE): $126,000
Pros: High earning potential through commissions and bonuses, direct impact on company revenue.
Cons: Success depends on the quality of the product and market demand.
Opportunities for Advancement: Sales Manager or VP of Sales.
HubSpot reports that AEs with strong product knowledge and sales skills can significantly increase their closing rates, leading to faster career advancement.
2.3. Outside Sales Representative
Outside Sales Representatives build relationships in external markets, often working remotely. They need to be self-motivated and capable of managing their time effectively.
Description: These reps build relationships in outside markets, often working independently and remotely.
Pros: Independence and flexibility in schedule, opportunity to explore new markets.
Cons: Requires strong self-discipline and may face challenges in maintaining regular communication with the main office.
Opportunities for Advancement: Transition to Account Executive or Sales Management roles.
A study by the Harvard Business Review found that outside sales reps who use mobile CRM tools are 65% more likely to achieve their sales targets.
2.4. Post-Sales Account Manager
Post-Sales Account Managers focus on maintaining client relationships after a deal is closed. They work to renew contracts, upsell additional services, and ensure client satisfaction.
Description: These managers ensure client satisfaction, renew contracts, and identify opportunities for upselling.
Pros: Opportunity to build long-term relationships with clients, less pressure compared to direct sales roles.
Cons: Lower commission potential compared to AEs, requires excellent problem-solving skills.
Opportunities for Advancement: Sales Manager or VP of Sales.
According to a report by Bain & Company, increasing customer retention rates by 5% can increase profits by 25% to 95%, highlighting the importance of post-sales account managers.
2.5. Sales Manager
Sales Managers oversee sales teams, providing training, setting goals, and monitoring performance. They play a critical role in driving team success and achieving sales targets.
Description: These managers lead sales teams, set goals, provide training, and monitor performance.
Base Salary: $89,000 – $95,000
On-Target Earnings: $127,000 – $147,000
Pros: High earning potential, leadership opportunities, and significant impact on team performance.
Cons: Requires strong leadership skills, pressure to meet team targets, and less client-facing work.
Opportunities for Advancement: VP or Head of Sales.
Research from the Sales Management Association indicates that effective sales managers can improve team performance by up to 27%.
2.6. VP of Sales
The VP of Sales is an executive role responsible for the overall sales strategy and performance of the company. They work closely with marketing and other departments to align sales efforts with business goals.
Description: As an executive, the VP of Sales is responsible for the entire company’s sales performance, strategy, and execution.
Pros: High earning potential, opportunity to shape the company’s sales direction, and significant influence on business strategy.
Cons: High responsibility, pressure to meet company-wide sales targets, and potential for high turnover if sales targets are not met.
Opportunities for Advancement: Lateral transition to other executive positions like CFO or CEO, or founding their own company.
A study by McKinsey & Company found that companies with strong sales leadership are 1.3 times more likely to achieve above-average revenue growth.
2.7. Sales Operations
Sales Operations professionals support sales teams by providing marketing materials, evaluating processes, and reporting to sales leadership. They ensure the smooth functioning of the sales process.
Description: Sales Operations provides support to sales teams, ensuring smooth operations, evaluating processes, and reporting to sales leadership.
Pros: Good starting salary, opportunity to work behind the scenes and contribute to sales success.
Cons: Little to no commission-based earnings, requires strong analytical and organizational skills.
Opportunities for Advancement: Sales Leadership roles, such as VP of Sales.
Gleanster Research reports that companies with strong sales operations functions see a 20% improvement in sales productivity.
2.8. Sales Engineer
Sales Engineers provide technical expertise during the sales process, answering questions about software products and services. Their knowledge helps clients understand the technical aspects of the software.
Description: Sales Engineers provide technical expertise during the sales process, answering technical questions and demonstrating the software’s capabilities.
Pros: High earning potential, opportunity to combine technical skills with sales acumen, and involvement in cutting-edge technology.
Cons: Requires deep technical knowledge, strong communication skills, and ability to explain complex concepts to non-technical clients.
Opportunities for Advancement: Account Executive, Sales Manager, or executive roles such as CTO, CRO, or CEO.
According to a study by Forrester, sales engineers can increase win rates by up to 20% by providing technical expertise and building trust with clients.
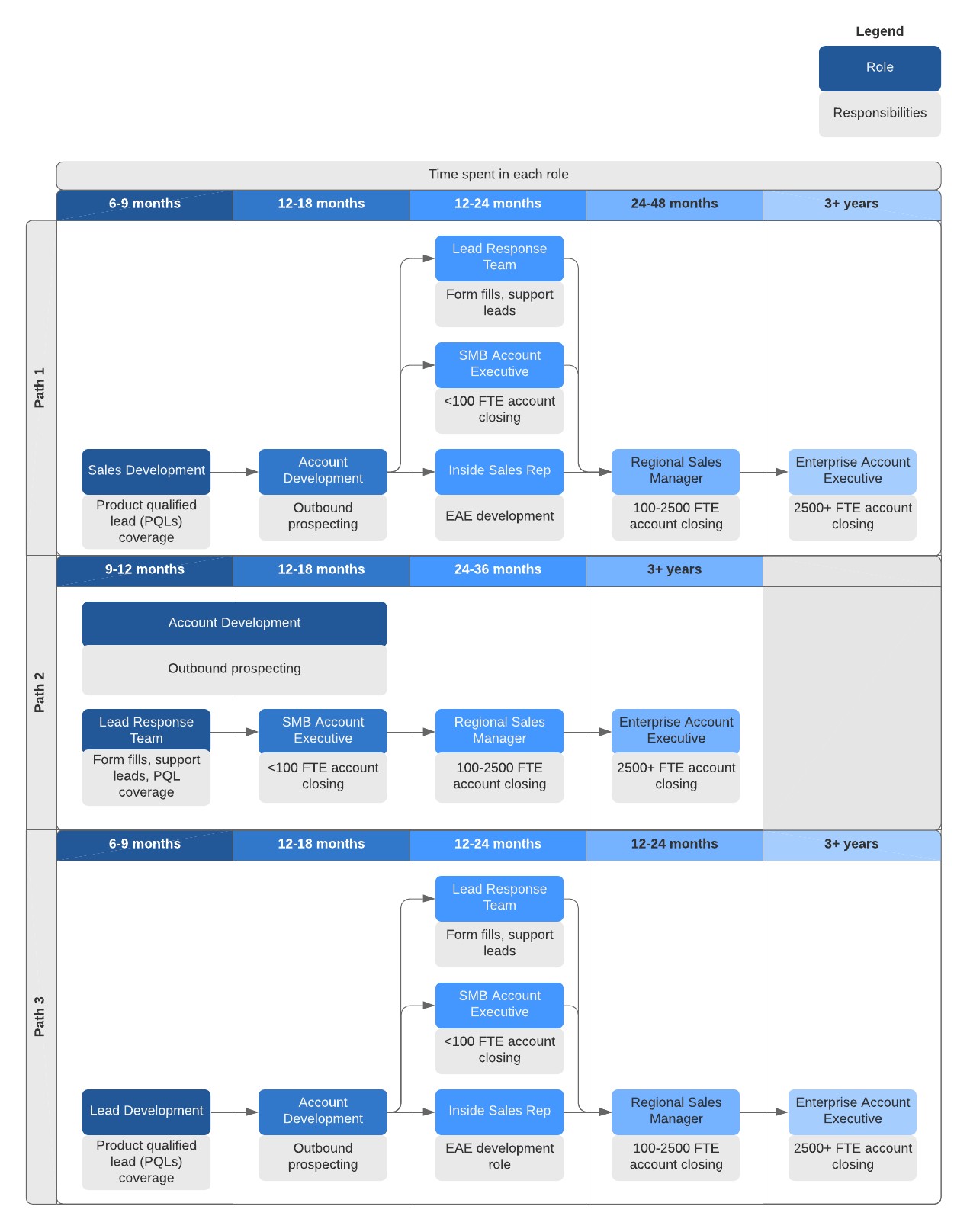 software sales career path
software sales career path
2.9. How to Choose the Right Sales Role for You
Choosing the right sales role depends on your skills, interests, and career goals. Consider your strengths and what you enjoy doing to find a position that aligns with your aspirations.
Selecting the ideal sales role requires careful consideration of your unique skills, interests, and long-term career objectives. By aligning your strengths with the demands of a particular role, you can increase your chances of success and job satisfaction. Here’s how to make an informed decision:
- Assess Your Strengths:
- Communication Skills: Evaluate your ability to articulate ideas clearly and persuasively. Sales roles like Account Executive and Sales Manager require excellent communication skills to build rapport and close deals.
- Technical Aptitude: If you have a strong understanding of technology, a role as a Sales Engineer might be a good fit. Sales Engineers need to explain complex technical concepts to clients.
- Relationship Building: Roles such as Post-Sales Account Manager require strong relationship-building skills to maintain client satisfaction and foster long-term partnerships.
- Persistence and Resilience: Sales Development Representatives (SDRs) need to be persistent and resilient, as they face frequent rejection while generating leads.
- Leadership Abilities: If you enjoy leading and motivating teams, a Sales Manager position could be ideal. Sales Managers need to set goals, provide training, and monitor team performance.
- Consider Your Interests:
- Direct Sales: If you enjoy the thrill of closing deals and directly impacting revenue, roles like Account Executive or Outside Sales Representative might be appealing.
- Technical Sales: If you are passionate about technology and enjoy explaining technical concepts, a Sales Engineer role could be a good fit.
- Relationship Management: If you prefer building long-term relationships and ensuring customer satisfaction, a Post-Sales Account Manager position might be a good choice.
- Strategic Planning: If you enjoy developing sales strategies and aligning sales efforts with business goals, a VP of Sales role could be a good fit.
- Define Your Career Goals:
- Entry-Level Positions: If you are just starting your career, roles like Sales Development Representative (SDR) provide a great entry point into the sales field.
- High Earning Potential: Roles like Account Executive and VP of Sales offer high earning potential through commissions and bonuses.
- Leadership Opportunities: Sales Manager and VP of Sales positions offer opportunities to lead and mentor sales teams.
- Executive Roles: Experienced sales professionals can advance to executive positions like VP of Sales, CFO, or CEO.
- Research Different Sales Roles:
- Job Descriptions: Review job descriptions for different sales roles to understand the required skills, responsibilities, and qualifications.
- Salary Ranges: Research the average salaries for different sales roles to understand the earning potential.
- Career Paths: Explore the typical career paths for different sales roles to understand the potential for advancement.
- Network with Sales Professionals:
- Attend Industry Events: Attend industry events to network with sales professionals and learn about different sales roles.
- Join Sales Communities: Join online sales communities to connect with other sales professionals and ask questions about different sales roles.
- Seek Mentorship: Seek mentorship from experienced sales professionals who can provide guidance and advice on choosing the right sales role.
- Consider the Company Culture:
- Company Values: Research the company’s values and mission to ensure they align with your own.
- Work Environment: Consider the company’s work environment and whether it is a good fit for your personality and work style.
- Growth Opportunities: Explore the company’s growth opportunities and whether they offer training and development programs to help you advance your career.
By carefully assessing your strengths, interests, and career goals, you can choose the right sales role that aligns with your aspirations and sets you up for success. Additionally, researching different sales roles, networking with sales professionals, and considering the company culture can help you make an informed decision and find a fulfilling career in sales.
3. Essential Skills for a Software Sales Career
To succeed in software sales, certain skills are indispensable. These include communication, negotiation, technical knowledge, and problem-solving.
Succeeding in a software sales career requires a combination of technical expertise, interpersonal skills, and strategic thinking. Here are some indispensable skills:
- Communication Skills:
- Active Listening: Listening attentively to clients to understand their needs and pain points.
- Clear Articulation: Communicating complex technical concepts in a clear and concise manner.
- Persuasion: Influencing clients to see the value of the software product or service.
- Technical Knowledge:
- Product Knowledge: Having a deep understanding of the software product or service being sold.
- Industry Knowledge: Understanding the trends, challenges, and opportunities in the software industry.
- Technical Proficiency: Being able to use and demonstrate the software product or service effectively.
- Sales Techniques:
- Lead Generation: Identifying and qualifying potential clients.
- Sales Process: Following a structured sales process to close deals.
- Negotiation: Negotiating terms and conditions with clients to reach mutually beneficial agreements.
- Business Acumen:
- Market Analysis: Understanding the market landscape, including competitors and target customers.
- Financial Literacy: Being able to understand financial statements and calculate ROI for clients.
- Strategic Thinking: Developing sales strategies and aligning them with business goals.
- Interpersonal Skills:
- Relationship Building: Building and maintaining strong relationships with clients.
- Empathy: Understanding and responding to clients’ emotions and concerns.
- Teamwork: Collaborating effectively with colleagues to achieve sales targets.
- Problem-Solving Skills:
- Analytical Skills: Analyzing complex problems and identifying potential solutions.
- Creativity: Developing innovative approaches to overcome challenges.
- Decision-Making: Making informed decisions based on available data and insights.
- Time Management Skills:
- Prioritization: Prioritizing tasks and activities to maximize productivity.
- Organization: Keeping track of leads, clients, and deals in an organized manner.
- Efficiency: Streamlining sales processes to improve efficiency and reduce time wasted.
- Adaptability:
- Flexibility: Being able to adapt to changing market conditions and client needs.
- Resilience: Bouncing back from setbacks and maintaining a positive attitude.
- Continuous Learning: Staying up-to-date with the latest trends and technologies in the software industry.
By developing and honing these essential skills, software sales professionals can increase their chances of success and excel in their careers. Additionally, continuous learning, networking with industry peers, and seeking mentorship from experienced professionals can further enhance their skills and expertise.
3.1. How to Improve Your Communication Skills
Improving communication skills involves active listening, clear articulation, and effective use of different communication channels. Practice and feedback are essential.
To enhance your communication skills, consider these strategies:
- Active Listening:
- Focus Your Attention: Concentrate fully on the speaker, avoiding distractions and interruptions.
- Show Empathy: Try to understand the speaker’s perspective and emotions.
- Ask Clarifying Questions: Ask questions to ensure you understand the message correctly.
- Provide Feedback: Summarize what you’ve heard to confirm your understanding.
- Clear Articulation:
- Use Simple Language: Avoid jargon and technical terms that the audience may not understand.
- Structure Your Thoughts: Organize your ideas logically before speaking.
- Speak Clearly and Slowly: Enunciate your words and speak at a pace that is easy for others to follow.
- Use Visual Aids: Use visual aids like charts and graphs to support your message.
- Effective Use of Communication Channels:
- Choose the Right Channel: Select the most appropriate communication channel for the message, whether it’s email, phone, video conference, or in-person meeting.
- Tailor Your Message: Adapt your message to the specific communication channel and audience.
- Follow Up: Follow up after the communication to ensure the message was received and understood.
- Practice and Feedback:
- Seek Feedback: Ask colleagues, mentors, and clients for feedback on your communication skills.
- Record Yourself: Record yourself speaking and analyze your performance.
- Join a Public Speaking Group: Join a public speaking group like Toastmasters to practice and improve your communication skills.
- Take a Communication Course: Consider taking a communication course to learn new techniques and strategies.
- Nonverbal Communication:
- Maintain Eye Contact: Maintain eye contact with the speaker to show engagement and interest.
- Use Positive Body Language: Use positive body language like smiling, nodding, and open posture to convey confidence and approachability.
- Be Aware of Facial Expressions: Be mindful of your facial expressions to ensure they align with your message.
- Written Communication:
- Use Proper Grammar and Spelling: Proofread your writing to ensure it is free of errors.
- Write Clearly and Concisely: Use clear and concise language to convey your message effectively.
- Organize Your Thoughts: Structure your writing logically with clear paragraphs and headings.
- Cultural Sensitivity:
- Be Aware of Cultural Differences: Be aware of cultural differences in communication styles and adapt your approach accordingly.
- Use Inclusive Language: Use inclusive language that is respectful of all individuals.
- Avoid Stereotypes: Avoid making assumptions or stereotypes about people from different cultures.
By implementing these strategies and continuously practicing your communication skills, you can become a more effective communicator and build stronger relationships with clients, colleagues, and other stakeholders. Effective communication is essential for success in software sales and can help you achieve your career goals.
3.2. Developing Technical Knowledge
Staying updated with the latest technology trends, attending workshops, and hands-on experience with software products are key to developing technical knowledge.
To develop technical knowledge effectively, consider these strategies:
- Stay Updated with the Latest Technology Trends:
- Read Industry Publications: Subscribe to industry publications, blogs, and newsletters to stay informed about the latest trends and technologies.
- Follow Industry Experts: Follow industry experts on social media and online forums to gain insights into emerging technologies.
- Attend Webinars and Conferences: Attend webinars and conferences to learn about new technologies and network with industry professionals.
- Hands-On Experience with Software Products:
- Use the Software: Use the software products you are selling to gain hands-on experience and understand their features and benefits.
- Experiment with Different Use Cases: Experiment with different use cases and scenarios to understand how the software can be applied in various situations.
- Participate in Beta Programs: Participate in beta programs to gain early access to new software products and provide feedback to developers.
- Attend Workshops and Training Programs:
- Enroll in Technical Courses: Enroll in technical courses to learn about specific software products, programming languages, or technical concepts.
- Attend Workshops and Seminars: Attend workshops and seminars to gain practical skills and knowledge.
- Get Certified: Get certified in relevant technologies to demonstrate your expertise and enhance your credibility.
- Networking and Collaboration:
- Join Technical Communities: Join online and offline technical communities to connect with other professionals and share knowledge.
- Participate in Hackathons: Participate in hackathons to collaborate with other developers and work on challenging technical projects.
- Attend Meetups: Attend meetups to learn from industry experts and network with peers.
- Self-Study and Online Resources:
- Online Courses: Take online courses on platforms like Coursera, Udemy, and edX to learn about various technical topics.
- Tutorials and Documentation: Read tutorials and documentation to understand how to use different software products and technologies.
- Practice Projects: Work on practice projects to apply your knowledge and develop your skills.
- Seek Mentorship:
- Find a Mentor: Find a mentor who can provide guidance and support as you develop your technical knowledge.
- Ask Questions: Ask questions and seek advice from your mentor to gain insights and perspectives.
- Learn from Their Experiences: Learn from your mentor’s experiences and mistakes to avoid common pitfalls.
- Stay Curious and Inquisitive:
- Ask Why: Ask why things work the way they do and seek to understand the underlying principles.
- Experiment and Explore: Experiment with different technologies and explore new ideas to expand your knowledge.
- Be Open to New Ideas: Be open to new ideas and perspectives and challenge your assumptions.
By implementing these strategies and continuously investing in your technical knowledge, you can become a more valuable and effective software sales professional. Technical knowledge is essential for understanding the software products you are selling, communicating effectively with technical clients, and providing tailored solutions to meet their needs. Additionally, staying updated with the latest technology trends can help you identify new opportunities and stay ahead of the competition.
4. Building a Software Sales Career in the Automotive Repair Industry
Focusing on the automotive repair industry requires understanding its specific needs and challenges. Tailoring your sales approach to these factors can lead to greater success.
Building a successful software sales career in the automotive repair industry requires understanding its specific needs, challenges, and opportunities. Here’s how to focus your efforts:
- Understand the Automotive Repair Industry:
- Industry Trends: Stay informed about the latest trends in the automotive repair industry, such as the increasing use of technology in vehicle diagnostics and repair.
- Challenges: Understand the challenges faced by automotive repair shops, such as the shortage of skilled technicians and the complexity of modern vehicles.
- Opportunities: Identify the opportunities for software solutions to address these challenges and improve efficiency, productivity, and profitability.
- Identify Target Customers:
- Independent Repair Shops: Target independent repair shops that may lack the resources and expertise to invest in advanced technology.
- Dealership Service Centers: Target dealership service centers that need to improve their efficiency and customer satisfaction.
- Mobile Mechanics: Target mobile mechanics who need portable and easy-to-use software solutions.
- Tailor Your Sales Approach:
- Highlight the Benefits: Highlight the benefits of your software solutions in terms of improved efficiency, reduced costs, and increased revenue.
- Address Specific Pain Points: Address the specific pain points of your target customers, such as the need for remote diagnostics and the shortage of skilled technicians.
- Provide Case Studies: Provide case studies and testimonials from other automotive repair shops that have successfully implemented your software solutions.
- Build Relationships with Key Stakeholders:
- Attend Industry Events: Attend industry events to network with key stakeholders, such as shop owners, service managers, and technicians.
- Join Industry Associations: Join industry associations to connect with other professionals and stay informed about industry trends.
- Offer Free Training and Support: Offer free training and support to help your customers get the most out of your software solutions.
- Leverage Technology:
- CRM Software: Use CRM software to manage your leads, track your sales pipeline, and communicate with your customers.
- Remote Demo Tools: Use remote demo tools to showcase your software solutions to potential customers without having to travel.
- Social Media: Use social media to promote your software solutions and connect with potential customers.
- Stay Updated with Technology:
- Continuous Learning: Continuously learn about new technologies and trends in the automotive repair industry.
- Attend Technical Training: Attend technical training courses to stay updated with the latest software products and features.
- Get Certified: Get certified in relevant technologies to demonstrate your expertise and enhance your credibility.
- Focus on Customer Satisfaction:
- Provide Excellent Customer Service: Provide excellent customer service to ensure your customers are satisfied with your software solutions.
- Respond Promptly to Inquiries: Respond promptly to customer inquiries and address their concerns in a timely manner.
- Seek Feedback: Seek feedback from your customers to identify areas for improvement and ensure their needs are being met.
By focusing on the automotive repair industry, tailoring your sales approach, building relationships with key stakeholders, leveraging technology, staying updated with technology, and focusing on customer satisfaction, you can build a successful software sales career in this dynamic and growing market. The automotive repair industry is constantly evolving, and software solutions are playing an increasingly important role in helping shops stay competitive and provide high-quality service to their customers.
4.1. Understanding the Needs of Automotive Repair Shops
To effectively sell software, it’s crucial to understand the daily operations, challenges, and technological needs of automotive repair shops.
To effectively sell software to automotive repair shops, it is crucial to have a deep understanding of their daily operations, challenges, and technological needs. Here’s how to gain that understanding:
- Daily Operations:
- Workflow: Understand the workflow of an automotive repair shop, from customer check-in to vehicle diagnosis, repair, and check-out.
- Tasks: Identify the tasks performed by different members of the shop, such as service advisors, technicians, and shop managers.
- Tools and Equipment: Be familiar with the tools and equipment used in automotive repair shops, such as diagnostic scanners, repair tools, and lifts.
- Challenges:
- Shortage of Skilled Technicians: Understand the challenges faced by automotive repair shops due to the shortage of skilled technicians.
- Complexity of Modern Vehicles: Understand the challenges posed by the increasing complexity of modern vehicles, with their advanced electronics and computer systems.
- Keeping Up with Technology: Understand the challenges faced by automotive repair shops in keeping up with the latest technology and software updates.
- Competition: Understand the challenges posed by competition from other repair shops and dealerships.
- Customer Expectations: Understand the challenges of meeting customer expectations for fast, reliable, and affordable service.
- Technological Needs:
- Diagnostic Software: Understand the need for diagnostic software to quickly and accurately diagnose vehicle problems.
- Repair Information Systems: Understand the need for repair information systems to provide technicians with detailed instructions and diagrams.
- Shop Management Software: Understand the need for shop management software to streamline operations, manage inventory, and track customer data.
- Customer Communication Tools: Understand the need for customer communication tools to keep customers informed about the status of their repairs and schedule appointments.
- How to Gain Understanding:
- Visit Automotive Repair Shops: Visit automotive repair shops to observe their operations and talk to shop owners, service advisors, and technicians.
- Attend Industry Events: Attend industry events, such as trade shows and conferences, to learn about the latest trends and technologies in the automotive repair industry.
- Read Industry Publications: Read industry publications, blogs, and newsletters to stay informed about the challenges and opportunities faced by automotive repair shops.
- Talk to Software Users: Talk to automotive repair shops that are already using software solutions to understand their experiences and challenges.
- Conduct Surveys: Conduct surveys to gather feedback from automotive repair shops about their needs and challenges.
- Use Your Understanding to Sell Software:
- Highlight the Benefits: Highlight the benefits of your software solutions in terms of addressing the specific challenges faced by automotive repair shops.
- Provide Customized Solutions: Provide customized solutions that meet the specific needs of each automotive repair shop.
- Offer Training and Support: Offer training and support to help automotive repair shops get the most out of your software solutions.
- Build Relationships: Build relationships with shop owners, service advisors, and technicians to gain their trust and loyalty.
By understanding the daily operations, challenges, and technological needs of automotive repair shops, you can effectively sell software solutions that address their specific pain points and improve their efficiency, productivity, and profitability. Additionally, by building relationships with shop owners, service advisors, and technicians, you can gain their trust and loyalty, leading to long-term partnerships and increased sales.
4.2. Tailoring Your Sales Approach for the Automotive Industry
A tailored sales approach involves highlighting the specific benefits of your software for automotive repair, providing relevant case studies, and understanding the industry’s terminology.
Tailoring your sales approach for the automotive industry involves understanding the specific needs, challenges, and opportunities of automotive repair shops and tailoring your sales message, strategies, and tactics accordingly. Here’s how to do it:
- Research the Industry:
- Industry Trends: Stay informed about the latest trends in the automotive industry, such as the increasing use of technology in vehicles and the growing demand for electric and hybrid vehicles.
- Challenges: Understand the challenges faced by automotive repair shops, such as the shortage of skilled technicians, the complexity of modern vehicles, and the need to keep up with changing technology.
- Opportunities: Identify the opportunities for software solutions to address these challenges and improve efficiency, productivity, and profitability.
- Identify Target Customers:
- Independent Repair Shops: Identify independent repair shops that may lack the resources and expertise to invest in advanced technology.
- Dealership Service Centers: Identify dealership service centers that need to improve their efficiency and customer satisfaction.
- Specialty Shops: Identify specialty shops that focus on specific types of vehicles or repairs, such as collision repair shops or transmission shops.
- Understand Customer Needs:
- Talk to Customers: Talk to automotive repair shops to understand their specific needs, challenges, and pain points.
- Conduct Surveys: Conduct surveys to gather feedback from automotive repair shops about their needs and priorities.
- Observe Operations: Observe the operations of automotive repair shops to understand their workflow and identify areas for improvement.
- Tailor Your Message:
- Highlight Benefits: Highlight the benefits of your software solutions in terms of addressing the specific needs and challenges of automotive repair shops.
- Use Industry Terminology: Use industry terminology and language to communicate effectively with automotive repair shops.
- Provide Case Studies: Provide case studies and testimonials from other automotive repair shops that have successfully implemented your software solutions.
- Adapt Your Sales Strategies:
- Demonstrations: Offer demonstrations of your software solutions to show automotive repair shops how they work and how they can benefit their business.
- Pilot Programs: Offer pilot programs to allow automotive repair shops to try out your software solutions before committing to a purchase.
- Customized Solutions: Offer customized solutions that meet the specific needs of each automotive repair shop.
- Build Relationships:
- Attend Industry Events: Attend industry events to network with automotive repair shops and build relationships with key decision-makers.
- Join Industry Associations: Join industry associations to connect with other professionals in the automotive industry.
- Offer Support: Offer ongoing support and training to help automotive repair shops get the most out of your software solutions.
- Stay Updated:
- Continuous Learning: Continuously learn about new technologies and trends in the automotive industry.
- Attend Training: Attend training courses and workshops to stay updated with the latest software products and features.
- Read Industry Publications: Read industry publications and blogs to stay informed about the challenges and opportunities faced by automotive repair shops.
By tailoring your sales approach for the automotive industry, you can increase your chances of success and build long-term relationships with automotive repair shops. The key is to understand their specific needs, challenges, and opportunities and to communicate effectively how your software solutions can help them improve their efficiency, productivity, and profitability. Additionally, by building relationships with key decision-makers and offering ongoing support and training, you can establish yourself as a trusted partner and advisor.
5. Leveraging CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN for Career Advancement
CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN provides specialized training and resources to help you excel in software sales within the automotive repair sector.
Leveraging CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN for career advancement in software sales within the automotive repair sector involves taking advantage of its specialized training and resources to develop the skills, knowledge, and network needed to succeed. Here’s how to do it:
- Take Specialized Training Courses:
- Software Sales Training: Enroll in software sales training courses offered by CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN to learn the fundamentals of software sales, including lead generation, sales process, negotiation, and closing.
- Automotive Repair Industry Training: Enroll in automotive repair industry training courses to gain a deep understanding of the industry, its trends, challenges, and opportunities.
- Technical Training: Enroll in technical training courses to learn about the software products and technologies used in the automotive repair industry.
- Utilize Resources:
- Online Resources: Utilize online resources offered by CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN, such as articles, tutorials, and webinars, to stay informed about the latest trends and technologies in software sales and the automotive repair industry.
- Case Studies: Study case studies of successful software sales in the automotive repair industry to learn best practices and strategies.
- Templates and Tools: Utilize templates and tools offered by CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN, such as sales scripts, presentation templates, and CRM tools, to streamline your sales process and improve your efficiency.
- Network with Professionals:
- Attend Events: Attend industry events organized by CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN to network with other professionals in software sales and the automotive repair industry.
- Join Online Communities: Join online communities and forums hosted by CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN to connect with peers, share knowledge, and ask questions.
- Seek Mentorship: Seek mentorship from experienced professionals in software sales and the automotive repair industry through CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN’s mentorship program.
- Stay Updated with the Latest Trends:
- Industry News: Stay updated with the latest news and trends in software sales and the automotive repair industry through CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN’s newsfeed.
- Research Reports: Read research reports and white papers published by CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN to gain insights into emerging technologies and market opportunities.
- Webinars and Conferences: Attend webinars and conferences organized by CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN to learn about the latest developments and innovations in the industry.
- Get Certified:
- Software Sales Certification: Get certified in software sales through CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN’s certification program to demonstrate your expertise and enhance your credibility.
- Automotive Repair Industry Certification: Get certified in automotive repair industry through CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN’s certification program to validate your knowledge and skills in the industry.
- Technical Certification: Get certified in relevant software products and technologies to demonstrate your proficiency and expertise.
- Leverage Placement Assistance:
- Job Board: Utilize the job board offered by CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN to find job opportunities in software sales within the automotive repair industry.
- Resume Review: Get your resume reviewed by CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN’s career services team to ensure it is optimized for software sales roles.
- Interview Preparation: Participate in interview preparation sessions to practice your interviewing skills and get feedback from experienced professionals.
By leveraging CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN’s specialized training,