Are you curious about the “Software Testing Career Path Uk” and where it can lead you? At CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN, we’re here to illuminate the diverse roles and opportunities within the software testing field, helping you find a fulfilling and prosperous career. Explore how you can advance from a junior tester to a leadership role or even specialize in exciting areas like cybersecurity testing and discover the career journey with remote car repair skills in the UK.
Contents
- 1. Understanding the Landscape of Software Testing Career Path UK
- 1.1. What is the typical software testing career path UK?
- Breaking Down the Roles in UK Software Testing
- 1.2. What are the key skills needed to advance in a software testing career path UK?
- Enhancing Your Skill Set for Career Advancement
- 1.3. How do certifications impact career progression in software testing in the UK?
- The Value of Certifications in the UK Job Market
- 1.4. What is the salary range for different software testing roles in the UK?
- Factors Influencing Salary in the UK Software Testing Market
- 1.5. What are the emerging trends in software testing in the UK, and how do they affect career paths?
- Staying Ahead of the Curve in UK Software Testing
- 2. Detailed Career Paths in Software Testing in the UK
- 2.1. QA Analyst/Test Engineer path
- Climbing the Ladder as a QA Analyst/Test Engineer in the UK
- 2.2. Test Automation Engineer path
- Mastering Test Automation in the UK Job Market
- 2.3. Performance Tester path
- Becoming a Performance Testing Expert in the UK
- 2.4. Security Tester path
- Securing Your Career as a Security Tester in the UK
- 2.5. Test Manager/QA Lead path
- Leading the Way as a Test Manager/QA Lead in the UK
- 3. Specializing in Niche Areas of Software Testing in the UK
- 3.1. AI and Machine Learning Testing
- Becoming an AI and Machine Learning Testing Specialist
- 3.2. Mobile App Testing
- Excelling in Mobile App Testing in the UK Market
- 3.3. IoT Testing
- Navigating the World of IoT Testing
- 3.4. Cloud Testing
- Becoming a Cloud Testing Expert in the UK
- 4. Building a Standout Resume for Software Testing Roles in the UK
- 4.1. Highlighting relevant skills and experience
- Crafting a Compelling Resume
- 4.2. Showcasing certifications and education
- Leveraging Certifications and Education to Stand Out
- 4.3. Tailoring your resume to specific job descriptions
- Customizing Your Resume for Success
- 5. Finding Software Testing Jobs in the UK
- 5.1. Online job boards and recruitment agencies
- Navigating Online Job Boards and Recruitment Agencies
- 5.2. Networking and industry events
- Building Your Network and Attending Industry Events
- 5.3. Company websites and direct applications
- Maximizing Your Success with Direct Applications
- 6. The Future of Software Testing Career Path UK
- 6.1. Impact of artificial intelligence on testing roles
- Preparing for the AI Revolution in Software Testing
- 6.2. The growing importance of soft skills
- Developing Essential Soft Skills for a Thriving Career
- 6.3. Continuous learning and adaptation
- Embracing Lifelong Learning in Software Testing
- FAQ: Your Questions About Software Testing Career Path UK Answered
- 1. What qualifications do I need to start a software testing career in the UK?
- 2. How long does it take to become a senior test engineer in the UK?
1. Understanding the Landscape of Software Testing Career Path UK
1.1. What is the typical software testing career path UK?
The typical software testing career path in the UK starts with entry-level roles like Junior QA Tester or Trainee Test Analyst, progressing to mid-level roles such as QA Analyst or Test Engineer, then advancing to senior positions like Senior Test Analyst, Test Lead, or Test Manager, and potentially leading to roles such as QA Manager, Head of Testing, or even Director of Quality Assurance. Along the way, individuals might specialize in areas like automation testing, performance testing, or security testing, each offering its own trajectory for advancement.
Breaking Down the Roles in UK Software Testing
The software testing landscape in the UK offers a variety of roles, each with specific responsibilities and skill requirements. Here’s a breakdown of the common roles you’ll find:
- Junior QA Tester/Trainee Test Analyst: Entry-level positions focused on executing test cases, identifying bugs, and learning the basics of software testing.
- QA Analyst/Test Engineer: Mid-level roles that involve creating test plans, writing test cases, executing tests, and reporting defects. They may also be involved in automation testing.
- Senior Test Analyst/Test Lead: More experienced roles that require designing complex test scenarios, leading testing efforts, mentoring junior testers, and ensuring the quality of the software.
- Test Manager: Responsible for overseeing all testing activities, managing a team of testers, creating testing strategies, and ensuring adherence to quality standards.
- QA Manager/Head of Testing: Senior management roles that involve setting the overall quality strategy for the organization, managing testing resources, and ensuring the delivery of high-quality software.
- Director of Quality Assurance: Executive-level positions that focus on setting the strategic direction for quality assurance, driving continuous improvement, and ensuring alignment with business goals.
- Automation Tester: Specializes in creating and maintaining automated test scripts using tools like Selenium, JUnit, or TestNG.
- Performance Tester: Focuses on evaluating the performance of software applications, identifying bottlenecks, and ensuring scalability and responsiveness.
- Security Tester: Specializes in identifying security vulnerabilities in software applications through techniques like penetration testing and security audits.
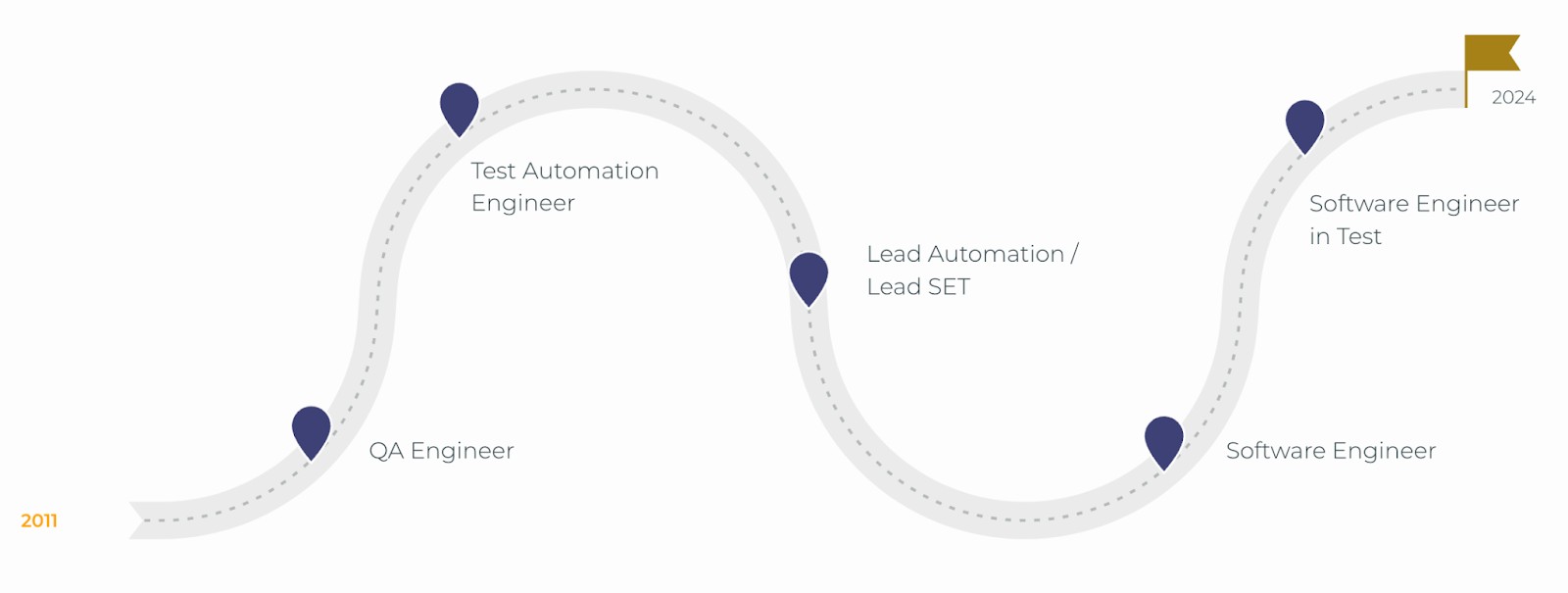 A software testing career path timeline from 2011 to 2024, with key milestones along this path: 2011 – QA Engineer, Test Automation Engineer, Lead Automation / Lead SET, Software Engineer, and 2024 – Software Engineer in Test (final milestone with a flag symbol), with a wavy, dotted line connecting each career role, symbolizing progression over time.
A software testing career path timeline from 2011 to 2024, with key milestones along this path: 2011 – QA Engineer, Test Automation Engineer, Lead Automation / Lead SET, Software Engineer, and 2024 – Software Engineer in Test (final milestone with a flag symbol), with a wavy, dotted line connecting each career role, symbolizing progression over time.
1.2. What are the key skills needed to advance in a software testing career path UK?
To advance in a software testing career path in the UK, key skills include a strong understanding of testing methodologies (Agile, Waterfall), proficiency in test automation tools (Selenium, JUnit), expertise in test management software (Jira, TestRail), solid analytical and problem-solving abilities, effective communication skills, knowledge of programming languages (Java, Python), and familiarity with performance and security testing principles. Continuous learning and adaptation to new technologies are also crucial.
Enhancing Your Skill Set for Career Advancement
To enhance your skill set and progress in your software testing career in the UK, consider the following:
- Testing Methodologies: Understand different testing methodologies such as Agile, Waterfall, and V-model, and know when to apply each one.
- Test Automation Tools: Master test automation tools like Selenium, JUnit, TestNG, and Cypress to automate repetitive tasks and improve testing efficiency.
- Test Management Software: Become proficient in using test management software such as Jira, TestRail, and Zephyr to manage test cases, track defects, and generate reports.
- Analytical and Problem-Solving Skills: Develop strong analytical and problem-solving skills to identify root causes of defects and propose effective solutions.
- Communication Skills: Improve your communication skills to effectively collaborate with developers, project managers, and other stakeholders.
- Programming Languages: Learn programming languages such as Java, Python, or JavaScript to write custom test scripts and automation frameworks.
- Performance and Security Testing: Gain knowledge of performance testing principles and tools like JMeter and Gatling, as well as security testing techniques and tools like OWASP ZAP and Burp Suite.
1.3. How do certifications impact career progression in software testing in the UK?
Certifications significantly impact career progression in software testing in the UK by validating skills and knowledge, increasing credibility, and demonstrating a commitment to professional development. Common certifications like ISTQB and Certified Tester Foundation Level (CTFL) are highly regarded by employers, often leading to better job opportunities, higher salaries, and faster career advancement. Earning specialized certifications in areas such as Agile testing or test automation can further enhance career prospects.
The Value of Certifications in the UK Job Market
In the UK job market, certifications hold significant value for software testing professionals. Here’s why:
- Validation of Skills: Certifications validate your skills and knowledge in specific areas of software testing, providing employers with confidence in your abilities.
- Increased Credibility: Holding certifications enhances your credibility as a software tester, making you a more attractive candidate to potential employers.
- Professional Development: Certifications demonstrate your commitment to continuous professional development and staying up-to-date with industry best practices.
- Better Job Opportunities: Certified testers often have access to better job opportunities and are more likely to be hired for senior-level positions.
- Higher Salaries: Certified professionals typically command higher salaries compared to their non-certified counterparts, reflecting the value employers place on their expertise.
- Career Advancement: Certifications can accelerate career advancement by opening doors to leadership roles and specialized positions.
1.4. What is the salary range for different software testing roles in the UK?
The salary range for software testing roles in the UK varies widely based on experience, skills, location, and company size. Entry-level roles like Junior QA Tester can start from £22,000 to £30,000 per year. Mid-level positions such as QA Analyst or Test Engineer typically range from £30,000 to £45,000. Senior roles like Test Lead or Test Manager can earn between £45,000 and £65,000. Specialized roles such as Automation Tester or Security Tester may command salaries from £50,000 to £80,000 or more, while senior management positions like Head of Testing can reach £80,000 to £120,000+.
Factors Influencing Salary in the UK Software Testing Market
Several factors influence the salary levels for software testing roles in the UK. These include:
- Experience: The number of years of experience in software testing is a significant factor, with more experienced professionals commanding higher salaries.
- Skills: Specialized skills such as test automation, performance testing, and security testing can significantly increase earning potential.
- Location: Salaries tend to be higher in major cities like London, Manchester, and Edinburgh compared to smaller towns or rural areas.
- Company Size: Larger companies and multinational corporations typically offer higher salaries and more comprehensive benefits packages.
- Industry: Certain industries, such as finance, technology, and e-commerce, may offer higher salaries for software testing roles due to the complexity and criticality of their systems.
- Certifications: Holding relevant certifications such as ISTQB or Certified Tester Foundation Level (CTFL) can positively impact salary negotiations.
- Education: A higher level of education, such as a bachelor’s or master’s degree in computer science or a related field, may lead to higher starting salaries.
- Demand: High demand for specific skills or roles in the market can drive salaries up, particularly for niche areas like cybersecurity testing or DevOps testing.
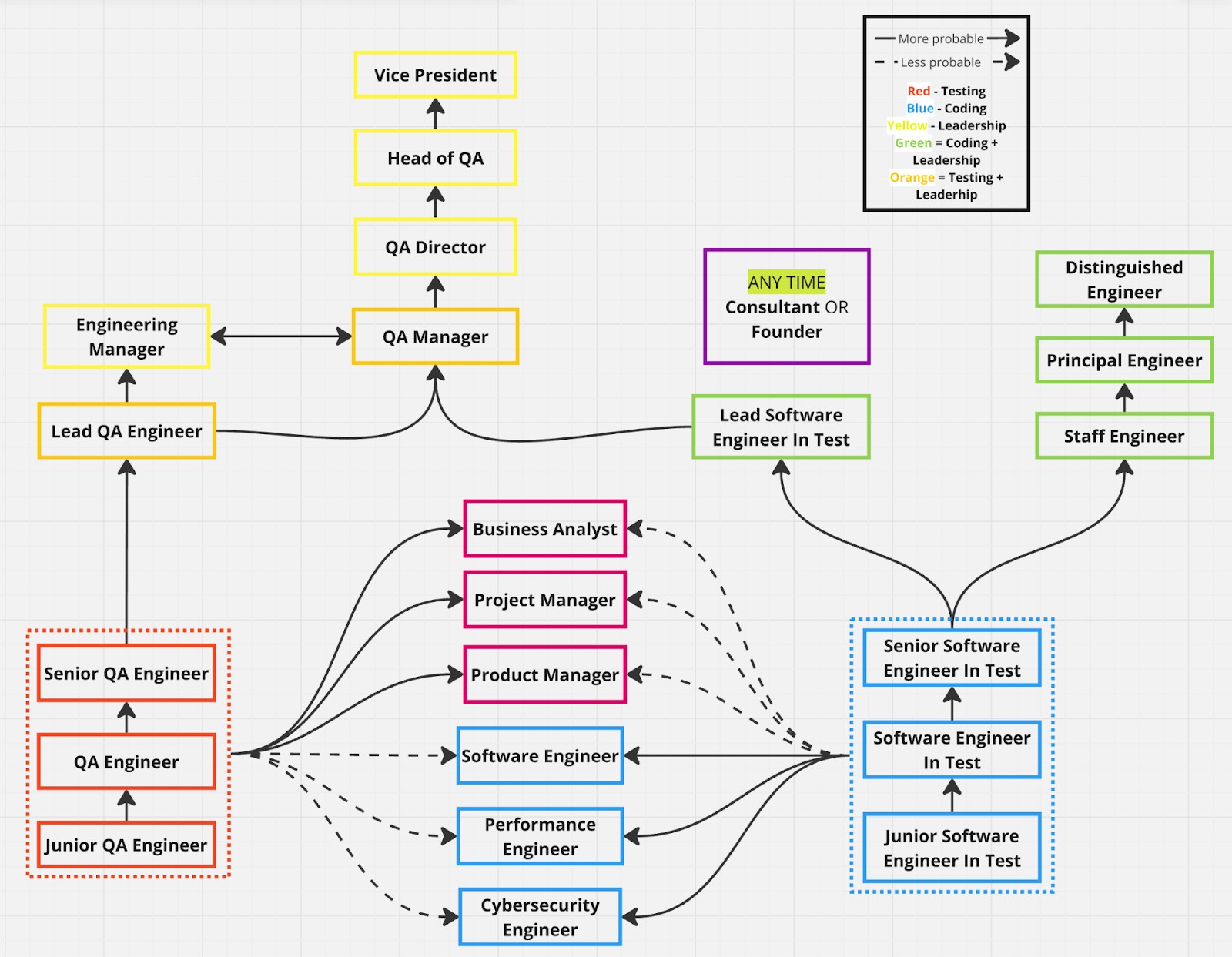 The career roadmap shows paths in software testing: Testing Track: Junior QA Engineer → Senior QA Engineer → QA Manager → Vice President. Coding Track: Junior Software Engineer → Performance/Cybersecurity Engineer. Testing & Coding: Junior Software Engineer in Test → Distinguished Engineer. Leadership Track: QA Manager → Vice President. Flexible Role: Consultant or Founder at any stage. Arrows indicate likely and less likely transitions, with paths based on coding, testing, and leadership focus.
The career roadmap shows paths in software testing: Testing Track: Junior QA Engineer → Senior QA Engineer → QA Manager → Vice President. Coding Track: Junior Software Engineer → Performance/Cybersecurity Engineer. Testing & Coding: Junior Software Engineer in Test → Distinguished Engineer. Leadership Track: QA Manager → Vice President. Flexible Role: Consultant or Founder at any stage. Arrows indicate likely and less likely transitions, with paths based on coding, testing, and leadership focus.
1.5. What are the emerging trends in software testing in the UK, and how do they affect career paths?
Emerging trends in software testing in the UK include the rise of AI and machine learning in testing, increased adoption of DevOps and Agile methodologies, the growing importance of cybersecurity testing, and the shift towards cloud-based testing solutions. These trends are creating new career paths and opportunities for testers with skills in automation, data analytics, and cloud technologies. Testers who adapt to these trends and acquire relevant skills will have a competitive advantage and better career prospects.
Staying Ahead of the Curve in UK Software Testing
To stay ahead of the curve in the rapidly evolving field of software testing in the UK, consider the following:
- AI and Machine Learning in Testing: Explore how AI and machine learning can be used to automate test case generation, predict defects, and improve testing efficiency.
- DevOps and Agile Methodologies: Embrace DevOps and Agile principles to integrate testing seamlessly into the software development lifecycle and ensure faster feedback loops.
- Cybersecurity Testing: Develop expertise in cybersecurity testing techniques and tools to identify vulnerabilities and protect software applications from cyber threats.
- Cloud-Based Testing Solutions: Familiarize yourself with cloud-based testing platforms and services to scale testing efforts and reduce infrastructure costs.
- Big Data Testing: Learn how to test big data applications and ensure data quality, performance, and security.
- Mobile Testing: Gain proficiency in mobile testing techniques and tools to test mobile applications across different devices and platforms.
- Internet of Things (IoT) Testing: Understand the challenges of testing IoT devices and applications, and develop skills in areas such as sensor testing and connectivity testing.
- Continuous Learning: Commit to continuous learning and professional development to stay up-to-date with the latest trends and technologies in software testing.
2. Detailed Career Paths in Software Testing in the UK
2.1. QA Analyst/Test Engineer path
The QA Analyst/Test Engineer path involves starting with entry-level roles, gaining experience in test planning, execution, and reporting, and then progressing to senior positions with responsibilities for leading testing efforts and mentoring junior testers. This path emphasizes a strong understanding of testing principles, methodologies, and tools, as well as excellent analytical and problem-solving skills.
Climbing the Ladder as a QA Analyst/Test Engineer in the UK
To advance along the QA Analyst/Test Engineer path in the UK, consider the following steps:
- Entry-Level Roles: Start with entry-level positions such as Junior QA Tester or Trainee Test Analyst to gain foundational knowledge and practical experience in software testing.
- Test Planning and Execution: Develop skills in creating test plans, writing test cases, executing tests, and reporting defects using industry-standard tools and techniques.
- Testing Methodologies: Gain a thorough understanding of different testing methodologies such as Agile, Waterfall, and V-model, and know when to apply each one.
- Analytical and Problem-Solving Skills: Enhance your analytical and problem-solving skills to identify root causes of defects and propose effective solutions.
- Communication Skills: Improve your communication skills to effectively collaborate with developers, project managers, and other stakeholders.
- Senior Positions: Progress to senior positions such as Senior Test Analyst or Test Lead by demonstrating leadership skills, mentoring junior testers, and taking on more complex testing assignments.
- Continuous Learning: Stay up-to-date with the latest trends and technologies in software testing through continuous learning and professional development.
2.2. Test Automation Engineer path
The Test Automation Engineer path focuses on developing expertise in test automation tools and techniques to automate repetitive testing tasks, improve testing efficiency, and reduce testing costs. This path requires strong programming skills, knowledge of test automation frameworks, and experience with tools like Selenium, JUnit, and TestNG.
Mastering Test Automation in the UK Job Market
To excel as a Test Automation Engineer in the UK job market, consider the following:
- Programming Skills: Develop strong programming skills in languages such as Java, Python, or JavaScript to write custom test scripts and automation frameworks.
- Test Automation Frameworks: Gain expertise in test automation frameworks such as Selenium WebDriver, Appium, and Cypress to design and implement robust automation solutions.
- Automation Tools: Master test automation tools like Selenium, JUnit, TestNG, and Cucumber to automate repetitive testing tasks and improve testing efficiency.
- Continuous Integration: Integrate automated tests into the continuous integration pipeline using tools like Jenkins or Bamboo to ensure continuous feedback and faster release cycles.
- Performance Testing: Learn how to use performance testing tools like JMeter or Gatling to assess the performance and scalability of software applications.
- Security Testing: Gain knowledge of security testing techniques and tools to identify vulnerabilities in software applications and ensure their security.
- Agile and DevOps: Embrace Agile and DevOps principles to integrate test automation seamlessly into the software development lifecycle.
2.3. Performance Tester path
The Performance Tester path involves specializing in evaluating the performance of software applications, identifying bottlenecks, and ensuring scalability and responsiveness. This path requires a deep understanding of system architecture, performance testing methodologies, and tools like JMeter, Gatling, and LoadRunner.
Becoming a Performance Testing Expert in the UK
To become a performance testing expert in the UK, consider the following steps:
- System Architecture: Develop a deep understanding of system architecture, including hardware, software, and network components, to effectively design and execute performance tests.
- Performance Testing Methodologies: Learn different performance testing methodologies such as load testing, stress testing, and endurance testing, and know when to apply each one.
- Performance Testing Tools: Master performance testing tools like JMeter, Gatling, and LoadRunner to simulate user traffic, measure response times, and identify performance bottlenecks.
- Performance Monitoring: Gain expertise in performance monitoring tools and techniques to collect and analyze performance data, identify trends, and diagnose issues.
- Bottleneck Identification: Develop skills in identifying performance bottlenecks such as CPU utilization, memory leaks, and database queries, and propose effective solutions.
- Scalability Testing: Learn how to conduct scalability testing to ensure that software applications can handle increasing user loads and transaction volumes.
- Continuous Integration: Integrate performance tests into the continuous integration pipeline to ensure continuous performance monitoring and faster feedback loops.
2.4. Security Tester path
The Security Tester path focuses on identifying security vulnerabilities in software applications through techniques like penetration testing, security audits, and vulnerability assessments. This path requires a strong understanding of security principles, ethical hacking techniques, and tools like OWASP ZAP and Burp Suite.
Securing Your Career as a Security Tester in the UK
To secure your career as a Security Tester in the UK, consider the following:
- Security Principles: Develop a strong understanding of security principles such as confidentiality, integrity, and availability, and how they apply to software applications.
- Ethical Hacking: Learn ethical hacking techniques and tools to simulate real-world attacks and identify security vulnerabilities in software applications.
- Penetration Testing: Gain expertise in penetration testing methodologies and tools to assess the security posture of software applications and identify potential weaknesses.
- Vulnerability Assessments: Learn how to conduct vulnerability assessments using automated tools and manual techniques to identify and prioritize security vulnerabilities.
- Security Audits: Develop skills in conducting security audits to review software code, configurations, and infrastructure for security flaws and compliance issues.
- Security Tools: Master security testing tools like OWASP ZAP, Burp Suite, and Metasploit to automate security testing tasks and improve testing efficiency.
- Security Standards: Familiarize yourself with security standards such as OWASP, NIST, and PCI DSS to ensure compliance and mitigate security risks.
2.5. Test Manager/QA Lead path
The Test Manager/QA Lead path involves leading and managing testing teams, creating testing strategies, and ensuring the quality of software applications. This path requires strong leadership skills, excellent communication skills, and a deep understanding of testing principles and methodologies.
Leading the Way as a Test Manager/QA Lead in the UK
To lead the way as a Test Manager/QA Lead in the UK, consider the following:
- Leadership Skills: Develop strong leadership skills to effectively manage and motivate testing teams, set goals, and delegate tasks.
- Communication Skills: Improve your communication skills to effectively collaborate with developers, project managers, and other stakeholders, and communicate testing progress and risks.
- Testing Strategies: Learn how to create comprehensive testing strategies that align with business goals and ensure the delivery of high-quality software applications.
- Test Planning: Develop skills in creating detailed test plans that outline testing scope, objectives, resources, and timelines.
- Test Execution: Oversee test execution activities, monitor progress, and ensure that testing is conducted according to the test plan.
- Defect Management: Implement effective defect management processes to track, prioritize, and resolve defects in a timely manner.
- Quality Assurance: Champion quality assurance principles and practices throughout the software development lifecycle to ensure that software applications meet quality standards.
3. Specializing in Niche Areas of Software Testing in the UK
3.1. AI and Machine Learning Testing
AI and machine learning testing involves evaluating the performance, accuracy, and reliability of AI-powered systems and algorithms. This specialization requires a strong understanding of AI and machine learning concepts, as well as expertise in testing methodologies and tools for AI applications.
Becoming an AI and Machine Learning Testing Specialist
To become an AI and Machine Learning Testing Specialist, consider the following:
- AI and Machine Learning Concepts: Develop a strong understanding of AI and machine learning concepts such as supervised learning, unsupervised learning, and deep learning.
- Testing Methodologies: Learn testing methodologies specific to AI applications, such as model validation, data quality assessment, and bias detection.
- Testing Tools: Master testing tools for AI applications, such as TensorFlow, Keras, and PyTorch, to automate testing tasks and improve testing efficiency.
- Data Analysis: Develop skills in data analysis to assess the quality and reliability of training data and identify potential issues.
- Performance Metrics: Learn how to measure and evaluate the performance of AI models using relevant metrics such as accuracy, precision, and recall.
- Bias Detection: Develop skills in detecting and mitigating bias in AI models to ensure fairness and ethical considerations.
- Security Testing: Gain knowledge of security testing techniques for AI applications to protect against adversarial attacks and data breaches.
3.2. Mobile App Testing
Mobile app testing focuses on evaluating the functionality, usability, performance, and security of mobile applications across different devices and platforms. This specialization requires expertise in mobile testing tools, techniques, and best practices.
Excelling in Mobile App Testing in the UK Market
To excel in Mobile App Testing in the UK market, consider the following:
- Mobile Platforms: Gain a thorough understanding of different mobile platforms such as iOS and Android, and their respective testing requirements and challenges.
- Mobile Testing Tools: Master mobile testing tools such as Appium, Espresso, and XCUITest to automate testing tasks and improve testing efficiency.
- Usability Testing: Learn how to conduct usability testing to assess the user experience of mobile applications and identify areas for improvement.
- Performance Testing: Develop skills in performance testing to evaluate the responsiveness, scalability, and stability of mobile applications under different network conditions.
- Security Testing: Gain knowledge of security testing techniques for mobile applications to protect against vulnerabilities and data breaches.
- Cross-Platform Testing: Learn how to conduct cross-platform testing to ensure that mobile applications function correctly across different devices, operating systems, and screen sizes.
- Automation Frameworks: Develop skills in building automation frameworks for mobile app testing to streamline testing efforts and improve test coverage.
3.3. IoT Testing
IoT testing involves evaluating the functionality, performance, security, and interoperability of Internet of Things (IoT) devices and applications. This specialization requires a strong understanding of IoT architecture, protocols, and security considerations.
Navigating the World of IoT Testing
To navigate the world of IoT Testing, consider the following:
- IoT Architecture: Develop a strong understanding of IoT architecture, including devices, gateways, cloud platforms, and communication protocols.
- IoT Protocols: Learn different IoT protocols such as MQTT, CoAP, and HTTP, and their respective strengths and weaknesses.
- Security Considerations: Gain knowledge of security considerations for IoT devices and applications, including authentication, encryption, and data privacy.
- Testing Methodologies: Learn testing methodologies specific to IoT devices, such as sensor testing, connectivity testing, and interoperability testing.
- Testing Tools: Master testing tools for IoT devices, such as Wireshark, tcpdump, and JTAG debuggers, to capture and analyze network traffic and debug firmware issues.
- Performance Testing: Develop skills in performance testing to evaluate the responsiveness, scalability, and reliability of IoT devices under different environmental conditions.
- Security Testing: Gain expertise in security testing techniques for IoT devices to protect against vulnerabilities and cyber threats.
3.4. Cloud Testing
Cloud testing focuses on evaluating the performance, scalability, security, and reliability of cloud-based applications and infrastructure. This specialization requires expertise in cloud computing concepts, testing methodologies, and tools for cloud environments.
Becoming a Cloud Testing Expert in the UK
To become a Cloud Testing Expert in the UK, consider the following:
- Cloud Computing Concepts: Develop a strong understanding of cloud computing concepts such as Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS).
- Cloud Platforms: Gain expertise in cloud platforms such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP), and their respective testing tools and services.
- Testing Methodologies: Learn testing methodologies specific to cloud environments, such as load testing, stress testing, and security testing.
- Testing Tools: Master testing tools for cloud environments, such as JMeter, Gatling, and LoadView, to simulate user traffic and measure performance metrics.
- Scalability Testing: Develop skills in scalability testing to ensure that cloud-based applications can handle increasing user loads and transaction volumes.
- Security Testing: Gain knowledge of security testing techniques for cloud environments to protect against vulnerabilities and data breaches.
- Automation Frameworks: Develop skills in building automation frameworks for cloud testing to streamline testing efforts and improve test coverage.
4. Building a Standout Resume for Software Testing Roles in the UK
4.1. Highlighting relevant skills and experience
When building a standout resume for software testing roles in the UK, it’s crucial to highlight relevant skills and experience that align with the job requirements. This includes showcasing proficiency in testing methodologies (Agile, Waterfall), test automation tools (Selenium, JUnit), test management software (Jira, TestRail), programming languages (Java, Python), and any specialized skills in areas like performance or security testing. Quantify achievements whenever possible to demonstrate the impact of your work.
Crafting a Compelling Resume
To craft a compelling resume that showcases your skills and experience, consider the following tips:
- Tailor Your Resume: Customize your resume for each job application, highlighting the skills and experience that are most relevant to the specific role.
- Use Keywords: Incorporate keywords from the job description into your resume to ensure that it gets past applicant tracking systems (ATS).
- Quantify Achievements: Quantify your achievements whenever possible to demonstrate the impact of your work. For example, “Reduced defect density by 20% through implementation of automated testing.”
- Highlight Certifications: Include any relevant certifications such as ISTQB or Certified Tester Foundation Level (CTFL) to validate your skills and knowledge.
- Showcase Projects: Showcase any personal or professional projects that demonstrate your skills in software testing, such as open-source contributions or side projects.
- Use Action Verbs: Use strong action verbs to describe your responsibilities and accomplishments, such as “Developed,” “Implemented,” “Managed,” and “Led.”
- Proofread Carefully: Proofread your resume carefully for any typos or grammatical errors before submitting it.
4.2. Showcasing certifications and education
Showcasing certifications and education on your resume is essential to demonstrate your knowledge and commitment to professional development. Include details of relevant certifications such as ISTQB, Certified Tester Foundation Level (CTFL), or specialized certifications in areas like Agile testing or test automation. Also, list your educational qualifications, including degrees, diplomas, and any relevant coursework or projects.
Leveraging Certifications and Education to Stand Out
To leverage certifications and education to stand out from the competition, consider the following:
- Highlight Key Certifications: Prominently display your key certifications at the top of your resume to grab the attention of hiring managers.
- Provide Details: Provide details about your certifications, including the certifying organization, the date of certification, and any relevant skills or knowledge gained.
- List Educational Qualifications: List your educational qualifications in reverse chronological order, including the name of the institution, the degree or diploma earned, and the dates of attendance.
- Include Relevant Coursework: Include any relevant coursework or projects that demonstrate your skills in software testing, such as programming courses, testing methodologies, or software development projects.
- Tailor to Job Requirements: Tailor your education and certifications section to match the requirements of the job description, highlighting the qualifications that are most relevant to the role.
- Consider Additional Training: Consider pursuing additional training or certifications to enhance your skills and knowledge and stay up-to-date with the latest trends and technologies in software testing.
4.3. Tailoring your resume to specific job descriptions
Tailoring your resume to specific job descriptions is crucial to demonstrate that you possess the skills and experience required for the role. Carefully review the job description and identify the key skills, qualifications, and responsibilities. Then, customize your resume to highlight how your skills and experience align with those requirements, using keywords from the job description whenever possible.
Customizing Your Resume for Success
To customize your resume for success, consider the following steps:
- Review the Job Description: Carefully review the job description and identify the key skills, qualifications, and responsibilities.
- Identify Keywords: Identify keywords from the job description that are relevant to your skills and experience.
- Highlight Relevant Skills: Highlight the skills and experience that are most relevant to the job requirements, using the keywords you identified.
- Quantify Achievements: Quantify your achievements whenever possible to demonstrate the impact of your work.
- Tailor Your Summary: Tailor your summary or objective statement to reflect the specific requirements of the job description.
- Proofread Carefully: Proofread your resume carefully for any typos or grammatical errors before submitting it.
- Seek Feedback: Seek feedback from friends, colleagues, or career advisors to ensure that your resume is clear, concise, and compelling.
5. Finding Software Testing Jobs in the UK
5.1. Online job boards and recruitment agencies
Finding software testing jobs in the UK can be achieved through various online job boards such as Indeed, LinkedIn, Reed, and Glassdoor, as well as recruitment agencies specializing in IT and technology roles like Hays, Robert Half, and Michael Page. These platforms offer a wide range of opportunities, from entry-level positions to senior management roles, across different industries and locations in the UK.
Navigating Online Job Boards and Recruitment Agencies
To navigate online job boards and recruitment agencies effectively, consider the following tips:
- Use Multiple Platforms: Use multiple online job boards and recruitment agencies to increase your chances of finding the right job.
- Set Up Job Alerts: Set up job alerts on online job boards to receive notifications when new jobs are posted that match your criteria.
- Network with Recruiters: Network with recruiters on LinkedIn and attend industry events to build relationships and learn about potential job opportunities.
- Tailor Your Resume: Tailor your resume to match the requirements of each job application, highlighting your skills and experience in software testing.
- Prepare for Interviews: Prepare for interviews by researching the company, practicing common interview questions, and showcasing your passion for software testing.
- Follow Up After Applying: Follow up with recruiters or hiring managers after applying for a job to express your interest and inquire about the status of your application.
- Be Patient: Be patient and persistent in your job search, as it may take time to find the right opportunity that matches your skills and career goals.
5.2. Networking and industry events
Networking and attending industry events are valuable ways to find software testing jobs in the UK. Networking can involve connecting with professionals in the field through platforms like LinkedIn or at local meetups, while industry events like conferences and workshops provide opportunities to learn about new trends, meet potential employers, and expand your professional network.
Building Your Network and Attending Industry Events
To build your network and attend industry events effectively, consider the following strategies:
- Attend Conferences: Attend software testing conferences and workshops to learn about new trends, network with professionals, and meet potential employers.
- Join Professional Organizations: Join professional organizations such as the British Computer Society (BCS) or the International Software Testing Qualifications Board (ISTQB) to access resources, training, and networking opportunities.
- Attend Meetups: Attend local meetups and networking events to connect with software testing professionals in your area and learn about job opportunities.
- Use LinkedIn: Use LinkedIn to connect with software testing professionals, join relevant groups, and participate in discussions.
- Volunteer: Volunteer at industry events or conferences to gain exposure, network with professionals, and demonstrate your commitment to the field.
- Follow Up: Follow up with contacts you meet at industry events or through networking to build relationships and explore potential job opportunities.
- Be Proactive: Be proactive in reaching out to potential employers or mentors to inquire about job opportunities or seek career advice.
5.3. Company websites and direct applications
Checking company websites and submitting direct applications can be an effective way to find software testing jobs in the UK, especially for companies that may not always advertise on job boards. By visiting the career pages of companies you’re interested in, you can discover opportunities that align with your skills and career goals, and submit your application directly to the company.
Maximizing Your Success with Direct Applications
To maximize your success with direct applications, consider the following tips:
- Research Companies: Research companies you’re interested in to identify their values, culture, and testing practices.
- Visit Career Pages: Visit the career pages of company websites regularly to check for new job openings in software testing.
- Tailor Your Application: Tailor your application to match the requirements of the specific job description, highlighting your skills and experience in software testing.
- Write a Cover Letter: Write a compelling cover letter that explains why you’re interested in the company and how your skills and experience make you a good fit for the role.
- Follow Up: Follow up with the company after submitting your application to express your interest and inquire about the status of your application.
- Network with Employees: Network with employees at the company through LinkedIn or other platforms to learn more about the company culture and potential job opportunities.
- Be Persistent: Be persistent in your job search, as it may take time to find the right opportunity that matches your skills and career goals.
6. The Future of Software Testing Career Path UK
6.1. Impact of artificial intelligence on testing roles
The impact of artificial intelligence on testing roles in the UK is expected to be significant, with AI-powered tools automating many repetitive testing tasks, such as test case generation, execution, and defect analysis. While some entry-level testing roles may be automated, AI will also create new opportunities for testers with skills in AI testing, machine learning, and data analysis, who can work alongside AI tools to improve testing efficiency and effectiveness.
Preparing for the AI Revolution in Software Testing
To prepare for the AI revolution in software testing, consider the following strategies:
- Learn AI and Machine Learning: Learn the basics of AI and machine learning concepts, such as supervised learning, unsupervised learning, and deep learning.
- Develop AI Testing Skills: Develop skills in testing AI-powered systems and algorithms, including model validation, data quality assessment, and bias detection.
- Master AI Testing Tools: Master AI testing tools and frameworks, such as TensorFlow, Keras, and PyTorch, to automate testing tasks and improve testing efficiency.
- Enhance Data Analysis Skills: Enhance your data analysis skills to assess the quality and reliability of training data and identify potential issues.
- Focus on Critical Thinking: Focus on developing critical thinking and problem-solving skills that cannot be easily automated by AI, such as test planning, test design, and exploratory testing.
- Embrace Continuous Learning: Embrace continuous learning and professional development to stay up-to-date with the latest trends and technologies in AI and software testing.
- Seek Training and Certification: Seek training and certification in AI and machine learning testing to validate your skills and knowledge and stand out in the job market.
6.2. The growing importance of soft skills
The growing importance of soft skills in software testing roles in the UK reflects the increasing need for testers to collaborate effectively with developers, project managers, and other stakeholders. Soft skills such as communication, teamwork, problem-solving, and adaptability are essential for testers to understand requirements, communicate testing progress, and contribute to the overall success of the software development project.
Developing Essential Soft Skills for a Thriving Career
To develop essential soft skills for a thriving career in software testing, consider the following tips:
- Improve Communication Skills: Improve your communication skills by practicing active listening, speaking clearly and concisely, and writing effective emails and reports.
- Enhance Teamwork Skills: Enhance your teamwork skills by collaborating effectively with colleagues, sharing knowledge and resources, and resolving conflicts constructively.
- Develop Problem-Solving Skills: Develop your problem-solving skills by analyzing complex issues, identifying root causes, and proposing effective solutions.
- Increase Adaptability: Increase your adaptability by embracing change, learning new technologies and methodologies, and adapting to evolving project requirements.
- Improve Time Management: Improve your time management skills by prioritizing tasks, setting realistic deadlines, and managing your workload effectively.
- Develop Leadership Skills: Develop your leadership skills by taking initiative, leading small projects or teams, and mentoring junior colleagues.
- Seek Feedback: Seek feedback from colleagues and mentors on your soft skills and identify areas for improvement.
6.3. Continuous learning and adaptation
Continuous learning and adaptation are essential for software testing professionals in the UK to stay relevant and competitive in a rapidly evolving industry. Testers need to continuously update their skills and knowledge to keep pace with new technologies, methodologies, and tools, and adapt to changing job requirements and industry trends.
Embracing Lifelong Learning in Software Testing
To embrace lifelong learning in software testing, consider the following strategies:
- Set Learning Goals: Set specific and measurable learning goals to guide your professional development.
- Take Online Courses: Take online courses and tutorials on platforms such as Coursera, Udemy, and LinkedIn Learning to learn new skills and technologies.
- Attend Conferences and Workshops: Attend software testing conferences and workshops to learn about new trends, network with professionals, and gain hands-on experience.
- Read Industry Publications: Read industry publications, blogs, and articles to stay up-to-date with the latest news and trends in software testing.
- Join Online Communities: Join online communities and forums to connect with other software testing professionals, share knowledge, and ask questions.
- Experiment with New Tools: Experiment with new testing tools and technologies to expand your skill set and improve your testing efficiency.
- Seek Mentorship: Seek mentorship from experienced software testing professionals to gain guidance and support in your career development.
FAQ: Your Questions About Software Testing Career Path UK Answered
1. What qualifications do I need to start a software testing career in the UK?
While a computer science degree is helpful, it’s not always mandatory. Many start with certifications like ISTQB and a passion for quality.
2. How long does it take to become a senior test engineer in the UK?
Typically, it takes 5-7 years of experience to progress to a senior test engineer role, with continuous learning and skill development.