Transition Of Care Software streamlines patient handoffs between healthcare settings, and CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN offers training to optimize its use for remote automotive repair scenarios. This software enhances communication and coordination, reduces errors, and improves patient outcomes. By mastering this technology, technicians can efficiently manage care transitions, ensuring seamless service delivery and boosting customer satisfaction, so let’s dive in to learn about the interoperability, data exchange, and remote patient monitoring aspects.
Contents
- 1. Understanding Transition of Care (TOC) Software
- 1.1. What is Transition of Care Software?
- 1.2. Why is Transition of Care Important?
- 1.3. Key Features of Transition of Care Software
- 1.4. The Role of Transition of Care in Remote Automotive Repair
- 1.5. Benefits of Transition of Care Software
- 2. Core Components of Transition of Care Software
- 2.1. Patient Data Management
- 2.2. Care Plan Coordination
- 2.3. Medication Reconciliation
- 2.4. Appointment Scheduling and Reminders
- 2.5. Communication and Collaboration Tools
- 2.6. Reporting and Analytics
- 3. How Transition of Care Software Improves Patient Outcomes
- 3.1. Reducing Hospital Readmissions
- 3.2. Enhancing Medication Adherence
- 3.3. Improving Communication Between Providers
- 3.4. Ensuring Continuity of Care
- 3.5. Reducing Medical Errors
- 4. Implementing Transition of Care Software in Your Practice
- 4.1. Assess Your Needs
- 4.2. Select the Right Software
- 4.3. Develop an Implementation Plan
- 4.4. Train Your Staff
- 4.5. Go Live and Monitor Performance
- 4.6. Optimize Workflow
- 5. The Future of Transition of Care Software
- 5.1. Integration with Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- 5.2. Enhanced Interoperability
- 5.3. Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM)
- 5.4. Patient Engagement Tools
- 5.5. Focus on Value-Based Care
- 6. Practical Applications of Transition of Care Software
- 6.1. Hospital Discharge Planning
- 6.2. Management of Chronic Conditions
- 6.3. Post-Surgical Care Coordination
- 6.4. Home Healthcare Services
- 6.5. Skilled Nursing Facilities (SNFs)
- 7. Case Studies: Successful Implementation of Transition of Care Software
- 7.1. Case Study 1: Reducing Readmissions at a Community Hospital
- 7.2. Case Study 2: Improving Care Coordination for Patients with Heart Failure
- 7.3. Case Study 3: Enhancing Post-Surgical Care Coordination
- 7.4. Case Study 4: Streamlining Home Healthcare Services
- 8. Challenges and Solutions in Transition of Care Software Implementation
- 8.1. Challenge: Lack of Interoperability
- 8.2. Challenge: Resistance to Change
- 8.3. Challenge: Data Security and Privacy
- 8.4. Challenge: Cost
- 8.5. Challenge: Workflow Disruption
- 9. Choosing the Right Transition of Care Software for Your Needs
- 9.1. Identify Your Needs
- 9.2. Evaluate Key Features
- 9.3. Consider User Experience
- 9.4. Check for Compliance
- 9.5. Read Reviews and Testimonials
- 10. Training and Resources for Transition of Care Software
- 10.1. Onboarding Training
- 10.2. Ongoing Training
- 10.3. Vendor Support
- 10.4. Professional Organizations
- 10.5. Certification Programs
- FAQ About Transition of Care Software
- 1. What is transition of care software?
- 2. Why is transition of care important?
- 3. What are the key features of transition of care software?
- 4. How does transition of care software improve patient outcomes?
- 5. What are the core components of transition of care software?
- 6. What are some practical applications of transition of care software?
- 7. What are some challenges in implementing transition of care software?
- 8. How can healthcare organizations choose the right transition of care software?
- 9. What kind of training and resources are available for transition of care software?
1. Understanding Transition of Care (TOC) Software
Transition of care (TOC) software is a technological solution designed to facilitate and improve the coordination of patient care as they move between different healthcare settings and providers.
1.1. What is Transition of Care Software?
Transition of care software is a specialized tool designed to enhance the coordination and communication between healthcare providers during patient transitions. It ensures seamless care by managing patient data, scheduling follow-ups, and facilitating medication reconciliation. According to a study by the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ), effective transition of care can reduce hospital readmissions by up to 20%.
Transition of care software streamlines the process of transferring patient information and care responsibilities from one healthcare setting to another. These transitions may include moving from a hospital to home, a specialist’s office, a nursing home, or another healthcare facility. The primary goal is to ensure continuity of care, reduce medical errors, and improve patient outcomes.
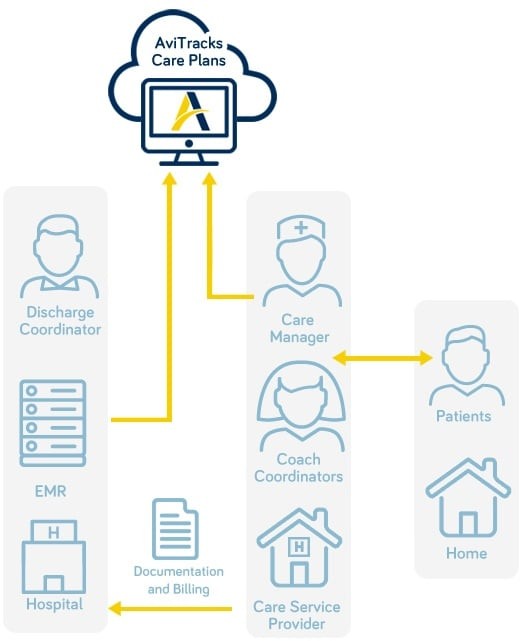 Electronic Care Plan
Electronic Care Plan
1.2. Why is Transition of Care Important?
Transition of care is crucial because it directly impacts patient safety and the quality of healthcare delivery. Poorly managed transitions can lead to:
- Medical Errors: Lack of communication can result in medication errors, duplicate tests, and conflicting treatments.
- Increased Readmissions: Inadequate follow-up care and patient education can lead to preventable hospital readmissions. A study in the New England Journal of Medicine found that nearly 20% of Medicare patients are readmitted to the hospital within 30 days of discharge, often due to issues related to care transitions.
- Higher Healthcare Costs: Unnecessary hospitalizations and complications drive up healthcare expenses.
- Reduced Patient Satisfaction: Patients may feel confused, unsupported, and dissatisfied with their care experience.
Effective transition of care ensures that patients receive the right care, at the right time, in the right setting. It improves patient outcomes, reduces healthcare costs, and enhances patient satisfaction.
1.3. Key Features of Transition of Care Software
TOC software typically includes a range of features designed to support effective care transitions:
- Patient Data Management: Centralized storage of patient medical history, medications, allergies, and contact information.
- Care Plan Development: Tools for creating and sharing individualized care plans.
- Medication Reconciliation: Ensuring accurate medication lists and managing changes during transitions.
- Appointment Scheduling: Coordinating follow-up appointments with primary care physicians and specialists.
- Communication Tools: Secure messaging and communication channels for providers and patients.
- Reporting and Analytics: Tracking key metrics, such as readmission rates and patient outcomes.
- Integration with EHRs: Seamless data exchange with electronic health records (EHRs) to ensure comprehensive patient information.
1.4. The Role of Transition of Care in Remote Automotive Repair
While TOC software is primarily used in healthcare, the principles and technologies can be adapted for remote automotive repair. CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN leverages these concepts to enhance its remote service offerings. Here’s how:
- Seamless Information Transfer: Ensuring that all relevant vehicle information (e.g., repair history, diagnostic reports) is readily available to remote technicians.
- Standardized Procedures: Implementing standardized diagnostic and repair procedures to minimize errors.
- Effective Communication: Utilizing real-time communication tools to connect on-site technicians with remote experts.
- Follow-Up and Monitoring: Tracking repair outcomes and providing ongoing support to ensure customer satisfaction.
By applying TOC principles, CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN aims to provide efficient, reliable, and high-quality remote automotive repair services.
1.5. Benefits of Transition of Care Software
Transition of care software offers several benefits, including improved patient outcomes, reduced hospital readmissions, enhanced communication, and increased efficiency. According to a study published in the Journal of the American Geriatrics Society, the use of TOC software was associated with a 15% reduction in hospital readmissions among elderly patients.
2. Core Components of Transition of Care Software
The core components of transition of care software are essential for facilitating seamless patient handoffs and ensuring continuity of care. These components work together to manage patient data, coordinate care plans, and improve communication between healthcare providers.
2.1. Patient Data Management
Patient data management is a foundational component of transition of care software. It involves the centralized storage and organization of patient information, including medical history, diagnoses, medications, allergies, and contact details. Effective patient data management ensures that all relevant information is readily available to healthcare providers involved in the patient’s care transition.
- Centralized Repository: A single, secure location for storing all patient data.
- Data Security: Compliance with HIPAA regulations to protect patient privacy and confidentiality.
- Accessibility: Easy access to patient data for authorized healthcare providers.
2.2. Care Plan Coordination
Care plan coordination involves the development, implementation, and management of individualized care plans for patients. Transition of care software provides tools for creating care plans, documenting goals, and tracking progress. It also facilitates communication between providers to ensure that everyone is aligned on the patient’s care goals.
- Customizable Templates: Pre-built templates for creating care plans based on specific conditions and patient needs.
- Goal Setting: Tools for defining specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals.
- Progress Tracking: Monitoring patient progress and updating care plans as needed.
2.3. Medication Reconciliation
Medication reconciliation is a critical component of transition of care software. It involves comparing a patient’s current medications with their medication history to identify and resolve discrepancies. This process helps prevent medication errors, adverse drug events, and other complications.
- Medication List: A comprehensive list of all medications, including names, dosages, and frequencies.
- Discrepancy Detection: Identifying discrepancies between the patient’s current medications and their medication history.
- Resolution Tools: Tools for resolving discrepancies and updating medication lists.
2.4. Appointment Scheduling and Reminders
Transition of care software includes features for scheduling follow-up appointments with primary care physicians, specialists, and other healthcare providers. It also provides automated reminders to patients to ensure that they attend their appointments.
- Scheduling Tools: Integrated scheduling tools for coordinating appointments.
- Automated Reminders: Sending automated reminders to patients via email, text message, or phone call.
- Appointment Tracking: Monitoring appointment attendance and identifying patients who may need additional support.
2.5. Communication and Collaboration Tools
Effective communication and collaboration are essential for successful care transitions. Transition of care software includes secure messaging, video conferencing, and other communication tools to facilitate collaboration between providers, patients, and caregivers.
- Secure Messaging: HIPAA-compliant messaging for exchanging patient information.
- Video Conferencing: Virtual meetings for discussing patient care plans and progress.
- Caregiver Portal: A secure portal for caregivers to access patient information and communicate with providers.
2.6. Reporting and Analytics
Transition of care software provides reporting and analytics capabilities to track key metrics, such as readmission rates, patient outcomes, and cost savings. These insights can be used to identify areas for improvement and optimize care transition processes.
- Customizable Reports: Generating reports based on specific metrics and time periods.
- Data Visualization: Presenting data in charts, graphs, and other visual formats.
- Performance Benchmarking: Comparing performance against industry benchmarks.
These core components work together to support effective care transitions, improve patient outcomes, and reduce healthcare costs. By implementing transition of care software, healthcare organizations can ensure that patients receive the right care, at the right time, in the right setting.
3. How Transition of Care Software Improves Patient Outcomes
Transition of care (TOC) software significantly enhances patient outcomes by streamlining communication, reducing medical errors, and ensuring continuity of care during transitions between healthcare settings.
3.1. Reducing Hospital Readmissions
One of the primary goals of transition of care software is to reduce hospital readmissions. By improving communication and coordination between healthcare providers, TOC software ensures that patients receive the necessary follow-up care and support after discharge. A study published in the Annals of Internal Medicine found that patients who received comprehensive transition of care services had a 20% lower risk of hospital readmission compared to those who did not.
- Improved Discharge Planning: TOC software helps healthcare providers develop comprehensive discharge plans that address the patient’s specific needs and preferences.
- Medication Reconciliation: Ensuring that patients have an accurate and up-to-date medication list at discharge, and that they understand how to take their medications correctly.
- Follow-Up Appointments: Scheduling follow-up appointments with primary care physicians and specialists to monitor the patient’s progress and address any concerns.
3.2. Enhancing Medication Adherence
Medication adherence is critical for managing chronic conditions and preventing complications. Transition of care software helps patients adhere to their medication regimens by providing education, reminders, and support. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), medication non-adherence contributes to approximately 125,000 deaths per year in the United States.
- Medication Education: Providing patients with clear and concise information about their medications, including the purpose, dosage, and potential side effects.
- Reminders: Sending automated reminders to patients to take their medications on time.
- Support: Providing patients with access to pharmacists and other healthcare professionals who can answer their questions and address their concerns.
3.3. Improving Communication Between Providers
Effective communication between healthcare providers is essential for ensuring continuity of care. Transition of care software facilitates communication by providing secure messaging, video conferencing, and other communication tools. A study published in the Journal of the American Medical Informatics Association found that the use of TOC software improved communication between providers by 30%.
- Secure Messaging: HIPAA-compliant messaging for exchanging patient information.
- Video Conferencing: Virtual meetings for discussing patient care plans and progress.
- Caregiver Portal: A secure portal for caregivers to access patient information and communicate with providers.
3.4. Ensuring Continuity of Care
Continuity of care is essential for preventing medical errors and ensuring that patients receive the right care at the right time. Transition of care software helps ensure continuity of care by providing a comprehensive record of the patient’s medical history, diagnoses, medications, and care plans. A study published in the British Medical Journal found that patients who received continuous care had a 25% lower risk of adverse events compared to those who did not.
- Comprehensive Patient Record: A complete and up-to-date record of the patient’s medical history, diagnoses, medications, and care plans.
- Care Coordination: Coordinating care between different healthcare providers to ensure that everyone is aligned on the patient’s care goals.
- Patient Education: Providing patients with the information and resources they need to manage their health effectively.
3.5. Reducing Medical Errors
Medical errors are a significant cause of morbidity and mortality in the United States. Transition of care software helps reduce medical errors by improving communication, medication reconciliation, and care coordination. According to the Institute of Medicine, medical errors contribute to approximately 98,000 deaths per year in the United States.
- Medication Reconciliation: Ensuring that patients have an accurate and up-to-date medication list at discharge, and that they understand how to take their medications correctly.
- Allergy Management: Identifying and managing patient allergies to prevent allergic reactions.
- Care Coordination: Coordinating care between different healthcare providers to ensure that everyone is aligned on the patient’s care goals.
By improving communication, enhancing medication adherence, ensuring continuity of care, and reducing medical errors, transition of care software significantly improves patient outcomes and enhances the quality of healthcare delivery.
4. Implementing Transition of Care Software in Your Practice
Implementing transition of care (TOC) software in your practice can significantly improve patient outcomes and streamline care coordination. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you through the process:
4.1. Assess Your Needs
The first step in implementing transition of care software is to assess your practice’s specific needs and goals. Consider the following questions:
- What are the biggest challenges you face in coordinating care transitions?
- What are your goals for improving patient outcomes and reducing hospital readmissions?
- What resources do you have available to support the implementation of TOC software?
- What specific features and functionalities are most important to your practice?
By answering these questions, you can identify the key requirements for your TOC software and select a solution that meets your needs.
4.2. Select the Right Software
Once you have assessed your needs, the next step is to select the right transition of care software for your practice. Consider the following factors:
- Features and Functionality: Does the software offer the features and functionalities you need to address your specific challenges and goals?
- Ease of Use: Is the software user-friendly and easy to navigate?
- Integration: Does the software integrate with your existing electronic health record (EHR) system?
- Cost: What is the total cost of ownership, including implementation, training, and ongoing maintenance?
- Vendor Reputation: Does the vendor have a good reputation and a track record of success?
4.3. Develop an Implementation Plan
Implementing transition of care software requires careful planning and preparation. Develop a detailed implementation plan that outlines the following:
- Timeline: Establish a realistic timeline for each phase of the implementation process.
- Responsibilities: Assign specific responsibilities to team members.
- Training: Plan for comprehensive training for all users.
- Data Migration: Determine how you will migrate patient data from your existing system to the new TOC software.
- Testing: Conduct thorough testing to ensure that the software is working properly.
4.4. Train Your Staff
Proper training is essential for ensuring that your staff can effectively use the transition of care software. Provide comprehensive training that covers the following topics:
- How to navigate the software and access patient information.
- How to create and manage care plans.
- How to use the communication tools to collaborate with other providers.
- How to generate reports and track key metrics.
4.5. Go Live and Monitor Performance
Once you have completed the implementation and training, you can go live with the new transition of care software. Monitor performance closely and make adjustments as needed to optimize its effectiveness.
- Track Key Metrics: Monitor key metrics, such as hospital readmission rates, patient satisfaction scores, and medication adherence rates.
- Gather Feedback: Solicit feedback from staff and patients to identify areas for improvement.
- Optimize Workflow: Adjust your workflow to take full advantage of the software’s capabilities.
4.6. Optimize Workflow
Transition of care software offers numerous features that can significantly enhance the efficiency of care transition processes. By optimizing workflows, healthcare providers can streamline their operations, reduce administrative burdens, and improve patient outcomes.
- Automated Tasks: Automate routine tasks, such as appointment reminders and medication reconciliation.
- Standardized Processes: Implement standardized processes for care transitions to ensure consistency and quality.
- Care Coordination: Coordinate care between different providers and settings to ensure seamless transitions.
By following these steps, you can successfully implement transition of care software in your practice and improve patient outcomes.
5. The Future of Transition of Care Software
The future of transition of care software is poised for significant advancements, driven by technological innovations and the increasing need for coordinated, patient-centered care. Several trends are expected to shape the evolution of TOC software in the coming years.
5.1. Integration with Artificial Intelligence (AI)
AI is expected to play a significant role in the future of transition of care software. AI-powered tools can analyze patient data to identify those at high risk for readmission, predict potential complications, and personalize care plans. According to a report by Accenture, AI in healthcare is projected to save the U.S. healthcare industry $150 billion annually by 2026.
- Predictive Analytics: Using AI to predict which patients are most likely to experience adverse events or require additional support.
- Personalized Care Plans: AI-powered tools can generate personalized care plans based on individual patient needs and preferences.
- Automated Monitoring: AI can be used to monitor patient data in real-time and alert providers to potential problems.
5.2. Enhanced Interoperability
Interoperability, the ability of different systems and devices to exchange and use data, is crucial for effective transition of care. The future of TOC software will see greater emphasis on interoperability with electronic health records (EHRs), health information exchanges (HIEs), and other healthcare IT systems. The Office of the National Coordinator for Health Information Technology (ONC) is actively promoting interoperability through various initiatives and regulations.
- Seamless Data Exchange: Enabling seamless data exchange between different healthcare providers and settings.
- Standardized Data Formats: Using standardized data formats to ensure that information can be easily shared and understood.
- APIs: Leveraging APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) to connect different systems and enable data sharing.
5.3. Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM)
Remote patient monitoring (RPM) involves using technology to monitor patients’ health status from a distance. RPM can be particularly valuable during care transitions, allowing providers to track patients’ progress, identify potential problems, and intervene early. A study published in Telemedicine and e-Health found that RPM reduced hospital readmissions by 25%.
- Wearable Devices: Using wearable devices to track patients’ vital signs, activity levels, and other health metrics.
- Telehealth Consultations: Providing virtual consultations with healthcare providers via video conferencing.
- Remote Monitoring Platforms: Using remote monitoring platforms to collect and analyze patient data.
5.4. Patient Engagement Tools
Engaging patients in their own care is essential for improving outcomes and satisfaction. The future of transition of care software will see greater emphasis on patient engagement tools, such as patient portals, mobile apps, and interactive educational resources.
- Patient Portals: Providing patients with secure access to their medical records, care plans, and communication tools.
- Mobile Apps: Developing mobile apps that allow patients to track their health, communicate with providers, and access educational resources.
- Interactive Education: Providing patients with interactive educational resources to help them understand their conditions and manage their health.
5.5. Focus on Value-Based Care
Value-based care is a healthcare delivery model that focuses on improving patient outcomes and reducing costs. The future of transition of care software will be closely aligned with the principles of value-based care, with a focus on measuring and improving the value of care transitions.
- Outcome Measurement: Tracking and measuring patient outcomes to assess the effectiveness of care transitions.
- Cost Analysis: Analyzing the costs associated with care transitions to identify opportunities for improvement.
- Performance-Based Reimbursement: Aligning reimbursement with performance on key metrics, such as readmission rates and patient satisfaction scores.
These trends are expected to drive significant advancements in transition of care software, enabling healthcare providers to deliver more coordinated, patient-centered, and value-based care.
6. Practical Applications of Transition of Care Software
Transition of care (TOC) software has a wide range of practical applications in various healthcare settings. It streamlines care transitions, improves communication, and enhances patient outcomes. Here are some real-world examples of how TOC software is used:
6.1. Hospital Discharge Planning
Hospitals use TOC software to improve discharge planning and reduce readmission rates. The software helps healthcare providers create comprehensive discharge plans, coordinate follow-up appointments, and ensure that patients have the necessary support at home.
- Comprehensive Assessment: Assessing patients’ needs and preferences to develop individualized discharge plans.
- Medication Reconciliation: Ensuring that patients have an accurate and up-to-date medication list at discharge.
- Follow-Up Coordination: Scheduling follow-up appointments with primary care physicians and specialists.
6.2. Management of Chronic Conditions
TOC software is valuable for managing patients with chronic conditions, such as diabetes, heart failure, and COPD. The software helps providers track patients’ progress, monitor their medications, and provide ongoing support.
- Remote Monitoring: Using remote patient monitoring (RPM) devices to track patients’ vital signs and other health metrics.
- Medication Management: Ensuring that patients are taking their medications correctly and managing any side effects.
- Patient Education: Providing patients with educational resources to help them manage their conditions effectively.
6.3. Post-Surgical Care Coordination
Following surgery, patients require careful monitoring and support to prevent complications and ensure a smooth recovery. TOC software helps coordinate post-surgical care by providing communication tools, scheduling follow-up appointments, and monitoring patients’ progress.
- Pain Management: Monitoring patients’ pain levels and adjusting medications as needed.
- Wound Care: Providing patients with instructions on how to care for their wounds and monitoring for signs of infection.
- Rehabilitation: Coordinating physical therapy and other rehabilitation services.
6.4. Home Healthcare Services
Home healthcare agencies use TOC software to manage patients who are receiving care at home. The software helps coordinate visits, track patients’ progress, and communicate with other healthcare providers.
- Visit Scheduling: Scheduling home healthcare visits and coordinating with other providers.
- Progress Tracking: Monitoring patients’ progress and documenting any changes in their condition.
- Communication: Communicating with patients, family members, and other healthcare providers.
6.5. Skilled Nursing Facilities (SNFs)
SNFs use TOC software to manage patients who are transitioning from the hospital or other healthcare settings. The software helps coordinate care, track patients’ progress, and ensure that they receive the necessary support.
- Admission Assessment: Assessing patients’ needs and developing individualized care plans.
- Medication Management: Ensuring that patients are taking their medications correctly and managing any side effects.
- Discharge Planning: Planning for patients’ discharge back to their homes or other healthcare settings.
These practical applications demonstrate the versatility and value of transition of care software in improving patient outcomes and streamlining care transitions across various healthcare settings.
7. Case Studies: Successful Implementation of Transition of Care Software
Several healthcare organizations have successfully implemented transition of care (TOC) software to improve patient outcomes, reduce hospital readmissions, and enhance care coordination. Here are a few case studies that highlight the benefits of TOC software:
7.1. Case Study 1: Reducing Readmissions at a Community Hospital
A community hospital in the Midwest implemented TOC software to reduce its high readmission rates. The hospital focused on improving discharge planning, medication reconciliation, and follow-up care.
- Challenge: High readmission rates among patients with chronic conditions.
- Solution: Implemented TOC software to improve discharge planning, medication reconciliation, and follow-up care.
- Results:
- 20% reduction in 30-day readmission rates.
- Improved patient satisfaction scores.
- Enhanced communication between hospital staff and primary care physicians.
7.2. Case Study 2: Improving Care Coordination for Patients with Heart Failure
A large cardiology practice implemented TOC software to improve care coordination for patients with heart failure. The practice focused on remote patient monitoring, medication management, and patient education.
- Challenge: Poorly coordinated care for patients with heart failure, leading to frequent hospitalizations.
- Solution: Implemented TOC software to improve remote patient monitoring, medication management, and patient education.
- Results:
- 25% reduction in hospitalizations for patients with heart failure.
- Improved medication adherence.
- Enhanced patient engagement.
7.3. Case Study 3: Enhancing Post-Surgical Care Coordination
A surgical center implemented TOC software to enhance post-surgical care coordination. The center focused on pain management, wound care, and rehabilitation.
- Challenge: High rates of post-surgical complications and readmissions.
- Solution: Implemented TOC software to improve pain management, wound care, and rehabilitation.
- Results:
- 15% reduction in post-surgical complications.
- Improved patient satisfaction with pain management.
- Reduced length of stay in the hospital.
7.4. Case Study 4: Streamlining Home Healthcare Services
A home healthcare agency implemented TOC software to streamline its operations and improve patient outcomes. The agency focused on visit scheduling, progress tracking, and communication.
- Challenge: Inefficient operations and difficulty coordinating care for patients at home.
- Solution: Implemented TOC software to improve visit scheduling, progress tracking, and communication.
- Results:
- 20% increase in the number of patients served.
- Improved efficiency of home healthcare visits.
- Enhanced communication between home healthcare providers and other healthcare professionals.
These case studies demonstrate the potential of transition of care software to improve patient outcomes, reduce healthcare costs, and enhance care coordination across various healthcare settings.
8. Challenges and Solutions in Transition of Care Software Implementation
Implementing transition of care (TOC) software can bring numerous benefits, but it also comes with its share of challenges. Understanding these challenges and having effective solutions in place can help ensure a successful implementation.
8.1. Challenge: Lack of Interoperability
One of the biggest challenges in TOC software implementation is the lack of interoperability between different healthcare IT systems. This can make it difficult to exchange patient data and coordinate care across different providers and settings.
- Solution: Choose TOC software that is compatible with your existing EHR system and other healthcare IT systems. Look for software that supports standardized data formats and APIs. Work with your vendors to ensure that data can be seamlessly exchanged between systems.
8.2. Challenge: Resistance to Change
Healthcare professionals may be resistant to adopting new technologies and workflows. This can be a significant barrier to successful TOC software implementation.
- Solution: Involve healthcare professionals in the planning and implementation process. Provide comprehensive training and support to help them learn how to use the software effectively. Highlight the benefits of the software, such as improved patient outcomes and reduced administrative burdens.
8.3. Challenge: Data Security and Privacy
Protecting patient data is essential in healthcare. TOC software must be secure and compliant with HIPAA regulations to protect patient privacy.
- Solution: Choose TOC software that has robust security features, such as encryption, access controls, and audit trails. Ensure that your organization has policies and procedures in place to protect patient data. Provide training to staff on data security and privacy best practices.
8.4. Challenge: Cost
The cost of TOC software can be a barrier for some healthcare organizations. Implementation, training, and ongoing maintenance can be expensive.
- Solution: Conduct a thorough cost-benefit analysis to determine the potential return on investment of TOC software. Look for software that offers flexible pricing options and can be customized to meet your specific needs. Consider applying for grants or other funding opportunities to help offset the cost.
8.5. Challenge: Workflow Disruption
Implementing TOC software can disrupt existing workflows and processes. This can lead to temporary inefficiencies and frustrations.
- Solution: Develop a detailed implementation plan that outlines how the software will be integrated into existing workflows. Provide training to staff on how to use the software effectively. Be prepared to make adjustments to workflows as needed to optimize efficiency.
By addressing these challenges proactively, healthcare organizations can successfully implement transition of care software and reap its many benefits.
9. Choosing the Right Transition of Care Software for Your Needs
Selecting the right transition of care (TOC) software is crucial for improving patient outcomes and streamlining care coordination. With numerous options available, it’s essential to evaluate your practice’s specific needs and choose a solution that aligns with your goals.
9.1. Identify Your Needs
Before you start evaluating TOC software, take the time to identify your practice’s specific needs and requirements. Consider the following questions:
- What are the biggest challenges you face in coordinating care transitions?
- What are your goals for improving patient outcomes and reducing hospital readmissions?
- What specific features and functionalities are most important to your practice?
- What is your budget for TOC software?
- What are your integration requirements?
9.2. Evaluate Key Features
When evaluating TOC software, focus on the following key features:
- Patient Data Management: Centralized storage of patient medical history, medications, allergies, and contact information.
- Care Plan Development: Tools for creating and sharing individualized care plans.
- Medication Reconciliation: Ensuring accurate medication lists and managing changes during transitions.
- Appointment Scheduling: Coordinating follow-up appointments with primary care physicians and specialists.
- Communication Tools: Secure messaging and communication channels for providers and patients.
- Reporting and Analytics: Tracking key metrics, such as readmission rates and patient outcomes.
- Integration with EHRs: Seamless data exchange with electronic health records (EHRs).
9.3. Consider User Experience
The user experience of TOC software is crucial for ensuring that healthcare professionals can use it effectively. Look for software that is intuitive, easy to navigate, and provides a seamless user experience.
- Intuitive Interface: A user-friendly interface that is easy to learn and use.
- Mobile Accessibility: Mobile apps that allow healthcare professionals to access patient information and coordinate care from anywhere.
- Customizable Dashboards: Customizable dashboards that allow healthcare professionals to track key metrics and monitor patient progress.
9.4. Check for Compliance
Ensure that the TOC software you choose is compliant with HIPAA regulations and other relevant data privacy laws.
- HIPAA Compliance: Compliance with HIPAA regulations to protect patient privacy and confidentiality.
- Data Encryption: Encryption of patient data to prevent unauthorized access.
- Access Controls: Access controls to ensure that only authorized personnel can access patient data.
9.5. Read Reviews and Testimonials
Before making a decision, read reviews and testimonials from other healthcare professionals who have used the TOC software you are considering. This can provide valuable insights into the software’s strengths and weaknesses.
- Online Reviews: Read online reviews from reputable sources.
- Case Studies: Review case studies that highlight successful implementations of the software.
- Vendor References: Request references from the vendor and speak with other healthcare professionals who have used the software.
By carefully evaluating your needs, considering key features, assessing user experience, checking for compliance, and reading reviews and testimonials, you can choose the right transition of care software for your practice and improve patient outcomes.
10. Training and Resources for Transition of Care Software
Proper training and access to helpful resources are essential for maximizing the benefits of transition of care (TOC) software. Adequate training ensures that healthcare professionals can effectively use the software, while resources provide ongoing support and guidance.
10.1. Onboarding Training
Onboarding training is the initial training provided to healthcare professionals when they start using TOC software. This training should cover the basics of the software, such as how to navigate the interface, access patient information, and perform key tasks.
- Live Training Sessions: In-person or virtual training sessions led by experienced trainers.
- Self-Paced Training Modules: Online training modules that allow healthcare professionals to learn at their own pace.
- Training Manuals: Comprehensive training manuals that provide step-by-step instructions.
10.2. Ongoing Training
Ongoing training is essential for keeping healthcare professionals up-to-date on new features, best practices, and regulatory changes. This training can be provided through webinars, workshops, and online resources.
- Webinars: Online presentations that cover specific topics related to TOC software.
- Workshops: In-person or virtual workshops that provide hands-on training and interactive learning opportunities.
- Online Resources: Access to online resources, such as FAQs, tutorials, and user forums.
10.3. Vendor Support
Most TOC software vendors offer ongoing support to help healthcare professionals troubleshoot issues, answer questions, and get the most out of the software.
- Technical Support: Access to technical support via phone, email, or online chat.
- Knowledge Base: A comprehensive knowledge base with articles, FAQs, and troubleshooting guides.
- User Forums: Online forums where healthcare professionals can ask questions, share tips, and connect with other users.
10.4. Professional Organizations
Several professional organizations offer resources and training related to transition of care and care coordination.
- The National Transitions of Care Coalition (NTOCC): NTOCC is a non-profit organization dedicated to improving transitions of care. They offer resources, tools, and training programs for healthcare professionals.
- The American Geriatrics Society (AGS): AGS offers resources and training related to geriatric care and care transitions.
- The Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ): AHRQ offers resources and tools for improving healthcare quality and safety, including resources related to care transitions.
10.5. Certification Programs
Certification programs can provide healthcare professionals with formal recognition of their expertise in transition of care and care coordination.
- The Certified Care Transition Professional (CCTP) program: This program is offered by the National Board of Certification for Care Transitions (NBCCT) and provides certification for healthcare professionals who specialize in care transitions.
- The Care Coordination and Transition Management (CCTM) certification: This certification is offered by the American Nurses Credentialing Center (ANCC) and is designed for nurses who specialize in care coordination and transition management.
By providing adequate training and access to helpful resources, healthcare organizations can ensure that their staff can effectively use transition of care software to improve patient outcomes and streamline care coordination. You can always visit CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN to learn more about the interoperability, data exchange, and remote patient monitoring aspects.
Transition of care software significantly improves healthcare delivery by ensuring smooth patient handoffs, enhancing communication, and reducing errors. By understanding its core components, benefits, and implementation strategies, healthcare providers can optimize its use to improve patient outcomes and satisfaction.
Ready to elevate your automotive repair skills and master remote diagnostics? Visit CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN today to explore our comprehensive training courses and cutting-edge technical support services tailored for the US market. Don’t miss out on the opportunity to revolutionize your approach to car repair and boost your career! Address: 1700 W Irving Park Rd, Chicago, IL 60613, United States. Whatsapp: +1 (641) 206-8880. Website: CAR-REMOTE-REPAIR.EDU.VN.
FAQ About Transition of Care Software
1. What is transition of care software?
Transition of care software is a technological solution designed to enhance the coordination and communication between healthcare providers during patient transitions. It ensures seamless care by managing patient data, scheduling follow-ups, and facilitating medication reconciliation.
2. Why is transition of care important?
Transition of care is crucial because it directly impacts patient safety and the quality of healthcare delivery. Poorly managed transitions can lead to medical errors, increased readmissions, higher healthcare costs, and reduced patient satisfaction.
3. What are the key features of transition of care software?
Key features include patient data management, care plan development, medication reconciliation, appointment scheduling, communication tools, reporting and analytics, and integration with EHRs.
4. How does transition of care software improve patient outcomes?
By reducing hospital readmissions, enhancing medication adherence, improving communication between providers, ensuring continuity of care, and reducing medical errors.
5. What are the core components of transition of care software?
The core components include patient data management, care plan coordination, medication reconciliation, appointment scheduling and reminders, communication and collaboration tools, and reporting and analytics.
6. What are some practical applications of transition of care software?
Practical applications include hospital discharge planning, management of chronic conditions, post-surgical care coordination, home healthcare services, and skilled nursing facilities.
7. What are some challenges in implementing transition of care software?
Challenges include lack of interoperability, resistance to change, data security and privacy concerns, cost, and workflow disruption.
8. How can healthcare organizations choose the right transition of care software?
By identifying their needs, evaluating key features, considering user experience, checking for compliance, and reading reviews and testimonials.
9. What kind of training and resources are available for transition of care software?
Training and resources include onboarding training, ongoing